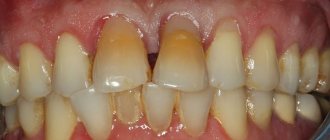
Not the most common, but nevertheless occurring, dental defect is when the front teeth, the most important for the “smile line,” are different in length, and one is noticeably shorter than the other. Sometimes this is even more noticeable than the usual unevenness of the front teeth, leads to psychological discomfort and impaired diction, and in addition, it is fraught with dental health. After all, the load on the front incisors is uneven, which ultimately can lead to problems with loosening and loss of teeth.
What to do if your teeth are of different lengths, and how to fix it?
Causes of dental defects
Lengthening or shortening of one of the incisors is usually a congenital anomaly. This feature of dentition development is associated with genetic factors. Experts also include the following as possible causes of the problem:
- periodontitis,
- malocclusion,
- presence of supernumerary teeth,
- abnormal shape of the alveolar process,
- disruption of the process of resorption of the roots of baby teeth.
Changes in the length of the central incisor can also be a consequence of jaw trauma. If a tooth is mechanically damaged, its lower part may chip. Because of this, the appearance of the smile deteriorates, discomfort occurs when chewing, and the risk of developing various diseases increases.
Anomalies in the shape and size of teeth - symptoms and treatment
Anomalies in the shape and size of teeth are variations in the development of teeth and the dental system that deviate from the norm.
Malformations of the dental system are divided into major (congenital) and minor. Congenital anomalies include facial clefts, such as cleft lip, cleft palate, etc.; to small ones - anomalies in the eruption, number, shape, size and structure of teeth. Unlike congenital malformations, minor anomalies are not accompanied by significant impairments and do not threaten the patient’s life, but they significantly affect the aesthetics of the tooth and treatment tactics, and can also lead to caries, malocclusion and other complications [1].
This article describes frequently occurring minor anomalies in the shape and size of teeth: macro- and microdentia, fusion of teeth, etc. Absolute and relative indicators of their frequency and prevalence are shown in the table below [11].
| Types of anomalies | Anomaly subtypes | Frequency of anomalies in the population (%) | Prevalence of anomalies (%) |
| Size anomalies | Macrodentia | 0,42 | 0,16 |
| Microdentia | 7,87 | 3,08 | |
| Shape anomalies | Fusion and fusion of teeth | 0,21 | 0,08 |
| Taurodontism | 11,27 | 4,41 |
Subtypes of anomalies and reasons for their development
All anomalies in the shape and development of teeth can be formed under the influence of negative factors that disrupt the development of fetal tissues and organs during pregnancy. These include:
- medications;
- nutritional supplements;
- viruses;
- industrial poisons;
- alcohol;
- tobacco smoke, etc.
Macrodentia is characterized by an increase in the size of the teeth - a large crown and a tapering root. It can affect both all and individual teeth [5]. The prevalence of macrodentia in permanent teeth is 0.03-1.9%. This pathology occurs more often in men. The large size of the crown causes problems with teething and leads to deformation of the dentition [9][10].
Microdentia is characterized by the reduction of one or all teeth [6]. According to epidemiological studies, the prevalence of the anomaly ranges from 1.5% to 2%, and is more common in women than in men [19]. Teeth with this pathology usually have a cone shape.
Macro- and microdentia can be hereditary. Since the formation of follicles (buds) of permanent teeth occurs at different times, starting from the 5th month of intrauterine development and up to 3 years, the number of abnormal teeth will depend on the impact of negative factors during this period.
Taurodontism (bull tooth) refers to abnormalities in tooth shape. It manifests itself in the form of an enlarged pulp chamber - the “core” of the tooth, consisting of connective tissue, nerves, blood and lymph vessels. The base of the pulp moves closer to the apex of the tooth, and there is no narrowing at the level of the cemento-enamel junction [12].
Taurodontism can occur at any age; it is most often found in patients 13-19 years old [11]. As a rule, the anomaly does not appear before this age, since the roots of permanent chewing teeth form before the age of 13.
Dental evagination (protrusion) affects the crown of the tooth. The anomaly occurs during the period of formation and formation of tooth buds. It appears in the form of an additional tubercle that protrudes from the crown of the tooth. This tubercle consists of enamel and dentin. Its size, structure and location vary widely. It can be horny, conical or pyramidal in shape. Otherwise, such an anomaly is called a tuberculate protrusion, a claw-shaped tubercle, a Leong premolar, and an occlusal enamel pearl.
The reasons for the development of evagination are not fully understood. The influence of X-linked and autosomal dominant inheritance is assumed [2]. With X-linked inheritance, the anomaly appears only in men, and women are only carriers of the mutant gene. With autosomal dominant inheritance, boys and girls with dental evagination are born equally often, and at least one of the child’s parents also has this anomaly.
Dental invagination causes the enamel to retreat into the dental crown. Otherwise, such an anomaly is called a “tooth in a tooth.” Intussusception occurs before calcification of dental tissues during fetal development [13]. It can affect any tooth, but most often occurs on the upper lateral incisors (front teeth).
Possible consequences
Dental defects must be corrected in a timely manner. On chipped teeth, the enamel becomes thinner, so they quickly turn yellow and soon acquire a brown tint. In addition, the cracks are filled with plaque, which mineralizes and becomes a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Because of this, the risk of developing caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and periodontitis increases.
Congenital dental anomalies also lead to various problems. Let's list the main ones:
- speech dysfunction,
- formation of mouth breathing,
- uneven distribution of chewing load,
- development of gastrointestinal tract diseases.
To avoid serious health problems and maintain the integrity of the dentition, it is necessary to correct uneven incisors.
Why do teeth come apart?
- due to genetic predisposition;
- if the patient has a short frenulum of the upper lip;
- due to artificial feeding of a child in infancy (using a pacifier);
- due to loss of teeth due to caries, periodontal disease;
- if the germ of an erupting tooth is located between the roots of adjacent dental units;
- for malocclusions;
- due to underdevelopment of the jaw, etc.
Note! A large gap between the crowns itself can cause malocclusion.
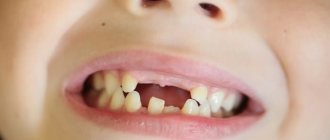
When should you see a doctor?
Dentist help is necessary if one of the incisors is in a high or low position. In children, this defect can disappear without any intervention when replacing milk teeth with molars. If different lengths of the front teeth persist despite a fully formed bite, you should consult a doctor.
You should also contact a specialist:
- when the enamel darkens,
- increased sensitivity of teeth,
- acute toothache,
- cutter mobility,
- formation of a sharp cutting edge.
The dentist will conduct an examination, determine the cause of the problem and help solve the problem.
Let's consider a clinical example of transposition correction using orthodontics
Patient N., 14 years old, came with her mother to the dental clinic. Complaints were made about the incorrect location of the canine on the upper jaw on the right. We already had a panoramic radiograph in hand, which complemented the analysis of the clinical situation in the oral cavity. To clarify the diagnosis and determine the optimal treatment plan, the patient was referred for a computed tomography scan of the jaws
After analyzing the diagnostic data, it was found that the root of the first premolar 1.4 is inclined towards the persistent primary canine 5.3, and the root of the permanent canine 1.3 is projected into the area between the roots of the premolars. Consequently, the situation was complicated by the fact that it was necessary not only to move the crowns, but also to “separate” the roots of the canine and premolar in their places.
When discussing the treatment plan with the patient and parents, a clear decision was made: to put the teeth in their places, despite the duration and complexity of the correction. The treatment method involved fixing a metal brace system initially only on the upper jaw, and after moving the crowns and roots, installing a brace system on the lower jaw for final correction and detailing the position of the teeth.
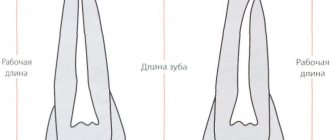
Methods for correcting front teeth of different lengths
Discrepancy in the coronal height of the central incisors can be corrected in several ways.
- Filling. Photopolymer restoration is the most affordable method of restoring the optimal length of teeth. Using composite material, you can build up the missing part of the crown.
- Wearing braces. Orthodontic treatment allows you to eliminate various defects in the dentition, including shortening and lengthening of one of the incisors.
- Installation of veneers. Ceramic or porcelain onlays replace the outer layer of teeth and provide the desired length. You can choose plates of a natural shade or snow-white.
When choosing an appropriate correction method, it is necessary to take into account the degree of deviation of the tooth height from the norm and the characteristics of the bite.
Elimination methods
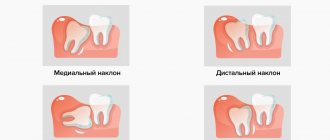
Methods for correcting malposition will depend on the degree of deviation in tooth height. Correction of supraocclusion with a slight deviation in height is carried out by grinding the surface of the cutting and chewing parts.
A slight deviation in height during infraocclusion can be corrected with crowns or ceramic onlays.
In the case of a complex anomaly, they resort to hardware treatment, the options of which will depend on the age of the patient and the cause of the deviation.
The low position is corrected using devices that extend the teeth simultaneously with the alveolar ridge.
For this purpose, classic orthodontic plates are used, equipped with an elastic rod, screws, springs and other additional devices that enhance the effect of the device.
High position is corrected through the use of mouthguards, inclined plates and braces.
The treatment method will, first of all, be selected based on the patient’s age. So, for children with primary and mixed dentition, more gentle options are used than for correcting anomalies with a permanent dentition.
Let's find out what impacted teeth are and how the pathology is eliminated.
In this publication we will talk about the reasons for the development of awl-shaped teeth.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/polozheniya/tremyi.html to learn more about gaps between teeth.
In children
To correct the height of teeth in childhood, removable appliances are most often used. In case of low position of single teeth, such a device is an orthodontic plate made of plastic, with a built-in vestibular metal arch located at the level of the cutting part of the teeth.
The arm of the device is curved in such a way that it exerts constant pressure only on the problem area in the area of the alveolar process. In addition to the bow, the device has a ring that is fixed on the abnormal organ.
A special hook is soldered onto the ring, designed to fix the vestibular arch. While wearing the device, the arc is thrown with force over the hook, creating force in the vertical direction.
To treat supraocclusion in childhood, they resort to the method of rebuilding the alveolar process of the problem area, due to the influence of a plate with a bite pad or special plastic overlays.
In order to ensure constant pressure on the pads and platform, light-curing plastic is periodically applied to them, which is then ground to the required height.
Treatment of anomalies in the position of tooth height in mixed dentition takes from 2 months to 1.5 years, depending on the severity of the anomaly.
For information on correcting the shape and position of teeth in the anterior part of the lower jaw, see the video.
In adults
In adults, as well as in children, intermaxillary traction is used to eliminate infraocclusion. Only in this case, non-removable devices are used, equipped with a rubber rod and wire ligatures.
This device consists of four support rings, two of which are fixed on the upper jaw and two on the lower teeth. On each ring, hooks are soldered on the vestibular side, on which an elastic rod is fixed.
Due to its influence, dentoalveolar elongation occurs. To enhance the effect, special beams with notches are soldered to the rings in a horizontal position to secure a wire ligature or additional elastic traction.
To achieve the effect, it may take from 6 months to 2 years, after which this device can be used as a retention option. It must be worn for at least 2 hours a day with the most minimal tension.
To eliminate supraocclusion, a complex technique is used using braces and orthodontic aligners. Combined use will allow the formation of a new shape of the alveolar bed and the correct position of the tooth.
The combination of methods significantly shortens the treatment period, the average duration of which is 1 year.
The third stage of transposition treatment is normalization of the teeth position
The photo clearly shows the incorrect inclination (torque) of the tooth crowns. Especially the palatal inclination of the canine. It was from this stage that rectangular arches began to be used (first Niti, and then TMA) with torque bends for canine 1.3 and first premolar 1.4 in order to normalize the position of their roots in the bone tissue and give the crowns an aesthetically and functionally correct inclination. Just before the start of this stage, the braces on the lower jaw were finally fixed
This required about 10 more months of treatment. Including detailing and improving contact between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw.
Before removing the bracket system, a control CBCT was performed, a close study of which showed the excellent location of the roots of the canine and premolar teeth, as well as the absence of clinically significant resorption of their roots.