Injuries to teeth and gums are common among children of all ages. If a child breaks a baby tooth, then first of all you need to remain calm and competently provide pre-medical care, while trying not to scare the baby. Most often, children are injured when they accidentally fall or when trying to chew hard food or an object. Therefore, children of primary preschool age, who are not yet accustomed to being careful, are most at risk; they may fall hard on the playground or injure their oral cavity with a foreign object.
Symptoms
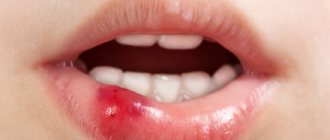
To suspect that a child has broken a front tooth is quite simple:
- Violation of the shape and integrity of the dental crown. Upon examination, you may notice a chipped tooth and a defect;
- Appearance of a crack. Characteristic of an incomplete fracture, part of the tooth may wobble, but not break off;
- Strong pain. The pain can be localized in the tooth, gum, or even spread to the entire jaw, depending on the severity and nature of the injury. Pain in the jaw occurs with impacted fractures, which are most often the result of trauma. Young children who cannot say what happened begin to cry and refuse food;
- Swelling, redness, bleeding of the gums. In some cases, the fracture is also accompanied by injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity. In severe cases, pathological mobility of adjacent teeth may appear.
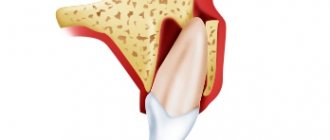
Damage to hard dental tissues
- Ifraction of enamel. It is a crack on the surface of the tooth without loss of dental tissue.
- Fracture within the enamel. Belongs to the category of chips without complications, but with the loss of some tissue.
- Enamel-dentin fracture. The fracture has no complications, and is distinguished by the passage of the chip line simultaneously along the enamel and dentin. Part of the dental tissue is lost.
- Enamel-dentin-pulp fracture. Refers to the number of fractures with complications, which result in exposure of the pulp.
What complications can there be?
The main complications of fractures of primary teeth are:
- Formation of a malocclusion (if a broken tooth has fallen out or been removed);
- Pulpitis. Damage to the enamel and tooth crown facilitates the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the pulp, where after some time an inflammatory process can develop;
- Periodontal abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis and other purulent complications. They are a consequence of advanced infection after tooth trauma.
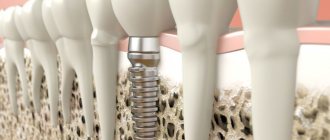
If a child breaks his molar front teeth, it is important to make sure that the roots of the teeth are not damaged. Injury or fracture of the root of a permanent tooth is dangerous because the tooth may have to be removed from the roots, and expensive implantation will be required to restore the dentition.
Tooth fracture - symptoms and treatment
Transverse (horizontal) fracture
In case of a fracture of the crown part of the tooth without damage to the pulp, caries may develop in the absence of treatment and subsequently pulpitis and periodontitis. In case of a fracture accompanied by exposure of the pulp, acute pulpitis is a complication. The occurrence of pulpitis is accompanied by pronounced pain in the area of the causative tooth with irradiation (spread) along the branch of the trigeminal nerve to the area of neighboring teeth or antagonist teeth. The pain mainly occurs at night. Without appropriate treatment, acute pulpitis can turn into chronic pulpitis, and later into periodontitis, characterized by the symptom of an “overgrown tooth” (the feeling that a tooth has come out; you cannot bite on it, as it causes pain). You can clearly identify the causative tooth by performing percussion - tapping on the tooth. Pain also occurs when eating hot food.
In the absence of treatment, after some time the process of pulp sclerosis begins - degeneration, pulp atrophy, its replacement with connective tissue. As a rule, there is no acute pain at this stage, but chronic inflammatory processes - osteitis or radicular cysts - begin to develop in the bone surrounding the tooth.
Vertical tooth fracture
This injury is incompatible with the continued existence of this tooth in the alveolus. Without treatment (in this case it involves tooth extraction), the situation leads to the rapid development of an inflammatory local process - dental periodontitis, which can later develop into periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), osteomyelitis (chronic inflammation of the bone, which leads to resorption of bone tissue in the area of the lesion). ) and into extensive inflammation of soft tissues - an abscess of the maxillofacial area.
In this case, a purulent infiltrate appears around the tooth, melting the surrounding tissue. The patient's general condition worsens, the temperature rises, and swelling of the buccal or submandibular area occurs. Without appropriate treatment (tooth extraction, opening of periostitis or abscess), the process quickly becomes diffuse. In this case, phlegmon of the soft tissues of the face and neck may occur. Such a rapid and dangerous course of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity is due to the structural features of the cellular spaces of the face and neck. Cellular spaces are located between the muscle fascia. They are loose connective tissue. A distinctive feature of this tissue is the rapid development of purulent inflammation in it, which then spreads to nearby muscles and tendons.
Complications of a fracture also include resorption (external and internal) of the tooth root after injury. It appears after a few months. Resorption can be in the area of the apex (apex) of the root or in the area of the tooth root fracture. It occurs due to the lack of a “replacement callus”, which should restore the tissues of the tooth root - dentin and cement. The symptoms are quite sparse. This may be tooth mobility or pain when biting on a tooth. As a rule, it is possible to clearly diagnose resorption after an X-ray examination. This situation is a late complication of a tooth fracture. The tooth must be removed [9].
How are they treated?
The dentist determines treatment tactics depending on the severity of the injury and the condition of the tooth. The following methods are used:
- Tooth restoration. Suitable only in cases where a small piece of the tooth has broken off and the pulp is not involved in the pathological process. Various types of composite materials are used to restore the integrity and normal appearance of the tooth;
- Depulpation. This procedure is used for more severe fractures when the child has symptoms of pulpitis. The process removes the infected pulp, which allows you to save the tooth and prevent the child from developing a malocclusion;
- Delete. A radical measure that is used in cases where it is no longer possible to save the tooth.
Tooth fracture exposing the pulp
This type of fracture is characterized by exposure of the pulp
X-ray
An X-ray reveals not only the absence of hard tissue fragments, but also a transformation in the shape of the periodontal fissure.
Biology
The pulp tissues are prone to healing and the creation of dentinal barriers, provided that the specialist uses the correct coating material. Direct pulp capping is most effective, and it is advisable to carry it out in the first hours after injury.
Among the most effective coating materials, it is necessary to highlight calcium hydroxide or mineral trioxide aggregate. Previous studies have shown that with their use, a dentinal bridge is successfully formed in 90% of cases.
Treatment
If a child's tooth breaks off and the pulp is exposed, it is possible to restore the hard tissue barrier only under certain conditions:
- The pulp was in normal condition before the injury;
- The blood supply to the pulp is not impaired;
- Using the direct coating method;
- No bacteria that can cause inflammation.
In conditions where the formation of the tooth root has not yet been completed, every possible effort must be made to preserve the pulp and the subsequent full development of the tooth root.
First aid
If you see a small chip on a tooth, but nothing bothers your child, then make an appointment with the dentist as planned. Many parents do not know what to do if their child breaks a front molar. Your actions should depend on the child's condition. If there is bleeding from the gums and severe pain, then you need to immediately go to the nearest dental clinic to see a doctor. If there is slight pain, but overall health is not affected, then you can give an anti-inflammatory drug (for example, paracetamol) in an age-appropriate dosage and make an appointment with a doctor the next day.
A child's tooth chipped. What to do?
Most often, a child, especially a small one, gets a chip as a result of an impact accompanied by pain. What to do in such a situation?
- First of all, the child needs to be reassured;
- Next, a visual inspection and rinsing the mouth with water is required;
- If the lip is damaged, it should be treated with antiseptics;
- If there is a broken fragment, it must be placed in saline or milk;
- Visit the dentist as quickly as possible. This must be done within 24 hours, or preferably a few hours.
The faster a specialist sees a tooth, the greater the chance of its survival and absence of infections.
Today, there is a broad classification for dental injuries based on etiology and anatomy. The proposed classification is based on the standards of the World Health Association, and is included in the ICD Appendix in the “Dentistry” category.
When is it necessary to install a crown?
Having a crown installed on an adult is common. But when a child needs a crown, parents are often scared. Meanwhile, crowns have a lot of advantages: they allow you to restore damaged areas of baby teeth lost due to complex caries or injury, they are aesthetically pleasing and inexpensive. We recommend installing crowns if:
- The tooth is significantly damaged, the child will not be able to fully chew food.
- The baby tooth has fallen out, and more than a year remains until the permanent one appears.
There are two types of crowns:
- Metal crowns with veneer made of composite material. These crowns are placed on the front teeth. They have an aesthetic appearance and protect the tooth from re-infection. Such crowns are not installed on chewing teeth, since the composite material often cannot withstand the chewing load.
- Metal crowns without veneer. Such crowns protect the tooth from infection, withstand the load of chewing, and even with the widest smile, are not noticeable to others. Currently, this material is considered the best for the restoration of baby teeth.
The use of such crowns allows a child’s tooth to be restored in one visit, which ensures the most comfortable treatment.
Injuries to baby teeth
Treatment of primary teeth plays an important role in dental health. Some moms and dads don't think so. This is a misconception. It is the strong temporary incisors, canines, and molars that are the foundation for the strength of the permanent masticatory organs. Therefore, therapy of temporary units must be carried out necessarily.
Mechanical damage varies in nature. They are:
- sharp
- chronic
The first group includes pathologies resulting from falls, impacts, and accidents. Injuries that have a chronic stage of development are associated with anomalies of the dental system and the habit of chewing hard objects. Because of this, the front milk tooth may suffer, as its tissues are injured. The unit may be damaged due to incorrect dental treatment due to the use of low-quality tools and equipment. Also, after removal of an organ, damage may remain. Injuries are classified into several types. This:
- Bruises
- Dislocations
- Fractures
In case of bruises, the structure of the crown is slightly damaged, its integrity is preserved. When the neurovascular bundle ruptures, the blood supply to the pulp is disrupted. The crown often becomes bluish. If there is no therapy, an inflammatory process develops. The child is constantly tormented by aching pain. After the examination, the dentist prescribes treatment:
- Protecting the pathological masticatory organ from stress for 15-20 days.
- The use of ointments and gels with an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Conducting electroodontodiagnosis, as well as radiography, to assess the condition of the pulp.
- Physiotherapy.
If a child breaks a front baby tooth, it may be a chip, crown fracture, or root fracture. For varying degrees of damage, different treatment technologies are used. When the fracture is complicated, visual inspection is not enough. For diagnosis, an electroodontic examination is performed, especially if a pulp defect is suspected. A radiograph is ordered to evaluate the unit's root canals. In such situations, therapy is recommended:
- The damaged enamel is polished and a filling can be placed, which reconstructs the anatomical shape of the unit.
- Serious crown pathologies require endodontic treatment or orthopedic measures.
- In case of slight injury to the root system, the problem is solved with a filling. Severe situations require removal of the anomalous unit.
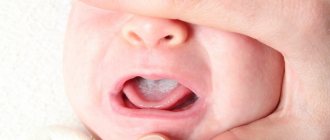
If a child knocks out a baby tooth, it becomes mobile, falls out of its socket, and changes position in relation to other organs. Dislocations can be partial, complete, or impacted. In the first case, periodontal fibers are torn and the alveolar wall is damaged. Such units wobble, shift, and form bleeding periodontal pockets. When pressed, children experience severe pain. The dentist’s main task is to fix the organ in the socket using a mouth guard or splinting.
Complete rupture of the connective tissue leads to the organ falling out of the socket. If the bleeding is profuse, the baby will be hospitalized. If the parents see a doctor within an hour, the unit can be replanted. The parents can return the tooth to its socket. When this manipulation cannot be performed, the organ is placed in a bottle, filled with milk, and a doctor is immediately consulted. If a unit is lost, it is replaced with a prosthesis.
When the unit is buried in the socket, soft tissue swelling and bleeding are observed. In such a situation, reposition is used. Orthodontic therapy is sometimes performed. It happens that unformed units are cut through again. In any case, the child should be under the supervision of a pediatric dentist.