April 5, 2020
Neoplasms (neoplasia) is the medical name for tumors, i.e., excessive growth of any tissue in the body. Tumors are the result of uncontrolled proliferation of cells that have not yet reached maturity and therefore have lost their ability to fully perform their functions.
Tumors can occur in internal organs and on the surface of the skin. Many people, not knowing what types of skin tumors there are, when any skin tumor appears, mistakenly believe that it is cancer. In fact, this is not always the case.
According to the main classification, skin tumors are divided into benign and malignant. There are also precancerous formations - borderline between the two main types. Each type has its own subtypes and characteristics, and correct diagnosis is needed to make an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of papillomas
The cause of the appearance of papillomas in intimate places is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which circulates in the blood of almost every man and woman, starting from adolescence.
According to WHO, 80-90% of the population is infected with HPV. Most often, papillomas occur in young people who have a large number of sexual partners. Genital-anal papillomas are typical manifestations of human papillomavirus infection. In 90% of cases they are caused by the sixth and eleventh types of HPV.
In the daily life of every person, the following exposures increase the risk of infection:
- smoking;
- stress;
- using other people's hygiene products;
- visiting baths, saunas;
- shaking hands with carriers at the acute stage;
- decreased immunity.
Globally, the spread of HPV is influenced by many factors, including socioeconomic, medical, hygienic and geographic. The virus can stay in the body for years without showing itself. Its activation is provoked by a weakening of the protective forces of the immune system, which entails the appearance of papillomas in intimate places, both in women and men.
Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, acute viral infections, long-term chronic diseases, poor nutrition and lack of sleep can also trigger the growth of papillomas in intimate places.
Benign formations.
Atheroma.
A tumor of the sebaceous gland formed after its blockage. Most often it occurs on the scalp, neck, back, and groin area, that is, in places with a high concentration of sebaceous glands. It looks like a dense formation with clear contours, elastic and mobile upon palpation.
When suppuration occurs, redness and swelling of the tissues, pain, and increased body temperature appear. The inflamed atheroma can break out on its own, releasing purulent-sebaceous contents. This epithelial cyst has a tendency to transform into a malignant form - liposarcoma. Atheroma can only be removed through surgical excision.
Hemangioma.
A benign vascular tumor formation. Capillary hemangioma can reach large sizes, its color varies from red to bluish-black, and grows predominantly to the sides. If the heangioma is located on a complex area of the body (for example, on the face in the orbital area) or occupies a large area, it is removed beam method.
Lipoma.
A tumor of the fatty layer (often called a “wen”) located in the subcutaneous layer of loose connective tissue. It can penetrate deep into the body to the periosteum, seeping between vascular bundles and muscles. Most often found in areas where the fat layer is thinnest - the outer surface of the hips and shoulders, shoulder girdle, upper back. It looks like a soft formation, mobile and painless upon palpation. Lipoma grows quite slowly and is generally safe for the body, although in rare cases it can degenerate into a malignant formation - liposarcoma. At the same time, if the wen grows and begins to put pressure on surrounding tissues, surgical removal is indicated. It is better not to wait for this moment, since the larger the tumor, the more noticeable the postoperative scar will be. But small fatty deposits are easily removed using laser, radio wave or puncture-aspiration methods, after which there are practically no traces left on the skin.
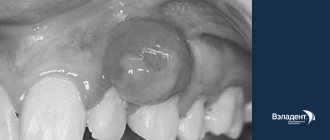
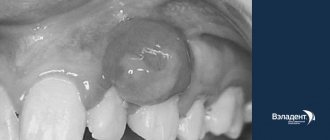
Papillomas and warts.
Formations in the form of a nodule or papilla, having a viral nature. They are caused by various strains of human papillomavirus (HPV), usually due to decreased immunity, stress and vegetative disorders. Externally they are very diverse, most often they look like growths of various shapes and sizes, coloring from light to dark brown and gray. Treatment: treatment with chemically active acids, interferon injections, cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, electrocoagulation, radio or laser exposure, surgical excision .
Moles and nevi.
Benign skin tumors, congenital or acquired. They are a cluster of cells filled with the pigment melanin. They can have different sizes, shapes, colors and surface textures. Some of them have a high potential for degeneration into a malignant form - melanoma. For example, a pigmented border nevus, a flat nodule of dark brown or gray color with a dry, uneven surface. Such formations must be removed, and only surgically. Melanoma-dangerous moles and nevi do not require treatment, but experts recommend getting rid of those that are constantly injured or located in open areas of the body and are often exposed to sunlight in order to avoid complications. The method here is not so critical: in addition to a scalpel, a mole can be removed with a laser, cryodestruction or radio waves.
Fibroma (dermatofibroma).
Formations in connective tissue, which are most often found in women at a young and mature age. They are small in size (up to 3 cm), look like a deeply sealed nodule, spherically protruding above the surface of the skin, the color is gray to brown, sometimes blue-black, the surface is smooth, less often warty. It grows slowly, but there is a possibility of oncological complications: in rare cases, fibroma can degenerate into malignant fibrosarcoma.
Routes of infection
Infection is possible not only through sexual intercourse, although this is the most common cause. HPV infection is also possible through household means:
- when using common hygiene and tableware;
- through contact with an infected person in the acute stage in the presence of microtraumas;
- the possibility of HPV transmission through household items is still being debated.
The transplacental route of infection is rare - from mother to child, even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Probability of infection
Women and men have an approximately equal risk of becoming infected without knowing it at all, since the peak of infection occurs in adolescence and older, when alertness to herpesvirus, papillomavirus, and HIV infection decreases.
At the same time, more attention is paid to sexually transmitted diseases, which, however, are also characterized by high dynamics of infection.
The number of sexual partners remains an important point, since today more than 190 types of HPV have already been described and every year there are more strains of the virus. The International Agency for Research on Cancer identifies 12 strains that are associated with the development of cancer of various locations:
- cervix;
- vulva;
- vagina;
- anal canal;
- penis.
By choosing the smallest number of sexual partners, the risk of becoming infected with HPV, including its oncogenic strains, is significantly reduced.
It is necessary to remember about personal hygiene, as well as the existence of vaccination, which reduces the risk of developing HPV by 95%. It is more effective to vaccinate before the age of 14 years, but up to 25 years of age is also possible. The vaccine provides the greatest protection if it was administered before the onset of sexual activity.
Symptoms
If there are papillomas in intimate places, symptoms are divided into subjective (sensations, complaints) and objective (which can be directly seen by a specialist). Subjective ones include:
- the presence of growths (single or multiple);
- spots on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- itching and other unpleasant superficial sensations in the affected area;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- if male papillomas in intimate places are located in the urethra, burning and painful itching and difficulty urinating may be observed.
The pathology is characterized by the presence of painful cracks and bleeding of the skin and mucous membranes.
Objective symptoms include:
- rashes;
- papules and spots;
- wart-like papillomas;
- pointed condylomas localized in the perineum and perianal area.
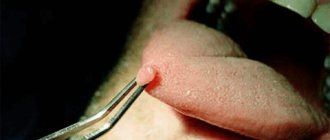
Methods for removing skin tags
There are several known ways to remove skin growths:
- Simple cutting with scissors or a scalpel;
- Removal with radio knife;
- Removal with a coagulator;
- Removal with liquid nitrogen;
- Laser removal;
- Plasma removal.
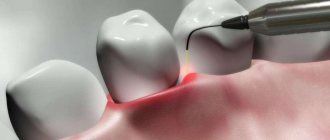
Rice. 5A. Stages of removing skin growths with a laser. Anesthesia
Rice. 5 B. Stages of removing skin growths with a laser. Laser vaporization
Rice. 5V. Stages of removing skin growths with a laser. Laser vaporization.
Rice. 5G. Stages of removing skin growths with a laser. Laser vaporization
Rice. 5D. Stages of removing skin growths with a laser. Final result
Each of them has the right to exist. However, since skin growths in most cases are removed solely for cosmetic reasons, removal methods should be chosen that will not subsequently leave a visible mark on the skin. These methods include: laser and plasma vaporization.
Diagnostics
In order to more reliably determine whether the neoplasm belongs to anogenital warts, a test is carried out with a 5% solution of acetic acid, after treatment with which papillomas in intimate places retain a grayish-white color with a changing, intensifying vascular pattern of normal skin. Laboratory tests can also be used in diagnosis - identification of the HPV genotype with a prognosis for the course of the disease.
To diagnose precancerous conditions against the background of papillomas in intimate places in women, consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist and urologist is recommended when papillomas are localized in intimate places in men, for example, with intraurethral localization. If there are papillomatous processes in the anal area, consultation with a proctologist is recommended.
Depending on the clinical picture, they are usually divided into 3 types:
Benign
(atheroma, hemangioma, lymphangioma, lipoma, papilloma, mole, nevus, fibroma, neurofibroma)
They do not pose a threat to human life, but if poorly placed or large in size, they can cause disturbances in the functioning of other systems and/or organs of our body. Under external influences they can sometimes transform into malignant neoplasms.
Malignant
(basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, sarcoma, liposarcoma)
They grow quickly and aggressively, penetrating into surrounding tissues and organs, often with the formation of metastases. The prognosis of such diseases is often unfavorable, given the difficulty of curing them and the tendency for frequent relapses, and in some cases, active metastasis leads to death if vital organs are irreversibly damaged.
Borderline or precancerous skin conditions
(senile keratoma, xeroderma pigmentosum, cutaneous horn, Bowen's dermatosis)
Formations, the tissues of which, under the influence of hereditary or current causes, have changed, having the potential to degenerate into malignant tumors.
Treatment
To the question of how to treat papillomas in intimate places , modern medicine gives a clear answer: they need to be removed. Destruction of benign neoplasms can be carried out using various methods:
- electrocoagulation – exposure to high frequency current;
- cryodestruction - removal using cold treatment;
- laser removal – layer-by-layer treatment with laser radiation;
- chemical destruction - using special chemical solutions.
Classic surgical removal is also an option.
A specific scheme for how to completely and safely remove papillomas in intimate places is prescribed by a specialist in accordance with the localization of the process, the severity of the course, and concomitant diseases.
An important aspect of treating papillomas in intimate places is changing lifestyle and strengthening the immune system. An integrated approach avoids the emergence of new formations.
Are bumps on the lips dangerous?
The danger of bumps on the lips depends on the cause of their occurrence. Small blisters that appear after eating hot food or an insect bite will not harm the body.
Complications can result from:
- retention cyst caused by trauma;
- inflammation due to infections;
- herpes and papilloma on the lip.
Important!
New growths that appear due to smoking or drinking alcohol are also dangerous. If you don't change your lifestyle and give up bad habits, they can develop into lip cancer. A lump on the lip is a neoplasm caused by injury or disease. To prevent the pathology from developing into cancer and causing further complications, consult a specialist.