Questions of physiology
The tongue is an organ consisting of striated muscle tissue, externally covered with a mucous membrane. It relates to the digestive system, participates in the process of grinding food, preparing products entering the oral cavity for the further process of digestion. The spade-shaped body of the tongue helps to mix food, crushed into small fragments and moistened with saliva.
The tongue contains many taste buds, which determine the sensation of taste. At the tip there is an area responsible for recognizing sweet taste, on the sides of the front of the tongue the salty taste is determined, and on the lower part - sour. The root zone is responsible for the perception of bitterness. The tongue is the most mobile organ of the speech apparatus, so it ensures the reproduction of a huge number of words and individual sounds.
Causes of bleeding
Why does my tongue bleed? The most common cause is trauma, which can be thermal (burn), mechanical (cut, bite), chemical (irritation) or physical in origin. The taste of blood in the mouth may appear when eating quickly, after talking, or when chewing. Injury can be caused by sharp protrusions of dentures or the edges of decayed teeth, fragments of food (bones), cutlery (fork, knife), during dental procedures (preparing the dentition for the installation of crowns).
Mechanical damage
If your tongue is bleeding, the cause is most likely mechanical damage. As a rule, this is an injury caused by negligence during eating, talking or dental procedures. Physical injuries are mainly caused by a maxillofacial blow or an accident. Thermal damage occurs when burned with steam, drinking too hot drinks, the cause may be fire, radiation, or an electrical appliance. Chemical damage occurs when aggressive chemicals come into contact with the mucous membrane.
Which doctor should I contact for help?
When a vessel on the tip of the tongue bleeds, you need to visit a doctor. Do not hesitate to visit a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- Prolonged bleeding.
- The wounded area of the muscle organ was severely swollen.
- Painful sensations increase.
- A hematoma formed, pus, strong furrows and plaque appeared.
- There is a burning sensation when eating.
- Damage to the muscle due to penetrating damage to the organ.
These problems are aggravated by the entry of pathological microflora into the wound. The first thing you should do is see a dentist. In difficult cases, consultation with a therapist, ENT doctor, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and other specialized specialists may be required.
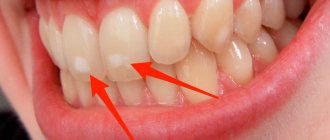
Pathological condition
If your tongue bleeds, this may be one of the symptoms of glossitis. Inflammation is caused by viral or bacterial microflora; it can be an independent pathology or accompany some systemic diseases. For example, stomatitis is often caused by the entry or activation of the herpes virus into the body. Mechanical injuries contribute to the development of the disease; smokers and people who abuse alcohol are at risk.
If the tongue bleeds, common causes of this condition are concomitant pathologies: liver diseases (carcinoma, cirrhosis, hepatitis), chronic renal failure, chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, intestinal inflammation, peptic ulcer. This symptom is characteristic of intoxication with salts of heavy metals, helminthiases, and vitamin deficiencies.
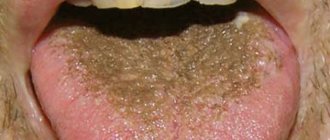
Symptoms of glossitis
The first sign of the disease is a feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity. Then salivation increases, swelling occurs, the tongue becomes bright red, taste sensations become dull, and eating becomes painful and difficult. Often the patient's speech becomes slurred due to swelling. If left untreated, mushroom-shaped growths may form on the tongue. If the disease is caused by an infection, then symptoms of inflammation are characteristic: local fever, swelling, general deterioration of well-being.
What symptoms to look out for
Patients with the diagnoses we listed above should be especially monitored for the appearance of alarming symptoms. If you are taking medications for the liver and gastrointestinal tract, carefully monitor your well-being. If you are concerned about the changes discussed below, consult your doctor. However, knowing these signs is useful for every person, since many diseases of the lower and upper gastrointestinal tract develop without obvious painful sensations. Often their first manifestation may be the symptoms of bleeding.
Weakness
This is the main sign of any prolonged bleeding. Weakness gradually increases, the patient's skin turns pale, he feels cold sweat, a ringing in the ears, and trembling of the limbs. The weakened state may last for several minutes, after which it passes and returns periodically. If blood is bleeding actively, fainting or semi-fainting and even shock are possible.
Vomit
This symptom accompanies severe blood loss - more than 0.5 liters. If the vomit is dark cherry in color, it is most likely coming from a vein near the esophagus. If unchanged blood is clearly visible in the vomit, the integrity of the artery in the esophagus is most likely compromised. If the patient vomits so-called “coffee grounds” of brown color, the problem lies in the gastric vessels. Only a doctor can accurately determine the nature, location and intensity of blood loss.
Chair
Traces of blood in the stool may appear within a few hours or 1-2 days after the integrity of the blood vessels is damaged. With significant problems with the stomach or duodenum, as well as blood loss in a volume of more than 0.5 liters, you can observe melena - loose stools that resemble tar in color and consistency. If the blood loss is smaller, which often happens, for example, with intestinal bleeding, then the stool remains formed, but its color darkens.
Please note that darkening of the stool can occur due to eating foods that contain dark coloring substances, for example, blueberries and cherries. Dark stools are not an absolute sign of the presence of blood in the stool and problems in the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. The diagnosis can only be made by a qualified specialist.
Diagnosis and treatment
If your tongue hurts or bleeds, you should consult a doctor. The specific clinical picture allows a diagnosis to be made during a routine dental examination. To clarify, bacteriological, biochemical, histological, cytological or serological diagnostic methods are used. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will make a diagnosis. Glossitis can be:
- deep, localized in the area of the floor of the oral cavity;
- diamond-shaped, usually developing against the background of chronic diseases;
- folded - congenital anomaly;
- desquamative (“geographical language”);
- Gunter's, which is a symptom of folic acid or vitamin B12 deficiency;
- interstitial, accompanying syphilis in the third period.
If your tongue bleeds, what should you do? To make eating easier, you should give preference to pureed soft dishes and soups. During the day, as well as before and after meals, rinsing with a weak antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine, furatsilin) is recommended. In cases of severe pain, applications with antiseptics are used. Plaque is removed with a swab soaked in proteolytic enzymes. The skin regeneration process is accelerated by local products with vitamin A.
In rare cases, surgery may be required. Strong anti-inflammatory, antifungal agents and antibacterial drugs are prescribed according to indications. Hormonal medications (hydrocortisone, prednisolone) in the form of ointments for topical use are used in short courses for difficulty breathing.
Possible reasons
There can be many factors that provoke the development of the problem. The reasons may be simple trauma or even pathology of systems and internal organs. Blood from the tongue appears in the following cases:
- Bite, injury, cut due to mechanical action;
- Irritation or cracking of chemicals;
- Burn, inflammation, growth;
The surface of the mucous membrane can be damaged by a knife, fork, or sharp edges of food products. Injuries are caused by protrusions of prosthetic structures and emergency situations. Hot steam, drinks, and current have a burning effect on soft tissues. With severe damage from pesticides and aggressive acids, even capillaries are exposed. If the damage is severe, anomalies of the venous ducts appear. In this case, you should consult a doctor. Diagnostics in dentistry will accurately determine the provoking factor. It may be glossitis, that is, an inflammatory process. He is called:
- Pathogenic bacteria that have entered the wound.
- Allergy to hygiene products.
- Low-quality alcohol, cigarettes, chemical food additives.
- Hot spices.
The cause of the pathology is problems of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the circulatory system and the central nervous system. Deficiency of vitamins B, PP, A negatively affects health.
Possible complications
In advanced forms of the disease (if the tongue constantly bleeds, removal of plaque is accompanied by severe pain, there are purulent ulcers), an abscess may form. At the same time, salivation increases significantly, the tongue greatly increases in size, acute throbbing pain occurs, and speech is impaired. A serious complication is the development of phlegmon. Suppuration becomes pronounced, speech and breathing become difficult, the patient refuses to eat, and possible attacks of suffocation. Symptoms of general intoxication of the body become pronounced.
Treatment of cracked tongue
If the tongue bleeds in the morning, then first of all mechanical factors and an allergic reaction to oral care products should be excluded. It is necessary to adjust dentures and fillings, correct the bite, change toothpaste or brush (replace with a softer one). Treatment usually includes rinsing with disinfectants and sanitation of the mouth.
First, you should contact a dentist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to a therapist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists. Complex vitamin supplements, pharmaceuticals, and physical therapy are often prescribed. If there is a concomitant disease that can cause the tongue to bleed, then treatment must be started.
It is important to adjust your diet. Usually it is recommended to exclude smoked, spicy and salty foods, and give up bad habits. As part of drug therapy, painkillers (Lidocaine, Novocaine), disinfectants (potassium permanganate, soda, furatsilin solution) and normalization of blood supply (Trental, Capoten), and electrophoresis are used.
Modern medicine offers hirudotherapy among the methods of treating cracks in the tongue that cause bleeding. Leeches are placed directly on the tongue and lips, sometimes on the palate. Many years of experience in using this method of therapy have shown excellent results, but not every patient will decide on a specific procedure.
Pharyngeal bleeding
Causes.
Gunshot and non-gunshot wounds of the pharynx, incl. Iatrogenic after adenoidectomy, tonsillectomy, juvenile angiofibromas, angiomas, disintegrating malignant tumors, varicose veins of the palatine arches, the posterior wall of the pharynx, the root of the tongue, disorders of the blood coagulation system.
Symptoms.
Discharge of fresh blood from the oral cavity, sometimes from the nasal cavity. Coughing and vomiting mixed with altered dark blood are possible. The source of bleeding is identified during oropharyngoscopy. Usually, fresh blood is visible flowing down the back wall of the pharynx and soft palate, as well as blood from the tonsil niches, and traces of blood on the tongue.
Complications.
Hemorrhagic shock, posthemorrhagic anemia.
First medical aid.
The patient is placed on his side, cold is applied to the neck area, and hemostatic drugs are prescribed. According to indications, nasopharyngeal tamponade (posterior nasal tamponade) is performed, a bleeding wound in the oropharynx (tonsil niche) is pressed with a gauze swab on a clamp with solutions of hemostatic drugs, and a hemostatic sponge. The victim is urgently evacuated to the otorhinolaryngology department.
Specialized assistance
are provided taking into account the etiological factor, the location of bleeding, the degree of blood loss, the severity of the patient’s condition, and the effectiveness of previous treatment.
To do this, they repeatedly perform adenoidectomy, nasopharyngeal tamponade, ligation of blood vessels, application of a tonsillocompressor, suturing of the tonsil niches with catgut, and influence the bleeding areas with physical factors - an electrocoagulator, cryoapplicator, low-frequency ultrasound, high-energy laser, radio wave.
Stopping bleeding from the throat can be difficult. In some victims, after preliminary tracheostomy, tight pharyngeal tamponade is performed, and in case of threatening bleeding, ligation of the external carotid artery is performed.
For vascular tumors of the pharynx, sclerotherapy and hemostatic therapy are performed. For posthemorrhagic anemia, red blood cells and plasma are administered intravenously.
How to stop bleeding
If the tip of the tongue is bleeding, then in most cases it is enough to hold cold water or ice in the mouth so that the blood vessels narrow and the bleeding stops. Later, the oral cavity should be disinfected. If the blood flows strongly, then in most people it causes panic. If veins are damaged in the deep layers of muscle tissue, you need to act in a collected manner.
First, you should treat your hands with a disinfectant solution, and only then begin to study the extent of damage to the organ. Unwashed hands can introduce many bacteria into an open wound. To prevent the risk of infection, all precautions must be taken. The head must be lowered down over a sink or some kind of container and the oral cavity should be opened slightly so that the blood can flow freely. It cannot be assumed that blood flowed down the larynx into the respiratory organs.
You can stop bleeding by applying pressure to the injury site. To do this, you need to use a sterile cloth, napkin, cotton wool or bandage. You need to hold it until the bleeding stops completely. You can wrap a piece of ice in a cloth and apply it to the damaged area. Usually such measures are enough to stop the bleeding. If severe pain occurs, you can take a general pain reliever. If damaged by acids, the aggressive effect can be neutralized with a moderate alkali solution. After exposure to any chemicals, the mouth should be rinsed with plenty of running water.
In case of complex organ injuries, it is necessary to call an ambulance. Urgent medical attention will definitely be required if the bleeding cannot be stopped within thirty minutes.
Why is there a problem?
Medicine knows about 200 causes of bleeding in the digestive tract. At the first symptoms, you should seek professional help from a doctor and under no circumstances self-medicate, as this will only worsen the condition.
Ulcer
The most common reason. With an ulcer, the integrity of the mucous membrane of the organ is disrupted, and the main difference of the disease is deep tissue damage. The disease is chronic - with remission and exacerbations. On the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus or duodenum, areas of inflammation are formed, in which the protective function (mucus secretion) is reduced. Gradually, the mucosal tissues, including the walls of blood vessels, become thinner, which leads to their rupture.
Phlebeurysm
The problem may occur in the esophagus or stomach due to increased pressure in the portal vein. The most common cause is cirrhosis of the liver. Rupture of a large vessel with varicose veins is extremely dangerous, since at this moment there is a copious outflow of blood. According to statistics, in 40% of cases it stops spontaneously. And the activity of bleeding depends on the degree of liver damage.
Colon diverticulosis
With this disease, the lining of the colon bulges, forming diverticula. The reasons for their formation in medicine are not completely clear; they are mainly associated with increased intraluminal pressure. Basically, the pathology is typical for adult patients over 50 years of age. In the acute course of the disease and rupture of intrawall blood vessels in the area of diverticula, intestinal bleeding occurs.
Tumors and polyps
They occur in the small and large intestines and are benign neoplasms that grow into the intestinal lumen. Most often, bleeding is minor and chronic. The danger lies in possible degeneration into malignant tumors.
Haemorrhoids
This is the formation of venous nodes around the rectum in the anal area. The main causes are thrombosis or tissue inflammation. The disease can be acute or chronic, and its common causes are a sedentary lifestyle, excessive exercise, and obesity. Bleeding (the color may be scarlet or dark) is minor and occurs most often after bowel movements.
More rarely, esophagitis, acute hemorrhagic gastropathy, erosive duodenitis, and Mallory-Weiss syndrome are found as causes of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. In the lower part, bleeding can be caused by tumors, vascular malformations, and various inflammations.