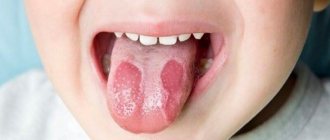
Tongue diseases do not develop as often as pathologies of teeth and gums. However, they cause a lot of trouble and pain. As a rule, people are faced with the problem of enlargement of the papillae, changes in their color and texture. Their hypertrophy causes pain and discomfort, signaling an inflammatory process and problems in the body.
The cause of an increase in receptors may be infections of the oral cavity, bacterial microflora, tongue injuries, or hidden ailments. Each specific case is individual, so if you have a similar problem, you should see a dentist. After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe effective therapy.
Causes of inflammation of the papillae on the tongue
If you have an inflammatory process in your mouth, contact your dentist immediately. Family dentistry in St. Petersburg is a clinic where every patient will be provided with assistance. The doctor will determine the causes of the disease and prescribe treatment. Problems may arise:
- When the patient’s diet includes excessive amounts of sour, sweet, spicy foods;
- If chronic stress develops in the body;
- When the patient received a tongue injury, burn, cuts, punctures;
- If the organ is affected by an allergic reaction;
- For some diseases of internal organs;
The surface of the muscular organ changes significantly under aggressive influence. The provoking factor is xerostomia, disease of the salivary glands, Sjogren's syndrome, diabetes mellitus. With glossitis, the sensitivity of the papillae increases. During the examination, the doctor must exclude HPV, leukoplakia, aphthous stomatitis, syphilis, and oral fibroma. Children are examined for scarlet fever.
Sometimes the disease can be triggered by acid reflux, gastritis, throat infections, systemic inflammation of the gingival tissues when the pathogenic microorganism develops rapidly. Taking some medications can cause pain. High concentrations of alkali or acid have a negative effect on the condition of the muscular organ. Injuries on the tongue can occur from a hard brush, dentures, or tartar.
Black tongue
Definition and symptoms
Black (hairy) tongue is a condition in which the surface of the tongue becomes keratinized and there is hyperplasia of the filiform papillae. The epithelium sloughs off, and bacteria begin to multiply on the lesions, producing a dark pigment, as a result of which the tongue becomes brown or black. The colored papillae resemble short hair in appearance, hence the name. The lesion spreads along the center line of the tongue, acquiring an oval or triangular shape.
Black tongue
The papillae reach a length of up to 2 cm and a diameter of up to 2-3 mm. Black tongue is not an independent pathology, but a symptom of various diseases or a consequence of the influence of a number of provoking factors. Occurs most often in men over 40 years of age. The disease occurs in two stages - in the first, the papillae grow and thicken without changing color. Timely treatment can prevent darkening and eliminate symptoms. During the second stage, the papillae begin to become keratinized and blacken.
Reasons for development
Factors causing lesions are divided into three groups:
- physical and chemical: antibiotic therapy, alcoholic beverages, cigarette smoke, insufficient oral hygiene, burn of the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- infectious: candidiasis, systemic fungal infections;
- pathological conditions of the body: fever, dehydration, decreased saliva production, metabolic disorders, diseases of the stomach and intestines, impaired trophism of the papillae of the tongue.
Treatment
Therapy consists of eliminating provoking factors, treating concomitant pathologies and following a diet. When diagnosing, diseases of the stomach and intestines, diabetes and fungal infection should be excluded. If candidiasis is detected, in addition to the main treatment, rinsing the mouth with salicylic acid and resorcinol is prescribed.
It is undesirable to eat salty, sour and bitter foods, which aggravate the course of the disease. If the papillae are severely overgrown, the cryodestruction method is used. The overgrown tissues are exposed to cold, after which they are removed.
Article on the topic: Candidiasis balanoposthitis in men
Prevention and prognosis
Prevention consists of timely treatment of the main pathologies, daily cleaning of the tongue with a special brush, and giving up alcohol and smoking. With adequate therapy and elimination of provoking factors, the prognosis is favorable, the tongue returns to normal within a few weeks.
Symptoms
When the papillae on the tongue become inflamed, tissue sensitivity increases significantly and taste changes. Patients complain of unpleasant discomfort in the mouth. The taste spectrum is distorted and becomes unnatural. In addition, a number of other symptoms appear.
- Noticeable tissue swelling.
- Marked increase in size of the papillae.
- Tingling and itching.
- Burning, mild soreness.
If you do not consult a dentist in time, complications may develop: lingual eruptive papillitis. This disease occurs over a long period of time with an increase in body temperature. Most often the disease affects children. An alarming symptom is the appearance on the surface of the vocal organ of bubbles (pustules) filled with a transparent liquid. When the first signs of illness appear, you should immediately visit the dentist. Timely treatment of the disease minimizes complications and speeds up recovery.
Anatomical and physiological features of the papillae
In both children and adults, the papillae cover the entire anterior surface of the tongue: the back, tip, root and edges . Their surface is formed by epithelium that does not become keratinized throughout life.
Based on their structure and functions, doctors divide papillae into the following types:
| Variety | Location (tongue area) | Functions |
| Filiform | Edge surface | Responsible for the sense of touch and help hold food; they are not involved in the perception of the taste of food |
| Conical | Edge surface | Responsible for the sensation of pain and temperature, contribute to the mechanical processing of food |
| Gutter-shaped | Root | Perception of bitterness |
| Leaf-shaped | The area of the tongue near the palatine arches | Perception of bitterness |
| Mushroom | The entire surface except the central part of the back | Sweet perception |
Despite the fact that only the groove-shaped, mushroom-shaped and leaf-shaped papillae are responsible for the perception of taste, all of their varieties are equally important for humans. Any change associated with them indicates a problem in the body and causes discomfort.
Localization
If the papilla on your tongue is inflamed, visit the dentist. Only he will be able to correctly determine the causes of the disease, find out what caused the damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth and the body of the tongue. The area where the disease is localized plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis. Pathology can cover the entire organ, part of it, or the sides. Based on this factor and the clinical picture, we can assume what exactly caused the inflammation.
In all languages
When the mucous layer of an organ is affected over its entire surface, the most common cause is a thermal or chemical burn. One can assume the infectious nature of the pathology. If the damage is severe, there may be no taste at all. Patients complain of severe burning.
On the root
Most often, the papillae on the tongue at the base become inflamed due to the action of allergens. The affected root of the muscular organ causes difficulties such as the perception of bitterness, because the inflammatory process has affected the circumvallate papillae. They are the ones responsible for this function. The patient's salivation increases, and the tissues in the oral cavity swell. This condition can also be caused by problems with the digestive system, too high or low acidity of gastric juice. It is on the back of the speech organ that bacterial or fungal glossitis is localized.
On the tip
The disease can affect the tip. This often occurs due to mechanical injuries or damage. The edge of the tongue is the first to come into contact with excessively hot food or aggressive drinks, which burns this area. Soft tissues often rub against sharp chips of crowns and are subject to accidental biting.
Side
The delicate surface on the sides often suffers from various anomalies. Leaf-shaped, conical, filamentous, mushroom-shaped structures are exposed by the teeth. This leads to an increase in the papillae, their hyperemia due to mechanical damage from fangs and molars. Also provoking factors are painful microorganisms and burns of chemical origin.
Anatomy of the tongue with photos
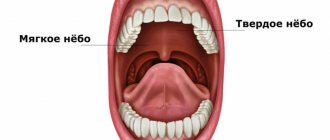
The tongue is formed by striated muscle tissue covered with a mucous membrane. It is involved in digestion, speech formation, allows you to express emotions, sense tastes, and regulates salivation. In a healthy person, the tongue has a pale pink color, with an even hollow running along it. Normally, it is covered with a whitish coating, which allows the grooved papillae of the tongue to be clearly visible.
Anatomically, the tongue consists of a root (1/3) and a body (2/3), separated by a terminal groove, as can be seen in the photo. The part facing the sky is called the back. On the lower surface there is a frenulum attached to the floor of the mouth. The tongue moves freely in the oral cavity and is rarely at rest. Thanks to the muscles, it can rise, shorten and thicken.
INTERESTING: photo of the root of a person’s tongue and the reasons for its color change
Diagnostics
Basic diagnostic methods in dentistry allow a thorough examination to be made in order to make the correct diagnosis. During the initial examination, the dentist determines the size of the pathological zones, appearance, color, and shape of the organ. The doctor finds out whether there is swelling of the tongue, ascertains plaque and its localization, abrasions, punctures, eczema, ulcers. The health of gum tissue and teeth is important.
In order to determine the type of pathogen and the form of the disease, a number of tests are prescribed:
- Histological smear;
- Sensitivity is determined using a special test;
- A general blood test is informative;
Systemic pathologists are also excluded: HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, AIDS. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, or immunologist.
Structure of the papilla
Any papilla is an outgrowth of the mucous membrane itself. Its shape is determined by the primary papilla, from which the secondary ones arise. The primary is covered with epithelium, like a crown.
Tongue histology specimen:
- Secondary papillae extend from the apex of the primary papilla; there are usually 5-20 of them.
- They grow into the epithelium and do not define the relief.
The connective tissue of the tongue papillae contains many capillaries. They shine through the epithelium, giving the mucosa a pink color. Histology of the taste buds of the tongue shows that they are located deep in the epithelium of the papillae. These taste buds, or buds (gemmaegustatoriae), are the terminal receptors of the taste organ.
They are groups of spindle-shaped curved cells in the amount of 40-60, among which there are receptor cells. They are distinguished by the presence of microvilli at the apical end. The taste bud is oval in shape. And its apical surfaces are formed in the form of dimples, where the taste pore is located.
Food particles enter here with saliva and are absorbed here by a special electron-dense (structureless) substance. These proteins are built into the membrane of microvilli; they are capable of changing and interacting ion flows. The tip of the tongue reacts to sweetness, the side surfaces to salty and sour, and the root to bitterness.
With this interaction, the potential of the cell membranes changes, and the signal is transmitted to the nerve endings.
Treatment
The diagnostic result allows you to prescribe treatment. Therapeutic dentistry has new methods and technologies that will return the patient to health.
- The patient is advised to adjust his diet and reduce spicy and sour foods in his diet. Dishes should not be hot.
- Fillings and dentures that injure the mucous membranes need to be replaced.
- You should have your oral cavity professionally sanitized.
- Remove soft and hard deposits on crowns.
- Cure caries, gum inflammation.
The therapeutic course may include taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and a course of treatment for diseases of internal organs. Regular visits to the dentist are a way to prevent oral problems and complications of existing diseases.
An injured, inflamed muscle organ requires tissue regeneration. For this purpose, drugs containing carotene are prescribed: Aekol, Retinol, Chlorophyllipt, Lugol. Ointment applications are made from Solcoseryl and Cholisal. For pain, anesthetics are used: Trimecaine solution, Anastezin emulsion. Patients are recommended medications to stimulate the body's defenses and vitamins.
If the disease is infectious, a scraping is first done. A pathogenic microorganism is identified in the laboratory. Then therapy is carried out according to the obtained strains. Candidiasis is eliminated with fluconazole. Acyclovir is prescribed against herpes. Metrogil-denta treats protozoal infections.
Folded tongue
A folded tongue is a congenital structural anomaly characterized by the appearance of deep folds resembling wrinkles on the back of the tongue. The mucous membrane is not damaged, and the person does not experience any discomfort. The folds are located in the longitudinal and transverse directions and can appear both in childhood and in adulthood. Sometimes a folded tongue is a symptom of Melkersson-Rosenthal disease, but in general it is a variant of a normally developed organ.
Folded tongue
The reasons for the appearance of a folded tongue are not clear. No treatment is required, but it is necessary to regularly remove food debris from the folds. If you do not take care of your tongue, it may become inflamed and cause bad breath.
Inflammation of the papillae on a child's tongue
If the child’s body is weakened and he complains of discomfort in the mouth and pain in the muscle organ, parents should immediately show him to the pediatrician and pediatric dentist. The doctor will determine whether his papillae are red and whether there is an inflammatory process in the mouth. Once the diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed. As a preventive measure, parents should ensure that the baby regularly brushes his teeth and rinses his mouth thoroughly. Children's immunity is not strong enough, so the body cannot cope with the disease on its own. The situation is complicated by the fact that children are curious; they put most objects in their mouths. To avoid serious complications, take your child to the dentist regularly.
Purpose and functions of language
The tongue takes part in several important processes occurring in the human body, and some diseases can be identified by its condition. Based on research, experts have found that the purpose of the human language is to perform the following functions:
- Digestive - takes part in the process of primary food processing (mechanical). The organ is responsible for proper salivation.
- Articulation – thanks to its structure, it becomes possible to speak,
- Absorption - mucous membranes have high permeability, which allows various substances to better penetrate the human body,
- Gustatory - thanks to this function we feel taste.
Interesting
Pigs are more sensitive than people. The person is a fairly average taster. He only has 3 thousand taste analyzers. The whale, which swallows a lot of fish without even chewing, has only a few or none at all. The pig, oddly enough, is more taste-sensitive than humans: it has 5,500 taste analyzers. A cow has 35,000 of them, and an antelope has more than 50,000! So not only do animals have a sense of taste, but many of them are much better tasters than humans. Marine animals are often covered in taste buds on the outside. Fish, for example, sense taste over the entire surface of their body. But creatures such as flies and butterflies can taste with their paws. Snakes and lizards use language for this purpose, but not quite in the same way as we do. They seem to shoot out the tip of their tongue, which catches small particles of food. These particles are delivered using the tongue to a special organ in the upper part of the mouth, which tastes and smells food.
Innervation
There are a lot of free endings in the language. This is what causes such acute pain if you accidentally bite it. The anterior part of the tongue, 2/3, is innervated by the trigeminal nerve. The posterior third is glossopharyngeal.
The mucous membrane itself contains its own nerve plexus, which has nerve fibers in the tongue bulbs, glands, epithelium and blood vessels. When a child is born, his tongue is short and wide, inactive.
Vital papillae
The circumvallate, or circumvallate, papillae are surrounded by a ridge (hence the name). Localized between the body and the root of the tongue on its dorsal surface. There are from 6 to 12 of them, stretching along the border line. Their length is 3-6 mm. They rise clearly above the surface of the tongue. In the PCT of the base of the papilla there are the ends of the ducts of the salivary protein glands; they just open into this groove. Their secretion cleanses by washing the grooves of the papilla from microbes, food particles and desquamated epithelium that accumulate in it.
By the way
It's sweeter to be a girl! Our perception of the taste of food depends not only on the state of the tongue, but also on many other factors, including the gender and age of the person. This is exactly the conclusion that Danish scientists came to. Experts conducted a large study involving almost 9,000 schoolchildren. All children received a set of samples of different foods, with the help of which experts had to find out how well boys and girls distinguished tastes of different intensities. It turned out that girls are better at distinguishing one or another taste than boys. Thus, the sensitivity threshold of boys to sour is 10%, and to sweet – 20% lower than that of girls. An important factor in the perception of taste is also the age of a person. Children's taste buds work better than adults'.