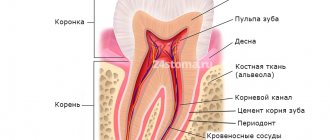
One of the most dangerous complications in aesthetic medicine is arterial embolization, which can lead to ischemia, necrosis and even blindness.
In order to ensure the prevention of this side effect, detailed knowledge of anatomy . However, this is not always enough, due to the presence of individual characteristics of the location of blood vessels in humans. In this regard, doctors resort to an aspiration test.
Read about how effective this method is, and whether you should trust it, in this article on estet-portal.com.
Pain relief methods
The most common method is local anesthesia, designed to reduce the patient's sensitivity to pain in the desired area. Under its influence, a person understands what is happening and can speak and hear calmly. At the same time, he does not feel anything in the place where the dentist is working.
Indications for such anesthesia may be:
- removal of the tooth and its root (not always suitable if we are talking about the “eight”);
- minor surgical interventions;
- removal of tartar (various sprays and gels are used for this);
- treatment of incompletely erupted teeth;
- elimination of periodontal disease;
- treatment of caries, especially advanced ones;
- removal of nerves;
- root canal filling;
- installation of a metal-ceramic crown.
Partial anesthesia is not relevant for major operations, injuries to the bones of the maxillofacial area and allergies to the drugs used.
General anesthesia is used extremely rarely, mainly only when the patient experiences extreme fear and stress. And it can also be recommended for psychosomatic diseases, allergic reactions to local anesthetics and extensive surgical interventions, for example, prosthetics on implants.
General anesthesia in dentistry is not allowed in the following situations:
- if more than six months have passed since the stroke and/or heart attack;
- with cardiopulmonary failure in the stage of decompensation;
- if there are serious heart rhythm disturbances;
- for diseases of the thyroid gland;
- while intoxicated;
- when the patient is under the influence of drugs;
- in case of impaired functioning of the kidneys and liver.
Artery embolization in cosmetology: how to prevent the irreparable
Safety issues in aesthetic medicine always remain relevant. Every doctor strives to minimize the risks of complications, and especially those that can lead to irreversible changes.
Intra-arterial injection of gel-like drugs leads to a critical decrease in blood flow in a certain anatomical area, which can cause ischemia and then necrosis.
To limit the risk of embolization, many experts advocate performing aspiration before injection, since blood in the center of the needle during this manipulation will confirm its intravascular location.
Types of local anesthesia
Infiltration anesthesia is most often used in dentistry. It involves injecting an anesthetic with a thin needle under the mucous membrane next to the problem tooth or inside the bone, which begins to act 10 minutes later. The resulting effect lasts for 2–3 hours, depending on the drug used, the depth of its administration and the amount.
Another type of anesthesia is application. It is used quite rarely and can relieve pain only with shallow interventions. In this case, various ointments and sprays are used, which are applied to the desired area with a sterile cotton swab or gauze.
This technique is best suited for cases such as:
- treatment of superficial caries;
- removal of tartar;
- anesthesia of the area before another anesthesia (deeper);
- installation or removal of a crown;
- manipulation at the edge of the gum.
The third method of local anesthesia is the use of conduction anesthesia. It stops the transmission of nerve impulses for some time. This method is based on the administration of an anesthetic through the branches of the trigeminal nerve. Relief from painful sensations occurs within 2–3 hours. The technique of performing such anesthesia is somewhat more complicated than others. It is recommended mainly for the treatment and removal of molars (large molars) or intervention in the gums.
Trunk anesthesia is very rare in dental practice; it is justified only by obtaining a long-lasting effect. Its essence lies in the introduction of special drugs using a thin needle at the base of the skull that block the maxillary and mandibular nerves. Such anesthesia is most often performed during major operations in a hospital setting and in the case of clearly defined pain syndrome.
These are the main types of anesthesia in dentistry, which allow you to take care of dental health relatively painlessly and without much discomfort.
Free consultation
30-40 minutes
inspection and diagnostics
treatment plan and cost
Make an appointment
Improving the technique of aspiration test when performing local anesthesia in dentistry
S. V. Tarasenko Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Faculty Surgical Dentistry of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova
E. A. Belyaeva , dental surgeon, MAU "Balashikha Dental Clinic"
A. V. Kuzin Assistant of the Department of Faculty Surgical Dentistry of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova
A. A. Kurtyshov student of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova
Systemic complications caused by intravascular injection of anesthetic can be life-threatening for the patient. Some dentists perform the aspiration test on an ongoing basis, but evidence suggests that therapists perform it in 50% of cases, surgeons in 52% of cases, but orthopedists only in 25% of cases (S. A. Rabinovich, O. N. Moskovets, M. V. Lukyanov, E. V. Zoryan). When blocking the inferior alveolar nerve in children and adolescents, the needle more often ends up inside the vessel than in adults.
Ophthalmological disorders after intraoral anesthesia are a common complication. Symptoms include blurred vision and blindness (temporary blindness). In addition, motor neuron anesthesia can lead to mydriasis (dilation of the pupil), ptosis (dropping of the eyelids), and diplopia (double vision). Symptoms of similar manifestations involving ptosis, enophthalmos (collapse of the eyeball in the orbit) and miosis (papillary restrictions) have also been described [6].
According to many authors, intravascular injection is a common phenomenon in general anesthesia. To prevent intravascular injection of anesthetic, it is imperative to carry out an aspiration test.
Aspiration - the reverse absorption of the medium from the area of injection of the local anesthetic - is used to ensure that the tip of the needle is not inside a blood vessel by the absence of blood in the solution. This is necessary in order to prevent the introduction into the bloodstream of highly concentrated substances used in modern local anesthesia technology.
The purpose of our study was to improve the safety of local anesthesia in dentistry using an aspiration test. To achieve this goal, we compared the effectiveness of performing an aspiration test with carpule syringes of different designs, studied the frequency of positive aspiration tests during anesthesia of the inferior alveolus nerve with various conduction methods of pain relief, and also developed an algorithm for the prevention of intravascular injection of anesthetic during conduction anesthesia of the LLN (inferior alveolar nerve) .
Aspiration is used to ensure that the tip of the needle is not inside a blood vessel by the absence of blood in the solution. This prevents the introduction into the bloodstream of highly concentrated substances used in modern local anesthesia technology.
In our study, we used anesthetic carpules with rubber pistons of different structures: with a retention rim around its perimeter (Ubistesin 3MESPE), without retention (Septanest). Also carpule syringes, which differ in the structure of the end part of the piston (Fig. 1 a, b): a syringe with an “anchor” type piston, which has three hooks in its end part that hold the rubber piston; a syringe with a “corkscrew” type piston, having at its end part one corkscrew-shaped hook that is screwed into the rubber piston of the carpule; a syringe with a “hook” type piston, having at its end part two mutually oppositely directed hooks holding the rubber piston of the carpule; a syringe with an “arrow-shaped” piston, which has an arrow-shaped hook at its end that holds the rubber piston of the carpule.
The practical part of the study was carried out as follows. The needle of the assembled carpule injector was positioned into the dye-tinted water. An aspiration test was carried out with each syringe by capturing the solution into the cartridge with the reverse movement of the piston. Data on the results of the aspiration test were photographically documented and entered into a table.
The clinical part of the study was carried out on the basis of LHO No. 2 of the Balashikha Dental Clinic. The study involved 270 patients aged 25 to 75 years with a diagnosis of chronic periodontitis of the lower jaw teeth.
As a technique for anesthetizing the inferior alveolar nerve, we used the five most popular methods in domestic dentistry:
- mandibular anesthesia by palpation;
- torusal anesthesia;
- anesthesia using the Gow-Gates method;
- anesthesia using the Vizirani-Akinozi method;
- anesthesia using the Ibragimov method.
Pain management was carried out under careful assessment of systemic hemodynamic parameters. When using the ArmedYX 300 pulse oximeter, a monitored increase in heart rate of 30 units immediately after local anesthesia indicated intravascular administration of the anesthetic. Additionally, the doctor conducted a survey about the patient’s well-being for the presence of palpitations, fear, abdominal pain, nausea, which also indicated the cardiotoxic effect of epinephrine in the local anesthetic solution.
The results of our study were the following data.
When comparing various systems for performing aspiration testing, the best performance was found in combinations of syringes with “anchor” and “corkscrew” type pistons and carpules with a retention notch. More informative data on the results of the practical part of the study are given below (Table No. 1).
Table No. 1. Possible combinations of injection instruments used in dentistry and the effectiveness of aspiration
| Rate of successful dye aspiration per 100 samples | ||||
| Carpule type | Syringe with an “anchor” type piston | Syringe with a “corkscrew” type piston | Syringe with a hook-type piston | Syringe with arrow-shaped piston |
| With retention rim | 100 | 89 | 55 | 5 |
| Without retention rim | 0 | 38 | 37 | 15 |
Based on our results, we believe that the use of carpules with a retention notch facilitates the aspiration test. We can consider them to be “intended” for performing an aspiration test. The retention notch allows the use of most carpule syringes, with best results when used with syringes with an "anchor" and "corkscrew" plunger style. The “anchor” grip of the piston is the most reliable; it fixes the rubber piston of the carpule so strongly that it is possible to remove it entirely by applying significant force to the injector ring, not to mention carrying out an aspiration test.
It is worth mentioning that the type of piston of the carpule injector involves the use of only carpules with a retention recess. Hook-type syringes can be used with any type of carpule, but require a lot of time and force to assemble the syringe. We do not recommend the use of syringes with a “arrow-shaped” piston, since they are not suitable for performing an aspiration test, which is confirmed by the data of our experimental study.
In the clinical part of the study, when conducting an aspiration test in patients undergoing outpatient surgical treatment, the following data were obtained. The lowest frequency of intravascular injection was observed during anesthesia using the Gow-Gates technique, and the highest frequency of positive aspirations was obtained in the group where torus anesthesia was performed. Data on performing aspiration tests during anesthesia using other methods were also obtained and documented (Table No. 2).
Table No. 2. Frequency of positive aspiration tests during blockade of the inferior alveolar nerve using various methods of anesthesia used in domestic dentistry.
| Anesthesia method | «-» | «+» | % | Symptoms |
| Mandibular | 103 | 8 | 7,6 % | 0 |
| Torusal | 51 | 9 | 17,6 % | 1 |
| Go - Gates | 67 | 3 | 4,91 % | 0 |
| Akinozi | 21 | 1 | 4,76 % | 0 |
| Ibragimov | 28 | 2 | 7,14 % | 0 |
From the above data it is clear that approximately every eighth patient who undergoes torus anesthesia may be at risk for complications of local anesthesia. Perhaps such a high frequency of positive aspiration tests when using this method is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the maxillary artery (a.maxillaris). Further research is required to confirm this hypothesis.
Of interest are the data obtained on the frequency of positive aspirations when performing other methods. A certain pattern can also be observed. Mandibular anesthesia by palpation and the Ibragimov technique are carried out at approximately the same level and have a similar value in terms of the frequency of intravascular administration of anesthetic (7.6 and 7.14%, respectively). The Akinozi and Gou-Gates methods are also carried out at approximately the same level in relation to the jaw branch (they are also called high) - they do not differ from each other in the frequency of intravascular administration. This fact once again indicates the presence of a pattern in the structure of the maxillary artery in relation to the branch of the mandible. It is possible that the main branch of the mandibular artery is located at the level of the lower jaw - the zone of anesthesia of the same name.
The aspiration test must be performed multiple times. In the case of positive aspiration when blood appears in the carpule, it is recommended not to redo the anesthesia, but to change the position of the needle.
When performing the aspiration test technique, we assessed the general condition (pulse, oxygen saturation) of the patient at all stages of dental treatment. Of 270 patients, positive aspiration was detected in 23 patients; after preventive measures: changing the position of the needle, repeated aspiration, symptoms of intravascular injection were detected in only one patient. The patient presented “typical” complaints for this complication: sudden palpitations, fear, nausea. Objectively, on the face in the area of the infraorbital foramen, the area of facial ischemia from the side of the anesthesia was determined. The pulse oximeter reading changed, heart rate increased from 128 to 165 (20-30 units).
This case clearly demonstrates the clinical picture of such a systemic complication of anesthesia as intravascular administration. Prevention of intravascular injection using an aspiration test, carried out by us, allows us to completely eliminate this complication of local anesthesia in dentistry, reducing the risk from 8.52 to 0.37%.
Practical recommendations
Based on our experience, we have developed the following practical recommendations (algorithm) for performing an aspiration test to prevent intravascular injection of local anesthetic.
We recommend using carpuled forms of local anesthetic with a retention rim. Carpule syringes with a “corkscrew” type piston and an “anchor” type piston allow you to tightly grip the rubber carpule piston; these gripping systems do not fly off the retention rim.
The aspiration test must be performed multiple times. In the case of positive aspiration when blood appears in the carpule, we recommend not to redo the anesthesia, but to change the position of the needle, performing aspiration repeatedly.
Conclusion
Prevention of intravascular injection of local anesthetic is a critical aspect of local anesthesia in dentistry. The success of its implementation depends on the type of carpule syringes and carpules used. Carpules with a retention rim and injectors with an “anchor” and “corkscrew” type piston allow an aspiration test to be performed in 89-100% of cases. It can be assumed that this combination of injection equipment used will significantly increase the safety of local anesthesia. Based on the results of our clinical study, we can conclude that the aspiration test is a highly effective method of preventing intravascular injection of anesthetic. Among all methods of anesthetizing the inferior alveolar nerve, torus anesthesia results in a higher rate of intravascular (anesthetic) administration. We do not recommend using this method of pain relief without following the aspiration test technique.
- B. Webber; H. Orlansky; C. Lipton; M. Stevens. Complications of an intra-arterial injection from an inferior alveolar nerve block. JADA, Vol. 132, December 2001.
- Brodsky CD, Dower JS. Middle ear problems after a Gow-Gates injection. J Am Dent Assoc 2001;132:1420–4.
- Blanton PL, RodaRS.The anatomy of local anesthesia. J Calif Dent Assoc 1995;23:55-65.
- Gary J. Wilkie Temporary uniocular blindness and ophthalmoplegia associated with a mandibular block injection. A case report; Australian Dental Journal 2000;45:(2):131-133.
- Heasman PA, Reid G. An unusual sequela to an inferior dental block injection. Dr Dent J 1995;179:97-98
- Ngeow WC, Shim CK, Chai WL. Transient loss of power of accommodation in one eye following inferior alveolar nerve block: report of two cases. J Can Dent Assoc 2006;72:927–31.
- Penarrocha-Diago M, Sanchis-Bielsa JM. Opthalmologic complications after intraoral local anesthesia with articaine. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod 2000;90:21–4.
- Pickering T, Howden R. Gray's anatomy, descriptive and surgical. 15th edition. London: Chancellor Press; 1985. p. 703–9.
- Pretterklieber ML, Skopakoff C, Mayr R. The human maxillary artery reinvestigated: I. Topographical relations in the infratemporal fossa. ActaAnat (Basel) 1991;142:281–7.
Activity factors
An aspiration test is an effective way to monitor the medical procedure being performed, as well as to collect material for further study. Any medical procedure must first and foremost be safe. To assess the risk and effectiveness of aspiration manipulation, the specialist must take into account several factors:
- rheology, that is, fluidity, of the drug and the biomaterial being taken;
- geometric parameters of the needle: its diameter and length;
- the dimensions of the syringe itself, its dimensions and, therefore, the physical capabilities of creating back pressure;
- aspiration time;
- back pressure value;
- patient's blood pressure.
Features of the event
Aspiration biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, in a specially equipped room. After the patient is placed on the gynecological chair, the doctor examines the vagina, then carefully inserts a special speculum, opening the cervix. Often, for a more comfortable examination, the cervix is treated with a local anesthetic solution. At this stage, proceed directly to the biopsy. Through the cervical canal, the tip of an instrument, a pipel, is inserted into the uterine cavity. In order to collect the endometrium, the piston is pulled back. It creates negative pressure, creates a vacuum, and tissue cells are released into the plastic tube. Carefully turning the pipel, the doctor removes it from the cervical canal. After this, the material is sent to the laboratory for histological examination. The duration of endometrial aspiration biopsy is about 20 minutes. Processing information and preparing a conclusion takes 1-2 weeks.
Microbiology
Particular importance is attached to such procedures as the aspiration method of air sampling, microbiology. Science that studies the inhabitants of the microworld helps many areas of knowledge and human activity to develop, taking into account and using the characteristics of the life of microorganisms. Aspiration samples of air intake are widely used in sanitary and epidemiological control. Moreover, the collection of material is the most critical stage, the correct execution of which determines the quality of the analysis performed. An aspiration test in this case is a forced method of deposition of microorganisms from the environment onto a nutrient material or a special collecting liquid. This way, experts can monitor their growth and conduct research.
Physics and medicine
Without air, a person cannot live even for a few seconds. This natural mixture, many gases, as well as their absence - vacuum, are widely used in human life. For example, in medicine and some areas of production, aspiration sampling is used. In medicine, this term refers to several concepts:
- a procedure that allows you to collect material using a vacuum;
- a physiological process based on the “suction” effect that occurs due to a decrease in pressure.
In the article we will consider another concept used in medical practice, called aspiration test. As a physical phenomenon, aspiration is the process of sucking air through special instruments or devices, which is then studied and analyzed for the content of substances in the material under study.
Research results
If no pathology is detected, then the results of the study will indicate that the mucous layer corresponds to the phase of the female cycle and age, and no signs of atypia were found.
If we talk about pathological conditions, then diagnostics allows us to identify:
- Endometritis.
- Underdevelopment of the endometrium or its atrophy.
- Discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous layer of the uterus and the day of the cycle.
- Atypical endometrial hyperplasia.
- Hyperplasia (glandular-cystic or simple diffuse).
- Adenomatosis (precancerous condition).
- Degeneration of the endometrium into a malignant tumor.
Additional examinations are possible if any disease from the list above is detected. The doctor will talk about this in detail during the consultation. If the biopsy provides enough data to establish an accurate diagnosis, then treatment will be prescribed.
Indications and contraindications
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed only as prescribed by a doctor. Such diagnostics can identify many different diseases. Most often it is prescribed for:
- Endometriosis.
- Infertility.
- Detection of polyps in the uterus.
- Endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the mucous membrane) of the uterus.
- Unstable menstruation.
- Continuous bleeding after childbirth or abortion.
- Chronic endometritis.
- Miscarriage.
- Pathologies during menopause.
Pipelle biopsy will be indicated in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF). The results of the analysis will allow you to find out the condition of the endometrium before starting the use of hormones.
Contraindications to aspiration biopsy are: pregnancy at any stage, acute infectious and inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, poor blood clotting (for example, hemophilia), severe cervical stenosis.
Benefits of the procedure
Experts highlight the following undeniable advantages of endometrial aspiration biopsy:
- Simplicity and painlessness.
- High information content.
- There is no need for general anesthesia.
- Atraumatic (uterine tissue is not damaged, the risk of inflammation is minimal).
- The ability to obtain material from hard-to-reach areas of the organ.
- It is performed without dilation of the cervix.
After endometrial aspiration biopsy, the patient can leave the clinic almost immediately.
The meaning of the test
In medicine, an aspiration test is used for self-monitoring of medical personnel during manipulations, for example, when administering an injection, as well as when removing biomaterial for further study. Used in ecology, sanitary and epidemiological control and in industry, the aspiration method of air sampling allows for analysis of gas or liquid. The aspiration technique is simple and in many cases does not require complex equipment. By drawing the material under study into special equipment using an artificially created vacuum, a specialist can even visually, if provided for by the operating algorithm used, determine the presence or absence of certain inclusions. Air sampling using the aspiration method is a quick and fairly informative way to obtain the necessary information about the composition and quality of the gas. In medicine, aspiration of biological fluid allows competent and high-quality self-monitoring of a medical worker when administering injections. After all, drug delivery must be carried out in a certain way: some drugs must enter directly into the blood, other substances must be delivered intramuscularly. It is the process of correct injection that allows monitoring the aspiration test.
Collection of biomaterial
Carrying out medical manipulations may also include the removal of a cytological sample for examination. An aspiration test also helps with this. The need for a biopsy, for example, is determined by the doctor. Often this procedure is carried out simultaneously with other diagnostic measures, for example, bronchoscopy, colonoscopy, and so on. The collection of tissues or liquids necessary for analysis is carried out either with a syringe or with an aspiration gun - a more powerful design intended only for these purposes. The cytological sample is then delivered to the laboratory for examination, so the sampling procedure is the most significant stage of the biopsy.
Preparation
Aspiration biopsy does not require lengthy or complex preparation. Before the examination, it is recommended to take a smear for vaginal microflora, standard blood tests, and undergo an ultrasound of the female genital organs. At the preliminary consultation, the gynecologist will definitely ask about all the medications the patient is taking. It is especially important to know if among them there are anticoagulants - medications that thin the blood. On the eve of the study, the specialist may cancel them. It is important to perform a pregnancy test before aspiration biopsy and make sure it is negative.
You should also keep a menstruation calendar and know the phase of the cycle, because the study can be scheduled for different periods. If chronic endometritis is suspected, the diagnostic procedure is carried out in phase 1 of the menstrual cycle (from the first day of menstruation until ovulation, while the egg matures). In all other cases, endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed any day.
It is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse, use tampons, and limit physical activity for three days. It’s a good idea to stick to proper nutrition and maintain hydration.