Who is a dentist surgeon
A dental surgeon is a specialist who graduated from a higher medical school and completed residency in the specialty “Surgical Dentistry”. This is a doctor who not only removes teeth, he performs complex maxillofacial surgeries that eliminate serious problems in the oral cavity, aimed at eliminating defects and preserving the integrity of the dentition.
By the nature of his work, the surgeon is in close contact with dentists of other specialties: prosthetist, implantologist, therapist, hygienist, etc. By performing their job duties, surgical doctors daily improve the quality of life of patients scheduled for scheduled operations. In addition, they provide necessary treatment in emergency situations.
How to avoid complications after removal?
Careful adherence to the surgeon’s recommendations will prevent the development of complications. Recommendations include:
- After removal, do not visit baths/saunas.
- Don't drink alcohol.
- Carry out antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity (medicines are prescribed by a doctor).
- Do not rinse the mouth, but only use oral baths, so as not to wash out the blood clot in the hole.
- Do not eat spicy, hot or sour foods.
- If medications are prescribed, be sure to follow the dosage regimen.
Field of professional activity of a dental surgeon
The competence of a dental surgeon includes the following responsibilities:
- examination, diagnosis of oral diseases;
- planning of invasive intervention;
- carrying out planned surgical operations (cystectomy, flap plastic surgery, gingivectomy, gingivotomy, hemisection, others);
- provision of emergency surgical dental care;
- treatment of fractures, jaw dislocations;
- removal of teeth, fragments, destroyed roots (if it is impossible to carry out tooth-preserving manipulations);
- introduction of conduction and infiltration anesthesia;
- invasive treatment of congenital and acquired pathologies of teeth and periodontium;
- performing operations to remove cystic formations, tumors (benign and malignant);
- providing advisory support to fellow dentists of other specialties.
In addition to dental surgery, the specialist has perfect knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and pathological physiology. He must be able to work with various dental instruments and equipment, determine pathology from X-rays, understand the indicators of laboratory tests, know the purpose, methods of taking medications, and much more.
Features of working with children
Working with children requires from the surgeon not only high professionalism, but also psychological preparation, as well as perseverance. It is a rare child who comes to see the dentist without fear.
Regardless of the upcoming manipulations, all children experience increased anxiety at the sight of dental equipment and many of them react violently with reluctance to listen to the doctor. To avoid this, the surgeon must be able to find an approach to every child of any age .
The process of establishing anesthesia is considered in a special way. The situation is greatly facilitated by topical anesthesia, used before the main anesthetic injection.
Children's age limits the volume of the drug administered and the time for the doctor's manipulations, so his actions must be quick and clear.
What diseases does a dental surgeon treat?
Using surgical correction methods, the dentist-surgeon treats the following diseases:
- Perimaxillary abscess is a purulent-inflammatory focus in the tissues of the maxillofacial area. Occurs as a result of chronic tonsillitis, furunculosis, trauma, and other reasons. It is characterized by significant pain, jaw deformation, hyperthermia, etc. The surgeon performs excision of the purulent formation and a simultaneous counter-aperture (additional incision), which facilitates the outflow of contents to the outside.
e - Gum recession is a decrease in the level of the gingival margin in the area of one or more teeth, leading to exposure of their necks and roots. One of the options for correcting pathology is flap surgery - gingivoplasty. This is an operation to form a smooth edge of the gum and cover the exposed areas with tissue.
- Atrophy of the bone tissue of the upper jaw. The pathology is detected when the patient plans to implant artificial roots for subsequent installation of an orthopedic structure. For correction, sinus lift surgery (subantral augmentation) is often used. It consists of building up bone tissue in the atrophied area.
- Granuloma of one of the canals of a multi-canal tooth. For the purpose of treatment, a surgical procedure is performed - hemisection (removal of the damaged root, followed by filling the hole with bone material and suturing the wound).
- Cyst of the root apex area. Excision of the root element (resection) affected by the inflammatory process is carried out.
In addition to the listed pathologies, the dental surgeon treats other diseases:
- temporomandibular arthritis;
- defects of the frenulum, tongue, lips;
- osteomyelitis;
- flux, other pathologies.
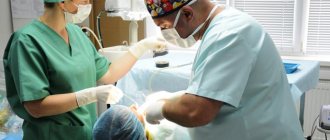
How is tooth extraction performed?
Patients may delay removal for a long time because they are afraid that it will hurt. But modern dentistry allows this procedure to be performed absolutely painlessly.
The surgeon at the SDent clinic individually selects the dose and type of anesthetic. This allows you to achieve complete pain relief in each specific case. Only after the patient feels numbness in the desired area of the jaw, the surgeon begins the operation: the doctor pushes back the gum and carefully removes the tooth from the bone. Atraumatic removal promotes rapid tissue healing. In addition, the postoperative period will be as comfortable as possible for the patient.
After removal, the surgeon gives recommendations and, if necessary, prescribes medications and painkillers.
In what cases should I contact
Patients are referred to the surgeon's office (from dental specialists of other specialties) if there are indications for invasive interventions. This happens for reasons:
- the crown part of the tooth is destroyed without prospects for its restoration;
- preparation for implantation, prosthetics;
- maxillofacial trauma;
- benign, malignant neoplasms;
- infections of the salivary glands, oral cavity, jaw;
- congenital defects of the lips, palate, frenulum;
- the need to remove the eighth teeth in a row;
- significant mobility of segments;
- indications for reconstructive surgery in the face and jaw.
You can routinely contact a dental surgeon for a follow-up examination after surgery. Before visiting a doctor, you must stop taking anticoagulants and alcohol 2-3 days before. On the day of your appointment, do not smoke, have a good breakfast, and brush your teeth.
Our dental center welcomes highly qualified dental surgeons who provide the full range of services within the competence of this specialty. Modern technologies, the latest equipment, and the best medications make it possible to carry out invasive interventions in a comfortable environment, without pain.
Why do wisdom teeth need to be removed?
Wisdom teeth are rudiments that we inherited from our ancestors. Modern man no longer needs these “eights”, since they are not involved in chewing, they do not have enough space in the jaw. In 99% of cases they are removed. If such teeth erupted painlessly, without causing any trouble to the patient, then due to their distant location, it is impossible to completely remove plaque and food debris from them with a brush. Caries develops, and then pulpitis.
If you do not consult a dentist in time for surgical treatment of wisdom teeth, a number of complications arise:
- painful eruption, inflammation, swelling;
- the horizontal position of the “eight” in the bone exerts destructive pressure on the adjacent tooth, which leads to the removal of both;
- due to lack of space in the jaw, crowding of teeth occurs in the anterior area, which negatively affects the aesthetics of the smile;
- due to the inability to carry out good hygiene, caries occurs, then pulpitis - inflammation of the nerve, characterized by acute pain.
If a wisdom tooth has already erupted and caries has developed on it, it is quite difficult to treat it. The “eight” is located far away, and it is not always possible for a doctor to get close to it and treat it competently. But each case is examined individually by a doctor: to treat or remove.
Pros and cons of the profession
pros
- A respected and socially important profession.
- Interesting job.
- Competitive salary.
- There are always vacancies; the profession has no territorial reference.
- Social guarantees, full protection of rights and interests.
- Business trips and trips to foreign conferences are possible.
- A constant circle of patients who prefer to see one doctor in whom they are confident.
Minuses
- Long-term training and the enormous responsibility that a doctor bears for the life and health of each of his patients.
- People are afraid of dentists, so they often put off visiting a doctor, ending up in a specialist’s office in critical condition.
- Floating schedule, frequent delays at work due to emergency situations.
- Insensitive patients who call and write to the doctor at any time of the day or night, wanting to get advice or consultation.
- In the first few years of work, a medical school graduate performs only simple operations, because he has no work experience.
Reviews
Most often, people encounter a dental surgeon when removing teeth. Implantation, patchwork and cosmetic surgeries, restoration of jaw proportions are rarer cases.
If you have undergone these operations, tell us about your impressions of them and the results of the dental surgeon’s work specifically in your case. By leaving your comment at the bottom of the page, you will help someone make the right choice.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Cosmetic interventions
Surgical procedures are performed not only for therapeutic purposes. Sometimes it is necessary to correct the shape and structure of fabrics to eliminate aesthetic defects.
There are a number of manipulations, the main ones of which will be discussed below.
Gingivoplasty
The procedure is used for deficiencies in gum tissue , if it is uneven or grows on the teeth, as well as if it is located too low relative to the line of the dentition.
The essence of the method is that with the help of surgical intervention, periodontal tissue is adjusted and its line is aligned.
A patch operation is used; if it is necessary to increase the area, tissue is used from the area where its amount is excessive. After alignment, stitches are applied, rehabilitation lasts up to ten days.
Vestibuloplasty
It is used when it is necessary to expand the oral vestibule. The movement of mimic muscle tissues into the depths of the oral cavity is carried out.
To do this, incisions are made in the soft tissues responsible for stretching the gums. This procedure allows you to avoid oral diseases in the future and improves diction.
Frenuloplasty
It is performed to trim the overgrown frenulum of the upper and lower lips or the membrane under the tongue. The presence of this defect impairs diction and creates general discomfort.
It is performed by making tissue incisions and is performed under local anesthesia.
Elimination of gum recession
Used for thinning gums. The mucosal donor site is taken from the palate . It is grafted into the problem area, after which sutures are applied.
Recovery lasts up to seven days.
Anomalies of the dental system
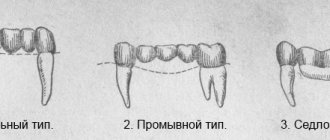
Where the orthodontist with his braces, plates, trainers and aligners is powerless, a dental surgeon comes to the rescue and corrects the proportions of the jaw through surgical intervention. But after this procedure, do not forget about the long period of rehabilitation and the fact that, most likely, you will have to finish what you started by wearing the same braces or other orthodontic devices in order to become truly healthy. After all, an incorrect bite brings, in addition to aesthetic inconveniences, a lot of other problems: dental diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, headaches, and can even provoke cancerous tumors as a result of constant trauma to the mucous membrane.
Scheme for correcting malocclusion surgically
Contact with related specialties
A large number of therapeutic activities that a dental surgeon is involved in involves his close cooperation with doctors of other areas and specialties - dental therapists, orthodontists, orthopedists, oncologists.
A dental surgeon must be well versed not only in orthodontics, orthopedics, pediatric dentistry, but also in areas that are not directly related to dentistry, but are necessary for successful surgical intervention or rehabilitation after it.
This is pharmacology (medicines for local and general anesthesia, antiseptic and antibiotic drugs), the procedure and scheme for routing patients when diagnosing other diseases, in particular oncological ones.
It is necessary to know the regulatory documents and laws that regulate the work of not only a dental surgeon, but also doctors in other fields.