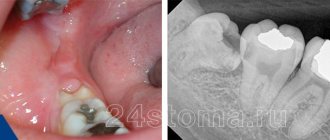
Increased sensitivity of teeth (hyperesthesia) is a short-term occurrence of pain under the influence of temperature, chemical or mechanical irritating factors. Usually occurs when drinking cold water, sour, sweet, salty, or touching with a toothbrush. The intensity of pain varies from mild to unbearable.
According to WHO, every second person in the world suffers from hypersensitivity. In Russia it is about the same: 45–65% of adults aged 20–55 years. More often women make complaints.
A little anatomy
A tooth consists of a crown and root part, connected by a neck. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part is covered with cement. Beneath the enamel and cement there is dentin, a hard tissue. Inside there is soft tissue - the pulp; blood vessels and nerves pass through it.
Dentin is not sensitive, but consists of many tubules in which fluid circulates. The irritant causes fluid movement, which is detected by the nerve endings of the pulp. A person feels their reaction as pain.
Installing a filling after caries treatment as a problem of discomfort
Caries has two degrees of progression: chronic and acute. There are also several forms of dental damage by this pathology: deep, medium and initial.
The dentist treats deep and medium forms of lesions by mechanical treatment of the affected area, followed by installation of a filling.
If during the treatment of the tooth part of the tissue affected by caries was left behind, this may become the root cause of pain when exposed to cold.
In some dental offices, doctors use a special liquid that stains the affected part of the dental tissue with a certain color. This is very convenient, since the dentist can clearly see which area needs to be removed. But not all doctors use this drug.
In a filled tooth, pain can also be caused by other reasons, for example, improper filling procedures for deep caries. The chronic course of caries will be expressed by dense pigmented dentin, in which case the procedure for removing the affected tissue can be stopped, followed by the installation of a filling.
If the dentin is soft, the dentist may decide to strengthen it with a lining containing calcium. In this case, it does not open the tooth cavity. The infection contained in the affected bottom of the cavity gradually penetrates into the dental cavity through the dentinal canals.
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle, accompanied by pain, is a response to infection.
The occurrence of pulpitis can be provoked by incorrect tactics of the procedure, when in the process of removing tissues affected by caries, sufficient air-water cooling of the tooth tissues was not applied. The consequence of this is heating of the pulp tissue, which provokes the occurrence and development of pulpitis.
Tooth sensitivity: causes
- Demineralization of enamel. It becomes more loose due to the leaching of calcium, phosphorus, and other trace elements.
- Thinning of enamel. As a result of increased abrasion due to malocclusion and the occurrence of wedge-shaped defects.
- Untreated caries or violation of the marginal seal of the filling.
- Exposure of roots as a result of injury, metabolic-dystrophic process or inflammation of the gums.
- Changes in the pH of saliva due to the consumption of certain drinks, foods, and medications. A pH of less than 5.5 is considered dangerous.
- Some diseases accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux and endocrine disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency, exposure to radiation, work in hazardous industries, living in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation.
- Smoking.
More often than not, several reasons are discovered at once. The enamel becomes thinner, loses strength, and cannot protect dentin from irritants. The result is pain.
Provoking factors
Hyperesthesia does not appear immediately. There are several factors that you need to pay attention to in order to eliminate them in time. Don't wait for discomfort to appear. It is better to initially develop healthy habits that will help you maintain your health so that you never experience acute dental pain. Sensitivity increases when any of the factors listed below are present.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. Soft plaque is an accumulation of microbes that eat food microparticles stuck in crevices, releasing organic acids that dissolve enamel minerals. Externally, the dental unit looks intact, but the density of the enamel is significantly reduced. Its demineralization occurs. The first alarm bell is increased sensitivity, then caries develops.
- Consumption of certain foods. Juices, wine, sweet soda, fruits, candies, and other sweets contain phosphoric and other acids that negatively affect the strength of enamel.
- Constant use of aggressive whitening pastes containing abrasive and chemical components.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. Under a dense coating, the enamel becomes thinner and becomes loose. After professional cleaning, it is exposed, its sensitivity increases sharply. Usually, dentists, taking this point into account, use strengthening pastes at the end of the procedure for the preventive treatment of tooth sensitivity.
Qualified help
Professional help for hypersensitivity involves two highly effective procedures - fluoridation and remineralization. These are safe techniques that can quickly increase the strength of enamel and make it more resistant to the irritating effects of external factors.
Remineralization normalizes the structure of the upper dental layer by saturating it with phosphate , fluorides and calcium. After the session, the unit almost immediately stops reacting acutely to temperature changes.
Fluoridation consists of the use of a fluorine-containing drug. It can be repeated at intervals of several months. The procedure is especially relevant for people living in areas with a lack of phosphorus in tap water.
After treatment and preventive measures, the doctor may prescribe a special remineralizing gel to the patient. It must be used within a month. This should be followed by a long break.
Types of hypersensitivity
If sensitivity is increased on one or more teeth, it is called limited. If for everyone - generalized.
Table 1. Types of hyperesthesia
| № | View | Reaction |
| 1. | Light | for cold, hot |
| 2. | Average | as with 1st degree plus for sour, sweet, salty |
| 3. | Expressed | as in grade 2 plus mechanical irritants (when brushing teeth, eating) |
Sensitivity of teeth. Stages of treatment
- Eliminate the cause of hyperesthesia: get rid of plaque, deposits, stones, caries, wedge-shaped defects.
- Carry out professional oral hygiene.
- Strengthen the enamel with calcium and fluoride.
- Teach the patient how to use a toothbrush and floss correctly.
- Choose suitable dental care products: toothpaste, mouthwash.
Table 2. Tooth sensitivity: causes and how to treat
| № | Cause | What to do |
| 1. | Soft coating. | Careful hygiene with home remedies. |
| 2. | Hard coating. | Professional hygiene in dentistry. |
| 3. | Caries in the white spot stage. | Deep fluoridation, remineralization. |
| 4. | Caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. | Dental treatment. |
| 5. | Exposure of the cervical part, wedge-shaped defect. | |
| 6. | Malocclusion. | Orthodontic therapy. |
Diagnostics
When diagnosing dentin hypersensitivity, it should be borne in mind that it is often a symptom of a disease. Therefore, when a patient approaches, the dentist begins treatment with a survey, during which he receives answers to the following questions:
- duration and nature of the pain syndrome;
- number of units with dentin sensitivity;
- localization of increased susceptibility;
- characteristics of stimuli that cause pain.
After the examination, the patient is required to undergo probing of sensitive areas and other diagnostic tests (thermal, electrical, osmotic, evaporative), as well as percussion (tapping on individual areas of the tooth). At the same time, they find out whether the element is sensitive when biting, identify microcracks in the enamel, damage inside and around the filling, malocclusion, and signs of bruxism.
In addition, diagnostics are carried out using hardware methods and “hidden” carious lesions and periapical changes are identified if they are present.
Much attention is paid to determining the level of pain and the degree of tooth sensitivity:
- no pain;
- mild discomfort;
- medium intensity;
- severe pain or unbearable.
The patient's pain reaction may occur to a greater extent to thermal stimuli (cold, heat), tactile (tactile), evaporative (air), electrical or osmotic (solutions of weak acids).
Dentists note that the reaction most often occurs to cold, brushing teeth, heat and sweets.
The more dentin is exposed due to dental diseases and other factors contributing to enamel loss, the higher the degree of hyperesthesia. This is explained by the fact that in completely exposed dentin there are more dilated tubules with open holes.
Elimination of tooth sensitivity
Using ultrasound, the doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the teeth. After removing plaque, teeth become more sensitive for a short time, so remineralization or deep fluoridation is immediately carried out. During remineralization, the enamel is treated with active compounds of calcium and phosphates. Deep fluoridation – coating with sodium fluoride. Both procedures significantly strengthen the enamel's resistance to irritants.
The doctor uses agents that reduce the movement of fluid in the dentinal tubules. It “seals” them using desensitizers or reduces their volume through remineralization. Protecting exposed dentin reduces the force of transmission of the irritant impulse from the enamel to the nerve.
What is periostitis and how does it develop?
Periostitis (flux) is an inflammation of the periosteum - the tissue covering the bones of the upper and lower jaw. The inflammatory process in this case usually proceeds very intensely: a large amount of pus is formed, the patient’s well-being is disturbed, and a significant rise in body temperature may be observed.
- The pain in this case is intense and can be bursting, throbbing or tearing.
- Upon examination, the gums of the diseased tooth are inflamed, swollen, and painful when pressed. The swelling extends to the cheek and can be so severe that the face becomes asymmetrical.
- On the mucous membrane of the cheek in the immediate vicinity of the diseased tooth there may be a swelling with a hole for the release of pus. If there are no ways for the outflow of pus to the outside, then it can break into the soft tissues of the cheek and neck, posing a threat to the health and life of the patient.
Basic points of proper hygiene
Use a synthetic, medium-hard or soft brush. Change it every three months.
The toothpaste should be suitable for very sensitive teeth. Typically, such products contain hydroxyapatite, strontium chloride, fluorides, potassium nitrate, or a combination of calcium carbonate and arginine.
Take enough paste. For children under 3 years old - the size of a grain of rice, from 3 to 14 years old - the size of a pea, for adults you need to squeeze out about one centimeter.
Brush your teeth for 2 minutes: 30 seconds on each surface, top and bottom. Monitor time using an hourglass or mobile phone timer. Electric toothbrushes emit a short beep every 30 seconds and a long beep every 2 minutes from the start of brushing.
Cleaning sequence
- Using sweeping movements, clean the outer and then the inner surfaces of the bottom row. Move from molars to incisors. Then do the same on the top row. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle and do not use a sawing motion. This leads to damage to the enamel.
- Brush chewing surfaces with small circular movements.
- Close your jaws and walk along your gums in a circular motion.
- Brush your tongue using a leisurely four to five strokes from root to tip.
- Treat the interdental spaces with dental floss.
- Rinse your mouth.
It is more effective to clean with an electric brush or irrigator. The quality of hygiene increases 3–4 times. Hyperesthesia can be dealt with faster.
Is it possible to strengthen sensitive teeth at home?
Yes. If you can’t get to the dentist, you can try to help yourself. There are several remedies that can solve the problem of hyperesthesia at home.
Table 3. Popular products for home use
| № | Name | Mechanism of action | Age category |
| 1. | ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse | Remineralizing gels | Adults and children |
| 2. | Colgate Duraphat 2800 ppm | Fluoridating paste | 10–15 years |
| 3. | Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm | From 16 years old | |
| 4. | ELMEX junior | Fluoridating paste | 6–12 years |
| 5. | ELMEX | From 13 years old | |
| 6. | LACALUT Extra Sensitive | Paste that reduces tooth sensitivity | For adults |
| 7. | Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief | ||
| 8. | PRESIDENT Sensitive | ||
| 9. | LACALUT Sensitive, 300 ml | Rinse for sensitive enamel | From 15 years old |
What can you do to relieve pain?
If the pain is severe and it is impossible to get to the dentist in the next few days, hyperesthesia can be pacified for a short time. The simplest, but, alas, not always effective way is to rinse your mouth with a soda solution: 1 teaspoon of soda per glass of warm water.
Painkillers based on ketoprofen: “Ketonal”, “Flexen” and ibuprofen: “Nurofen”, “MIG” relieve symptoms of hyperesthesia well. They act quickly and allow you to completely forget about pain for 5-6 hours.
Local anesthetics in the form of gels give an even stronger effect: “Cholisal”, “Kamistad”, “Dentinox”. These drugs contain lidocaine, so they begin to act instantly. The effect, however, does not last long - for 2-3 hours, after which you can apply another drop of the product to the surface of the teeth.
Traditional medicine gives its own recipe for pain relief: rinsing the mouth with warm water with the addition of 3-4 drops of clove oil or tea tree oil.
Algorithm of actions for hyperesthesia
- Adjust your diet. Avoid completely or significantly reduce the consumption of foods and drinks containing acids and sugar. Especially fruit and berry juices, wine, candies. Eat more green vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and whole grains.
- Change your toothpaste. Never use bleach. Choose from those labeled "Sensitive".
- Check if you are practicing proper oral hygiene. If it's wrong, correct it.
- Make an appointment with your dentist to find out the type of tooth sensitivity, find out the cause and get treatment.
- Visit the dentist twice a year, even if nothing hurts.
Why does a tooth without a nerve hurt from cold and hot?
It is generally accepted that after the nerve is removed, the tooth will no longer be able to hurt. In fact, the reaction of a dead tooth to temperature is rather normal, and there is no need to worry. Over time, the pain will subside on its own, because most often the cause lies in microtraumas to the enamel of neighboring teeth that were received during treatment.
If after a few days the reaction to hot or cold does not decrease, but intensifies, you should not hesitate! It is likely that the dentist did not completely remove the nerve, and the inflammatory process was not stopped. Such mistakes are extremely rarely made by dentists with extensive experience, but among beginners it is not at all uncommon.
There is no point in blaming the aesculapians: what we are accustomed to calling a nerve is, in fact, a branched system of tiny hairs, spreading in all directions of the tooth. It is sometimes impossible to see all the “tentacles” even on an x-ray. And only with experience comes an intuitive feeling of how the “labyrinth” of nerves is located in a particular patient.
In the practice of Western dentistry, a separate specialty has long been distinguished: an endodontist, a specialist in root canal treatment. In Russia, only large, well-equipped clinics can afford specialists of such a narrow profile.
Treatment of hyperesthesia in the “Family Doctor”
If hyperesthesia occurs, make an appointment with a dentist by calling the contact center in Moscow +7 (495) 775 75 66 or using the online appointment form. Our clinic has been operating for more than 26 years. Experienced doctors help patients cope with pressing problems, including hypersensitivity.
The doctor will find out the cause of tooth sensitivity and provide effective treatment. In most cases, it is enough to select suitable oral care products and carry out proper hygiene procedures. In more complex situations, full treatment is used, and if necessary, surgical treatment.
The clinic takes a gentle approach to patients. All procedures are accompanied by adequate pain relief, which eliminates the occurrence of discomfort and pain. Increased sensitivity of teeth is not just a feature of them. This is the beginning of a disease that must be cured. And it's better to do it as quickly as possible.
What complications may arise?
If the disease is not treated, it will certainly cause very extensive complications. Hyperesthesia is no exception. If we take into account the fact that the reaction of teeth to cold and hot can be the result of a variety of pathologies, then this problem needs to be solved as quickly as possible, without waiting for these complications to make themselves felt.
Untreated hyperesthesia at an early stage eventually leads to severe toothaches - patients complain of the inability to eat, and feel pain when air enters the mouth. At stage 3, it is much more difficult to cope with the problem - after all, by this time the enamel is already quite badly destroyed, which is why numerous carious cavities are formed, etc., and drastic measures may be required.
Enamel is the protective layer of the tooth. When it is abraded, deformed or mechanically damaged, soft tissue becomes vulnerable to a huge number of bacteria. Therefore, you should not put off going to the dentist at the first signs of a reaction to cold or hot foods.