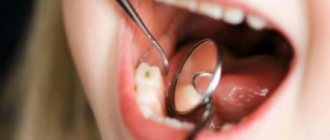
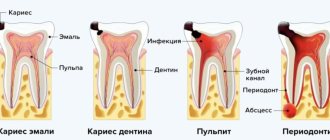
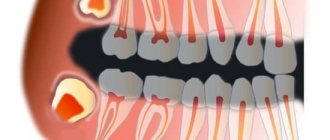
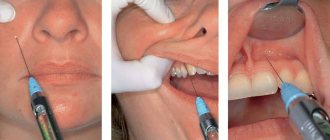
The level of effectiveness of a patient's dental treatment in dentistry largely depends on whether the treatment is painless. After all, the problem of pain in patients is important and quite relevant. People, by postponing a visit to their dentist, trigger the disease because they are afraid of the pain of dental treatment.
However, there are different methods of dental anesthesia, which can completely eliminate all pain through high-quality anesthesia. Effective local anesthetics in dentistry are an excellent solution to completely eliminate pain when treating the oral cavity or teeth, because they allow you to maintain a connection between the patient and the doctor. The anesthetic dulls the receptors, which leads to blocking pain during dental or oral treatment.
Types of anesthesia used in dental practice
When treating the oral cavity and teeth, anesthesia is used - general or local.
Anesthesia (general anesthesia) is used quite rarely. With this anesthesia, the patient is unconscious while the treatment is underway and does not feel anything. Anesthesia (general anesthesia) is used only for major operations or when treating children. This type has too many contraindications and all sorts of complications, so dentists almost always prefer local anesthesia. This is the best option for dental intervention.
Local anesthesia - pain relief by freezing or injection into the gum. In this form, the anesthetic temporarily disables the sensitivity of pain in the area specified for treatment. Tactile sensations are preserved during local anesthesia. The patient feels touch or pressure on the tooth or gum, but the patient has no pain. To numb the patient's upper tooth, a local anesthetic is injected into the gum near the painful tooth. This is infiltration anesthesia. Lower teeth - by injecting the patient with a local anesthetic near the mandibular nerve. This will be a conduction anesthesia. It will lead to numbness of the tongue and lower jaw. In dental practice, there is also topical anesthesia, which will make treatment of a certain area of the oral mucosa painless by applying a special gel or spray to it. This anesthesia will be appropriate before infiltration anesthesia, so that the needle prick is imperceptible to the patient.
Anesthesia methods
Anesthesia can be local or general. The local form is divided into external and injection methods.
The external method allows you to anesthetize superficial tissues using medicinal substances. These can be special ointments, gels, devices with electromagnetic waves, simply applications. The last method is used most often. The application is a cooling plate. It is applied to the gums, and the patient does not feel pain. This method is usually used to remove baby teeth in children.
The injection method involves injecting an anesthetic substance through a needle.
There are 4 types of anesthesia:
- Conductor. The method allows you to anesthetize several teeth at once. An anesthetic is injected into the area of the last tooth where the branch of the nerve is affected, resulting in blockage of the entire nerve.
- Infiltration. An anesthetic substance is injected into the projection area of the apex of the tooth root.
- Intraligamentous. The medicine is administered through the gum. As a result, the tooth and the surrounding gum area are numbed. For this method, a special syringe with a dispenser is used. It allows you to administer a minimum of anesthetic substance.
- Intraosseous. It is the best anesthesia. In this case, the injection is made directly into the spongy bone. It is she who covers the dental alveoli.
General anesthesia (anesthesia) is done very rarely.
It should not be used for people who have heart problems. This method of anesthesia is used only in the most difficult cases. Dentistry must be equipped with a special office and all the necessary equipment. And also during surgical operations, the presence of an anesthesiologist next to the patient is mandatory.
Only the doctor decides which anesthesia is best for tooth extraction. Everything will depend on the complexity of the procedures and the general condition of the tooth.
Components of anesthetics
The anesthetic contains local anesthetics, preservatives, vasoconstrictors and stabilizers. The drug used for local anesthesia for pain relief may not contain all of the listed components. To effectively block impulses from nerve endings, one anesthetic is used, and to prolong the period of action and enhance the analgesic effect, vasoconstrictors (adrenaline) are needed. It is used to create and maintain a sufficient concentration of the drug in the treatment area. Preservatives and stabilizers are used in practice to increase the shelf life of anesthesia.
Basic requirements for modern anesthetics
An anesthetic is a unique substance that suppresses the excitability of the receptor, turns off the impulse to the patient’s nerve fibers, after which pain relief occurs.
The anesthetic has basic requirements:
- do not cause dilation of the patient’s blood vessels;
- do not provoke tissue irritation;
- high resistance to sterilization of the drug;
- slow absorption into the blood;
- greater strength and duration of analgesic effect;
- have low toxicity to the patient;
- good analgesic effect during dental treatment.
The local anesthetic has a direct inhibitory effect on the receptor and the permeability of the sodium channels in the patient begins to decrease, while the entry of sodium into the human cell is completely disrupted, after which an action potential is generated and this all leads to a lack of sensitivity and analgesia during treatment. Sensitivity is switched off one by one: at the beginning pain, then taste, then temperature and finally tactile. This is how the process of pain relief occurs.
To prolong the effect of painless treatment, a vasoconstrictor (for example, adrenaline) must be added to the local anesthetic. However, in patients with heart disease, it poses a greater risk of heart attack. A vasoconstrictor can cause the patient to relax the muscles of the bronchi and intestines, dilate the pupils, significantly increase blood sugar, increase tissue metabolism and cause many adverse reactions. But if you exclude adrenaline from the local anesthetic drug, this will lead to ineffectiveness and the patient will not experience pain relief.
The decision to use this substance in treatment should be made by an experienced dentist, as a last resort. After all, after adding adrenaline to the local anesthetic, the effectiveness of anesthesia itself during dental treatment increases significantly and its toxicity for the patient decreases. This occurs due to the very slow absorption of the painkiller into the blood. And sometimes toxic complications that appear during local anesthesia are mistakenly attributed to a side effect of the substance adrenaline.
Anesthesia after tooth extraction
After the tooth has been removed and the anesthesia has begun to wear off, pain may occur. Sometimes the pain symptoms are very strong and unbearable to endure. In this case, they resort to repeated anesthesia. The most common pain reliever offered by dentists is Ketanov.
Ketanov is able to relieve a person from severe and sharp pain.
It is often prescribed after surgery. The drug can be used every six hours, but not more than one week.
Like any medicine, Ketanov has side effects. These include:
- drowsiness;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- the appearance of dry mouth;
- accelerated heartbeat.
The drug should not be taken by people who have:
- bronchial asthma;
- ulcer of the duodenum and stomach;
- kidney diseases.
It is also undesirable for women to use during lactation and pregnancy.
If after three days pain or swelling occurs again, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Classification of anesthetics in dentistry
Before dental treatment, the doctor should choose an effective local anesthetic agent individually for each person. The appropriate anesthetic is selected depending on the procedure itself, the duration of the procedure, and the patient's tolerance to the anesthetic drug.
Chemical properties divide the local anesthetic into groups such as substituted amides (articaine, lidocaine, trimecaine) and esters (novocaine, anesthesin, dicaine). These two groups have differences in biotransformation, and most importantly, in side effects for the patient.
Classification according to the method of administration divides local anesthetics in dentistry into those that are used for surface anesthesia and those that are used for conduction and infiltration anesthesia. Based on the duration of its action, anesthetics are classified into short, medium and long-acting.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Complex one-stage implantation of the lower jaw
Case: there was a loose bridge of 4 front teeth on the lower jaw; after diagnosis, removal of the remaining teeth and complex basal implantation were prescribed.
Restoration of all teeth using basal implantation method (March 2012)
Case: partial adentia, exposed roots of natural teeth, periodontitis, increased tooth mobility, severe atrophy of bone tissue in some places beyond the possible norms for classical dental implantation.
Simultaneous implantation and removable prosthetics (June 2012)
Case: complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw; at the time of treatment, an old removable denture was used and was to be replaced.
Classical implantation and dental prosthetics (October 2012)
Case: need for implantation of a primary canine.
Local anesthetic preparations for dental treatment
For high-quality pain relief, the dental clinic uses the latest generation local anesthetic. To administer the drug with a local anesthetic, take carpules and carpule syringes, which already contain the solution itself. The quality of dental treatment for patients using such syringes is much higher than with a simple disposable syringe. After all, the needle is much thinner than simple disposable syringes and the injection is not so painful.
Carpule anesthetics in dentistry are good because they have the following advantages:
- Complete sterility, 100% guarantee against excess substances entering the local anesthetic.
- Exact dosage of the required components. The syringe contains a ready-made anesthetic drug.
- There is no pain from the injection, since the needle is thinner than that of a disposable simple syringe.
The previously used novocaine or lidocaine has long faded into the background, as they have low effectiveness and allergic manifestations. Today they are practically not used, mainly as anesthesia in public clinics.
In advanced dental clinics, effective drugs based on articaine or mepivacaine are used to provide good anesthesia.
Articaine is an effective anesthetic that is used for high-quality local anesthesia (for example, Ultracaine). It consists of articaine and adrenaline. Mepivacaine has a great ability to constrict blood vessels, but it also has a slightly less effect from local anesthesia. The drug is used for dental treatment in young children, pregnant women, as well as patients who have hypertension and those for whom adrenaline is completely contraindicated. In such cases, a drug that contains mepivacaine (for example, Scandonest) is used to treat the patient’s oral cavity.
Indications and contraindications for anesthesia during dental treatment
Pain relief is indicated in the following cases:
- Low pain threshold and pain intolerance;
- Severe psychological discomfort, anxiety, fear during treatment;
- Serious surgical interventions, tooth extraction, treatment of deep caries, removal of plaque and tartar, dental implantation.
Local anesthesia has almost no contraindications, mainly due to individual intolerance to the components of the anesthetic;
Anesthesia is excluded in the following cases:
- Pregnancy (due to the negative effects of medications on the fetus);
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia components;
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- Mental disorders, epilepsy;
- Early childhood;
- Recent stroke, heart attack or traumatic brain injury;
- Acute viral disease.
Criteria for choosing a high-quality local anesthetic
The main criterion for choosing an effective local anesthesia will be the nature of the upcoming dental intervention. The doctor selects the drug taking into account the required depth of treatment, the duration of local anesthesia according to the nature and scope of the upcoming intervention. The choice of anesthetic is influenced by pregnancy, great fear of the upcoming manipulation, and possible pathology in the patient. Take into account the presence of contraindications during treatment. There are age restrictions for the use of anesthetics. The dosage of anesthesia for dental treatment of the teeth of young children or elderly patients is always specified.
General anesthesia
Anesthesia involves the suppression of all human reflexes, including protective ones. The patient completely loses consciousness and falls into deep sleep. Anesthesia can be prescribed only for strict indications and necessarily requires special training of personnel and the dental department as a whole. Despite the fact that in modern medicine, dental treatment under anesthesia has reached a much higher level than before, this procedure is only relatively safe.
There is a risk of negative consequences for the body, which are much higher than the level of risk during the dental procedure itself. In this regard, treatment under anesthesia is indicated only in the most extreme cases, when it is impossible to do without it, for example, in case of dental phobia or serious surgical interventions.
The consequences of anesthesia can be:
- Allergic reactions;
- Anaphylactic shock;
- Cardiac arrest in the presence of chronic diseases;
- Nausea and vomiting after waking up;
- Loss of orientation;
- The recovery of consciousness after anesthesia may be impaired, which, in turn, can even lead to mental disorders.
According to many anesthesiologists, the best anesthesia is the one that the patient refuses.
Contraindications for the use of local anesthetic
To ensure that the local anesthetic is safe for the patient, contraindications for use should be taken into account. They can be grouped:
- Allergic manifestations in a patient to an anesthetic. It is a complete contraindication to the use of such a remedy to anesthetize the patient’s teeth. It is imperative to warn your dentist about the presence of allergic manifestations or a possible reaction to previous treatment of the oral cavity and teeth.
- There is a deficiency of metabolic systems. Many painkillers have a strong toxic effect in case of overdose of local anesthesia, insufficient metabolism and excretion. In this situation, it is better to use the drug in small doses.
- Age. For small children, the local anesthetic is taken in a lower dose than for anesthetizing the teeth of adult patients. To achieve effective dental pain relief, it is necessary to use a safe local anesthetic drug, limiting the dosage.
In modern dental practice, there is a wide selection of over-the-counter products that contain an anesthetic and will make dental treatment painless. After all, it is the main reason for the strong fear of patients in dental clinics.
Modern clinics offer painless treatment of the oral cavity or teeth using a local anesthetic. There is no need to be afraid of going to the doctor, put off this visit and make the disease worse, because today you can cure, remove a tooth or install an implant without pain. You need to decide on a dental clinic and choose a good doctor. He will be able to qualitatively cure the tooth by selecting an effective local anesthetic to numb the mouth or teeth. This is the key to painless treatment of the patient’s teeth and oral cavity.
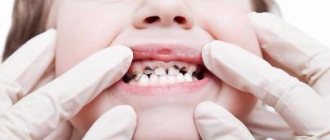
Removing baby teeth
Milk teeth that can no longer be cured, but they provoke the development of acute inflammation of the bone or periosteum, must be removed. Which method to use will depend on the specific situation.
For example, the milk tooth being removed is already well loosened and the pain when pulled out will be minimal. In this case, the doctor may advise putting on an application, gel or aerosol.
Lidocaine aerosol is used quite often. There are 3 mg per 1 kg of body weight. For children, it is better to apply this substance using a cotton swab.
For more serious dental problems, children are given infiltration anesthesia. Lidocaine, Ubistezin Forte and similar medications are used. Two injections are made - from the gum and from the tongue.
Children tolerate these painkillers well. But before using them, it is necessary to undergo tests to identify allergens. It is also worth clarifying whether the child has problems with the cardiovascular system.