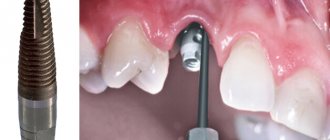
The term “ dead tooth ” is used in dentistry to refer to a tooth whose pulp has been removed or has lost its vitality.
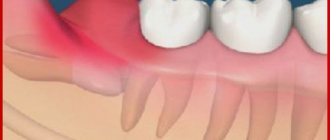
The pulp is loose connective tissue with a huge number of lymphatic, blood vessels and nerves. It is this neurovascular bundle, located in the so-called pulp chamber, that provides nutrition to the tooth, perceives various irritations, stimulates regenerative processes and acts as a biological barrier that prevents pathogenic microscopic organisms from entering the carious cavity into the periodontium.
A tooth with dead pulp quickly becomes brittle, darkens and loses its ability to regenerate.
What is a “dead” tooth?
This is what dentists call a tooth without nerve endings that no longer receives blood. Consequently, the tooth stops receiving nutrients and its work stops, the tooth dies. The disruption of blood supply is explained by damage to the pulp, the area where blood vessels and nerve endings gather into a single bundle. If the vessels and nerves do not function, then the nutrients no longer support the life of the tooth.
Method of treatment
The use of analgesics numbs the pain, but when a dead tooth appears, a trip to the dentist is inevitable. Doctors will take therapeutic measures:
- remove the remains of decomposed pulp;
- root canals are filled with gutta-percha;
- restore the front part of the tooth with a filling or crown
Restoration of the coronal part is carried out using a filling, or a filling on a pin, in case of a large volume of lost tooth tissue. If the filling is ineffective, the doctor will install a crown or inlay.
The indication for pulp removal is its extensive inflammation, which threatens decomposition processes and further development of infection.
Is it possible to cure such a tooth?
You can cure, but you cannot resurrect. The dentist will remove all affected tissues, nerves, root canals, expand them, clean them and treat them with an antiseptic, and then seal them hermetically so that infection does not enter from outside. The crown, if more than half of it is preserved, will be restored with a filling. For more severe lesions, an artificial crown will be installed. However, in case of extensive inflammation, the tooth can be removed and replaced with a prosthesis - an implant.
A “dead” tooth must be shown to a doctor, otherwise there is a risk of complications from the infection, which will develop into gumboil, osteomyelitis. A cured tooth can perform its function fully, but it can withstand the load worse, so its service life is significantly lower than that of “living” teeth.
Removing the pulp of the affected tooth
Pulp removal is a complex dental procedure that requires a highly qualified doctor.
Stage 1 – local anesthesia or general anesthesia
At the first stage of treatment, local anesthesia is administered in the area of the affected tooth. In exceptional cases, the patient may require general anesthesia. The use of anesthetics allows one to avoid preliminary killing of the nerve with arsenic.
Stage 2 – x-ray
At the next stage, the doctor conducts an X-ray examination to determine the length of the root canals.
Stage 3 – pulp removal and tooth filling
All video presentations
After reviewing the x-rays, the dentist:
- gently removes pulp,
- cleans, rinses with antiseptic preparations and fills root canals,
- and then restores the natural anatomical shape of the tooth.
If all procedures are carried out competently, and the patient carefully and impeccably observes personal hygiene, then the service life of a pulpless tooth can reach several decades.
Severe toothache is a consequence of unprofessional dentists
Evidence that the dental operation was performed incorrectly is a sharp toothache accompanied by an increase in temperature. If depulpation is of poor quality, the patient may need repeated surgery. At the same time, aching, mild pain after removal of the dental nerve is considered normal.
What is atraumatic tooth root removal?
What instruments does the surgeon use to achieve atraumaticity? For atraumatic removal, special instruments are used - thin, neat and elastic elevators that can minimally invasively penetrate and expand the periodontal tissue that connects the tooth root directly to the jaw. Using special instruments, the periodontal ligaments are cut so that the root can be removed as carefully as possible, in its “pure form.”
The vestibular plate that surrounds the bone is very thin. And we work with her carefully when removing teeth. It may also be necessary to saw the root of the tooth so that it can be removed in pieces. Sawing can be carried out with oscillating ultrasonic attachments - ultrasonic knives. Cutting the root of a tooth can be done quite effectively with a high-quality thin surgical dental bur, which has a certain length.
After cutting the root, the medial wall of the root is first removed, and then the vestibular wall of the root is removed. This allows for maximum preservation of surrounding tissue.
Then, after such removal, you can preserve the tooth socket or place an implant so that the bone is preserved as much as possible. Preservation of the tooth socket is carried out if there are no conditions for installing an implant at once, or if the patient undergoes delayed implantation.
If the roots of wisdom teeth are removed, the socket is not preserved; it is enough to remove them as atraumatically as possible. Let's talk about this in a little more detail.
Features of root removal of decayed wisdom teeth
Are there any difficulties when removing the roots of wisdom teeth? Removing the roots of wisdom teeth requires that the surgeon has sufficient experience. Often the roots of these third molars (wisdom teeth) are located close to the mandibular canal. Often the roots of molars are adjacent to the upper or lateral wall of the mandibular canal. The configuration of wisdom tooth roots is extremely diverse and sometimes extremely difficult to remove:
Therefore, when removing the roots of wisdom teeth, it is imperative that the patient undergo a CT scan. And the surgeon, as I said, needs to have some experience in surgical training in order to avoid the risks of removing the roots of such teeth and carry out the manipulation as efficiently as possible.
Like any root teeth, the roots of wisdom teeth are removed by cutting them along the roots. Wisdom teeth do not have problems because they are close to the angle of the lower jaw and there are strong cortical plates there. When I talked about thin vestibular walls, this comparison refers to the aesthetic zone of the smile, to the frontal group of teeth, including the premolars:
.
What happens to the tooth after the nerve is removed?
What happens to the tooth when the nerve is removed? Is it true that it will definitely darken, become brittle and break? Let's take it in order.
Modern dentistry does not imply any color change in the tooth after treatment. Yes, in ancient times they didn’t really know how to treat canals, so sometimes there was an infection in the canals, remnants of the pulp, and all this led to staining over time.
In addition, materials were used for filling that actually changed color over time. For example, resorcinol-formalin paste gave the teeth a reddish-brown tint (in the West they were called “red Russian teeth”), and silver pins and cements containing silver caused the teeth to turn black and blue and sometimes even the gums were stained.
Moreover, if the tooth could still be removed or a regular white crown placed on it, then the gums were forever impregnated with silver. Otherwise it was called silver tattooing. It is impossible to whiten such gums.
Modern methods involve the overwhelming use of gutta-percha when filling the canal, which never causes any staining. All other materials are also designed to avoid staining teeth under any circumstances. So today this process is completely safe for the aesthetic condition of teeth.
Now about the fragility of teeth after depulpation. This is a very persistent myth, which is believed to this day not only by patients, but also by many dentists.
Let us briefly say that in fact there is no special nutrition from the dental pulp that makes the tooth stronger. Also, the tooth does not become “dry and brittle.” Dentinal tubules are equally permeable on all sides, so moisture from the oral cavity enters the dentin in the same way as from the inside of the tooth. And the tooth simply physically cannot dry out in a wet oral cavity.
Many comparisons have been made between the tissues of living and dead teeth, and studies of their tensile and fracture resistance. All these studies have shown that there is no noticeable difference in the strength of living and dead teeth.
At the same time, we often observe chips and breaks of entire walls of dead teeth. What explains this? It's a very simple geometry and biomechanics. While the tooth is alive, its cusps hold tightly to each other with the help of enamel, and the forces acting on separation are extinguished at the very base of the cusp. The leverage of the force is very small.
If the tooth is depulped, then it lacks the main connecting link between the cusps - the lid of the pulp chamber. After all, it is through this place that the doctor enters the tooth canals and performs pulp removal and filling of the canals.
The filling, of course, sticks to the walls of the tooth, but sooner or later the so-called degradation of the bonding (adhesive) layer occurs, and the filling no longer holds the bumps so well. Now they are held on a long wall and have a very long arm that holds the tubercle. This is where a fracture occurs, but not because the tooth has dried out, but because the shoulder and the forces applied to it are too great.
In general, if you don’t go into all these complex details that most people don’t need, the conclusion is this: a dead tooth does not change color and does not become more fragile. But if a lot of tooth tissue necessary to maintain its strength has been lost, then it is better to cover the tooth with a crown.
How long does a tooth live without pulp?
This period varies greatly. In some patients, the tooth is destroyed within a year, and in others it can last for another ten years. What's the difference? Here are the factors that affect the condition of the tooth after depulpation:
- the degree of initial destruction of the crown of the tooth;
- pulp removal technique, quality of root canal filling;
- the method by which the tooth was restored after removal of the nerve (filling/inlay/crown);
- caring for the tooth after treatment, performing the necessary hygiene procedures.
After the tooth is depulped, treatment procedures are required that will improve its vitality. First of all, this is filling. Empty root canals are filled with special material. Complete and high-quality removal of the entire pulp, as well as hermetically filling the canals with filling material over the entire length, reduces the risk of inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth and the appearance of a cyst.
Depending on the degree of tooth decay and the specific clinical situation, the doctor may suggest restoring the tooth with either a filling, a ceramic inlay, or an artificial crown. An inlay and a crown are the optimal methods for restoring “dead” teeth, because they cover the tooth from above and fit hermetically to the tooth, thereby reducing the contact of the internal environment of the tooth with bacteria in the oral cavity, moisture and air, and protecting the tooth from chips and cracks. In addition, it is comfortable for the patient and has an aesthetic appearance.
For chronic and acute inflammatory processes
In most cases, tooth extraction is accompanied by acute or chronic periodontitis, inflammation of the gum tissue, or even the formation of purulent foci. If such a process covers a large area of tissue and is accompanied by high temperature, the formation of fistulas and edema, then most likely the attending physician will prescribe enhanced antibacterial therapy to slightly reduce the severity of inflammation. And only after this will surgery be performed in the oral cavity. On the other hand, there may be a need for immediate surgical intervention if the surgeon considers such intervention urgent. There can be many criteria for this choice, and only an experienced doctor can make an adequate decision.
Reasons why the pulp dies
There are many reasons why pulp dies. Most often, it is removed when pulpitis has already developed, the nerve is inflamed, it no longer brings any benefit, but is only a cause of torment (this situation leads to the development of severe pain) and a source of infection. It is important to understand that an attempt to endure the pain from pulpitis, when a person uses various painkillers that relieve discomfort, but do not stop the destructive process, can also destroy a tooth.
Also on the list of reasons why pulp dies is injury. For example, if a person hit his jaw hard, and after that did not visit a doctor, leaving everything as it was. Against the background of such a situation, pain often persists for some time, and then gradually subside, while the tooth inside dies.
A tricky problem. What you need to know about toothbrushes and how to choose them? More details
What can lead to the need to remove a “dead” tooth:
- damage to the tooth root by caries;
- the occurrence of longitudinal fractures and root cracks (below the gum level);
- the presence of a cyst or granuloma on the root of the tooth, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth, the treatment of which is not possible.
There are several rules that patients can follow to prolong the life of their teeth:
- cover the tooth with a ceramic inlay or crown;
- visit the dentist once every 6 months for a check-up, hygienic cleaning and, if necessary, a control X-ray of the tooth;
- do not chew hard food (nuts, seeds, crackers, etc.);
- Avoid temperature changes when eating (for example, hot coffee with cold ice cream).
As we see, a patient can do a lot for his health. But in order for the tooth to last longer, it is much more important to choose a specialized clinic that uses modern technologies, high-quality equipment and materials. An experienced and knowledgeable doctor will ensure the vital activity of a pulpless tooth for a long time.
What causes a tooth to die?
Trauma or damage to a tooth is one of the possible causes of tooth death. For example, putting something dangerous in your mouth that can cause the death of your tooth. The tooth can die quickly, over a few days, or slowly, over a period of months or years.
A tooth can also die as a result of poor oral hygiene. This can lead to cavities which, if left untreated, can slowly destroy your tooth. Cavities start with the enamel, which is the outer protective layer of your tooth. If left untreated, they can slowly eat away at the enamel and eventually reach the pulp. This leads to contamination of the cellulose, which separates the blood from the pulp and eventually causes it to die. You will likely experience severe pain as the decay reaches the cellulose.
A dead tooth can be identified during a routine dental examination, which includes an x-ray. You should always see your doctor after any tooth injury or if you have signs of a dying tooth. This way, your dentist can begin treating the tooth as soon .
Stuck root
The most common complication of tooth extraction can be a stuck, broken off root. If the root tip remains in the tissue, then the dentist has to use the entire arsenal of tools to get to the fragment: sometimes the tissue is drilled out or a section of the alveolus is removed to get to the desired depth. When hard tissues are crushed, this process can take quite a long time, since the dentist faces the difficult task of removing absolutely all the scattered fragments. In some cases this may take several hours.
External difference
Doctors note that a tooth devoid of pulp can often be recognized by external signs. For example, immediately after living tissue has been removed from it, it may acquire a grayish tint, which will become darker over time. In addition, such a tooth stops reacting to cold and hot. One of the disadvantages is the fact that, even if such a tooth is damaged by caries, a person may not feel the destructive processes in a timely manner, since due to the lack of nerve endings he simply will not feel pain. Such a tooth, in addition, over time begins to gradually deteriorate and crumble.
Teeth guarantee. Why is it important to read a contract in dentistry? More details