31.10.2019
A trip to the dentist does not always end the way you would like. A common situation is when a tooth reacts to exposure to cold after a filling procedure. The reaction of a tooth to cold is a complication that results from the installation of a filling. This material will tell you why this situation occurs and how you can deal with it.
Causes of hypersensitivity
After treatment does the tooth react to cold?
The increased reaction of the tooth to exposure to low temperatures indicates only one thing - the dental nerve is alive, and its reaction is hypersensitive.
This occurs under certain circumstances listed below.
If you have illnesses:
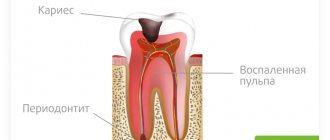
- Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle. Here the pain is prolonged and can last from a couple of hours to several days.
- Caries is the destruction of hard tooth tissues. In this case, the pain will occur for a short period of time and gradually fade away.
The dentist will carry out the process of installing a filling only after he has eliminated the true cause of the tooth disease.
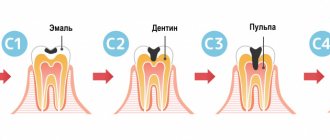
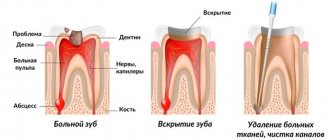
Tooth structure
The human tooth is quite complex. The crown (the outer protruding part) is covered with enamel, the hardest tissue in the body that protects the tooth from infections and mechanical damage. On the crown, immediately below the enamel, there is dentin - a durable tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth. Dentin is pierced by dentinal tubules, which, in turn, are connected to the pulp - loose connective tissue in the tooth cavity. The pulp contains a huge number of blood and lymph vessels, many nerve endings that instantly respond to any external influences on the tooth.
Any, even the slightest damage or even thinning of the enamel leads to the fact that the influence of external influences on the pulp and the nerves located in it increases. And a tooth, even at first glance quite healthy, treated and filled, reacts with pain - for example, to hot and cold. This reaction is called hyperesthesia.
Installing a filling after caries treatment as a problem of discomfort
Caries has two degrees of progression: chronic and acute. There are also several forms of dental damage by this pathology: deep, medium and initial.
The dentist treats deep and medium forms of lesions by mechanical treatment of the affected area, followed by installation of a filling.
If during the treatment of the tooth part of the tissue affected by caries was left behind, this may become the root cause of pain when exposed to cold.
In some dental offices, doctors use a special liquid that stains the affected part of the dental tissue with a certain color. This is very convenient, since the dentist can clearly see which area needs to be removed. But not all doctors use this drug.
In a filled tooth, pain can also be caused by other reasons, for example, improper filling procedures for deep caries. The chronic course of caries will be expressed by dense pigmented dentin, in which case the procedure for removing the affected tissue can be stopped, followed by the installation of a filling.
If the dentin is soft, the dentist may decide to strengthen it with a lining containing calcium. In this case, it does not open the tooth cavity. The infection contained in the affected bottom of the cavity gradually penetrates into the dental cavity through the dentinal canals.
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle, accompanied by pain, is a response to infection.
The occurrence of pulpitis can be provoked by incorrect tactics of the procedure, when in the process of removing tissues affected by caries, sufficient air-water cooling of the tooth tissues was not applied. The consequence of this is heating of the pulp tissue, which provokes the occurrence and development of pulpitis.
Pulpitis as a cause of pain after filling
With this pathology, inflammation of the nerves and blood vessels that are located in the dental tissue occurs.
Its occurrence can be provoked by nervous strain, infection and overheating of the pulp tissue.
Painful sensations after filling again indicate that the procedure was performed incorrectly.
Due to frequent night pain, the tooth is amputated, since the infection penetrates from the crown to the root area.
Another cause of pain is incomplete removal of the neurovascular bundle. There is a possibility that not all canals were found and passed through by the dentist.
The process of treating pulpitis most often extends over several visits to the doctor. In this case, the dentist will place a temporary filling from visit to visit until the treatment process is completed and the permanent filling is installed. If the treatment is delayed, after some time microscopic gaps appear between the temporary filling and the dental tissue, through which irritants (including cold ones) penetrate into the dental cavity, causing pain.
Dangerous post-filling pain
There are often cases when pain after the installation of a filling serves as a signal of a serious problem that can undermine the patient’s health. Such pain does not go away on its own, regardless of whether you treated caries or pulpitis.
Dangerous pain is associated with infection in the tissue and is characterized by:
- increased pain in the treatment area;
- pain when eating and drinking, even if the food is at room temperature;
- increased body temperature, in some cases - fever and chills;
- swelling of the gums;
- severe swelling and redness of the cheek;
- the appearance of a feeling that the tooth is in the way: it is sticking out, ready to fall out;
- tissue necrosis, which causes a putrid odor in the mouth.
If at least one of the above signs appears, you should seek help from a doctor to avoid complications.
Causes of dangerous pain
Diagnostics will help determine the cause that triggered the development of the infection. In this case, it is important to choose a competent dentist, since in most cases it is the inaccuracy of the examination
leads to
incorrect diagnosis
and the appearance of toothaches.
- Medical error (haste, negligence) includes several sub-reasons that prompted the patient to re-visit the dental office (usually in another clinic and with another specialist), treatment and refilling.
So, these reasons include:
- diagnosis without x-ray.
There is a risk that the doctor will not notice serious problems: for example, inflammation that began in the canals even before treatment. As a result, the treatment will be incomplete: caries is treated, but pulpitis and infected canals remain.
- installing a seal without complying with safety requirements.
This procedure will lead to sharp pain as soon as the anesthesia wears off.
- a filling that is too large or small and disrupts the bite.
At the same time, you need to understand that the shrinkage of any filling, even if selected with the utmost precision, takes time.
If a day or two after the filling the feeling of discomfort (the filling sticks out, puts pressure on the tooth or, on the contrary, settles; the tooth is in the way; it’s uncomfortable/painful to eat) has not disappeared, a re-examination and adjustment of the filling/installation of a new one is necessary.
Breaking off an instrument when cleaning canals is one of the causes of pain
- poor medical treatment of the tooth.
Rushing to prepare a tooth for treatment is fraught with further development of infection. A professional always carefully treats the tooth cavity, even taking into account the complex structure of the canals. Pedantry helps prevent the occurrence and further development of infection.
- drying the cavity.
It is important to properly dry the tooth cavity, because if you don’t dry the walls enough, the filling won’t stick; if you dry it too much, the tooth will become more sensitive.
- overheating of tissues.
The drill operates at high speeds, inevitably heating the treated area. If the doctor does not provide cooling (air and water), the tissues overheat and a nerve burn occurs.
In such a situation, the pain after filling will not disappear, but will develop, leading after some time to pulpitis.
- foreign body in the tooth.
Haste and inattention when working with medical instruments are unacceptable. Otherwise, when filling, a fragment may remain in the cavity. If not removed in time, it provokes severe pain, purulent inflammation, and leads to swelling.
- The second reason is no longer related to the doctor, but to the patient and consists in violating the recommendations.
The main requirement for the patient is not to overload the tooth and not to forget about regular hygiene.
After filling, the doctor explains how to properly care for the treated tooth and the entire oral cavity. In the first two to three days, it is important to take care of the tooth, avoiding strong mechanical impact. You should avoid solid foods (nuts, crackers) and viscous dishes (milk porridge, pureed soups).
After anesthesia, you should refrain from eating, because due to temporary loss of sensitivity, soft tissue can be damaged: cut with hard food, burned with a hot drink.
Itching and redness are some of the signs of an allergy to the composite.
- Allergy to material.
Individual intolerance to the components of the drug can provoke post-filling pain. An allergic reaction usually manifests itself to dyes and preservatives that are part of the filling material. If this is the problem, at the next visit the doctor will select a different filling composition.
Signs of an allergy to a filling:
- soreness;
- swollen gums;
- skin rash, itching;
- asthma attack.
When pain is normal
There are very frequent cases when the procedure for treating caries and pulpitis is carried out according to all the rules, but pain still occurs.
In this case, the cause of the pain is hyperesthesia.
Excessive sensitivity of dental tissues to various irritants is hyperesthesia.
Symptoms intensify if there are small cracks in the enamel of the teeth. Various factors contribute to the appearance of such cracks:
- Damage to the enamel from mechanical impact (hard bristles of a toothbrush, during the whitening process, due to impact or scratch with cutlery, etc.).
- Exposure of enamel tissue to aggressive nutrients (for example, citric acid).
Diagnosis of pathology
At home, you can check the correct installation of the filling in a simple way - pour cold or hot water into your mouth.
If pain occurs immediately and passes just as quickly, the cleaning procedure for removing tissue affected by caries has not been carried out sufficiently.
Taking into account the fact that not all procedures were performed correctly in the treatment of pulpitis, the pain will gradually increase and just as slowly go away.
In some cases, pulsation appears inside the tooth - this is the result of overheating of the dental tissue during the preparation process.
If symptoms do not go away within a few days, consult a doctor.
Dentists diagnose the cause of pain by examining the oral cavity. The tightness of the seal is examined and exposure to cold air and water is applied. After removing the filling, the doctor performs probing by tapping on the tooth. When painful sensations appear in various areas, the existing pathology is determined.
Pain in the walls is a sign of medium caries, in the bottom of the tooth – its deep form, and deep in the mouth of the canal – pulpitis.
Solution
If after the filling procedure pain is diagnosed, then you need to wait 2-3 days, perhaps they will pass.
During this period, it is recommended to take painkillers with anti-inflammatory properties.
The pain does not subside after 72 hours - you should contact your dentist.
At a repeated appointment, the dentist performs the following series of actions for caries:
- Produces local anesthesia.
- Removing the seal.
- Removal of the area affected by caries.
- Reinstallation of the filling.
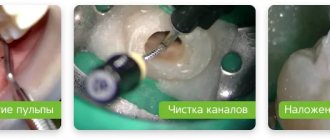
The stages of treatment of pulpitis (primary or repeated) are as follows:
- Administration of an anesthetic drug.
- Removing the filling and providing access to the tooth canals.
- Treatment of canal-containing areas using dental instruments with parallel exposure to an antiseptic.
- Installing a filling on a dental canal.
- Filling a tooth with a permanent or temporary filling (this is decided by the dentist).
If a doctor has installed a temporary filling for you, this means one thing - you will definitely have to visit him on the appointed day. If this is not done, the consequences may be negative.
When is there a reason to worry?
Sometimes doctors recommend that their patients take painkillers after treatment, as they objectively assess the complexity and assume temporary side effects. But symptom relief does not take longer than 3-4 days even after tooth extraction. You must understand that pain is not an enemy at all, but a benefit that signals a problem. And if it appears on an ongoing basis for a week or more, this is a good reason to visit a specialist.
Pay close attention to any accompanying symptoms:
- Fever or slight but constant increase in temperature;
- Bleeding gums around the treated tooth;
- Acute attacks that occur at night;
- A significant increase in sensitivity, encouraging you to completely abandon potential irritants in the form of ice cream or hot tea;
- Numbness of the soft tissues of the jaw at the site of the procedures;
- Darkening or blueness of the gums;
- General malaise and weakness without objective reasons.
Constant aching pain with periodic exacerbations can be associated with overdrying or underdrying of the formed cavity before filling. Both mistakes by the doctor are fraught with complications. When overdrying, persistent irritation of nerve endings can occur, leading to death. If it is not dried enough, the adhesive (sticky material) cannot be absorbed into the dentin, and when the filling shrinks, it comes off from the bottom of the cavity, creating a discharged space here like a vacuum. This also irritates the nerve endings (in professional language the phenomenon is called “debonding”).
In both cases, there is no point in enduring pain for more than a week. Perhaps after 7 days it will really stop bothering you, and the reason for going to the dentist will disappear by itself. But if a week after treatment has passed and the symptom persists, you should immediately visit a doctor.
How to relieve toothache yourself?
- If pain occurs, the right solution would be to take special painkillers. Dentists advise their patients Nurofen, Ketanov, Dexalgin, Baralgin. You can also take regular analgin in tablets. Specialists at Dr. Granov's clinic strongly recommend that you stop taking aspirin and medications containing high concentrations of acetylsalicylic acid. The analgesic effect from them is small, but in high dosages the substance provokes complications, sometimes very dangerous for general health.
- Temporarily stop chewing food on the affected side. Perhaps the symptom is associated specifically with biting - that is, mechanical irritation.
- Under no circumstances use “grandmother’s methods” in the form of heating, lotions or compresses. The procedure can significantly aggravate the current situation and even obviously complicate the process of subsequent treatment, if necessary.
- Antibiotics should not be taken without a doctor's prescription. The selection of antibacterial drugs is a responsible step in which the doctor carefully weighs the benefits and risks. Unauthorized use of antibiotics can lead to unpredictable consequences.
- You can purchase a natural product at the pharmacy - dental drops. It contains plant extracts of valerian, mint and camphor. Soak a tight cotton swab in the solution and apply it to the sore tooth. Change the tampon every 10 minutes until pain subsides.
- You can help yourself by rinsing with decoctions of soothing herbs: mint, lemon balm, chamomile.
Prevention and prevention
In order to prevent pathology from occurring, it is necessary to protect your enamel from various damages. To do this, follow a number of simple rules:
- Visit your dentist at least twice a year for a checkup.
- Balance your diet so that sour and sweet foods are found in minimal quantities.
- Avoid using toothbrushes with hard bristles. They can not only damage gum tissue, but also cause microscopic scratches on the enamel.
- Avoid eating excessively hot foods with cold foods (such as hot coffee and ice cream). Due to sudden temperature changes, tooth enamel can crack.
- Avoid teeth whitening procedures using aggressive chemicals. If you want your teeth to be snow-white, use whitening pastes. The process is longer, but safe for the enamel.
- Maintain personal hygiene: brush your teeth 2 times a day with toothpaste that does not contain aggressive elements.
A very effective prevention would be the use of mouth rinses. They can be produced by pharmaceutical companies and sold in finished form. Or you can make a special decoction at home, based on various herbs and plants.
If you experience pain while brushing your teeth or eating cold food, contact your dentist immediately. Delay will lead to destruction of the integrity of the tooth and nerve endings.
Oral care products
What to do if your teeth hurt from the cold? First of all, you should change your oral care products. The pharmacy sells special toothpastes for teeth with increased sensitivity. The list of such funds includes:
Biorepair toothpaste
- Sensodyne. Contains zinc and sodium fluoride. Due to these components, the enamel is strengthened and its sensitivity to external influences is reduced. In addition, toothpaste destroys pathogenic microorganisms on the enamel surface and reduces the amount of plaque.
- Lakalut. Contains active phosphorus, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the upper layer of the tooth. The effect of using toothpaste is observed after a certain time.
- Silca. In addition to active fluorine, it contains potassium citrate and urea. These substances reduce the sensitivity of enamel.
What can I do to stop my tooth from overreacting to food? Emergency assistance is provided by special gels:
- ROCS Composition is applied to enamel that is sensitive to cold and hot foods and drinks. The gel contains phosphorus, magnesium and calcium. The gel creates a film on the surface of the enamel, which protects it from external negative influences. At the same time, the surface of the element is intensively supplied with useful microelements. After treatment, the tooth lightened by several shades.
- Emofluor. The tin fluoride in the gel destroys bacteria that cause caries. The product is used to reduce tooth sensitivity and prevent periodontitis.
- Fluoridex. The product acts as a prevention of caries and other dental diseases. The gel is used together with toothpaste, adding a small amount of the substance to the brush. The procedure for treating enamel with gel is carried out twice a day - morning and evening.
Fluoridex contains a small amount of sodium fluoride, so it can be used to prevent caries in children and pregnant women