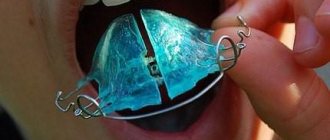
To correct bites in adults and children, the orthodontic department of the Dial-Dent clinic uses various orthodontic devices, braces, and transparent aligners. In this article we will look at the latest device for correcting bite ALF (Advanced Lightwire Functionals, made of wire from a special intelligent alloy.
Commentary by the chief physician of Dial-Dent S.V. Zukora: “The new alloy used to make the ALF is currently only available in North America. But since we want to provide Dial-Dent patients with the best dental developments, we have found the opportunity to order ALF devices in. There, using digital impressions, devices of the highest quality are manufactured individually for each patient.”
Anatomy of the upper jaw
The upper jaw consists of 6 bones connected to each other by sutures. This connection has micromobility due to cartilage tissue and does not fuse completely, like all the bones of the skull, which retain their micromobility throughout their lives.
The upper jaw has a spongy bone structure, which indicates its rather loose and pliable structure. Anatomically, bone trabeculae and pores are located in the thickness of the bone of the upper jaw, and are its main component. The direction of these bony trabeculae dictates the axis of tooth eruption
Operating principle of the ALF device
The principle of operation of the ALF apparatus was revealed by Darik Nordstrom and his colleagues, and is based on the unlocking and straightening of the 6 bones of the upper jaw, indirectly aligning the dentition. As soon as it is possible to align the bone itself, the tooth is automatically aligned according to the changed axis of the trabecular system of the upper jaw. At the same time, there is enough space for all teeth automatically.
The ALF device has a loop spring structure, which allows, when activated, to apply pressure to the blocked segment of the jaw, but it is also pliable in its loop bends, while providing a soft, non-rigid effect, thereby not blocking the cranial rhythm and breathing of the upper jaw itself.
The rhythm of the upper jaw and the entire skull is called the osteopathic term - cranial rhythm.
The upper jaw makes a rhythmic oscillatory movement, expanding along the median seam and narrowing back, rising slightly anteriorly and falling back. These vibrations occur around its axis, and are normally equal to 8-12 amplitudes per minute (the same amount as the breathing of the entire skull as a whole) and are called inhalation and exhalation -
inflection and extension.
To understand the functioning of the ALF apparatus and unlocking the upper jaw, it is necessary to take into account the biomechanics and micromobility of the entire skull as a whole
Design features
The Alf removable orthodontic device for changing the bite was developed more than 30 years ago in the USA. The technique is based on the application of the principles of cranial osteopathy: the therapeutic effect is achieved through special healing techniques, under the influence of which the body uses its own forces. Authorship belongs to Dr. Darik Nordstrom. The orthodontic design he invented is a wire product that looks like a metal frame with two loops. With the help of the latter, the device is activated.
The American doctor's design is made individually for each patient. The structural features of the teeth and skull must be taken into account. The wire product is attached using Alf technology to the inner surface of the dentition, that is, the device remains practically invisible to prying eyes.
The device does not have an exact design. Products of different parameters and configurations are manufactured based on the goals of therapy.
The experience of using soft wires demonstrates the high efficiency of the technology. Thus, the use of the Alf device in childhood eliminates the development of an abnormal bite, since light wires promote the correct development of bones, and when dealing with an existing problem, the Alf device for orthodontics allows you to reverse the pathological process.
Biomechanics
Normally, the plane of the upper jaw is one of the main horizontal planes in the human body, interconnected with each other and other horizontal planes:
- Plane along the eye line
- Maxillary plane
- Auricular plane (temporal bones)
- Shoulder level plane
- Plane along the pelvic line
BUTRFORTS
As James Carlson points out in his works, with the correct horizontal position of the upper jaw in the skull, there is a balanced distribution of force vectors along the base of the skull and along the buttresses when the occlusion is closed.
The uniform distribution of force vectors during teeth closure sets the symmetry of the cranial rhythm and the symmetrical functioning of the muscular apparatus of the dentoalveolar system.
The even, correct position of the upper jaw in the skull determines the presence of correct occlusion and axis of teeth, both primary and permanent in the subsequent period.
Causes of relapse after braces
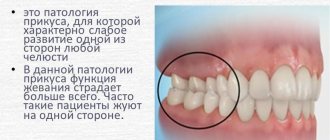
Uneven dentition is a consequence of an unevenly positioned asymmetrical upper jaw, which forms twisted bone trabeculae and displaces the axes of the teeth. The lower dentition most often becomes crowded precisely as a result of primary disorders associated with the upper jaw, adapting to it when the teeth are closed.
In this regard, orthodontic treatment with braces is often complicated by the return of the tooth axes to their previous position, that is, relapse. Teeth cannot be forcibly moved using braces systems across their physiological position, dictated by the direction of bone trabeculae and pores. This is fraught with relapses. Even retainers are not able to keep them in this violent position. If orthodontically, only with the help of a brace system, the position of the teeth is aligned, without correcting the position of the position of the skull bones, it will be impossible to create a harmonious occlusion.
Reviews
If we compare the light wire technique with other methods of orthodontic treatment, it is distinguished by a delicate effect on the elements of the dentition, which does not cause even the slightest painful sensations.
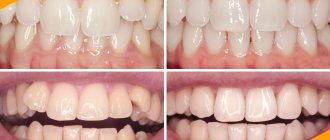
As a result of treatment, the patient receives an even and beautiful smile, which will allow him to feel confident in the company of people around him.
If you have treated bite problems using the presented technique, share your opinion about its effectiveness in the comments to this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
ALF orthodontics
- ALF orthodontics is the influence and elimination of the direct cause of malocclusion of the dental system. By aligning the bones of the upper and lower jaws themselves, ALF allows the teeth to take a truly correct position, in a non-violent, natural way.
- Often, with minor crowding, we can completely correct the bite using the ALF device without further treatment with a brace system.
- In case of severe occlusion pathology, it is advisable to combine methods in treatment, such as the ALF apparatus, cranial techniques, the GOA method, osteopathic treatment, orthodontic plates and bracket systems, as well as orthopedic restoration of the bite. With this combination of methods, the most effective comprehensive work is carried out to correct not only the bite, but also disorders of the entire body as a whole, including skull asymmetry, posture and the mental component. The ALF device is often used in this version almost as the very first at the beginning of treatment, to unblock the bony components of the upper and lower jaw in combination with eliminating the asymmetry of the skull manually.
- The dental level using braces or therapeutic-orthopedic restoration of the bite is considered the final stage of bite reconstruction, the dental final stage.
- When treated with a brace system, the ALF device also continues its influence on the upper jaw simultaneously with braces, not allowing them (to varying degrees of influence) to organize compression of the skull due to their rigid fixation of the arches and blocking the rhythm of the upper jaw. The ALF device in combination with cranial techniques and osteopathic control allows minimizing the negative effects of the brace system.
Operating principle of the ALF malocclusion correction device
The ALF malocclusion correction device uses the principles of cranial osteopathy - a gentle effect on the bones of the skull, fascia and meninges. Normally, in humans, the bones of the skull are not fixedly connected; there is minimal movement in the cranial sutures. The use of the ALF device allows you to gently remove various blockages in the bones of the skull, return natural “breathing” to the skull, thereby normalizing the development of the facial skeleton and improving the patient’s overall well-being.
The ALF device was developed by American researcher Darik Nordstrom in the early 1980s. Using the osteopathic principle that the correct structure of the body leads to healthy functioning, Nordstrom created a device that constantly exerts a gentle effect on the cranial structures, promoting the correct development of the facial skeleton and respiratory tract. The ALF device acts on the body logically and without violence, so there is no pain, discomfort or other unpleasant sensations.
Orthodontic treatment with the ALF device improves the quality of the patient’s overall health, as it uses a holistic approach to the body. Proper development of the facial skeleton improves aesthetics and reduces the risk of relapses after orthodontic treatment, and the development of the respiratory tract improves oxygen supply to the brain and helps eliminate snoring and sleep apnea.
It should be noted that the effectiveness of treatment with the ALF device largely depends on the qualifications of the orthodontist. The ALF Family Dental Method is owned by orthodontist O.A. Baranova, O.N. Selector, M.P. Sleptsova and M.N. Ostroukhov, who underwent special training.
The approximate duration of treatment with the ALF device is from 3 to 24 months.
The ALF appliance is a removable orthodontic appliance, but the patient wears it constantly. Only the orthodontist removes the device for activation at the appointment.
ALF device technology
The principle of operation of the ALF device is based on the gentle spring pressure of light wires with shape memory on the blocked bones of the upper jaw, without limiting its natural primary respiratory mechanism (PRM).
The ALF device rests on the teeth, exerting pressure on them, but its main effect is
associated with the unblocking of the bones of the upper jaw. Following this, the force vectors of the ALF apparatus installed on the upper jaw affect the frontal and sphenoid bones (as well as other bones of the skull), leading to their release (release from jamming) and unblocking. Compression of the skull associated with a blocked upper jaw, especially with its incisal segment, is almost impossible to eliminate with osteopathic manual techniques without the use of an ALF apparatus (especially with already erupted permanent teeth, the length of the roots of which firmly connects the blocked segments).
Consequently, it is often impossible to manually eliminate osteopathic patterns when they are firmly coupled with disorders of the upper jaw and incisive segment, without using constant persistent pressure from the ALF apparatus aimed at unblocking them and swinging the amplitude of the rhythm of the jaw and skull, removing them from compression.
Conversely, the use of an ALF device for serious cranial dysfunctions and malocclusion pathology will not give the necessary positive results without proper osteopathic manual support. It should be aimed at releasing the sutures, giving the pinched bones their proper micromobility and eliminating the asymmetry in the position of the skull bones.
Why does using ALF not always give 100% results?
- When the upper jaw is severely twisted, it is not possible to unblock it without simultaneously unblocking the frontal and sphenoid bones. This is due to the fact that in most cases the compression of the frontal bone is primary (for example, as a result of birth trauma). It was she who contributed to the shift of the frontal bone and, as a consequence, the formation of bite pathology (secondary manifestation). Consequently, the release of the frontal bone in the sutures and fascia contributes to the release of the upper jaw and gives it a positive vector aimed at its change and expansion. In this regard, the use of one ALF device will not give full positive results.
- Also, the ALF device cannot eliminate intraosseous damage in the thickness of the jaw, if any. Usually it is formed, for example, due to direct trauma to the upper jaw as a result of a blow, or during traumatic extraction of teeth with bone damage. It is also impossible to change the bite and influence it with ALF after jaw osteotomy surgery.
- If the area of intraosseous local damage is small, then the ALF device will work as best as possible with the remaining components of the upper jaw, which will significantly improve the overall clinical picture, with the exception of residual effects in the area of intraosseous damage. The histological trabecular apparatus of bone is capable of changing the overall density both in the direction of compression during compression, and in the direction of development/expansion to a neutral physiological value (according to its reserve capabilities when creating the necessary conditions). In the case of intraosseous damage, the natural physiological compact “packing”/compression of the trabeculae with each other is disrupted. Instead, scar changes and intraosseous calluses/tight adhesions of damaged areas are formed, without the possibility of their further physiological straightening.
Conclusions on the use of ALF
- The upper jaw is not rubber and cannot be expanded as we please if something remains that caused it to shrink and keeps it in this position.
- The upper jaw bone of each person has an individual size corresponding to the physiological characteristics of the given organism.
- The bone of the upper jaw has the physiological ability to compress/compress at the histological tissue level, and accordingly can also expand to physiological values (individual for each organism)
- In the conditionally physiological state of the upper jaw (reversible changes), shortening of its skeletal size in the presence of crowded teeth will be easily eliminated using the ALF apparatus with simultaneous alignment of the crowded dentition
- In pediatric orthodontics, the ALF device can prevent the lack of space for erupting permanent teeth, often 13 and 23. Whereas previously, to correct this type of teething disorder, orthodontists made decisions to remove permanent fourth premolars 14 and 24, thereby causing underdevelopment of the upper jaw and its significant narrowing for life.
- The size of the teeth always corresponds to the required physiological size of the teeth for a given upper jaw (with the exception of intrauterine and hereditary pathologies that affect the formation of teeth)\
- In the presence of crowding of teeth and in the absence of conditions for the development of pathology of tooth formation, the most likely reason for the discrepancy between the size of the upper jaw and teeth is a physiological narrowing of the upper jaw (tissue histological level).
Subsequently, underdevelopment of the upper jaw is possible in the presence of pronounced compression during the growth period. Often, for the formation of underdevelopment of the upper jaw, in addition to its compression in the skull, a combination of conditions is necessary:
- The absence of primary teeth during their early removal is a limitation of the growth of the edentulous segment due to the lack of necessary pressure and chewing load on the bone.
- The presence of intraosseous damage to the upper jaw as a result of impacts, traumatic removal of baby teeth - the formation of a scar-changed area with a disturbed bone growth zone.
- Previously, orthodontic treatment of occlusion using devices that block the physiological respiratory rhythm of the upper jaw (system braces in children during the period of active growth, plates without a spring mechanism, use of face masks)
In the case of emerging underdevelopment of the upper jaw, bite treatment aimed at unblocking and expanding the upper jaw must begin as soon as possible. If the underdevelopment of the upper jaw is already formed, treatment with the ALF apparatus may not give the required size of the upper jaw.
Hygiene during treatment with the ALF device
Oral hygiene during orthodontic treatment always requires increased attention. It is important to prevent caries and other problems with teeth and gums so as not to disrupt the progress of treatment. During treatment with the ALF device, maintaining oral hygiene is not particularly difficult; you need to pay attention to those teeth on which the fastening rings are installed. An oral irrigator helps in cleaning teeth. Professional hygiene (Air Flow teeth cleaning and tartar removal) is carried out every 4-6 months. At Dial-Dent you can conveniently combine an appointment with an orthodontist and a visit to a hygienist. In this case, the orthodontist will remove the device, the teeth will be thoroughly cleaned, and then the doctor will install the device again.
Treatment of malocclusion with ALF in the absence of a permanent tooth
Often, when trying to cure a malocclusion, the method of removing 1 or more permanent teeth was previously used. In this case, distortion of the dental arch of the upper jaw is accompanied by its shortening and narrowing, and with unilateral removal - deformation of the central line of the palatal suture with a displacement of the middle axis of the entire upper jaw, and with the development of facial asymmetry. The ALF device can return the lost space to restore the desired size of the upper jaw and to balance the symmetry of both the jaw and the entire facial skull as a whole. But to eliminate facial asymmetry associated with the absence of a permanent tooth and a place for it, certain conditions are necessary:
Indication for treatment
Treatment by installing an ALF apparatus should only be done when necessary, in the presence of malocclusion in combination with skull asymmetry, as well as in cases of already developing symptoms of impaired functioning of the body.
The presence of a symptom is not an indication for treatment. The need for treatment is determined by the doctor through a comprehensive comparison of the symptoms and the clinical picture, since the same symptom can be caused by various reasons.
There are also psychosomatic indicators of disorders in the body, they also need to be taken into account and assessed to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
- There is no evidence of traumatic removal with damage to a segment of bone tissue and the formation of a scar-modified bone callus, incapable of physiological expansion.
- Relatively recent tooth extraction. The more years have passed since the loss of space from the extracted tooth, the more difficult it is to expand the upper jaw in this segment.
- Lack of bone fusion of the roots of adjacent teeth. This can occur when permanent teeth are removed as a result of orthodontic treatment, creating rapid traction and moving adjacent teeth into the socket of the extracted tooth. In this case, the fusion of the bone tissue of the socket occurs with the involvement of the roots of neighboring teeth, with their tight adhesion.
- With unilateral removal, asymmetry of the bones of the upper jaw develops with their twisting and displacement of the palatal suture, with the loss of its central location. Following this, the asymmetry spreads to the entire facial skull as a whole. Indirectly through the palatal suture and fascial interrelations, the dura mater twists, and then this dysfunction in a descending manner leads to changes in the spinal column and posture (including subluxation of the atlas - the first cervical vertebra). Long-term adaptation and restructuring of the entire body is formed.
Insufficient anteroposterior size of the upper jaw, its reduction. Following this, there is a posterior displacement of the lower jaw, which takes a forced position with new dental contacts of the upper jaw, which has been reduced by one or more teeth. In this case, the temporomandibular joint gradually begins to be damaged, muscle spasms around the joint begin to develop, pain syndromes, neck pain or migraines appear. The whole body is undergoing a restructuring.
- The narrowing of the upper jaw, caused by the absence of one or more frontal teeth (front teeth), as well as premolars, affects nasal breathing. In this case, compression of the ethmoid bone and vomer develops, they lose their micromobility and are firmly blocked. Gradually, venous stasis begins in the nasal mucosa, swelling increases, and the trophism of soft tissues is disrupted. This leads to swelling and impaired nasal breathing, chronic rhinitis, frequent acute respiratory viral infections (impaired nasal breathing can develop when the upper jaw is narrowed and all teeth are present). Correct expansion/restoration of the size of the upper jaw also leads to unblocking the nasal bones and eliminating the causes of chronic rhinitis, nasal breathing and the sense of smell is restored (80-90%) even with long-term rhinitis (20-30 years)
- The tilt of the upper jaw or its tilt to the side, a violation of the horizontal plane also develops with the unilateral removal of one of the teeth. At the same time, it is possible to ideally align the position of the maxillary plane only if the ALF device fully expands the upper jaw and returns the space from the extracted tooth. At the same time, work with the sutures of the skull is mandatory.
- Narrowing of the upper and lower jaws
- Crowded teeth
- Frequent chipping of teeth and crowns
- Bruxism
- Pathological abrasion of teeth
- Periodontal disorders
- Bite pathology (mesial, distal, straight bite)
- TMJ dislocation
- Dysfunction of masticatory muscles
- Asymmetrical jaw arrangement
- Asymmetry of the facial skeleton
- Symptoms associated with speech, swallowing, and breathing disorders
- Symptoms associated with impaired nasal breathing
- Neuritis of the facial nerves caused by compression of the nerves by the bones of the skull
- Migraines, headaches
- Dizziness
- General weakness of the body and vegetative-vascular syndrome
- Pain in the neck, lumbar region
- Postural disorders
Pull-Forward
The “Pulforward” device is an orthodontic device for the lower jaw; it is removed only for the time of oral hygiene. Plate design with a vestibular arch, for holding and aligning the frontal group of teeth. The design may also include a screw to expand the jaw and create space for teeth when they are crowded. The device is used to treat dysfunction of the temporomandibular joints, normalize the position of the jaws, eliminate jaw tilts and for their expansion. And also for patients to prepare for complete prosthetics. Smile reconstruction using ceramic veneers and crowns, creating the correct physiological bite height and jaw position. The duration of wearing depends on the complexity of the case and the degree of dysfunction of the temporomandibular joints, the period takes from 5 to 12 months. The device is manufactured individually, based on the anatomy of the patient’s jaw.