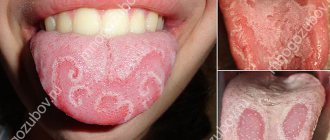
The tongue is an indicator of health. As soon as some non-standard processes begin to occur in the body, upon visual examination of the tongue, one can note: a change in color, shape, structure, the presence of itching.
This may be a signal of the development of a disease, both general and narrow.
If a child's tongue itches, the reasons may be: specific diseases of the oral cavity, allergic manifestations, or the first symptoms of the onset of ARVI.
Causes of tongue itching
In young children, itching of the tongue can be caused by food allergies . You should review the child's menu and exclude those foods that can provoke irritation of the organ. Against the background of an allergy, the tongue may not only itch, but also hurt, tingle and swell, and the stool may acquire a liquid consistency. With allergies, symptoms appear immediately upon contact with the allergen or after a short period of time.
A rash may appear on the cheeks or throughout the body. With obstruction, breathing becomes difficult and swelling occurs. It should be remembered that allergies can be a consequence of problems in the gastrointestinal tract, especially if the temperature rises and diarrhea appears.
Food allergies
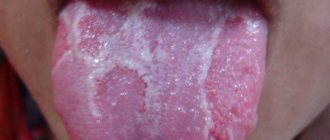
Candidiasis is manifested by the presence of a white coating on the mucous membranes of the mouth and tonsils, but the back of the tongue is clean. The child may experience a sour taste and pain when swallowing. Usually the fungus is contained in the baby’s body in a latent form and the catalyst for the disease can be a weakened immune system, injury to the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue. When the tongue is cleaned, under the coating you can see an inflamed focus of infection of a bright scarlet color.
Candidiasis
The tonsils may also become covered with white dots due to chronic tonsillitis , but in this case the formations are sporadic and the oral cavity is clean. The resulting crusts must be carefully removed with a cotton swab or bandage, as this is nothing more than purulent discharge.
Worm infestation in a baby manifests itself in the mouth area, and not just in the anus area. Itching can be either constant or periodic. The tongue may not only itch, but sometimes there is a burning sensation.
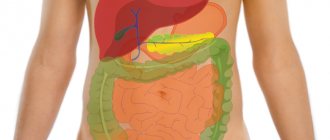
In diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, itching is not accompanied by other visual changes in the oral cavity, except for a white coating along the entire base of the tongue. But the patient may be bothered by pain in the right hypochondrium and itchy skin.
In case of caries, the damaged tooth should be filled immediately, otherwise the location of the disease becomes a favorable environment for harmful bacteria to live.
Infectious diseases of a long course can also provoke the appearance of microbes in the pharynx, penetrating there through the nasal passages.
Prevention
Bruxism at an early age can be prevented. Parents are advised to reconsider their daily routine. The last meal should be no later than 2 hours before bedtime. From 4-5 months, the baby can be given to gnaw on an apple or carrot in the evening so that his muscles get tired and do not shrink outward.
During the day, parents control that the child does not make voluntary movements with his jaws, does not creak them, expressing negative emotions. Watching TV and staying in front of a computer or phone monitor is limited to 2 hours a day. Before going to bed, it is advisable to completely abandon such entertainment and devote time to quiet board games, a walk in the fresh air or reading books. In the evening, they try to maintain a positive emotional mood to ensure a restful sleep.
To prevent calcium deficiency, pediatricians recommend taking small doses of vitamin D from October to March. Infants up to one year old need it, but studies show that calcium deficiency occurs even at older ages. Therefore, schoolchildren can switch to calcium complexes with vitamin D or multivitamins.
From early childhood, children can be taught to visit the dentist and take proper care of the oral cavity. This helps reduce the risk of bruxism due to periodontitis or fillings.
Diagnostics
The first doctor you should visit will be your dentist . It should exclude diseases of the mouth, teeth and gums. If the child’s tongue itches due to internal problems, then the pediatrician will help. He will prescribe general urine and blood tests, a biochemical blood test and, depending on the type of disease, prescribe treatment and, if necessary, give a referral to a gastroenterologist.
If the problem is gastrointestinal diseases, then it will be necessary to do a gastroscopy with a urease test and an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. All these examinations will show which organ needs treatment. In case of an allergic reaction, it is worth visiting an allergist and getting tested for allergens if the causative agent is initially unknown.
Treatment of teeth grinding
If a baby grinds his teeth in his sleep, special treatment is not always needed. If a symptom of lower jaw tremor appears in a one-month-old baby, this is an alarming sign. The mother should pay attention to how the baby takes the breast, at what time the jaw spasm or trembling of the chin appears. A consultation with a neurologist is required. It is possible that during pregnancy or childbirth the baby suffered a brain injury or suffered from hypoxia.
When a 7-8 month old baby begins to grind his jaws, the pediatrician may recommend a gel for easy teething. Experienced mothers purchase cooling silicone teethers in advance, against which the infant scratches his gums.
If the analgesic effect of cooling or dental gel is insufficient, the baby is given paracetamol or ibuprofen syrup. They relieve inflammation from the gums, eliminate pain and swelling.
In autumn and winter, a 4-5 month old child experiences calcium deficiency. At this time of year, the number of sunny days decreases, and the need for the mineral increases. Calcium is absorbed from milk if there is enough vitamin D in the intestines. It is produced under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. If there is a lack of sunlight, the vitamin is low, so it is necessary to take it in the form of an aqueous solution of drops. Vitamin D will not harm a one-year-old baby or schoolchildren in the winter. The dosage of the drug is selected by the pediatrician individually, so as not to cause a state of hypervitaminosis, which is dangerous for the kidneys.
Treatment of creaking, which often appears after overexertion or stress, is carried out with sedatives. For children, the doctor may prescribe sedatives of herbal origin or herbal teas with mint, valerian, motherwort and other combinations.
If the pediatrician cannot determine why the child continues to grind his teeth, an examination by a dentist is necessary. The doctor will grind off the protruding fillings and check the function of the temporomandibular joint. For periodontal inflammation and caries, he will prescribe special treatment. An incorrect bite is a reason to contact an orthodontist. He will select a mouthguard to protect your tooth enamel from being worn away. If the bite is defective, the use of braces or a corrective plate will be required, which is removed at night.
If there is a repeated creaking or the appearance of convulsive contractions in other muscle groups, be examined by a neurologist. The result of the electroencephalogram may indicate a mild form of epilepsy. For treatment, the doctor will prescribe anticonvulsants. They will help reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. If you refuse therapy, this phenomenon will occur more often and more severely.
Food allergies
Hives and facial swelling are the most common symptoms of food allergies. Hives appear as raised pink bumps with pale centers, similar to insect bites. Other symptoms include itching and swelling in the mouth, runny nose and cough, vomiting and diarrhea. Life-threatening allergic reactions may also include difficulty breathing and/or swallowing. The medical name for this phenomenon is anaphylaxis. Most of these reactions occur suddenly within 10-20 minutes. All this happens within 2 hours after eating a certain food containing allergens.
How do allergies occur in children?
Allergy symptoms occur when a child's body overreacts with a protective immune response to normally harmless substances. Instead of not reacting to dandelion, an allergic child's body will quickly release a series of chemicals (including histamines) upon encountering the flower that cause itchy and red eyes, swollen mucous membranes, a runny nose and sometimes a cough. There is no clear, accurate way to tell at a glance whether your child has seasonal allergies when they start sneezing in the spring (or fall).
Cross-reactions with other foods
Children with allergies to the following foods may react to other foods:
Cow's milk allergy: 90% also react to goat's milk and 40% to soy milk.
Egg: in 5% there is a reaction to chicken meat
Peanuts: In 5% of cases there is a reaction to other legumes (such as peas or beans). In 30% there is hypersensitivity to tree nuts.
Fish: in 10% a reaction to seafood is also observed.
Melon: 90% reacts to bananas and avocados
Ragweed pollen allergies can cause a cross-reaction with all melons, bananas and tomatoes.
Birch pollen allergies can cross-react with raw potatoes, carrots, celery and apples.
Grass pollen allergies may cross-react with tomatoes and kiwis.
How to treat seasonal allergies in children?
Over-the-counter antihistamines are most often used for allergy symptoms. Typical antihistamine active ingredients found in over-the-counter medications include diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine, or chlorpheniramine. Most often, antihistamines that do not have a sedative effect are used for children - loratadine or cetirizine.
Over-the-counter allergy medications should only be used in children over 6 years of age. If your child is under 6 years of age and has allergy symptoms, talk to your pediatrician about prescribing the best medications available at the lowest appropriate dose.
What else do parents need to know?
One in five people suffers from allergies at some point in their lives. Hay fever is the most common type of allergy. It is easily treated by avoiding allergens, washing the child in the shower after returning from outside during flowering season, over-the-counter medications, and sometimes additional prescription medications. Most children with hay fever only need allergy medication during seasonal outbreaks.
Allergy symptoms often change with age. Allergy symptoms can worsen during early childhood and often disappear as people get older.
Drug labels list the ingredients of allergy medications. Use the lowest dose possible to treat symptoms, and check with your child's doctor if he is younger than 6 years old before giving him an over-the-counter antihistamine.
Main causes of food allergies
8 foods cause 9 out of 10 food allergies.
In the first year of a child's life: cow's milk, soy milk and egg.
Older children: peanuts, tree nuts, fish, seafood and wheat.
Seafood includes shrimp, crab, lobster, clams, oysters and scallops.
Tree nuts include all nuts (such as almonds and cashews) except peanuts. Peanuts and tree nuts are the most common triggers for severe reactions.
Of children with a proven food allergy, 40% have severe reactions. The remaining 60% have a mild reaction.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading allergists in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
What is hay fever and why does it occur?
Hay fever is the most common type of allergy and is an allergic reaction to pollen in the air and environment. Children with seasonal allergies exhibit symptoms at certain times of the year when certain allergy triggers (such as grass or tree pollen) are circulating. However, some children and adults may be allergic to more than one pollen or trigger, causing symptoms to appear at different times throughout the year. Most children with hay fever experience a noticeable change in symptoms around the same time each year, which is during the flowering season.
Seasonal allergies typically first appear after preschool age, although they can develop at any time during childhood, usually before age 10. Allergy symptoms typically change with age, peaking in your 20s, and then often disappear as you get older. Allergies are usually inherited. If one parent has allergies, there is a 25% chance that the child will also have allergies. And if a child is lucky enough to have both parents with allergies, the risk of developing allergies increases to more than 60%.