When studying the price list of any dental clinic, patients see something like the following:
If everything is more or less clear with the first and last points, then what about an orthopedic dentist, periodontist, implantologist and orthodontist? Who are they and what do they do? And which of them wears dentures?
Everything is simple here:
- Dentist-therapist: treats caries, pulpitis and periodontitis, puts fillings. Works with tooth root canals. In our clinic, therapists are trained in artistic dental restoration.
- Dentist-surgeon: removes teeth, performs tooth-preserving operations. If he has the necessary knowledge, he carries out the surgical part of dental implantation - the direct installation of the implant.
- Orthopedic dentist: deals with dental prosthetics. Crowns, inlays, removable dentures are his element. Orthopedic dentists also perform prosthetics on implants that are pre-installed by his colleague, a dental surgeon.
- Dentist-periodontist: gum disease is the domain of the periodontist. Bandages, mouthguards, ointments are his arsenal. Performs hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity (tartar removal, Airflow). In difficult cases, he performs operations on the gums (periodontics is a discipline related to surgical dentistry).
- Implantologist: deals with the installation of dental implants and subsequent prosthetics on them. Sounds familiar? That's right, a dental surgeon and an orthopedic dentist can do the same thing, working in tandem.
- Orthodontist: corrects bites for adults and children. His tools are plates, trainers, and bracket systems. As a result, orthodontic patients receive straight teeth and their correct alignment.
- Pediatric dentist: deals with the treatment and removal of baby teeth, silvering. It can promptly prompt parents that it is time for their child to see an orthodontist in order to solve a bite problem at an early age.
Dentist (general dentist)
Job responsibilities.
Provides qualified medical care. Receives information about the disease: applies objective methods of examining the patient; identifies general and specific signs of the disease, especially in cases requiring emergency care; assesses the severity of the patient’s condition; determines the volume and sequence of resuscitation measures (including artificial respiration, cardiac massage, stopping bleeding, dressing and tamponade of the wound, transport immobilization, gastric lavage in case of poisoning, urgent tracheotomy in case of asphyxia) and provides them in case of traumatic and anaphylactic shock, acute vascular collapse, acute blood loss, acute cardiac and respiratory failure, hypertension and other life-threatening conditions. Conducts examination of the dento-maxillofacial apparatus: soft tissues of the face, temporomandibular joint, salivary glands, regional lymphatic system, probing of teeth, pathological periodontal pockets, fistulas; carries out percussion and thermometry of teeth, electrical odontometry, determines the severity of disease of the oral mucosa, as well as factors contributing to the development of periodontal pathology, symptoms of inflammation and destruction of periodontal tissue. Determines the need for special research methods (including laboratory, radiological, radioisotope, functional, interprets their results. Conducts differential diagnosis of major dental diseases in adults and children; substantiates the clinical diagnosis, plan and tactics of patient management in accordance with the standards of medical care for children and adults. Performs local (infiltration and conduction) anesthesia and determines indications for general anesthesia in the treatment of dental diseases. Carries out the prevention of major dental diseases in children and adults; organizes hygienic training and education of children and parents, teachers, paramedical personnel; plans dispensary work. Conducts assessments cariesogenic situation and the hygienic state of the oral cavity using indices. Teaches the rules of oral hygiene. Carry out measures for professional oral hygiene using mechanical and hardware methods, preventive treatment of teeth with anti-caries agents, sealing of fissures, whitening of teeth, removal of soft and pigmented plaque on teeth, application of air - abrasive systems, abrasive pastes, brushes, rubber bands and strips. Carry out the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures for developmental and teething disorders, caries and other diseases of the hard tissues of teeth; with increased abrasion, grinding (abrasive wear), erosion, pathological resorption, hypercementosis, deposits on teeth, discoloration of hard dental tissues, hypersensitivity of dentin and enamel, with diseases of the pulp and periapical tissues, with gingivitis and periodontal diseases, with changes in the gums and edentulous alveolar margin, stomatitis, diseases of the lips and mucous membrane of the mouth, tongue, with complete and partial loss of teeth. Establishes a diagnosis; provides symptomatic therapy; refers to a specialist doctor for treatment if somatic diseases occur in the mouth. Performs filling and restoration of teeth using all types of filling materials; application of rubber dam and its modifications; production of veneers using the direct method from composite materials; treatment of pulpitis, aimed at preserving or removing the pulp, endodontic treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis through mechanical and medicinal treatment of root canals using manual, machine and ultrasonic instruments; obturation of root canals using pastes and gutta-percha. Carrying out diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures for inflammatory periodontal diseases, removing supragingival and subgingival tartar (followed by polishing the surface of the teeth) manually and using machines; antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory treatment with the use of topical drugs through application, instillation, application of periodontal dressings, elimination of pain sensitivity on the surface of the roots of teeth using the fluoridation method and the use of films with drugs. Provides diagnosis and treatment for acute and chronic diseases of the oral mucosa due to mechanical, physical and chemical trauma, viral and bacterial infections, allergic reactions. Conducts orthopedic treatment of caries with inlays made by light or temperature polymerization, pulpitis and periodontitis with pin structures made by light or temperature polymerization, inlays, artificial crowns made by casting from base metals, light or temperature polymerization and a combined method. Provides treatment for partial tooth loss with bridges made by light or temperature polymerization, the supporting element of which is an inlay, a pin structure, an artificial crown, partial removable lamellar dentures made by light or temperature polymerization, the fixing elements of which are bent and cast metal clasps made of base material metal Provides treatment for complete loss of teeth with complete removable dentures, repair and correction of removable laminar dentures, treatment for periodontal diseases with temporary removable, splinting dentures, plastic mouth guards made by polymerization. Conducts diagnostic, therapeutic, rehabilitation and preventive measures for inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial region and oral cavity of odontogenic and non-odontogenic origin, provides emergency care for acute toothache; acute purulent inflammatory diseases; carries out surgical treatment of acute periostitis of the jaws, removal of roots and teeth (except impacted and dystopic), treatment of alveolitis, pericoronitis, stopping alveolar bleeding, suturing the wound, drainage and medicinal treatment of purulent wounds, dressing after surgical interventions. Provides treatment for dental trauma, for jaw fractures - production and application of wire splints, reduction of dislocation of the temporomandibular joint, application of temporary transport immobilization. In accordance with the approved routing scheme, when identifying (suspicious) signs of cancer, he refers patients to the primary oncology office (department), promptly refers patients with cancer to a specialized oncology medical organization, and monitors patients at risk.
Diagnosis of diseases in therapeutic dentistry
Two groups of methods help to identify pathologies of the oral cavity. The first is the main types. Which include:
- History of the disease. It is important for the doctor to determine when and how the problem appeared and what complaints there are.
- Examination of the oral cavity. The dentist visually conducts an examination to determine the condition of the mucous membrane and teeth. Foci of inflammation, injured areas and pathological formations are identified.
- Instrumental research. They mainly use a dental mirror and probe. The mirror allows you to further examine difficult areas. A probe is used to examine the sensitivity, consistency and depth of the affected areas. A special probe is used to identify periodontal pockets. This technique allows you to identify and clarify the diagnosis of caries and pulpitis.
- Thermometry. This is a determination of the reaction of the dental pulp to temperature stimuli. Thus, the dentist diagnoses pulpitis, caries or periodontitis.
- Vital coloring. Used for suspected caries and non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues. Special dyes are applied to the affected areas of the enamel and then washed off with water. In the presence of demineralization, the enamel becomes stained.
Diagnosis of oral diseases is also carried out using additional research methods. In therapeutic dentistry they will be as follows:
- Electroodontodiagnostics. The technique is aimed at testing the sensitivity of the nerve endings of the pulp to an electric current of low strength and voltage. The higher the electroodontometry readings, the more severe the lesion.
- X-ray examination. Indicated as a mandatory procedure for apical periodontitis, to clarify the nature of inflammation. If dental treatment was carried out for caries, then radiography allows you to determine the quality of the filling. To examine the salivary glands, a contrast agent is first injected into the salivary glands.
- Laboratory methods. Aimed at identifying the state of internal fluids saliva, blood, urine. In case of lesions of the oral mucosa, scrapings are required to determine the microflora and select appropriate drugs for treatment.
The Department of Therapeutic Dentistry focuses its activities on maintaining the health of teeth and other oral organs. Provides timely assistance to prevent the development of complications and premature loss of teeth.
Dentistry unified qualification directory
Modern equipment, instruments and materials used in dentistry. 1.5.5. Actions of personnel upon detection of a patient with signs of particularly dangerous infections, AIDS. 1.5.6.
Rules and regulations of occupational health, safety, industrial sanitation and fire protection. 1.6. During the period of temporary absence of the Employee, his duties are assigned to.
II. JOB RESPONSIBILITIES 2.1. Employee: 2.1.1. Carry out diagnostics, provide therapeutic and emergency care for diseases and lesions of the teeth, oral cavity and maxillofacial area. 2.1.2.
Dental hygienist
A dental hygienist works in private dental practices or in special needs care settings, such as nursing homes. It can be found in the dental office of a dental school or regular school, that is, wherever a healthy lifestyle is promoted, including oral hygiene.
A hygienist has his own professional responsibilities. Such a dentist performs the following procedures during an appointment:
- examines the oral cavity, assessing the condition of the gums and teeth itself, and draws up a dental chart; checks for tumors;
- examines the dentition using ultrasound;
- removes plaque, tartar and stains;
- takes impressions from teeth, thanks to which you can draw up treatment tactics and determine the necessary procedures;
- carries out educational work, explaining to the patient how to properly care for the oral cavity. He tells you how to brush your teeth, floss, whether you need to follow a certain diet;
- Provides periodontal preventative care, such as subgingival antibacterial irrigation.
Job description
Provides orthopedic treatment of defects and deformations of the maxillofacial area. Conducts orthopedic treatment of pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
Evaluates the quality of dentures manufactured by a dental technician. Carries out rehabilitation measures after the application of dentures and conducts clinical observation.
Provides education to patients regarding proper oral hygiene. Prepares accounting and reporting documentation approved for use in the Russian Federation. Determines the amount of necessary first and emergency aid and provides it. Identifies indications for urgent or planned hospitalization. Identifies possible complications of drug therapy.
Dental forum
I approve [position, signature, full name of the manager or other official authorized to approve the job description] [date, month, year] M.P. Job description of a dental therapist [name of organization, enterprise, etc.
p.] This job description has been developed and approved in accordance with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 14, 2003 N 101 “On the working hours of medical workers depending on their position and (or) specialty”, resolution State Labor Committee of the USSR and the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated October 25, 1974 N 298/P-22 “On approval of the list of industries, workshops, professions and positions with hazardous working conditions, work in which gives the right to additional leave and a shortened working day” and other normative legal acts regulating labor relations. 1.
Job description of a dental therapist
To occupy the position of a dental surgeon, you must additionally complete a residency in the specialty “Surgical Dentistry” or have professional retraining in the specialty “Surgical Dentistry” and an appropriate certificate. At the same time, we note that according to Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated July 23, 2010 N 541n, persons who do not have the appropriate additional professional education or work experience established by the qualification requirements, but have sufficient practical experience and perform high-quality and fully the job duties assigned to them, according to recommendations of the certification commission of a medical organization, as an exception, can be appointed to the appropriate positions as well as persons with special training and the necessary work experience.
Future profession
It is clear that a dentist deals with diseases of the oral cavity. This includes pathologies of teeth and periodontal tissues. After graduating from the specialty 08/31/72 general dentistry (residency), the doctor can not only fill or extract teeth, but also eliminate more complex problems. The competence of this specialist includes the treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, installation of fillings and restoration of teeth (installation of bridges and crowns).
In some cases, a specialist will have to obtain additional education in order to master a narrower profession (surgery, orthodontics, periodontology).
What positions can a general dentist hold?
A dentist must be prepared for independent professional activity and perform basic functions: organizational, diagnostic, advisory, therapeutic and preventive. He must combine deep theoretical training with practical skills, treat the assigned work responsibly, be demanding of himself and his subordinates, constantly improve his professional competence and level of general culture, engaging in continuous self-education. A dentist is obliged to apply in practice the principles of scientific organization of work, actively use electronic computing and medical diagnostic equipment in relation to the profile of their activities, be able to navigate modern scientific and technical information, effectively use it to solve practical problems, show initiative, integrity and conscientiousness in work.2.
Dental Treatment Options
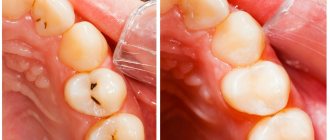
- Fillings. The doctor restores the voids formed after cleansing using filling materials. In his practice, he uses amalgam, porcelain, gold or rubber-based composite material. Each substance has its own advantages and disadvantages. Before installing a filling, the doctor discusses this information with the patient in order to determine what to choose.
- Treatment of dental canals. In this case, the damaged pulp is removed, and the tooth itself is filled with an antibacterial filling, after which it is isolated from external factors by covering it with a crown.
- Bonding. The essence of this cosmetic procedure is to apply a composite to the front or back of the tooth in order to restore it. This way you can improve its appearance, give it a healthy color, lighten stains, hide chips and uneven surfaces.
- Orthodontics. Long-term treatment of crooked teeth using retainers and braces to give your smile an aesthetic appearance.
Job Description of a Dentist Specialist
Carry out the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures for developmental and teething disorders, caries and other diseases of the hard tissues of teeth; with increased abrasion, grinding (abrasive wear), erosion, pathological resorption, hypercementosis, deposits on teeth, discoloration of hard dental tissues, hypersensitivity of dentin and enamel, with diseases of the pulp and periapical tissues, with gingivitis and periodontal diseases, with changes in the gums and edentulous alveolar margin, stomatitis, diseases of the lips and mucous membrane of the mouth, tongue, with complete and partial loss of teeth. Establishes a diagnosis; provides symptomatic therapy; refers to a specialist doctor for treatment if somatic diseases occur in the mouth.
Questions patients often ask:
Who whitens teeth?
If you want to whiten your teeth and don’t know, contact a dentist - in most clinics they do this. In large centers with high traffic, it is possible to hire a separate specialist: a dental hygienist who specializes in professional teeth cleaning or whitening.
A molar tooth is loose - who should I run to?
If your teeth have become loose as a result of an impact or injury, do not hesitate - your periodontist will perform splinting and give your teeth a chance to strengthen.
Bad breath - who can help?
First, see a therapist. If your bad breath is related to dental or gum disease, it will tell you what to do next.
One or more teeth are missing – should you see an implantologist, surgeon or orthopedist?
To an orthopedist. Unlike an implantologist, he will offer several options for restoring the dentition, both with and without the use of implants. Contact an implantologist only if you are 100% sure that you want to get an implant.
I have a toothache – which specialist can help?
Either a therapist or a surgeon will help. In most clinics, therapists are trained to remove teeth if necessary, so the best option is a general dentist.
Job description of a dentist
Performs local (infiltration and conduction) anesthesia and determines indications for general anesthesia in the treatment of dental diseases. Provides prevention of major dental diseases in children and adults; organizes hygienic training and education of children and parents, teachers, nursing staff; plans dispensary work. Conducts an assessment of the cariogenic situation and the hygienic state of the oral cavity using indices.
Teaches the rules of oral hygiene. Carries out measures for professional oral hygiene using mechanical and hardware methods, preventive treatment of teeth with anti-caries agents, fissure sealing, teeth whitening, removal of soft and pigmented plaque on teeth, the use of air abrasive systems, abrasive pastes, brushes, rubber bands and strips.
Therapeutic dental care at the ViDentis clinic
To treat teeth and gums, the ViDentis family clinic uses safe and low-traumatic therapeutic methods. The treatment option, as well as materials, instruments and anesthetics are selected individually. This allows our doctors to treat dental pathologies without complications and pain.
When treating caries, dentists use high-quality American, Japanese and German filling materials. Specialists work in optical binocular glasses. Using an optical device, it is possible to see all hidden pathologies and the smallest elements of the tooth. Thanks to the use of the latest therapeutic dentistry techniques, most problems are resolved on the day of the visit. Patients do not need to go anywhere to take a photo, get tested, or have a scheduled CT scan. All this is available in our clinic.
The cost of therapeutic procedures depends on the chosen technique, the duration of the treatment course, and the materials used. More accurate information about prices and services can be found on the clinic’s website or by phone.
Which document outlines the job responsibilities of a general dentist?
Performs a list of works and services for the prevention and treatment of dental diseases in children in accordance with the standard of medical care for malformations of hard dental tissues, dental caries, pulp, periodontal, periodontal diseases, as well as diseases of the oral mucosa and lips, including conditions of general anesthesia and sedation with preserved consciousness. Conducts the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic, rehabilitation and preventive procedures and measures for inflammatory diseases of the dentofacial apparatus and oral cavity of odontogenic and non-odontogenic origin: surgical treatment of dental periodontitis, acute periostitis of the jaws; removal of roots and teeth; treatment of alveolitis, pericoronitis, stopping alveolar bleeding; suturing the wound; primary surgical treatment of wounds of the oral mucosa.
Benefits of postgraduate study
After passing the exams, the specialist can enter graduate school. The advantages of this are:
- the graduate student continues to improve his skills and study new ways of diagnosing, treating and preventing dental diseases;
- a specialist writes scientific papers and articles;
- a graduate student receives a higher salary than a doctor without graduate school;
- the doctor publishes in scientific journals, attends conferences, and conducts his own research.
Thus, graduate school is suitable for those who are interested in research work.
Job description for a general dentist
HIV infections; - resuscitation techniques; — basics of asepsis and antiseptics; — methods of sterilization of instruments; — first aid methods for bleeding, collapse, anaphylactic shock; — basics of epidemiology; — basics of valeology and sanology; — medical ethics and deontology; — psychology of professional communication; — basics of clinical examination; — basics of disaster medicine; — the procedure for maintaining primary accounting and reporting documentation, including in electronic form; — basics of labor legislation; — labor protection and fire safety rules. 2. Job responsibilities of a dental therapist: 2.1.
Performs initial patient visits. Determines the tactics of patient management in accordance with established rules and standards. 2.2.
Job responsibilities of a general dentist
III. RIGHTS 3.1. The employee has the right to: - providing him with work stipulated by the employment contract; — a workplace that complies with state regulatory requirements for labor protection and the conditions provided for by the collective agreement; — complete reliable information about working conditions and labor protection requirements in the workplace; — professional training, retraining and advanced training in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws; — obtaining materials and documents related to its activities, familiarizing itself with draft decisions of the organization’s management relating to its activities; — interaction with other departments of the Employer to resolve operational issues of their professional activities; — submit proposals on issues of their activities for consideration by their immediate supervisor. IV.
Sep 10, 2019adminlawsexp
vote
Article rating