If the filling interferes after treatment
Even in the doctor’s office, after installing the filling, be sure to make sure that the restored tooth is not in the way (move your jaw back and forth, sideways, carefully close your teeth). The filling should not be felt or change the bite. Don’t be shy about talking to your doctor about any discomfort—sometimes the final stage of filling treatment can take even longer than removing cavities and applying filling material.
After treatment, anesthesia wears off within 1.5-2 hours. If a conductor type was used, then after 4-6 hours. Now you are beginning to fully feel the treated tooth, you can fully close your jaws and understand how comfortable you are after filling.
If you experience slight discomfort, it feels like the tooth is a little larger and your jaws aren't closing quite tightly—this is normal. The fact is that now you have been given a new filling in accordance with the bite, that is, with the shape and position of the tooth located on the opposite side. The treated tooth became taller than before - after all, there was caries and the old filling sagged. Therefore, if there is no sharp pain and obvious rejection, be patient for a few days. If the situation normalizes and you get used to it, then there is no reason to see a doctor. If discomfort persists for 1-2 weeks, you should visit your dentist to have the filling corrected.
Toothache after filling
4292 March 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Toothache: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
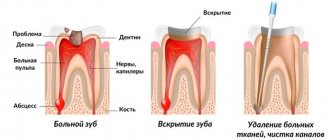
After filling a cavity or canal of a tooth, pressing or bursting pain may occur. Sometimes pain occurs when biting, chewing and tapping a tooth; in some cases, the pain becomes acute with the development of swelling of the gums in the area of the causative tooth.
Types of toothache after filling
Depending on the cause of the appearance, local or diffuse toothache after filling is distinguished. More often it is transient and goes away on its own after a short time (no more than a day).
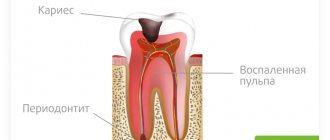
In some patients, after filling a carious cavity with deep caries or a canal with pulpitis, the intensity of pain gradually increases, it can be paroxysmal in nature, intensify under the influence of cold, and radiate along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. If left untreated, such pain becomes throbbing, the tooth may react to hot food, and swelling and redness of the gums develop. An infiltrate may form on the gum, from which pus or an abscess flows out when opened.
Possible causes of toothache after filling
Impact of irritants on the pulp.
First of all, you need to understand the location, intensity of pain and under what circumstances it occurs. If pain appears immediately after installation of a filling, this may be a consequence of the reaction of the nerves of the tooth and periapical tissues (tissues surrounding the root of the tooth) to mechanical, thermal and chemical influences.
Pain after the cessation of anesthesia indicates restoration of tissue sensitivity. As a rule, discomfort disappears within 24 hours after treatment.
Sometimes strong drugs placed into the tooth cavity lead to overdrying of dentin (the main solid substance of the tooth surrounding the pulp) and even to chemical burns of the pulp. This complication is accompanied by an acute pain reaction to cold and hot foods and sweets.
Incorrect installation of the seal
. If the upper border of the filling protrudes above the chewing surface of the tooth, then all the pressure of the opposite jaw during chewing falls on one tooth. This leads to overload of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, injury to the periapical tissues and the occurrence of dull local pain during chewing. To prevent such a complication, the doctor, after installing the filling, conducts a test with carbon paper. The paper is placed on the tooth with a filling and the patient is asked to close the jaws and make lateral and anteroposterior movements. The cusps of the tooth, which are marked with carbon paper, are ground off.
It is a mistake to think that excess filling material will wear off on its own over time.
The process of natural grinding lasts for years, during which time the patient experiences pain when chewing and, ultimately, this leads to traumatic periodontitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth). Inflammation of the periapical tissues
and the appearance of pain may be a consequence of pushing the filling material beyond the apex of the root canal. Together with the filling mass, infected tissues from the tooth canal enter the periodontium, which cause periodontitis. In this case, prolonged aching pain occurs, which intensifies when pressing on the diseased tooth. Tapping on a tooth is painful. Nearby lymph nodes (for example, submandibular) may enlarge. There is a risk of accumulation of purulent exudate in the area of the root apex and the formation of an abscess. The gums near the diseased tooth swell and turn red. Sometimes pus breaks through the gum, in these cases the swelling, redness and pain decrease. However, without treatment, this process constantly recurs.
Pain after filling can also occur in cases where one of the canals extending from the pulp chamber remains untraversed.
The number and location of canals in multi-rooted teeth varies from person to person.
If during tooth sanitation one of the canals remains unnoticed, the infection from it penetrates into the periodontium with the development of chronic periodontitis.
Close location of the carious cavity to the dental pulp
. In some cases, the bottom of the cavity is located too close to the pulp. The thin intermediate layer of dentin is penetrated by short tubes, through which infection from the carious cavity can enter the pulp and cause its inflammation (pulpitis). In these cases, hyperemia of the pulp develops (the initial stage of pulpitis), which, if left untreated, turns into acute pulpitis. There is no pain when tapping on the causative tooth.
A characteristic sign of initial pulpitis is pain that occurs upon contact with irritants (temperature and chemical) and goes away a few minutes after the cessation of their influence.
In other cases, the doctor may not recognize the initial stage of pulpitis when filling a tooth. In this case, sealing the infected pulp leads to acute pulpitis, which is accompanied by sharp, paroxysmal pain, intensifying at night and radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Which doctors should I contact for toothache after filling?
If pain occurs immediately after dental treatment, you should contact your dentist. However, in some cases, when there are no signs of malocclusion and periodontitis and pulpitis are not observed on radiographs, the patient may be referred for consultation to an otolaryngologist (if sinusitis is suspected) or (if inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is suspected).
Diagnosis and examination for toothache after filling
The connection between the occurrence of pain and previous dental treatment helps to make a preliminary diagnosis. The presence of an inflammatory process is confirmed by redness and swelling of the gums.
However, accurate diagnosis is only possible after radiography.
In the absence of clear radiological signs of periodontitis, they resort to electroodontodiagnostics (a method for assessing the condition of the pulp, in which its reaction to a weak electric current is checked), it allows one to assess the degree of damage to the pulp.
What to do if you have toothache after filling
Mild, aching pain after tooth treatment may continue for 1-2 days, and this is normal.
However, if the pain does not subside or intensifies, a consultation with a dentist is necessary to diagnose possible complications.
Treatment of toothache after filling
If the pain is caused by malocclusion due to excess filling material, it should be sanded off.
Pain due to the development of pulpitis requires opening the pulp chamber and depulping the tooth. Acute and chronic periodontitis also indicates the need for unfilling of root canals and their mechanical and medicinal treatment. After treating the cavity and canals, the doctor can apply therapeutic and insulating linings, covering the tooth with a temporary filling, then another visit will be required so that the doctor can re-treat the cavity and place a permanent filling.
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of periapical tissue disease // Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. – 2014.
- Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook / ed. Borovsky E.V. – M.: Medical Information Agency. 2004. - 400 p.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
How long should you not eat after having a filling installed?
If a filling made of chemical composites is installed, then you should refrain from eating and drinking for 2 hours. This is due to the fact that the material requires a certain time for final shrinkage and hardening.
If a “light” composite filling is installed, you can drink immediately, but you should abstain from food for 1.5-2 hours. But the reason is not in the material (it hardens a few seconds after application), but in anesthesia - with reduced sensitivity of the mucous membranes during eating, you can injure the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks on the inside.
During the day after the filling is installed, you should only eat warm foods - excessively hot or cold foods can lead to changes in the shape of the filling. It is necessary to chew food on the opposite side for the first day - this will allow the material to fully “adhere” to the tissues and take the desired shape, without the risk of damage.
Why does a tooth hurt after a filling is installed?
Minor soreness may persist for several days or even a couple of weeks, which is explained by overheating of the tissue due to the use of boron. In some situations, for example, with deep caries or when treating front teeth, increased sensitivity can persist even for several months. But in such a situation, you should still consult a doctor for an x-ray to make sure that there is no infected tissue left under the filling and that inflammation has not affected the nerve.
If the pain intensifies, the filling darkens, black spots appear under it - all this indicates that the treatment was carried out poorly and re-inflammation has begun. This is a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible.
In what cases is it important to visit a doctor?
Visit a specialist urgently if you have:
- Acute toothache;
- Pain combined with bleeding gums;
- Dull pain that sharply worsens when eating cold or hot food (this may indicate untreated chronic pulpitis);
- The temperature has risen;
- Discharge from the gums or changes in the gum tissue are observed.
If you don't trust the dentist who treated your tooth before symptoms began, find a better professional. The specialists at Dr. Granov’s clinic are ready to help you with dental treatment and correct the mistakes of others.
We are responsible for the health of our patients and choose progressive, safe, effective treatment methods.
What to do if your gums hurt after filling
The gums in the area where the anesthesia was administered may ache for several days - this is completely normal and does not require any measures. The mucous membrane may also be slightly inflamed if special rings were used during treatment, which are placed on the tooth to form the correct shape of its crown. The gums can also be damaged if the doctor had to install the filling material in close proximity to the mucous membrane or even under it - in such a situation the gums are deliberately pushed back. Therefore, pain is a normal reaction to external intervention.
All of these conditions are variations of the norm. But if the pain intensifies, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane progresses, you need to consult a doctor.
What can hurt a tooth?
A tooth consists of a root and a crown. It is covered as a frame with dentin and cement in the root area, dentin and enamel in the crown area. These are hard tissues that lack nerve endings, so they cannot hurt. Inside the tooth there is a space filled with tissue penetrated by branches of nerves. This is pulp. The pulp is also contained in the canals that connect the tooth cavity to the root. Any diseases (for example, inflammation - pulpitis) and injuries to the pulp are very painful.
Periodontitis is also a very painful disease - inflammation of the periodontium - the ligament that holds the root in the socket, since there are also many branches of nerves in the periodontium.
How to properly perform hygiene procedures
After treatment, brush the filled tooth carefully, applying minimal pressure to it. Do not use rinses containing abrasive substances and alcohol, which can increase the plasticity of the material - this will lead to a change in the shape of the filling. Also, do not use excessively hard brushes - they can leave microcracks in the material, which will quickly damage it.
In general, you should take care of teeth with fillings in a completely standard way:
- daily brushing of teeth twice a day - in the morning before breakfast and in the evening after all meals, after - rinsing the mouth with water and rinse,
- To clean the area of filled teeth after eating, it is better to replace dental floss with an irrigator. If you floss carelessly, you can touch the installed filling, especially if there are thin edges of the tooth, which will lead to its loss.
Causes of pain not related to the installation of a filling
Some non-dental diseases are similar to an attack of toothache. Patients go to the dentist, receive treatment or professional oral hygiene, but the pain after filling or other procedures persists. Only with repeated diagnosis are its true causes revealed: facial pain, for example, with neuralgia of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, glossalgia, neuritis [1, 3].
Unnoticed traumatic dislocation of a tooth (for example, when trying to chew something hard) occurs with inflammation of the bone tissue. In this case, when pressing on a previously filled tooth, pain appears [1, 2].
In older people, dentalgia is possible due to pulp dystrophy due to its involution [1, 3].
Is it necessary to follow a diet after caries treatment?
From the diet as a whole after caries treatment (especially if a large filling is installed and your own tooth has very thin walls), it is recommended to remove too hard foods - toffees, chewing gum, grilled fruit, nuts, etc. Or chew them with teeth located on the opposite side (if they do not have fillings).
Minimize the amount of consumed foods and drinks that contain coloring pigments (tea, coffee, beets) - under their influence, the filling material may slightly change its shade. This rule is especially relevant when restoring front teeth.
When to see a dentist
Normally, after dental treatment, the patient may not feel much pain or discomfort. The sensations should gradually become less intense and disappear completely after 3-4 days.
You should contact your dentist if, after filling, you are concerned not only about pain, but also about accompanying symptoms:
- increased temperature or fever;
- swelling of the gums and cheeks;
- feeling of a “grown” tooth;
- presence of bad breath.
You should not delay your visit to the doctor if, after filling, your tooth hurts when pressed.
How to maintain your treatment guarantee
As a rule, therapeutic treatment, that is, dental filling, is guaranteed from 6 months to 2 years - depending on the volume of work and the complexity of the situation. To maintain the guarantee, the patient must strictly follow all recommendations: do not overload the tooth, do not use it for other purposes (for example, open beer bottles), and also regularly see the doctor in accordance with the individual schedule of medical examinations. Unfortunately, many patients forget about this, and it is the last point that is the key to maintaining the guarantee for treatment.
You need to visit a doctor 1-2 times a year. During a preventive examination, the dentist will be able to make sure that the filling is in good condition and that caries does not develop again underneath it.
What treatment methods can be used for pain after a filling?
But what to do if you have a filling installed and your tooth hurts? Some types of pain are predictable. In these cases, doctors recommend the use of drugs that can relieve or reduce the severity of pain, reduce inflammation, and help if the tooth aches under a filling.
If the pain in a tooth after a filling is associated with a medical error, a pathological process, or the effect of the materials and medications used, a repeat diagnosis is prescribed (radiography, additional methods, consultation with a neurologist, surgeon, allergist). This allows you to understand why a tooth hurts after filling and what to do to eliminate the cause. Based on the results of the examination, an opening and re-treatment of the root canals, removal of the pathological focus, therapeutic treatment, and, if necessary, refilling are carried out.
As mentioned above, a tooth may hurt after a filling even if the cause is not related to dental problems. In this case, the corresponding disease is searched for and treated on an outpatient basis or in a specialized hospital department.
List of sources
- Borovsky E.V. Clinical endodontics // M.: Dentistry // 2003 // https://studfile.net/preview/1470124/ (access date 04/28/2020).
- Tronstad L. Clinical endodontics // M.: MEDpress-inform // 2008 // https://yadi.sk/i/V9lak7Ga3S6qU5 (access date 04/28/2020).
- Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook // Ed. Maksimovsky Yu. M. - M.: Medicine, 2002. // https://www.studmed.ru/view/maksimovskiy-yum-maksimovskaya-ln-orekhova-lyu-terapevticheskaya-stomatologiya_27630dac8ad.html (access date 04/28/2020 G.).
- Fillings do not last forever: the better way to treat caries // Moskovsky Komsomolets. 2022. March 19. // https://www.mk.ru/social/health/2020/03/19/plomby-ne-vechny-chem-luchshe-lechit-karies.html (accessed June 15, 2020).