Untreated teeth can cause the most serious health problems, including dermatitis, eczema, gastritis, even stroke or heart attack. Decayed or missing teeth make it difficult to chew food well, increasing the load on the digestive system. The result may be a stomach ulcer.
The cause of serious consequences can be ordinary caries. This pathology aggravates negative processes in the oral cavity, causing throat diseases, otitis media and conjunctivitis. People with periodontitis are especially at risk, as harmful bacteria enter the bloodstream, promoting the formation of blood clots. Chronic gum and dental disease increases the risk of migraines and stroke. Problems with sick teeth need to be addressed without delay.
Stages of caries
- The appearance of a stain - the enamel changes color. It's still hard, but the process is already underway. A doctor can detect the spot. It is important to come for a preventive examination on time.
- Superficial caries – demineralization of enamel. The appearance of discomfort when eating hot, cold or sweet foods. At this stage, the enamel can be strengthened.
- Damage to dentin. Painful sensations increase and become longer lasting. The carious area grows and deepens. A cavity appears in the tooth in which food particles remain. A favorable environment is created for the growth of bacteria. Pulpitis may develop.
- Deep caries. Pulp degeneration occurs and periodontitis occurs. You can lose a tooth or undergo nerve removal. At this stage, the patient experiences severe pain.
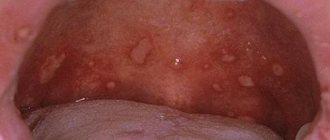
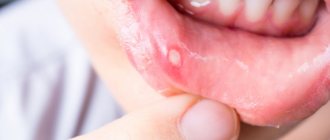
Stomatitis
Another disease that is within the competence of dentists is stomatitis . Since it does not directly affect the teeth, many do not seek help from dentists, although these are the doctors who will help to quickly and effectively cope with the unpleasant disease. Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. It manifests itself as painful ulcers in the mouth, increased body temperature, and deterioration in general condition. The cause of stomatitis can be various factors: allergic, infectious and traumatic. In addition, the same dental reasons can contribute to the occurrence of stomatitis: insufficient oral hygiene, accumulation of soft plaque and hard deposits on the tooth enamel. If such a diagnosis is made, the dentist will prescribe sanitation of the oral cavity, pain relief therapy and agents that eliminate inflammation and heal the mucous membrane.
Of course, these are not all common dental diseases. But all of them have one thing in common - the importance of timely consultation with a doctor at the first symptoms and the need for regular preventive examinations, even in a situation where nothing worries you.
Posted in Useful information
The most dangerous complications of caries
- Pulpitis
A sign of pulpitis is a sharp, acute pain radiating to the ear or jaw. It can occur at any time without connection with any specific stimuli. It is not always possible to determine which tooth is causing it.
- Periodontitis
The disease develops due to the lack of treatment for pulpitis. The problem is localized at the apex of the root of the affected tooth.
Dental diseases
Oral diseases, no matter what the cause (trauma, infection, allergen, heredity), greatly complicate everyday life and are a stress factor for the majority of the population.
And the fact that the beauty of the dentition and the charm of a smile are a social factor puts dental diseases in the forefront of diseases requiring immediate treatment.
The most common dental diseases and their symptoms are the topic of our research.
Since all dental diseases directly relate to the oral cavity, the symptoms of diseases are in one way or another tied to this particular part of the body.
What sensations help us understand that the cause of our suffering lies in the tooth, gum, jaw?
Diseases and symptoms
Let's try to compile a list of symptoms common to all diseases of the teeth and gums:
- Pain (aching, sharp, throbbing);
- Swelling of the gums, lips;
- Bleeding gums, purulent discharge;
- Bad breath;
- Feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity.
Common dental diseases and their symptoms.
Caries
With caries, there is a bad breath, discoloration of the teeth and insufficient salivation, acute pain, destruction of enamel and dentin.
Pulpitis
When the nerve is half exposed, the acute pain becomes periodic and prevents you from falling asleep. The tooth becomes hypersensitive to cold and hot.
Periodontitis
The main symptom of this dental disease is acute, increasing pain, aggravated by touching the sore tooth, often accompanied by swelling of the gums. Tooth mobility and the appearance of a fistula are possible.
Gingivitis
Symptoms of this disease are swelling and redness of the gums, pain, bleeding from the gums, and bad breath.
Periodontitis
The main signs by which periodontitis can be diagnosed are loose teeth, discharge from the gums, unpleasant odor, abscess, and detection of tartar.
Periodontal disease
The symptoms of periodontal disease are not very pronounced - they are exposure of the neck of the tooth without inflammation, itching in the gums, sensitivity to chemical irritants and temperature influences. There is often severe pain when chewing.
Tooth cyst
The insidiousness of the cyst lies in the vagueness of the symptoms and the unclearness of its expression.
This dental disease has the following symptoms: general malaise, increased body temperature, pain in the tooth when biting, swelling of the lymph nodes.
Tooth abscess
Swelling in the mouth, redness of the gums, prolonged pain in the tooth, fever, putrid odor, purulent ulcer on the gum - these are the main signs by which an abscess in the gum can be identified.
Symptoms in dentistry are an important aspect in diagnosis
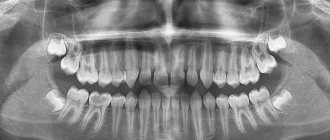
Oral diseases are characterized by a variety of symptoms and external manifestations, which can be hidden and difficult to identify when making a correct diagnosis. In addition, different dental diseases can have similar symptoms, so it is very important to correctly classify them and conduct additional diagnostics (x-rays). Only after all the necessary procedures can the disease be accurately diagnosed and dental treatment begin.
Signs of periodontitis
- Bad odor (halitosis);
- Reaction to temperature changes;
- Abscess on the gum;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Swelling of the periodontal tissues;
- Weakness;
- Fever.
Therapeutic or surgical treatment is used. In some cases, the tooth cannot be saved.
- Granuloma
Symptoms of the disease may not appear for a long time, but during exacerbation severe pain occurs. The danger of pathology is the development of complications, since the infection with the blood can spread throughout the body, causing cardiac and neurological disorders, and the development of flux and osteomyelitis is possible. There is a risk of blood poisoning.
Without treatment, the tooth will be lost.
Ignoring a dental problem will cause:
- Violation of smile aesthetics;
- Difficulty chewing food;
- Violation of facial symmetry;
- Headache;
- Change in articulation.
The following activities are carried out for diagnosis:
- Visual inspection;
- Palpation;
- X-ray;
- Use of dyes.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is not treated, it can lead to the development of periodontitis . Periodontal inflammation means inflammation of not only the gums, but also the tissues that support the teeth. These include bone, gums, mucous membrane and dental ligament. Their defeat can lead to exposure of the roots of the tooth, its loosening and, as a result, loss. Periodontitis, like gingivitis, is accompanied by bleeding gums and bad breath; in addition, it is characterized by itching and pulsation in the gum tissue, and tooth mobility. As the process progresses, mobility increases, the necks of the teeth become exposed and become increasingly sensitive to temperature stimuli. Treatment of periodontitis requires a serious approach and is carried out using both conservative and surgical methods.
Prevention of caries
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it.
Effective preventive measures for dental diseases:
- Carefully carried out hygienic procedures using rinses and irrigators;
- Minimum amount of sweets;
- Proper nutrition;
- Rinsing the mouth after each meal;
- A snack is also a meal;
- It is best to end the meal with a piece of solid food - part of a vegetable or fruit, which will help to naturally cleanse the teeth;
- Choose the right toothpaste, taking into account the advice of your dentist;
- Brush your teeth correctly, without making horizontal movements, so as not to damage the enamel;
- Eliminate bad habits;
- Have preventive examinations with a dentist at least twice a year.
Gingivitis
Perhaps the most common dental disease is not even caries, but gingivitis . At its core, gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. It is accompanied by bleeding, especially worse when brushing teeth and eating, as well as the appearance of bad breath. Gingivitis can be caused by a variety of factors, from malocclusion to poor oral hygiene. However, the latter factor not only provokes the problem, but in any case can aggravate it, since in this case an excess of soft plaque is formed, which is an accumulation of microbes and food particles, which actually cause inflammatory processes in the gums. In order to cope with gingivitis and prevent its occurrence in the future, it is necessary, first of all, to resolve the issue of proper oral hygiene and contact a dentist so that he can prescribe the appropriate treatment. Uncomplicated gingivitis, with timely treatment, often goes away within a week, while chronic gingivitis requires more intensive treatment.
Oral lichen planus
Lichen planus (LP) of the oral cavity manifests itself as pathological foci and defects of the mucous membrane. Depending on the clinical form of the disease, pathological elements can be in the form of nodules, erosions, plaques, blisters, and areas of hyperkeratosis. To clarify the disease, it is important to find out the presence of lesions on the skin. The most reliable diagnostic factor is a biopsy with further histological examination of the obtained material. Treatment of LP of the oral cavity is symptomatic and pathogenetic in nature. In case of exacerbation, corticosteroids are prescribed in short courses.
Oral leukoplakia
Oral leukoplakia is a condition characterized by areas of thickened epithelium. They resemble whitish or gray plaques, localized in the tongue, corners of the mouth or buccal mucosa. The reason for the appearance of such a sign is constant traumatization of the mucous membranes by an incorrectly installed filling or prosthesis, smoking, and professional factors, such as participation in the processing of petrochemical products. The concern is that leukoplakia is considered a precancerous condition.
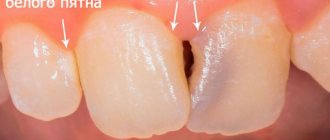
Teeth discoloration
Teeth discoloration is caused by a lack of minerals in the enamel. There are several reasons for the development of this symptom:
- hypoplasia due to genetic reasons;
- metabolic disease;
- improper hygiene;
- erosion resulting from the action of stomach acid during reflux disease, etc.
To make the right decision, you need to carefully study the reasons. The situation can be restored with the help of fluoridation, the use of composite varnish, and veneers.
Jaw clicks
If, when you open your mouth, you hear a crunching sound and there is pain that radiates to the ear - these are symptoms of temporomandibular joint dysfunction.
The reasons may be different: for example, during dental treatment, the balance was disturbed and crowns were placed too large, resulting in muscle tension, which developed into constant pain. In this case, it is enough to grind the points of contact of the teeth with each other.
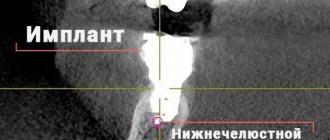
Another reason may be the loss of teeth, especially the lateral ones, which secure the bite. Because of this, increased stress is placed on joints and muscles. This problem can only be solved by restoring the dentition with implants.
Clicking jaws and pain when opening your mouth may indicate problems with the temporomandibular joint
The jaw can also click due to injuries, infectious diseases and musculoskeletal disorders. To establish the exact cause, you need to contact an orthopedic dentist.
Hairy tongue
A hairy, or black, tongue is manifested by hyperplasia and keratinization of the filiform papillae of the tongue, which can reach 2 cm in length. In their appearance and dark color, such changes resemble hair. In this case, complaints are purely aesthetic in nature. In rare cases, patients report a sensation of a foreign body on the tongue.
Keratolytic agents are used as a treatment method. With pronounced signs of hyperplasia, it is possible to remove the papillae by cryodestruction or radio wave method.