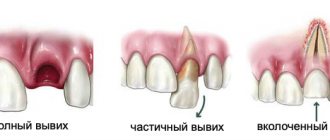
Why do we need baby teeth?
It's no secret that baby teeth perform their function for an average of 10 years, after which they are replaced by molars. If we compare this figure with the average human life expectancy, it turns out that we spend almost all our time with molars. What then is the function of baby teeth? Generally speaking, baby teeth are one of the main components of the proper development of the facial skeleton. As for the details, they are presented below.
- Milk teeth provide chewing load.
The bone tissue of the jaw is formed only under the influence of mechanical pressure. Milk teeth provide the necessary load, thanks to which the harmonious development of bone tissue and jaw bones occurs. - They form a bite.
If a child’s primary bite has any abnormalities, this will inevitably affect the permanent teeth in the future. That is why it is recommended to regularly show the child to the orthodontist until the complete change of the dentition. - They are the “progenitors” of molars.
The rudiments of molars are formed under the temporary teeth, and the milk teeth are a kind of navigators that determine the place of the permanent ones. A correctly formed row of baby teeth means that molars are likely to appear in their place. - Participate in the formation of diction.
Milk teeth are part of the speech apparatus and are directly related to the reproduction of sounds.
Classification
In orthodontic practice, various assessment criteria are used to determine which dental bite is correct and how to correct existing anomalies. The ideal situation, in which nothing needs to be corrected, is characterized by the following indications:
- Semi-elliptical shape of the upper and parabolic shape of the lower arc.
- Small - no more than a third - overlap of the vestibular surface of the mandibular elements.
- Contact of antagonists during closure and absence of obvious gaps.
Compliance on all points is quite rare, but in most cases the deviations are minimal and do not require medical intervention. Often the cause of imbalance is not congenital defects, but bad habits, some of which are formed at an early age.
Types of correct bite
In accordance with the generally accepted classification, there are four main types of occlusal relationships, characterized by the absence of problems and not having a negative effect on the jaw region.
Orthognathic
The optimal, from an aesthetic point of view, is a condition in which all elements of the dentition have an even shape, are located in the correct manner, without gaps or deviations from the midline.
Straight
A common phenomenon, the main feature of which is the lack of overlap - the cutting edges of the incisors meet along a line, which causes a specific type of smile, but is not considered as a pathology.
Biprognathic
Another type of even dentition without threes and diastemas, the distinctive feature of which is a slight deviation of the vertical growth vector of the units. With this development, the crowns are slightly tilted forward.
Progenic
In a normal state it is not accompanied by abnormal manifestations. The identifying feature is a slight frontal protrusion of the lower units.
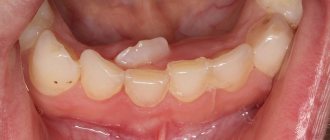
Milk and molar teeth: what are their differences?
Externally, baby teeth and molars are very similar, but if you look closely, you will notice some visual differences: baby teeth are smaller in size, and the incisors and canines have a more rounded shape. The main differences are related to anatomy and structure.
- Primary teeth have thinner enamel with less mineralization.
- The root canals of baby teeth are much wider and, accordingly, more susceptible to the entry of pathogenic bacteria.
- The dentin layer of baby teeth is thinner, and the pulp is thicker.
- Milk teeth have roots, but they are less pronounced and dissolve during the process of changing the dentition.
Molars
These are large molars. There are twelve molars in total, including wisdom teeth, six on each jaw. The crown of large molars is cuboidal. On the chewing surface of the crown there are from 3 to five tubercles. The presence of so many tubercles on the chewing surfaces of large molars provides numerous points of contact when closing the jaws and facilitates the grinding of food. They are located in the chewing zone and are used for primary food processing.
When do baby teeth appear?
The formation of a child’s teeth begins in the womb: this is partly why doctors recommend that pregnant women eat foods rich in calcium and other beneficial minerals. After birth, the first baby tooth (in the vast majority of cases, this is the lower incisor) appears when the baby is six months old. There are cases when the first teeth erupt already in the third month, and sometimes a child is already born with one or more teeth (among many peoples this is considered a lucky sign). Conversely, some children acquire their first teeth after reaching one year of age. Below you can see a table that shows the current timing of the appearance of baby teeth.
Milk teeth on the lower jaw
| Name of teeth | Age of appearance |
| Central incisors | 6 – 9 months |
| Lateral incisors | 10 – 14 months |
| Fangs | 17 – 21 months |
| Premolars | 13 – 16 months |
| Molars | 23 – 30 months |
Milk teeth on the upper jaw
| Name of teeth | Age of appearance |
| Central incisors | 8 – 11 months |
| Lateral incisors | 9 – 12 months |
| Fangs | 16 - 19 months |
| Premolars | 13 – 16 months |
| Molars | 25 – 32 months |
Causes of anomalies
Let's look at the main reasons why defects occur:
- Genetic factor. Mesial and distal occlusion are most often inherited.
For parents, knowing about the high risk of such a defect occurring in their child, it is easier to control treatment in childhood, during the formation of the maxillofacial system. - Developmental anomalies in the prenatal period. Various pregnancy pathologies can often affect the formation of the fetal dental system.
- Birth injury. Mesial occlusion is caused by displacement or dislocation of the baby's lower jaw during difficult childbirth.
- “Wrong” habits in childhood. These include constant pacifier or finger sucking, improper nipple latching, and improper sucking during bottle feeding. If the hole in the nipple is too large, the child’s lower jaw practically does not work when sucking and remains undeveloped.
- Frequent sinusitis and rhinitis, due to which the child constantly breathes through his mouth. With such breathing, the development of facial bones is disrupted.
- Violation of tooth change. Early removal of baby teeth often causes abnormal maxillofacial development.
- Incorrect prosthetics, lack of prosthetics.
- Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles due to stress provokes abrasion of the incisors and displacement of the jaws.
- Various injuries of the maxillofacial area.
Disorders during the eruption of primary teeth
The most common timing for the eruption of baby teeth is listed above. It is optimal when, upon reaching the age of three, the child has a full set of primary teeth. If baby teeth erupt late, experts advise parents not to worry unnecessarily: a delay of 2 to 3 months is considered normal. If after this period the teeth do not appear, then you should consult a doctor who will examine the child’s oral cavity, take tests and take panoramic photographs of the jaw, after which it will be possible to draw certain conclusions about the reasons for this delay. This usually occurs due to a lack of minerals and vitamins, which is easily solved with the help of restorative therapy. It is much worse when the rudiments of baby teeth are simply absent. This occurs extremely rarely and is usually caused by genetic abnormalities, periodontal inflammation and mechanical damage. In this case, to properly distribute the chewing load and develop the jaw bones, it is necessary to wear a removable denture.
When do baby teeth fall out?
“Childhood is over,” some parents say to their children whose baby teeth have been replaced by molars. Of course, this statement is mostly in a humorous form, since the average age when a child’s dentition ends is 12 years. At this time, the time of adolescence begins - one of the most interesting and eventful periods of our lives. As is the case with the eruption of baby teeth, their loss does not have a clear age limit. For example, today dentists are increasingly noting the early appearance of a full set of molars (as early as 10–11 years), whereas 20–30 years ago this could occur in adolescence (at 14–15 years). The service life of each baby tooth is on average 3-4 years: before the process of changing the dentition begins, the roots of the baby teeth are absorbed, so their loss does not bring severe pain and discomfort to children. Below is a table with the approximate timing of the loss of different groups of baby teeth.
Milk teeth on the lower jaw
| Name of teeth | Drop time |
| Central incisors | 5 - 6 years |
| Lateral incisors | 7 - 8 years |
| Fangs | 9 - 10 years |
| Premolars | 10 - 11 years |
| Molars | 11 - 12 years |
Milk teeth on the upper jaw
| Name of teeth | Drop time |
| Central incisors | 7 - 8 years |
| Lateral incisors | 8 - 9 years |
| Fangs | 10 - 11 years |
| Premolars | 11 - 12 years |
| Molars | 12 - 13 years old |
**Note: The first molar becomes the sixth molar, which does not have a primary tooth and erupts on its own at the back of the jaw.
Jaws don't grow because of soft food
One of the options for underdevelopment of the lower jaw. Specific “bird” profile.
The same patient. Stereolithography of the skull.
Reducing the load below the intended one leads to two very unpleasant consequences. The jaws begin to lag behind in development. As a result, lower and upper micrognathia is formed - underdevelopment of the jaws. The photos above show a very tough case. Most often this is a consequence of concomitant genetic disorders. But even on a less impressive scale, this is a wild headache for orthodontists. You can simply move and tilt individual teeth. It is almost impossible to adjust the position and size of the jaws, especially in adulthood. You will have to break bones, reshape the position of muscles, joints, tongue and much more.
Problems with changing teeth
As with the eruption of baby teeth, molars can also be difficult to erupt. Sometimes the crown part of the tooth does not appear completely or is completely hidden in the soft tissues. This situation is usually called retention: it can be caused by improper or too deep seating of the germ, as well as late loss of a baby tooth in its place. Just as in the case of baby teeth, a child may have no molar rudiments at all: this happens due to metabolic disorders, insufficient mineralization or damage to the rudiments at the intrauterine stage of development. This can also occur when infections and inflammations are transferred from baby teeth and in some other individual situations. This problem can only be corrected by prosthetics or implantation after reaching adulthood.
Milk teeth in adults: when childhood drags on
Yes, this happens, but very rarely. In dentistry, there are cases where baby teeth were found in thirty-year-old and even fifty-year-old people: doctors call such teeth persistent. What is the reason for such dental infantilism? This happens precisely for the reason that we talked about above. When a person lacks the rudiments of permanent teeth, the replacement mechanism does not start. Simply put, nothing puts pressure on the roots of baby teeth, which is why they do not dissolve, but remain in the oral cavity of an adult. It also happens that the rudiments of the molars are located too deep and also do not come into contact with the roots of the milk teeth. Treatment here is purely individual. If a person has a healthy baby tooth with intact roots, under which there is no molar rudiment, it makes sense to have it replaced with a veneer or crown in order to protect it from the external environment and give it the desired shape. If the baby tooth is unstable and its roots are resorbed, extraction is recommended. If there is a permanent tooth germ underneath, then it is “pulled” out; if not, a prosthesis is installed.
Prevention
The classic question: “When should you start brushing your teeth?”
At once. From the very first eruption. Here, of course, you will have to select games with children so that this does not turn into an unpleasant procedure. Let him try different types of toothpastes, brush his teeth with a plastic horse, and the like. To start, it is convenient to use silicone brushes that fit on your finger. And you still need to keep an eye on them, even if they already brush their teeth themselves. Believe me, they often brush their teeth terribly. Buy a plaque indicator - it's a dye. You can simply rinse your mouth with it and rinse with water. Uncleaned plaque will remain brightly colored. Unfortunately, so does the language for a while. Therefore, you can simply apply it to your teeth with an ear stick.
Do baby teeth need to be treated?
If you have carefully read the article up to this point, then you should have no doubts. Baby teeth must be treated, since they are directly involved in the formation of the bite and the appearance of permanent teeth. If baby teeth are not treated and cared for properly, there is a high risk of early loss. The enamel of baby teeth is thin; it quickly succumbs to the pressure of carious bacteria and the destructive effects of the external environment. Moreover, the inflammatory process, having penetrated into the depths of a baby tooth, can damage the rudiments of a molar, and then you will lose not one, but two teeth at once. Monitoring the child’s hygiene and regularly taking him for preventive examinations is the task of every parent.
Soft foods will cause tooth decay
This is the second consequence of feeding exclusively soft cereals and purees, when it is time for the child to chew solid food.
A colleague already talked about this in a post about caries. When we chew hard stems or gnaw on roots, we clean off plaque. In addition, there is a micro-massage of the gums, which improves their blood circulation and prevents the formation of tartar under the gums. The child should chew intensively and not drink instant cereals, jelly and banana puree. As a rule, if you see a child with severe multiple caries, then his diet will almost certainly consist of soft buns, cookies and all sorts of instant cereals. Well, in general, hygiene is also not very good.