Chlorhexidine poisoning is not a very common occurrence due to the fact that most of it is used in small doses and in low concentrations. Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic substance widely used in dental, gynecological, ENT, and other practices. However, this is a drug, which means it has certain contraindications and side effects, and must be used strictly according to the instructions.
The medicine has different release forms
In this article we will talk about the properties of chlorhexidine, and also get acquainted with the methods of its use and the symptoms of poisoning with this substance. In addition, we will learn how to help with chlorhexidine poisoning.
What is Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine has bactericidal, fungicidal and virucidal properties. It is most often used as an antibacterial, antiseptic and disinfectant. Antiseptic drugs are also prepared with Chlogexidine. Due to its wide spectrum of action on bacteria, fungi, viruses and mild irritating effects on the mucous membrane and skin, the drug is widely used in medicine:
- its effect is reduced or neutralized in the presence of organic alkaline substances, in particular soap;
- in bacterial cells, Chlorhexidine damages the membrane, which leads to the death of pathogens;
- Chlorhexidine is highly soluble in organic solvents such as dichloromethane.
Chlorhexidine was initially used in veterinary medicine and was also tested as a cure for malaria. Later it began to be successfully used to combat bacteria.
Drug interactions
- Concomitant use with iodine is not recommended.
- Chlorhexidine is incompatible with detergents containing anionic group (saponins, sodium lauryl sulfate, sulfonic acid, sodium carboxymethylcellulose) and soaps. The presence of soap can inactivate chlorhexidine, so before using the drug, any remaining soap must be thoroughly rinsed off.
- Forms a toxic compound when mixed with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) - para-chloroaniline ( p
-NH3C6H4Cl).
Parachloroaniline is reported to be toxic (Chhabra et al., 1991; Burkhardt-Holm et al., 1999) [ incomplete references
] and can cause the formation of methemoglobin (Chhabra et al., 1991). [
incomplete reference
] - Ethanol enhances the effectiveness of chlorhexidine.
What is hydrogen peroxide
The chemical hydrogen peroxide is considered one of the most effective disinfectants. The effectiveness of peroxide is even greater when used in concentrated form. Available in the pharmaceutical network in a concentration of 3-10%.
The starting substance is very powerful, and the chemical composition is quite simple - a water molecule made of hydrogen and oxygen with an additional oxygen atom. The substance is colorless and odorless. Due to the intermediate formation of atomic oxygen, it is a very good oxidizing agent, which is used in the laboratory in the form of aqueous solutions in various concentrations.
It is used not only in medicine, but also for household and cosmetic purposes, decomposing after a reaction into simple substances - water and oxygen.
Treatment of intoxication
The toxicity of Chlorhexidine is high only at high concentrations. In this case, the victim is hospitalized for further treatment in a hospital. There is no specific antidote that can neutralize the active ingredient, so therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of poisoning.
The following clinical and pharmacological groups are used:
- enterosorbents;
- gastroprotectors;
- hepatoprotectors;
- regeneration stimulants.
For fluid loss with vomiting and diarrhea, treatment regimens include Hydrovit or Regidron. Their use allows you to replenish the reserves of essential macroelements. Severe poisoning requires intravenous administration of solutions of sodium chloride, Ringer, and glucose.
What do Chlorhexidine and Hydrogen Peroxide have in common?
Some common properties of peroxide and Chlorhexidine are used in the professional medical field, Chlorhexidine is used as an analogue of hydrogen peroxide and vice versa:
- antiseptic - destruction of bacteria and microbes on the surface being treated;
- disinfectants - destruction of pathogenic organisms (except spores) outside the human body;
- bactericidal - destruction of microorganisms on living tissue.
Used for processing:
- surgical field;
- wounds and cuts;
- applications, rinses and washes;
- sterilization of medical instruments;
- clothes, bandages, napkins.
Using hydrogen peroxide or Chlorhexidine, the substance can be interpreted as both a disinfectant and an antiseptic depending on its concentration and time of contact.
Peroxide is related to Chlorhexidine by some other common characteristics, both drugs:
- are a colorless liquid;
- have no odor;
- do not relate to medicines;
- in pharmaceutical sale they are presented as an aqueous solution;
- usually do not cause irritation;
- well tolerated by tissues.
Additionally, hydrogen peroxide and Chlorhexidine have similar contraindications, namely:
- allergy;
- sensitivity to drugs;
- dermatitis.
Contraindications
Chlorhexidine is far from a harmless medicine. Frequent use leads to drying of the mucous membranes and the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the vagina. This applies to douching and washing. The microflora, altered due to vaginal dryness, may not be able to withstand it, then even more favorable conditions for the spread of candida will be formed in the body.
If you are allergic to the components, burning and redness appear in the groin and labia.
The drug is not prescribed:
- if the patient is under 16 years of age;
- there is a high sensitivity to the components;
- during menstruation (therapeutic value is extremely low).
Douching with Chlorhexidine during pregnancy increases the risk of infection of the fetus.
What is the difference between Chlorhexidine and hydrogen peroxide
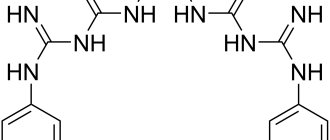
In Chlorhexidine, the starting substance is a secondary dichlorine-containing biguanide, a white crystalline powder.
The chlorhexidine compound is stable.
Mainly used in medicine, very widely in dentistry.
The most frequently studied drug, more than 3,000 scientific publications are devoted to it. Available in the form of creams, gels, ointments, tablets, suppositories and solutions.
The concentration of the aqueous solution ranges from 0.05 to 0.2%.
The main difference between Chlorhexidine and hydrogen peroxide is its ability to suppress the development and reproduction of bacteria, accelerating wound healing.
Peroxide, on the other hand, is unstable. The starting material is the simplest peroxide. It is sometimes called hydrogen peroxide. It does not have bacteriostatic properties; during antiseptic treatment it damages surrounding healthy cells, slowing down wound healing. This is a liquid with a metallic taste, highly soluble in water, ether or alcohol:
- limited use in medicine and dentistry;
- Available only in the form of an aqueous solution;
- the concentration of the drug sold by pharmacies is 3%;
- helps stop bleeding from cuts;
- may cause burns to mucous membranes.
Hydrogen peroxide and Chlorhexidine, the difference between them:
- Chlorhexidine inhibits the development of caries;
- in endodontics, dental canals are washed with Chlorhexidine;
- in the postoperative period, used for oral hygiene;
- removable dentures are kept in Chlorhexidine solution;
- it is used to treat ENT diseases;
- a toothpaste containing Chlorhexidine is produced;
- used for the prevention of sexually transmitted infections;
- included in veterinary products;
- used in medicines in the form of digluconate solution;
- non-toxic, if swallowed it is completely eliminated from the body;
- Wipes and sponges are impregnated with chlorhexidine for professional and household use;
- also impregnate the clothes of patients and medical personnel;
- its 7% solution is included in the list of vital drugs by the WHO directive of 2013;
- not compatible with iodine;
- neutralized by an alkaline composition.
By-effect:
- with prolonged use it affects the taste buds and stains the tongue, tooth enamel and fillings brown. The changes are reversible and completely disappear after cancellation;
- using the product for more than 2 weeks can have a depressing effect on beneficial bacteria and change the microflora of the oral cavity;
- limited use during pregnancy;
- Under 18 years of age, Chlorhexidine should be used with caution.
What is the difference between hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine:
- explosive in high concentrations;
- ingestion poisons or leads to death.
Widely used in various fields:
- in the textile industry;
- water and wastewater treatment;
- in the production of pulp, paper and detergents;
- used for chemical synthesis;
- in metal production and mining;
- in crude oil refining;
- in food production, hydrogen peroxide is used to disinfect surfaces;
- in livestock production: feed processing; food supplement.
Peroxide for cosmetic purposes:
- bleaches hair;
- serves as a detoxifier.
For household purposes, hydrogen peroxide:
- cleans the surfaces of windows, mirrors, furniture;
- whitens linens and clothes;
- removes stains.
Hydrogen peroxide neutralizes mold and fungi, including those affecting house plants.
Disinfecting vegetables and fruits with a 1:1 solution with water increases the shelf life of products.
Side effects
An important feature of the drug is its relatively low toxicity. It has almost no effect on the cells of the human body. However, this, of course, does not mean that the drug is completely harmless. It is still not recommended to use it internally. If this happens, then you should use sorbents, such as activated carbon, and perform gastric lavage. In addition, it can cause burns to mucous membranes. For this reason, chlorhexidine should not be used to treat eye infections such as conjunctivitis. If the drug gets into your eyes, rinse them thoroughly with water. You should also avoid getting the drug on the meninges, for example during open head injuries. It is prohibited to use the drug to treat ear diseases with a damaged eardrum.
Which is better: Chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide
In addition to the general ability to disinfect, be an antiseptic, or have a bactericidal effect, drugs have individual characteristics. Of the two agents, only hydrogen peroxide is capable of:
- instantly destroy bacteria, microbes and viruses along with spores, for example, anthrax;
- help administer therapy similar to hyperbaric oxygen therapy;
- peroxide revives aquarium fish;
- it acts as a deodorant and astringent;
- peroxide helps stop bleeding;
- bleach hair or lighten tooth enamel.
Therefore, it is better to store both products in your home medicine cabinet and use them selectively, depending on the situation.
When is Chlorhexidine better, or what does hydrogen peroxide not do? When to treat an infection:
- gonococcus;
- trichomoniasis;
- gingivitis;
- cystitis.
Apply the application to the wound or treat the interdental space.
The following video contains educational information about the action of various antiseptics, including hydrogen peroxide:
Diagnostics
To accurately determine whether you may be allergic to Miramistin or Chlorhexidine, you must consult a doctor for a laboratory examination. Skin testing is a common way to determine allergies. The patient is given a minimal dose of the irritant and the body’s reaction is observed.
There are a number of contraindications for the procedure:
- infectious diseases;
- presence of HIV infection;
- risk of anaphylactic reaction;
- pregnancy, lactation period;
- asthma;
- malignant neoplasms;
- mental disorders;
- allergies during exacerbation.
Disadvantages include the fact that the analysis can only be carried out during remission. This diagnostic method is used less and less, since the introduction of allergens may lead to complications, especially in children. Laboratory diagnostic methods are used more often.
The allergist prescribes the following examinations:
- determination of total immunoglobulin E;
- histamine and leukotriene tests;
- ELISA for immunoglobulins;
- radiosorbent method for immunoglobulins;
- fluorescent method.
The material for analysis is venous blood. These modern methods allow you to quickly and accurately obtain results; for each patient, the allergist selects an examination regimen individually.
How to treat
The first thing an allergy sufferer should do is to refuse treatment with chlorhexidine. It must be replaced with an analogue or a drug with a similar effect.
Treatment for mild symptoms
Antihistamines are prescribed, as well as various ointments that eliminate the manifestations of an allergic reaction on the skin.
- Zyrtec;
- Suprastin;
- Loratadine;
- Claritin;
- Cetirizine and others.
- Hydrocortisone;
- Advantan;
- Flucinar and others.
IMPORTANT! Although hormonal ointments are more effective than non-hormonal ointments, they should nevertheless be used with caution. The course of treatment should not exceed more than one week.
Folk remedies
Various decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, mint, yarrow, sage and others will help cope with allergies, namely eliminate manifestations on the skin. It is enough to wash the affected areas of the body with such decoctions or use lotions from them.
You can prepare an ointment yourself that effectively relieves itching and irritation. To do this, you need to take celery root, as well as butter.
Oatmeal, which is steamed in milk, moisturizes the skin well.
How to relieve moderate symptoms?
An allergy sufferer who has a moderate severity of allergy should take an antihistamine. Both first generation, second and third generation antihistamines are suitable for this. Treatment should be symptomatic.
Be sure to consult a doctor as soon as possible for advice.
Help with complications
In very rare cases, allergies can be severe. Then the patient may experience anaphylactic shock, which is accompanied by a sharp decrease in pressure, loss of consciousness, and increased heart rate. An allergy sufferer with such signs needs urgent medical attention.
What ways can you relieve the itching and burning sensation of thrush?
Thrush is a fungal disease caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida. If a fungal infection affects the genital mucosa, its main symptom is terrible itching and severe burning, with symptoms most pronounced in the evening and at night. The itching with thrush is so strong that it disrupts a woman’s sleep and normal rest. Moreover, in particularly sensitive people it can cause neuroses and neurosis-like conditions.
Itching can also intensify during the day - from water, when walking, from heat, during menstruation or just before it. Severe itching significantly worsens a woman’s quality of life and significantly affects her peace of mind, so many women strive to get rid of it at any cost in order to alleviate their condition at least for a short time.
How to eliminate unpleasant sensations
You can eliminate the burning and itching of thrush in several different ways. However, it is worth remembering that none of them brings complete recovery and does not cancel a visit to the doctor to prescribe full treatment.
All local methods of eliminating itching can be considered a kind of “first aid”, but a doctor will help you get rid of thrush completely.
Here's how to relieve severe itching and burning:
- Washing with baking soda solution.
For 1 liter of warm boiled water you should take 1 tbsp. spoon of soda, stir until completely dissolved. Gently wash yourself with the resulting solution and wipe the vaginal walls with a cotton pad soaked in the solution.
- Douching with hydrogen peroxide.
Under no circumstances should you just take a ready-made pharmaceutical solution! Hydrogen peroxide is dissolved in warm boiled water at the rate of 2 teaspoons per 1 liter of water. The resulting solution is used for 10-15 minutes of douching with a slow stream.
- Washing with herbal decoctions.
Decoctions of chamomile, calendula and oak bark soothe itching and reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane. For the best effect, it is advisable to use all three ingredients in one decoction.
- Treatment with antiseptic solutions.
A solution of miramistin or chlorhexidine applied to a cotton pad should be used to treat the vaginal walls and mucous membrane of the external genitalia.
- Antifungal ointment or cream.
Clotrimazole-based cream softens the mucous membrane well and can relieve itching in just a few minutes. It is highly advisable that the cream be prescribed by a doctor who will select the active ingredient in accordance with the severity of thrush and the individual characteristics of the body.
- Tea tree oil.
Dilute 2-3 drops of tea tree oil in warm boiled water, moisten a cotton pad or swab with the solution and treat the external genitalia and vaginal walls.
All these remedies will help relieve severe itching and alleviate the condition, but it should be remembered that they do not kill the fungal spores remaining in the glandular layer of the vaginal wall, so a relapse of the disease is possible after a while. For full treatment, systemic therapy, diet and proper care will be required.
Factors to consider
There are a number of factors that increase itching and provoke a recurrence of thrush, so they must be eliminated. Here's what you should definitely do to reduce discomfort and prevent it from recurring after treatment:
- Follow a diet: do not eat fatty foods, sweets, yeast baked goods, cheeses (especially blue cheeses), do not drink alcohol and carbonated sweet drinks. All these products create favorable conditions for fungus and provoke itching.
- Wear loose underwear made from natural fabrics. Tight synthetic underwear can cause severe itching and discomfort.
- Wash frequently with warm water without scented soaps and gels. It is better to use antiseptic solutions or herbal decoctions.
- Use only cellulose-based pads, without deodorizing or scented components. It is better to avoid tampons altogether and not use them even after treatment.
- To prevent itching from returning after treatment, the normal microflora of the vagina should be restored. To do this, you can use Lactagel topically, as well as drink natural yogurt with live cultures of lactic acid bacteria every day.
To prevent itching after treatment, you should follow a diet for another 2-3 weeks after the therapeutic course.
It is also necessary to observe the hygiene standards given above for a long time after treatment. And it’s better to give up synthetic underwear forever.
Sometimes burning and discomfort after treatment indicate vaginosis - vaginal dysbiosis caused by the treatment itself and the use of antiseptics. To avoid such complications after treatment, care should be taken to restore normal vaginal microflora.
Thrush is the most common disease, affecting every third woman. Vaginal candidiasis causes a lot of inconvenience and disrupts the usual way of life. One of the popular means of relieving discomfort is the common antiseptic Chlorhexidine. It is available without a doctor's prescription and has an affordable price.
Notes[ | ]
- Calibr ReFrame Drug repurposing library
- State register of medicines (unspecified)
. grls.rosminzdrav.ru. Retrieved April 21, 2022. - Zverkov A.V., Zuzova A.P.
Chlorhexidine: past, present and future of one of the main antiseptics // Clinical microbiology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. - 2013. - No. 4. - First study to link antibiotic resistance with exposure to the disinfectant chlorhexidine (undefined)
. EurekAlert!. Retrieved November 1, 2022. - WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 18th list (April 2013) (unspecified)
. - Ionov O.V., Nikitina I.V., Kirtbaya A.R., Balashova E.N., Lenyushkina A.A., Lyubasovskaya L.A., Rodchenko Yu.V., Priputnevich T.V., Zubkov V. .V., Degtyarev D.N.
“Chlorhexidine bigluconate solution and ethyl alcohol: which antiseptic is more effective in newborns?” (Russian) // Neonatology: News. Opinions. Training: Scientific journal. — Russia: All-Russian public organization for promoting the development of neonatology “Russian Society of Neonatologists,” 2022. — February 7 (No. 1). — P. 79-85. — ISSN 2658-7424. Archived from the original on February 27, 2020. - Alex Chin, Julie Chu, Mahen Perera, Kenrie Hui, Hui-Ling Yen, Michael Chan, Malik Peiris, Leo Poon.
“Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions” (English) // The Lancet Microbe : Medical journal[en]. - Hong Kong University: Elsevier, 2022. - April 2 (vol. 20, iss. 4). — ISSN 2666-5247. - doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3. Archived from the original on April 17, 2022. - Lai, P; Coulson, C; Pothier, D. D; Rutka, J (2011). “Chlorhexidine ototoxicity in ear surgery, part 1: Review of the literature.” Journal of Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery
.
40
(6): 437–40. PMID 22420428. - ↑ 12
Chhabra, R. S., Huff, J. E., Haseman, J. K., Elwell, M. R., & Peters, A. C. (1991). Carcinogenicity of p-chloroaniline in rats and mice. Food and chemical toxicology, 29(2), 119–124. - Zverkov A.V., Zuzova A.P.
“Chlorhexidine: past, present and future of one of the main antiseptics” (Russian) // Clinical microbiology and antimicrobial chemotherapy: Scientific and practical journal. - Smolensk: Interregional Association of Public Associations "Interregional Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy", 2013. - T. 15, No. 4. - P. 281. - ISSN 2686-9586. Archived from the original on April 18, 2022. - S. Malhotra, A. Dharmadasa, S. M. Yentis.
“One vs two applications of chlorhexidine⁄ethanol for disinfecting the skin: implications for regional anesthesia” (English) // Anaesthesia[en] : Medical journal[en]. - Association of Anesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland[en]: Wiley-Blackwell[en], 2011. - May 24 (vol. 66, iss. 7). — P. 574–578. — ISSN 1365-2044. - doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.06706.x. Archived from the original on April 20, 2022. - Shyh-Ren Chiang, Fang Jung, Hung-Jen Tang, Chung-Hua Chen, Chi-Chung Chen, Hsiu-Yin Chou, Yin-Ching Chuang.
“Desiccation and ethanol resistances of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii embedded in biofilm: The favorable antiseptic efficacy of combination chlorhexidine gluconate and ethanol” (English) // Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection : Medical journal[en]. - Taiwan: Elsevier, 2022. - December (vol. 51, iss. 6). — P. 770–777. — ISSN 1684-1182. - doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2017.02.003. Archived from the original on April 20, 2020.