To the reference book Ear pain or otalgia is a symptom that can manifest itself in various diseases. Self-medication is unacceptable, since there is a high risk of intracranial complications (meningitis, sepsis, labyrinthitis), and persistent hearing loss, even loss, is possible.
Author:
- Galkin Alexey Vladimirovich
ENT pathology expert
4.67 (Votes: 3)
Ear pain or otalgia is a symptom that can occur with various diseases. The ear and parotid region are a very sensitive reflexogenic area and are innervated by several large nerves. The branches of the trigeminal nerve, vagus, and cervical plexus nerves are involved in providing ear sensitivity, so inflammatory processes in the ear, neck, and maxillofacial area can be accompanied by pain. Also, ear pain is quite common with dental problems, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, inflammation of the lymph nodes and tonsils, and neurogenic problems.
Painful sensations in the ears are a serious concern and significantly impair the quality of life, so they cannot be ignored. Self-medication is unacceptable, since there is a high risk of intracranial complications (meningitis, sepsis, labyrinthitis), and persistent hearing loss, even loss, is possible. Contacting an otolaryngologist is a guarantee of a quick return to normal health and no risk of complications.
Causes of ear pain
The main factors causing pain in the ear:
- inflammation of the middle or outer ear;
- sulfur plug;
- changes in pressure in the tympanic cavity due to dysfunction of the auditory tube (during flight or diving to depths during diving);
- inflammation of the parotid salivary gland;
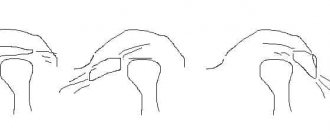
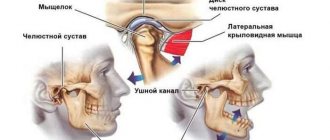
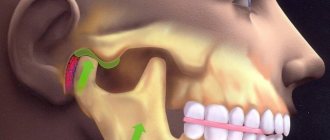
- inflammation of the temporomandibular joint;
- neuropathy of the greater auricular nerve and lesser occipital nerve;
- trigeminal neuropathies caused by inflammation of the teeth or paranasal sinuses;
- inflammatory processes in the area of the tonsils and cervical lymph nodes;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, spinal hernia of the cervical spine;
- neoplasms of the neck, parotid region, temporal bone, brain.
The appearance of ear pain can be caused by physical factors:
- traumatic injuries to the structures of the ear and parotid region (rupture of the eardrum, injury to the external auditory canal, temporomandibular joint, fracture of the temporal bone);
- getting contaminated water into the ear while swimming;
- foreign body in the external auditory canal;
- vibrations;
- annoying loud sound (acute trauma);
- temperature changes;
- exposure to UV, X-rays, ionized air.
There are also extra-ear diseases that can cause ear pain. In this case, this pain is radiating - radiating from other surrounding organs and areas of the body. Ear pain can be caused by:
- dental diseases;
- pathologies of the cervical spine;
- diseases of the pharynx (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis);
- tumors of the pharynx, larynx, auditory nerve, parotid gland;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint;
- sinusitis;
- mumps.
In childhood, ear pain in overwhelming cases indicates a progressive inflammatory process - otitis media. The disease develops against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, rhinitis, sinusitis, as a complication of inflammatory dermatological diseases (psoriasis, eczema), and can appear with infectious pathologies: influenza, measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria. The pain may intensify when chewing, pressing on the tragus, and may be sharp, throbbing, pressing or dull in nature. Along with pain, congestion, ringing, tinnitus, purulent discharge, headaches, fever, and fatigue may occur.
In children
The disease usually results from acute respiratory viral infections and upper respiratory tract infections. The younger the child, the more often bilateral eustachitis is diagnosed. Older children suffer from unilateral damage to the auditory tube. Without treatment, painful otitis media can quickly develop. The temperature is normal or slightly elevated, but the child gets tired quickly and eats poorly.
With inflammation of the Eustachian tube, children complain of:
- slight periodic congestion in one or both ears;
- mild pain;
- nausea, dizziness, noise;
- balance disorders;
- the feeling of an “echo” of your own voice in your head, its unusual volume;
- feeling as if water is pouring in the ear or ears.
Infants react to poor health with low-grade fever, tearfulness, refusal to eat, lethargy, poor sleep at night, and regurgitation.
Diagnostics
If discomfort is detected, you should immediately contact an ENT doctor to find out the cause of the pain in the ear. The specialist examines the auricle, mastoid area, and parotid lymph nodes. After this, the following diagnostic procedures may be prescribed:
- computed tomography of the temporal bone, paranasal sinuses, jaws;
- MRI of the brain;
- Ultrasound of soft tissues of the neck;
- bacteriological culture of ear discharge to determine the causative agent of inflammation;
- general or biochemical analysis of blood and urine;
- microotoscopy;
- acoustic impedance measurement;
- audiometry;
- analysis of Eustachian tube patency.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce otalgia, ear drops with local anesthetics or oral tablets with analgesics are used before visiting a doctor. Medicines can be used if the pain does not occur due to injury. The pathological process that affects the ear quickly involves the bones of the skull and the brain, so self-medication is unacceptable. A qualified ENT doctor should provide assistance to patients with otalgia.
Conservative therapy
Treatment involves the use of local or systemic medications, or a combination of both. For otitis, ear drops containing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic substances are used, and the ear is toileted. To improve the outflow of exudate from the tympanic cavity, vasoconstrictors are instilled into the nose. To reduce pain in the first days (before the eardrum ruptures), heated 96% alcohol is dripped into the ear.
To eliminate the consequences of taking ototoxic drugs, ATP and galantamine are prescribed, which stimulate regeneration processes. Nootropics help improve the nutrition of the auditory analyzer structures. To influence the neurological causes of otalgia, sedatives, anticholinergics, metabolic and vasoactive drugs are recommended. Severe painful paroxysms require the use of anticonvulsants.
Physiotherapy methods are effective in practical otolaryngology. To stop the inflammatory process and stimulate local immunity, microwave therapy, laser therapy, and UHF are performed. To prevent hearing disorders during the recovery period, pneumomassage of the eardrum is performed. Reflexology and amplipulse therapy help eliminate paroxysms of neuralgia of the ear node.
Surgery
The tympanic cavity is cleared of pus during myringotomy, followed by washing the ear with antibacterial solutions. In case of chronic otitis and the absence of effect from conservative measures, anthrodrainage is performed in the mastoid area. Indications for surgical treatment are external cholesteatomas, exostoses, and abscesses.
To eliminate the consequences of middle ear trauma, reconstructive surgeries are prescribed: myringoplasty, tympanoplasty, mastoidoplasty. In case of damage to the inner ear, otosurgical interventions are performed to restore the integrity of the anatomical structures. In case of severe illnesses and injuries accompanied by hearing loss, the patient requires selection of a hearing aid or cochlear implantation.
How is ear pain treated?
Treatment for ear pain depends on the cause. Since ear pain is a symptom indicating the development of pathology in the body, it is impossible to eliminate it forever without curing the underlying disease. However, during treatment, pain can be blocked by taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the cause of the pain is a foreign body or wax plug in the ear, it is necessary to remove them. For otitis media, treatment involves the use of medications, physical therapy and, in extreme cases, surgery. Among the medications used are anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and vasoconstrictor drugs. Physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- electrophoresis;
- tube-quartz;
- laser therapy;
- phototherapy.
Ear surgery is prescribed only if medications and physical therapy have not brought the desired effect. For otitis media, tympanostomy or paracentesis can be performed. These procedures involve cutting the eardrum to drain pus from the middle ear cavity.
In adults
Adult patients are characterized by left- or right-sided eustachitis affecting one side without fever, but with a complex of unpleasant symptoms. Patients suffer from:
- congestion in the ears, decreased hearing (low frequencies are almost not perceived);
- autophony (loud distorted perception of one’s own voice in the form of an echo);
- sensation of fluid in the ear;
- headaches or earaches.
Improvement occurs briefly when chewing or after swallowing saliva, food, or when tilting the head due to a short-term opening of the Eustachian tube and a change in fluid level.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is constant discomfort in the ear, spreading to the temporal area. The patient suffers from burning, throbbing and very sharp pain, similar to an electric shock. Other symptoms of inflammation of the ear node are also noted:
- Why does the jaw hurt near the ear on one or both sides, treatment options
- Decreased or complete loss of hearing . The pathological process develops over several hours or days. Deafness can affect only one side or spread to 2 ears at once.
- Extraneous noises . Patients are bothered by a strong ringing in the ear canal, which does not come from external stimuli. In addition to ringing, the patient feels a buzzing, whistling or hissing sound in the ears. The sign of pathology does not appear in cases of severe deafness.
- Dizziness.
- Impaired coordination . In the initial stages of the disease, the symptom is unsystematic. The clinical picture of the disease is complemented by vomiting and spontaneous movement of images with further progression. The reason for the lack of coordination of movement is the involvement of the cochlear nerve, which is responsible for the balance of the body, in the inflammatory process.
- Headache . _ Manifested for neuralgia caused by poisoning with toxic substances.
An attack can be triggered by drinking hot food or drinks, as well as hypothermia on the face. The duration of neuralgic pain varies from a few minutes to 1 hour.
Treatment of external otitis
The goal of treatment is to stop the spread of infection and allow the ear canal to clean itself as it normally does.
- Cleaning and rinsing the ear canal. As a rule, the doctor cleans it with a curette to free it from skin particles, stuck earwax and dried discharge (serous or purulent). This is necessary so that the ear drops can spill to the entire depth of the ear canal.
- Ear drops prescribed by an ENT or general practitioner (GP). Usually these are drops with antibiotics and/or corticosteroids. For severe pain, analgesics can be used.
- If there is severe swelling of the external auditory canal, the doctor may first replace the drops with turunda soaked in medicine. When the swelling subsides, the turunda can be easily removed from the ear, and you can continue to be treated with drops.
- When instilling cold drops, hold them in your palm for a while to reduce discomfort. After the drops are in your ear, lie down on your healthy side for a few minutes so that the drops are better absorbed. You can ask someone to instill drops for you - this is more convenient.
- If the infection is widespread, the doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics in addition to drops.
Acute eustachitis
An acute form of inflammation is a common complication of viruses and infections of the nasopharynx. With insufficient treatment, inflammation continues in the auditory tube. Children often experience pain in both ears; adolescents and adults suffer from unilateral manifestations. When asked how long it takes to treat eustachitis, doctors answer: adequate measures can get rid of it in 5-7 days. If:
- no treatment;
- therapy is insufficient or prescribed incorrectly;
- the course is not completed;
- there are pathologies in the nasopharynx or nasal cavities;
- there is constant allergic inflammation of the mucous membrane
there is a high probability of a prolonged course of tubo-otitis and its chronicity.
What is otitis externa?
This is an inflammation of the tissues of the external auditory canal, eardrum and auricle. Otitis externa is widespread. It is considered acute if it lasts less than 4 weeks, chronic if it lasts longer and/or occurs more than 4 times a year.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Complications
Over time, untreated eustacheitis causes:
- acute otitis after ARVI;
- hearing impairment;
- unpleasant sensations of echo, congestion, fluid in the ear;
- problems with coordination;
- headache.
During flights or when diving, patients with chronic eustachitis experience severe discomfort.
It is important to diagnose inflammation of the auditory canals in a child in a timely manner, since without treatment, ARVI will be complicated by catarrhal otitis. Chronic eustachitis and the changes it causes in the middle ear gradually worsen hearing.
Common diseases and symptoms
As medical practice shows, most often painful sensations appear with tonsillitis or sore throat. As such diseases progress, the pain intensifies while swallowing food. In this case, other symptoms also arise, namely:
- weakness;
- sore throat;
- poor appetite.
Painful sensations in the process of opening the mouth are diagnosed with “mumps,” a malignant formation in the larynx or other part of the mouth. With otitis media, pain occurs not only in the ears, but also in the jaw. In this case, it is not recommended to self-medicate, as this will only harm your health.
What else do you need to know?
As mentioned above, it is impossible to independently identify the cause of unpleasant sensations when opening your mouth. Even when the patient consults a doctor, additional examination is required. The specialist usually prescribes an X-ray of the jaw, computed tomography, and MRI. Do not forget that each specific ailment requires a special approach to treatment. The general condition of the patient, the nature of the disease, and its stage are taken into account. Usually the pathology disappears when the cause that provoked it is eliminated. So:
- Injuries. A fixing bandage is applied and analgesics are prescribed. Cold compresses are recommended for patients; they will help relieve swelling and pain.
- Dental diseases are quite common. Caries, cysts, and other ailments require immediate treatment. After eliminating the problems, the pain usually goes away. Patients are also prescribed antibiotics.
- Neuralgia. This category includes a number of dangerous ailments. For their treatment, vitamins, antiviral drugs, and special physical training are recommended (exercises will help strengthen the jaw and relieve discomfort when it opens).
- ENT diseases. With otitis media, sinusitis and other ailments, patients often complain of pain that occurs when opening the mouth. For treatment, antipyretics, antibiotics, physiotherapeutic procedures, and drugs to strengthen the immune system are prescribed.
Treatment of eustachitis
For the treatment of eustacheitis in adults and children in the acute period, the following can be used:
1. Medicines to destroy infection (antiseptics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory), relieve swelling (vasoconstrictors, antihistamines).
2. Physiotherapy to shorten the duration of the disease. UV irradiation, sessions on UHF devices, and electrical stimulation are prescribed.
3. Therapeutic manipulations - blowing out the ear (Politzer method), introducing medications directly into the ear canal through a catheter.
To eliminate allergic eustacheitis, or tubootitis, caused by pathology of the ENT organs, you should work with the root causes of the disease - allergies, deviated nasal septum, adenoid growths, etc.
At the multidisciplinary clinic "K+31", treatment of eustachitis in adults and young patients is carried out in the otolaryngology department. Specialists perform diagnostics, develop an action plan, monitor the progress of therapy and strive to prevent relapses of the disease.
Among the advantages of the medical center:
- qualified patient care on an outpatient basis or in a day hospital;
- a full range of necessary laboratory and hardware tests for diagnostics;
- drawing up a treatment regimen using drugs and physiotherapy, innovative techniques;
- if necessary, attracting doctors of other profiles;
- results in the form of recovery or attenuation of the chronic process.
For accurate diagnostics, expert-level equipment is used:
- special installation MODULA EUROPA Paris (Duo) HEINEMANN. It helps make a diagnosis and works as a device for therapeutic manipulations;
- audiometer-impedance meter for analyzing the hearing of young and adult patients.
Thanks to the professionalism of doctors and modern equipment of the department, diagnostics are performed quickly and accurately. After the first visit, the course of treatment begins.
Diagnosis of external otitis
Usually it is not difficult. Otitis externa is easily identified by its symptoms and the appearance of the ear and ear canal. The doctor may examine your ear with an otoscope. If he wants to make sure that the eardrum is intact, he can use a curette to clean the ear and take a deeper look.
If the otitis is diffuse, the doctor may need additional diagnostics of the condition of the middle ear, determining the nature of the otitis (bacterial or other), etc.
Prevention
Based on what was written above, we can conclude that painful sensations when opening the mouth do not just arise. They are a manifestation of dangerous illnesses. To prevent this phenomenon from occurring, it is necessary to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air, exercise your jaw, and strengthen the immune system. It is also recommended to respond in a timely manner to disruptions in the body, even minor ones, and undergo preventive examinations from specialized specialists. As mentioned above, a crooked bite can cause pain when opening the mouth. Therefore, this pathology must be eliminated at an early age. The price of veneers is quite affordable, and their installation does not take much time and is carried out by experienced specialists in a dental office.