Dentistry ARDC
The only branch of the American Clinic in Russia licensed by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Gnathology is a clinical area that deals with complex solutions to problems that arise at the intersection of dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. A gnathologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the temporomandibular joint, masticatory muscles, as well as dental pathologies associated with malocclusions and complex dental prosthetics.
What is the scope of activity of a gnathologist?
Most of the unpleasant symptoms that relate to the dental system are associated with the development of diseases of the teeth and gums. However, this complex system also includes the facial and chewing muscles, jaw bones, TMJ, and nerve endings.
All of the above structural components of the dentofacial system play equally important roles in maintaining the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus. It is the gnathologist who studies in detail the state of the constituent elements, the nature of their interaction, as well as the relationship of the structural components with other organs and systems.
The participation of a gnathologist in restorative dentistry is especially important. Unfortunately, during the restoration of lost teeth, not all clinics pay due attention to the condition of the muscles and joints of the dental system. This is why some patients, after completing restoration work, complain of discomfort when chewing, talking and smiling.
A notable feature of a gnathologist is its close relationship with other medical fields. The fact is that the science of gnathology was formed at the intersection of neurology, otolaryngology and other disciplines. A gnathologist works in tandem with orthopedists, orthodontists, and implantologists. Thanks to an integrated approach, the level of dental restoration is rapidly increasing.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
What does a gnathologist treat?
Analyzing all existing health problems, a gnathologist determines cause-and-effect relationships between phenomena and offers optimal treatment for such diseases:
- TMJ dysfunction, articular disc displacement;
- pathological occlusion;
- bruxism or generalized abrasion.
The specialist can determine the interalveolar height (the distance between the bone ridges of the jaws), restore the correct guidance of the jaw from below and recreate the correct incisal and canine separation.
If the lower jaw constantly cramps, only a gnathologist can determine the causes of the unpleasant phenomenon and plan a course of treatment for the dental apparatus. The specialist will plan muscle relaxation therapy using splints and a disconnecting mouthguard.
When is the help of a gnathologist needed?
Experts identify a number of typical symptoms that indicate the need to see a gnathologist. Among them:
- rapid fatigue of the masticatory muscles;
- muscle hypertonicity, which is felt during chewing;
- uncontrolled jaw clenching;
- localized or isolated pain in the masticatory muscles;
- discomfort when opening and closing the mouth;
- involuntary grinding of teeth (bruxism).
The progression of dysfunction of the mandibular nerve will be indicated by such obvious symptoms as clicking in the joint (occurs when chewing, opening and closing the mouth), joint block, displacement (the mouth opens in a zigzag or S shape). In the later stages of TMJ dysfunction, the patient complains of severe pain when chewing solid foods and the inability to fully open the mouth.
With problems with TMJ, patients report headaches, migraines, and stuffy ears. With pathology, not only the masticatory muscles hurt, but also the neck and occipital area. If the joint is dysfunctional, insomnia, snoring, dry mouth, and dizziness may occur.
If the described symptoms appear, you need to make an appointment with a gnathologist as soon as possible. If you ignore the problem, the improper functioning of the joint will gradually develop into irreversible degenerative processes and arthrosis.
Custom sports mouth guards
An orthodontist not only treats various pathologies, but also helps prevent dental injuries. Contact sports (boxing, hockey, football) require protection of the front teeth from accidental injury.
To protect the dentition, individual mouthguards are made. They fit precisely to the teeth, are securely fixed in the oral cavity and protect athletes from dental injuries. Made from hypoallergenic materials, used for adults and children.
To make such a mouth guard, you will need two visits to the doctor:
- Taking impressions of the jaws. They are sent to the laboratory, where plaster models are cast, and the mouthguard itself is then cast.
- When the mouth guard is ready, the patient is invited to try it on and is given the design. The doctor gives recommendations on how to care for the mouthguard.
Why does TMJ dysfunction develop?
The reasons for the development of dysfunction can be very different - from the position of the teeth to pathologies that have nothing to do with dentistry. Pathological changes in the mandibular joint can be provoked by:
- variable changes in the psyche (neurosis, constant stress);
- problems with the autonomic nervous system (heart rate irregularities, blood pressure surges);
- parafunction of masticatory muscles;
- injuries in the TMJ area;
- episodic microtrauma of the joint caused by irrational or poor-quality prosthetics;
- traumatic occlusion;
- incorrect dental treatment (fillings that are too high);
The cause of TMJ dysfunction can also be untimely restoration of lost teeth, except for “eights”.
What does an orthodontist treat?
A doctor of this specialty in dentistry in Otradnoye treats:
- bite pathologies: mesial, distal, deep, straight, open, cross;
- crooked teeth;
- anomalies in the timing of tooth eruption: delayed eruption, late eruption, etc.
- incorrect position of the tooth/teeth in the oral cavity, when one or more teeth are located abnormally, for example, outside the dentition;
The orthodontist also diagnoses abnormalities in the number, size, shape of teeth and refers the patient to related specialists for treatment: an orthopedist, a therapist, a surgeon.
How is an appointment with a gnathologist?
An appointment with a gnathologist begins with a conversation with the patient and collection of anamnesis. Then the specialist conducts a visual examination, checks the closure of the teeth, evaluates the functioning of the muscular system, the position of the head and the severity of facial asymmetry. During the examination, the doctor places the main emphasis on the temporomandibular joint - assesses the TMJ in a stationary position and during functioning.
The gnathologist also studies other elements of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus - checks the degree of tension in the muscles of the neck, back, and posture of a person. These measures help the gnathologist make a presumptive diagnosis and identify therapeutic tactics.
Mandatory additional diagnostic methods are computer and hardware studies. The doctor determines the list of relevant ones in a particular clinical case. Possible:
- orthopantomogram, survey x-ray of the temporomandibular joint - allow us to identify pathologies in the development of bone tissue of the ligamentous apparatus;
- CT scan – helps the gnathologist examine the joint layer by layer and detect degenerative changes in the tissues;
- magnetic resonance imaging – necessary to assess the condition of the periarticular soft tissues and articular disc;
- axiography, hardware recording of the movement of the lower jaw and graphic diagnostics;
- analysis of occlusal contacts;
- diagnostic jaw models made of plaster.
In the topic of functional diagnostics, myography occupies a special place - a method for diagnosing the masticatory muscles and the quality of teeth closure.
Computer programs help speed up diagnosis and increase the effectiveness of treatment for TMJ dysfunction. They allow us to offer the most optimal ways to correct the system.
How does an orthodontist perform diagnostics?
An examination and diagnosis is required before starting treatment. During the consultation, the orthodontist conducts:
- collection of patient complaints and anamnesis data;
- examination of the patient’s face: symmetry, proportionality, and facial profile are assessed;
- when examining the oral cavity, the doctor fills out the dental formula, determines the bite, examines the frenulum of the lips, tongue, etc.;
If parents and a child come to the clinic for orthodontic treatment, the doctor conducts a survey of the parents about the child’s condition, its characteristics, etc.
Additional research methods in orthodontics include:
- Measuring plaster models of jaws: the doctor takes impressions of the jaws and casts plaster models. They are used to measure the dentition, diagnose their symmetry, and more.
- Orthopantomography (OPTG): the resulting image shows all the teeth, their roots, rudiments, and the structure of the bone tissue of the jaws.
- Teleradiography (TRG) in the direct and lateral surfaces: allows you to study the structure of the facial skeleton, establish an accurate diagnosis, and also predict the success of treatment.
During the consultation, the orthodontist will tell you what studies will be required in this case and what treatment methods are possible.
D
Differential diagnosis
Since the symptoms described above are similar to the manifestations of pathologies that are in no way related to gnathology, the doctor additionally conducts a differential diagnosis. A patient who comes to see a gnathologist may develop the following serious pathologies:
- myocardial infarction (pain radiates to the neck, lower jaw and shoulders);
- otitis media of unknown origin (severe jaw pain and hearing loss);
- cerebral circulatory disorders (dizziness, flashing “flies” before the eyes, nausea);
- thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis (pain is localized in the same areas);
- pinching of the facial nerve (unilateral hypertonicity of the facial muscles and tissue swelling);
- complications of pathologies of teeth and gums (inflammation and limitation of mobility of the lower jaw).
To exclude an error in diagnosis, the gnathologist carefully examines the patient’s medical history and identifies possible relationships between a person’s chronic diseases and the symptoms that appear.
What treatment methods does a gnathologist use?
The therapy offered by a gnathologist is complex:
- To restore the correct position of the patient’s jaws, the specialist uses special joint splints. This tactic is justified if a person has bruxism, pathological tooth wear, muscle hypertonicity in the neck and maxillofacial region;
- To stimulate the masticatory muscles of the face and neck, the doctor uses a high-tech system - a deprogrammer. The development helps to deprogram the dysfunction reflex and bring the masticatory muscles to normal tone;
- in the treatment of joint dysfunction caused by poor-quality orthopedic therapy, a serious decrease in bite, the gnathologist uses an individual splint (splint) with a persistent memory effect. The device can be worn on either one or two jaws.
An individual occlusal splint not only corrects occlusion, but also copes with a number of functional tasks - evenly distributes the chewing load, reduces the activity of the masticatory muscles and corrects the direction of jaw movement from below.
How does TMJ arthrosis manifest?
Osteoarthritis of the maxillofacial joint can be caused by trauma, inflammation, the absence of a large number of teeth, or the use of dentures with poorly formed dentition. The causes of the development of pathology can also be metabolic disorders, connective tissue diseases or nerve conduction disorders.
Symptoms of arthrosis appear gradually as dystrophic changes develop. Most often patients complain of:
- aching pain that can radiate to the upper part of the skull - the area of the eyes or ears;
- characteristic crunching or clicking sounds that occur when the joint moves;
- decreased mobility of the bone joint, especially noticeable in the morning;
- displacement of the lower jaw to the right or left side from the center.
When is TMJ surgery performed?
If conservative therapy does not bring the desired results, a decision is made about the need for surgery on the temporomandibular joint. In such cases, the surgeon organizes one of the following types of interventions:
- TMJ puncture;
- removal of part of the pathological tissue, correction of the location of the cartilaginous disc and condyle;
- intra-articular surgery if a tumor process is diagnosed and bone tissue is destroyed.
The decision on the advisability of any operation is made by a medical council.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Gnathologist and orthodontist
Orthodontists often recognize the fact that bite pathologies in humans are very often caused not by dental problems, but by such anomalies as:
- disproportions in the sizes of individual elements of the dentofacial apparatus;
- incorrect position of the human jaws relative to the skull;
- pathologies of the temporomandibular joint;
- problems with the chewing muscles.
There are frequent cases of the development of bite pathologies due to orthopedic problems of the spinal column. 90% of clinical cases of abnormal dental occlusion are the subsequent development of pathological abrasion and a decrease in the height of the lower facial zone. It is not practical to solve emerging problems with braces and aligners.
If a patient has pathological abrasion, orthodontic therapy will not correct the situation and will not eliminate single and multiple defects in a row. This happens because dysfunction of the mandibular joint is to blame.
If, during the diagnosis, the orthodontist suspects that the patient’s problem is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the maxillofacial apparatus, he is obliged to refer the patient for a consultation with a gnathologist. This approach will avoid errors in diagnosis and speed up the patient’s recovery process.
If you approach the problem objectively and assume that an orthodontist will treat joint dysfunction, we can say with confidence that the result of therapy will be negative. Orthodontists are highly specialized specialists. They are far from gnathology and the peculiarities of the functioning of the temporomandibular joint. An orthodontist manages to cope with the abnormal arrangement of teeth in a row, improve the appearance of a smile, and restore the closure of teeth, but his knowledge and experience are not enough to cope with the pathology of the TMJ.
Gnathologist
Gnathology is a branch of dentistry that studies the problems of the dentofacial apparatus and solves problems associated with its functioning. Simply put, gnathology, as a medical specialty, deals with the pathology of the jaws.
A dentist who has specialized in gnathology is called a gnathologist. This is a very rare medical specialty, and not every clinic employs doctors with such a narrow specialization. At Kostamed, the chief physician of the clinic, Yuri Aleksandrovich Kostylev, works as a dentist-gnathologist.
Goals and objectives of gnathology
The main task of gnathology is to assess the functional status of all components of the dental system: masticatory muscles, temporomandibular joint, periodontium, dentition and individual teeth. Gnathology studies not just the static state of all these elements - using special research methods, dynamic parameters are assessed, for example, the biomechanics of chewing. Dentists who have specialized in gnathology study the geometry of the chewing part of the skull and determine the aesthetic relationship between the proportions of the jaws and the rest of the face.
The purpose of gnathological studies is to identify the pathology of the morphofunctional state of the dental system. The data obtained allows specialists to correct existing violations. A consultation with a qualified gnathologist dentist, which can be done in our clinic, will allow you to:
- determine the optimal scheme for correcting violations of intermaxillary interaction - a specialist will advise how best to correct the bite;
- develop tactics for treating pathology of the TMJ and lower jaw;
- optimize the selection and production of dentures;
- harmonize the work of the masticatory muscles.
What does a gnathologist do?
During the implementation of special examination methods, elements of pathological interaction between the upper and lower jaws, tooth surfaces, masticatory muscles, and dentition are identified. This sometimes requires instrumental examinations:
- Electronic condylography is the main method for diagnosing TMJ dysfunction.
- Rheoarthrography.
- MRI and CT scan of the TMJ and other parts of the dental system.
- Phonoarthrography.
- Axiography.
You should not think that a gnathologist uses only instrumental research methods - the classic examination and palpation of the muscles of the face and jaws has not been canceled. These elementary examination methods allow a competent specialist to immediately make a preliminary diagnosis and determine the scope of a detailed examination and treatment tactics.
Treatment of gnathological disorders by a gnathologist involves the use of therapeutic and diagnostic devices, such as:
- disconnecting and centering tires;
- stabilizing tires;
- relaxation bite blocks.
Gnathological treatment often requires selective grinding of teeth to eliminate pathological dental occlusion.
Important! Occlusion in gnathology refers to the contact or closure of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw.
In cases where the help of a gnathologist alone is not enough, orthodontists are involved in the treatment of the patient. They help to restore the normal relationship of teeth through prosthetics. One of the advantages of our clinic is that we have all the necessary specialists. This allows you to optimize the treatment process and not waste time searching for dentists of the right profile.
Problems requiring the help of a gnathologist:
- limited opening of the oral cavity;
- defective occlusion of the dentition;
- to determine the amplitude with which the lower jaw moves;
- complaints of clicking and crunching in the temporomandibular joint when chewing;
- to determine the optimal type of dentures during the implantation procedure;
- asymmetry of teeth closure;
- bruxism.
Tinnitus of unknown origin, tension in the masticatory muscles and pain during chewing also require consultation with a gnathologist. Often, consultation with this specialist is required after dental and orthodontic treatment. Often, a poorly executed filling, an incorrectly made or incorrectly installed denture are the source of gnathological problems.
This is interesting! Some problems in the gnathology profile are solved with the help of injections of botulinum toxin, which has the property of relaxing muscles. This effect will relieve pathological spasm and correct the bite.
Cost of treatment with a gnathologist at the Costamed clinic
Dentistry "Costamed" offers a comprehensive and effective solution to any dental problems, including those related to gnathology. The cost of the most detailed consultation with a gnathologist in our clinic is 5,000 rubles.
During the consultation, a comprehensive study of the functional status of the dental system is carried out. We solve both technical and aesthetic problems. During treatment, our specialists take into account the individual harmonious features of the face.
By contacting Kostamed dentistry, you are guaranteed to get rid of bite problems and pain when chewing. Our doctors will help restore the functioning of the TMJ after jaw injuries of any complexity and in case of chronic diseases of the dental system.
Make an appointment with a gnathologist in Perm by phone or through the online registration form on the website. You can call around the clock - at any time of the day, a specialist will answer the phone call and you will choose a convenient time for a consultation with a gnathologist.
Orthopedist-gnathologist - “gold standard”
If we consider the specialty of an orthopedist in dentistry more broadly, we can say that his specialization includes the diagnosis and treatment of defects of the musculoskeletal system. An orthopedic doctor who already has good experience working with the masticatory apparatus and deep knowledge in restoring its functions using prosthetics becomes an ideal candidate for the role of a gnathologist.
When organizing proper orthodontic treatment, this is exactly the case - the doctor determines a prosthesis design that would evenly distribute the chewing load and additionally take into account the condition of the patient’s TMJ and his masticatory muscles. Proper distribution of the load during chewing and ensuring the correct bite height is the main stage in the treatment of temporomandibular joint dysfunction.
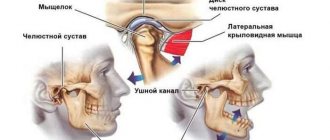
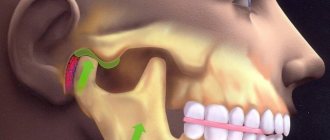
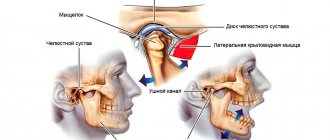
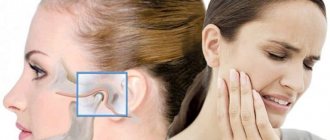
Structure and function of the mandibular joint
In order to better understand what causes pain and muscle dysfunction of the right and left TMJ joint, it is necessary to understand what it is - the temporomandibular joint, its structure and function.
Mandibular joint (TMJ), photo
In the broadest sense, the structure of the mandibular joint has the following elements and features:
- This is a double, in other words, paired (left and right), combined joint (the only one of its kind in humans).
- The jaw joint belongs to the category of complex joints in the human body, with maximum freedom of movement in different directions. It is divided into two floors (divisions): the upper floor is above the jaw disc, the lower floor is under the disc. The joint is covered by an articular capsule.
- Both joints of the lower jaw normally synchronously reproduce movements in 3 planes:
- horizontal: left - right
- vertical: up-down
- sagittal: back - forward (from back to stomach)
- Between the articular head of the lower jaw and the articular cavity of the skull there is a jaw disc, which covers the middle part of the articular head and serves to soften and absorb pressure in the joint.
- The articular mandibular disc is connected to the internal capsular ligaments, which regulate the movement of the disc forward, backward, left and right. The external ligaments of the joint determine the boundaries of the displacement of the lower jaw, together with the group of masticatory muscles.
- All articular surfaces are covered with cartilage, which secretes synovial fluid to lubricate the jaw joint and improve the sliding of the articular head in the joint.
Forecast and prevention of joint dysfunction
The prognosis for treatment of joint dysfunction depends on the degree of pathological changes in the bone and cartilage, and the ligamentous apparatus of the TMJ.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, when there are no noticeable changes in the structure of the joint tissue, conservative treatment shows good results, which form a favorable prognosis for curing the disease.
If, at the time of seeking medical help, the patient has a significant loss of cartilage tissue, rupture or perforation of the intra-articular disc, as well as bone deformity, the prognosis is uncertain. In such cases, even after surgery to replace the articular disc, osteoplasty and other therapeutic measures, it is not always possible to fully restore the functionality of the TMJ.
Prevention of dysfunction is multifaceted. Primary preventive measures consist in the timely elimination of dental pathologies and dental anomalies. It is also worth working on existing bad habits (clenching your jaw during severe nervous tension, chewing on your hands, chewing on only one side, etc.). They stimulate the development of pathology. If the disease has developed against the background of psycho-emotional stress, it is also necessary to include psychological methods in prevention.
Secondary prevention of temporomandibular joint dysfunction involves preventing the rapid deterioration of the patient's condition and includes measures to prevent recurrent muscle spasms and the prevention of adhesions.
How does an orthodontist treat?
Correcting a malocclusion is possible in several ways:
- The bracket system is a complex in design, but highly effective system in modern orthodontics. It allows you to create a functional and aesthetic optimum in the human dental system. Suitable not only for children. In adulthood, it is also possible to correct the bite with braces.
Braces are structures made of special metal locks and arches installed on the teeth. They are non-removable. Correcting the bite requires long-term wearing (from a year or more). The duration of wearing depends on the initial situation, the age of the patient and the characteristics of the maxillofacial system.
- Orthodontic plates are special structures that have a plastic base and various metal fasteners, screws, hinges, and springs. They are used in children, starting with primary occlusion, as well as during the period of teeth change: up to 12-14 years. They allow you to expand, shorten, lengthen the dentition, move teeth, change their position and much more.
Plates are removable orthodontic structures that must be maintained. The type of plate and duration of wearing is determined by the orthodontist. The production of plates takes place in a dental laboratory using individual casts of the jaws.
The success of treatment with plates in childhood depends not only on the correct manufacture of the desired design, but also on a responsible approach to wearing the plate by parents and the child. You should strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, wear the plate for the required number of hours a day, and perform the necessary hygiene procedures.