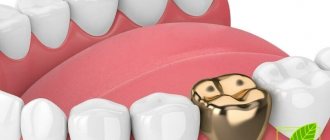
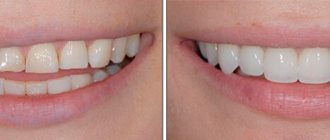
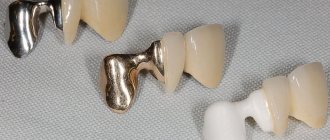
Advantages of glass ionomer cement
By choosing fillings made from this material, you get:
• guarantee of complete safety for dentin and pulp. This type of cement does not emit any toxins, does not react with tooth and oral tissues, and does not cause allergies; • a noticeable reduction in the price of treatment. Availability and relative cheapness; • glass ionomer cement can significantly reduce the overall cost of caries treatment; • increased adhesion. The cement adheres well to the tooth tissue, which ensures complete immobility and tightness of the filling; • additional therapeutic effect. After installing a cement filling, it releases fluoride compounds for a long time, which strengthen the tooth and improve its condition; • low thermal conductivity of the material.
Pros and cons of glass ionomers in dentistry
The main advantage of GIC is complete safety for pulp and dentin, non-toxicity of the chemical material, and its inability to cause allergic reactions. In addition, cement dental fillings reduce the cost of treatment. Serious shortcomings include:
- long hardening of cement (up to a day);
- roughness, inability to properly polish the surface;
- fragility, high shrinkage;
- short working time (cement quickly loses softness, leaving little time for the doctor to restore the correct shape of the tooth);
- unaesthetic due to unnatural colors (although for pediatric dentistry, colored fillings are rather an advantage).
Whether a glass ionomer filling is worth it depends on the specific situation. Experienced dentists work at the Dentalis clinic in Troitsk; they will assess the degree of tooth decay, take into account the patient’s financial capabilities and offer the best treatment option. For caries, time is a friend, so it is better not to aggravate the situation and contact the clinic as quickly as possible. To schedule a consultation, call or use the form below.
Disadvantages of glass ionomer cement
• long time for final hardening of the material. In some cases it can be about a day; • short working hours. In a short period of soft consistency of the material, the dentist cannot always adequately restore the chewing surface of the tooth; • surface roughness. Glass ionomer cement fillings are difficult to polish; • low aesthetics. Most glass ionomer materials are produced in colors that are not entirely typical of natural teeth. This partly contributed to the emergence of colored cements, which have become widespread in pediatric dentistry; • high shrinkage and abrasion of the material; • the need to form a cavity in the tooth with parallel walls.
Which material to prefer
The dental compositions described above have their own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Which filling do you prefer? Which is better - light or chemical (ordinary)? The choice will depend on financial capabilities and the location of the tooth in the oral cavity - posterior molar or frontal.
It is preferable to place fillings made of durable, indelible compositions on posterior chewing molars. For example, metal, glass ionomer or nanocomposite materials.
If we consider from an aesthetic point of view, it is better to put light or ceramic fillings on the front teeth, which are identical to tooth enamel and are invisible when smiling. Light dental products are characterized by a certain fragility, and therefore cannot withstand heavy chewing load on the rear molars.
To restore a chipped or damaged tooth in the front rows, light fillings are used. Using a composite material, you can completely restore the shape of a tooth, which will look organic. A distinctive feature of the light composite is the versatility of choosing a color to match the tone of the natural enamel of the teeth.
If we consider the quality of the composition from the standpoint of durability, then the most durable materials are metal and photocomposite - a service life of more than ten years. All other trains last from four to five years.
Sources used:
- Klyomin V. A., Borisenko A. V., Ishchenko P. V. Combined dental fillings. MIA, 2008
- Practical therapeutic dentistry" (Nikolaev A.)
- Scheller-Sheridan C (8 May 2013). Basic Guide to Dental Materials. John Wiley & Sons.
- https://www.dentalhealth.ie/
Features of the use of glass ionomer cement
Glass ionomer cements are most often used in pediatric dentistry, as they are unpretentious to difficult placement conditions. This type of material is used to fill carious cavities and seal the fissures of recently erupted permanent teeth.
In adult dentistry, glass ionomers are used for permanent fillings, as an insulating lining for more aggressive types of materials, and for fixation of orthopedic fixed structures (crowns and bridges). Also, in some cases, glass ionomer cements are used for filling root canals.
Filling teeth with glass ionomer cement is possible only if indicated. Using them in other situations, guided only by the desire to save on treatment, means creating a serious risk of rapid destruction of the filling and the occurrence of a relapse of the inflammatory process inside the tooth.
Popular dental materials
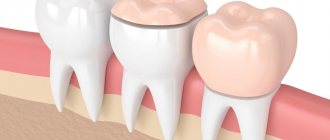
Fillings are divided into permanent and temporary. A permanent one is placed when there is minor damage to the tooth crown, a temporary one is used for long-term complex treatment or diagnostics. A temporary filling is also used to protect medicinal compounds during dental treatment: a medicinal compound is placed under it.
The materials from which fillings are made are divided into several types:
- cement, silicate;
- plastic;
- metal, amalgam;
- ceramics;
- composites.
Depending on the material used, fillings are divided into several main types:
- cement;
- composite;
- compomers.
The dental industry also produces other types of fillings - plastic, metal and ceramic.
The most durable material is made from light-curing composite. Such fillings are expensive, but the high price justifies the long service life. The fillings look aesthetically pleasing and have the ability to change their shade with changes in lighting.
The most popular material is dental cement. These fillings are still in demand among patients due to their low cost, high adhesion and strength. The fillings literally stick to the surface of the crown and do not form air gaps.
Cement composites
Dental cement (silicate cement, phosphate cement, zinc sulfate cement, etc.) is a time-tested material for filling teeth. Some varieties are used for the superficial layers of dentin, others for the deep ones. They are inexpensive, reliable and absolutely safe. They are the ones most often used in the treatment of children. Silicate cement is similar in color and transparency to natural enamel and is strong enough to withstand the loads of the front teeth.
The disadvantage of cement composites is their increased density. Over time, the hardened material destroys surrounding tissue, contributing to the development of secondary caries. Most often it is used to create a temporary filling for a tooth.
Types of fillings
For filling teeth the following is used:
- Cement - they are low cost and safe, but they shrink.
- Plastics are durable, but gradually lose volume and color.
- Metal alloys are reliable, durable and inexpensive, but unaesthetic.
- Ceramics are reliable and strong, used in the form of inlays.
- Composites are highly aesthetic and durable, but they shrink over time.
Important! The choice of material depends on the patient’s age and the degree of tooth damage. The most budget options are cements and metal (amalgam).
Plastic fillings
Carbondent and acrylic oxide are common materials for filling teeth. They are very durable, resistant to chemical attack and do not cause discomfort in the oral cavity.
The problems with plastic fillings are the gradual loss of original volume and discoloration. In addition, the material is quite toxic, especially acrylic oxide.
Chemically cured composites
Composite materials that harden chemically are rarely used in modern dentistry. Their basis is porcelain, which has a positive effect on durability. The material is perfect for filling miniature carious cavities. I am pleased with the price of composites.
The disadvantage of chemically cured material is the high degree of polymerization (during hardening) shrinkage. As a result of contraction of the walls of the crown, microcracks appear on it, and secondary caries develops. In addition, the material is inferior to light-curing composites in terms of adhesiveness (adhesion), which is why such a filling falls out of the tooth quite often.
A few words about the shortcomings
Nevertheless, despite such obvious advantages of the material, doctors also note some of its disadvantages:
- long-term hardening of the material: if the primary density appears 3-5 minutes after mixing, then the filling “ripes” completely only after a day, which increases the risk of destruction of its properties if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations. For example, he begins to chew on a treated tooth,
- GIC is less durable than its composite analogues, so for now in dentistry it is not used as a full-fledged filling material, but as an auxiliary or temporary one.
- not very suitable for aesthetic dentistry because it has low transparency, poor color range and does not polish well.
Prices for a tooth filling
| Service | Price | |
| Treatment of superficial caries without preparation ICON | 4,100 rub. | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with light-curing composite material 0.5 surface area | RUB 2,310 | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with light-curing composite material 1 surface | 4,050 rub. | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with light-curing composite material for 1-2 surfaces (medium caries) | RUB 3,950 | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with a composite light-curing material on 1-2 surfaces is complex (moderate caries) | 4,850 rub. | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with a light-curing composite material for 1-2 surfaces (deep caries) | 5,400 rub. | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with premium light-curing composite material, 1 surface | 6,450 rub. | Sign up |
| Removal of dental plaque (ultrasound + polishing) from one jaw | RUB 3,460 | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with a light-curing composite material on no more than two surfaces (deep caries) | RUB 5,950 | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with light-curing composite material 2 surfaces | 5,200 rub. | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with premium light-curing composite material, 2 surfaces | 7,150 rub. | Sign up |
| Restoration of a tooth with a composite light-curing material on no more than two surfaces (deep caries) is complex | 6,550 rub. | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with light-curing composite material 3 surfaces | RUB 6,360 | Sign up |
| Tooth restoration with premium light-curing composite material, 3 surfaces or more | RUB 8,950 | Sign up |
| Restoration of a tooth with a composite light-curing material when more than 2/3 of the lateral tooth tissues are destroyed | RUB 7,950 | Sign up |
| Artistic tooth restoration with color selection | RUB 9,240 | Sign up |
| Therapeutic veneer | RUB 11,550 | Sign up |