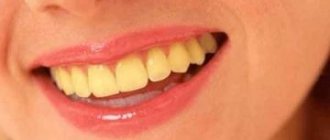
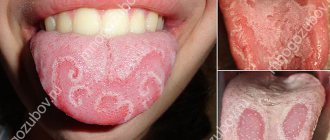
Burning sensation in the mouth and tongue - causes
Local factors:
- Decreased saliva secretion. The mucous membrane becomes dry, lips and tongue crack. Food and liquid irritate the damaged areas, and they sting quite severely.
- Fungal candidiasis. Popularly known as thrush. Fungi, during their rapid proliferation (which happens when the immune system is weakened), provoke a burning sensation in the oral mucosa and painful sensations.
- Hard dental deposits. The formation of tartar is accompanied by the simultaneous delamination of old layers. The separated particles affect the mucous membrane, causing an unpleasant reaction.
- Allergy. A burning sensation in the mouth is nothing new for those with intolerance to certain foods, medications, and even denture materials.
- Leukoplakia. Excessive keratinization on any part of the epithelium usually does not provoke tingling sensations, but this disease cannot be excluded from the list of possible persons involved.
- Diseases of the tongue. Desquamative glossitis, or “hairy” tongue, is a common cause of persistent burning sensation in the mouth. The papillae become very sensitive.
- Herpetic infection. The blisters, which quickly transform into erosions, cause severe itching and unbearable burning both in the normal state and when eating.
- Grinding of teeth. Unconscious movements of the teeth during sleep, called bruxism, automatically affects the tongue with the appearance of microtraumas on it, and, accordingly, a burning sensation.
- Lichen planus. Erosive damage to the mucous membrane, white ulcers haunt the patient during an exacerbation, causing severe discomfort.
General factors:
- Unbalanced diet
- Blood diseases
- Hormonal disbalance
- Stomach pathologies
- Nervous disorders
- Avitaminosis
- Insulin-dependent diabetes
- Bulimia
In these conditions, a burning taste in the mouth may appear and disappear, as it is a concomitant symptom.
The tip of the tongue stings: treatment
People often go to the dentist with the complaint that the tip of the tongue is red and stings. Treatment for these symptoms cannot be started immediately, as the doctor must first find out the cause of their occurrence. Infectious lesions of the oral cavity require antibacterial or antifungal therapy. For this purpose, Amoxicillin and Nystatin tablets are used. For herpes, the drug Zovirax or the drug Acyclovir is prescribed. If the cause of the disease is incorrectly selected prostheses, they must be replaced. For stomatitis, the oral cavity is treated with a solution of baking soda.
How does burning in the mouth and tongue manifest?
The symptom is clearly noticeable, may occur sporadically and disappear on its own. This happens when taking bitter medicines or eating spicy foods (“fire” in the mouth). A slight irritation of the mucous membrane may bother you after dental procedures; this is quite normal.
True diseases can be assumed if:
- Dryness and burning in the mouth often appear in certain areas of the oral cavity
- Unpleasant sensations intensify and are accompanied by numbness
- The tingling becomes constant
In most patients, the burning sensation manifests itself in the morning, intensifies during the daytime and subsides towards night.
Tingling tongue - what is it?
The complaint that the tip of the tongue stings is common. This problem is mainly faced by dentists who must treat pathologies of the oral cavity. However, this symptom does not always refer to diseases that require the help of a dentist. First of all, you need to figure out why the tip of your tongue stings. To begin with, it is important to clarify how often unpleasant sensations occur. Tongue tingling can be temporary or permanent. In the first case, they occur rarely - usually after eating some food. Moreover, this symptom is not a pathology, but only indicates that the papillae located on the surface of the organ react to the stimulus. It's a completely different matter when the tip of your tongue constantly stings. The reasons for this may lie in various diseases. Therefore, before contacting a doctor, you need to pay attention to the frequency of the unpleasant tingling sensation and determine after what it appears.
Diagnostics
How to find out what exactly caused the burning sensation in the mouth and tongue? Only a specialist can determine the reasons. First you need to visit the dentist. If there are no visible local causes that could cause this problem, you need to go to a therapist. The patient will be prescribed tests (urine, blood - general analysis and sugar, biochemical studies). It is necessary to exclude sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS. It would be useful to consult an endocrinologist - perhaps it is due to hormonal fluctuations. Based on complete information, a preliminary diagnosis can already be made. Get ready for the fact that at the same time you will have to visit a gynecologist, nutritionist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist and doctors of other specialties.
Diagnosis of pinching the tip of the tongue
To find out the cause of tongue tingling, a thorough examination of the oral cavity is necessary. If there are rashes on the organ of taste or gums, it is necessary to take a smear for genital infections. If the patient has dentures, an allergy test should be performed. If oral diseases are excluded, the patient should be referred to a general practitioner for further examination.
Burning mouth - treatment
The main goal is to eliminate the root cause found at the diagnostic stage. If it is not associated with dental pathology, the oral cavity is sanitized, worn fillings are removed and new fillings are placed, and dentures are corrected. Stomatitis and glossitis often require antibiotics. Candidiasis is treated with antifungal drugs.
General diseases are treated by a doctor of appropriate specialization, prescribing complex treatment depending on the type of pathology. Measures are being taken to improve immunity, normalize stomach function, stabilize blood glucose levels, and treat neuroses.
At home, you can alleviate the condition by rinsing your mouth with warm infusions of oak bark, sage, and chamomile. 1 tbsp is enough. per standard glass of water. Brew like tea, let cool and rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day. To prevent a burning sensation in the mouth, avoid or at least minimize spicy foods and caustic ingredients in your diet; it is better to avoid alcohol altogether.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures against a “burning” tongue include the following:
- Proper dental and oral hygiene.
- Clean your tongue daily with a special cleaner (but not with a brush!).
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Avoiding allergens, in particular food ones.
- Controlling blood sugar levels.
- Timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Compliance with the principles of balanced nutrition.
- Regular preventive examinations with a dentist (at least 2 times a year).
Appearance in children
Children often face this problem. The appearance of similar symptoms in a child almost always indicates the development of candidiasis. Here it is necessary to conduct a careful visual examination of the oral mucosa for the presence of a dense white coating with a cheesy consistency - this is the very first sign of the pathology in question. If your baby is still very young and cannot tell you about the symptoms that are troubling him, pay attention to whether he is constantly sticking out his tongue. This is how little children usually make it clear that they feel discomfort in the organ.
Stomatitis is common in infants
A common accompanying symptom is burning, and this is a good reason for parents to worry. Here you need to monitor the child’s psycho-emotional state, make sure that he does not experience any serious worries or stress. If you suspect that the cause of the itching lies precisely in the psychological state of the baby, it makes sense to show him to a neurologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe a course of sedatives. A childhood disease such as scarlet fever can also provoke itching in the tongue and even in the throat. In any case, if suspicious signs of pathology appear, the child should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible.
Features of treatment
Treatment of burning tongue is aimed at eliminating the cause and relieving symptoms. If you have tartar, it is recommended to have your teeth cleaned. If the prostheses are at fault, contact a specialist and replace/correct the design. In case of gastrointestinal diseases, treatment of the identified pathology should be carried out in parallel.
- Rinsing with antiseptics, for example, with “Furacilin”, using “Miramistin” in the form of a spray, will help remove a slight tingling sensation,
- in case of mucosal injury, Lugol's solution can be used,
- the application of “Lidocaine”, “Novocaine” or other anesthetics can relieve pain,
- in case of a neurotic nature, the doctor will prescribe appropriate medications (tincture of valerian, motherwort or more effective sedatives).
In some cases, Miramistin in the form of a spray will help.
In each case, treatment is prescribed only by a doctor, based on diagnostic data.
Aphthous stomatitis
Why does my baby's tongue hurt? The cause may be aphthous stomatitis. Indeed, with this pathology, painful ulcers form on the tongue, as well as on the inside of the lips and cheeks. They are represented by a yellowish-white center, which is surrounded by an inflamed red stripe.
Pediatricians cannot pinpoint exactly what is the cause of this disease. As a rule, pathology develops due to such provoking factors as:
- allergies (drug, microbial and food);
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system;
- chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- staphylococcal infection.
The main symptoms of aphthous stomatitis are:
- burning and itching on the mucous membrane;
- temperature increase;
- child's refusal to eat;
- the formation of a cloudy film on the surface of the ulcers.
Causes other than dental
A burning tongue can be caused by factors unrelated to dentistry:
- Glossitis and stomatitis are quite often diagnosed in patients with HIV infection
psychological disorders;
- heartburn;
- drug therapy;
- hormonal imbalance;
- endocrine diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- blood diseases;
- previous radiation and chemotherapy;
- unbalanced diet.
Glossitis and stomatitis are quite often diagnosed in patients with HIV infection, diabetes mellitus, and hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland.
Disruption of the normal microflora of the oral cavity occurs in chronic diseases of the digestive tract.
Herpetic infection
If a child’s tongue hurts, the causes of this condition may lie in the occurrence of painful ulcers. They entail uncomfortable sensations. The main cause of the disease is the herpes virus, which begins to multiply when the immune system reacts to foreign organisms.
The pathology manifests itself sharply. The child's tongue begins to hurt and the temperature rises. The baby becomes excessively sleepy, and when examining the oral mucosa, multiple blisters and ulcers are noticeable. Most often, the tip of the child’s tongue hurts. The baby's saliva becomes more viscous.
In addition to the tongue, rashes affect the surface of the cheeks, lips, and sometimes also appear at the entrance to the pharynx. These bubbles are watery and very small. They are grouped on the reddened mucosa. Over a short period of time, the bubbles open. The affected areas are covered with a yellowish-gray film. After it peels off, painful ulcers appear.
Vitamin deficiency and allergies
Such conditions also cause pain in the tongue. Vitamin deficiency most often occurs in the spring, when the child’s body is especially weakened. The cause of its manifestation is considered to be a severe lack of vitamins of one group or another. If a child has pain in the tip of the tongue or other parts of it, and red and white pimples appear on them, then this may well be a manifestation of vitamin deficiency. In addition to inflammation of the organ of speech, this pathology manifests itself in the formation of small cracks on the lips, peeling of the skin in the corners of the mouth, conjunctivitis, and the appearance of dandruff. If there is a lack of vitamin P in the body, in addition to blisters and pimples on the tongue, the child is bothered by loose stools. A lack of ascorbic acid is reflected in the appearance of white formations, bleeding gums, swelling, and the presence of hemorrhages on the skin.
If for this reason the child’s tongue tip hurts, what should parents do? Getting rid of a child from this condition is carried out by replenishing the lack of vitamins. This will eliminate the symptoms of the emerging pathology.
Often a child’s tongue hurts due to allergic stomatitis. It can be caused by citrus and red vegetables (carrots, beets and tomatoes), cocoa, chocolate, exotic fruits (papaya, passion fruit, mango), as well as strawberries and raspberries. When a food allergy occurs, red blisters and spots appear on the tongue, as well as on the oral mucosa. White pimples are observed at the tip of the speech organ. To eliminate discomfort and pain, you will need to remove allergenic foods from the child’s diet.
Diagnostic measures
The only correct decision regarding the appearance of the symptoms described above is to contact a knowledgeable specialist. Only a doctor can conduct a competent examination and identify the true cause of the discomfort. Thus, the main diagnostic procedures include:
- general blood analysis,
- taking a swab from the throat.
Tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Having the test results in hand, the doctor can significantly narrow the range of suspected diseases and even immediately make an accurate diagnosis. It is likely that at the stage of identifying the source of the problem, consultation with highly specialized specialists - a dentist, neurologist, gastroenterologist - may be required. Without knowing the exact doctor’s conclusion, you should not make any attempts to solve the problem yourself, otherwise you can only worsen the situation.
Glossitis
This pathology is a lesion of the mucous membrane of the tongue. Most often, glossitis is a consequence of injury, a symptom of other diseases, or the result of the negative effect of pathogens.
The disease can occur in both acute and chronic forms. In the latter case, the phenomena of exacerbations and remissions constantly alternate.
Glossitis in children often goes unnoticed. The child does not complain to his parents about anything. The pathology is discovered accidentally during an examination of the oral cavity. In this regard, pediatricians recommend that parents periodically check the appearance of their child's tongue.
The causes of glossitis are:
- Mechanical injuries. A child may well damage the mucous membrane of the tongue with braces, special plates for correcting the bite, as well as the edges of the teeth or fillings.
- Bad habits. Children love to chew on pens, pencils, or bite their tongues.
- Burns of the oral cavity. They occur when eating too hot food or drinks.
With the desquamative form of glossitis on the tongue of children, parents discover strange spots that change their location and shape. With such glossitis, the child is only sometimes bothered by a feeling of burning and tingling. The causes of this pathology are gastrointestinal diseases, infectious diseases, endocrine disorders, anemia and allergies. The source of this form of glossitis is sometimes helminthic infestation.
One of the manifestations of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue is rhomboid glossitis. In this case, children complain of roughness in the area of the back of the tongue, a burning sensation and pain. The cause of this type of glossitis has not yet been identified. This pathology is considered congenital.
Children sometimes experience catarrhal glossitis, which, as a rule, occurs in an acute form. This disease appears due to a bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the mucous membrane. In this case, the child’s tongue hurts on the side or on the back. Discomfort occurs when talking or eating. The tongue swells and turns red. Teeth imprints can be seen on its side surfaces. On the 2nd or 3rd day after the onset of the pathology, the tongue increases in size and becomes covered with plaque.
Pediatricians often note glossalgia in children. In this condition, the child’s tongue hurts, but no visible changes in this organ are observed. Children are bothered by a burning and tingling sensation that is either constant or occurs periodically. The child may also complain of dry mouth, which goes away after drinking a glass of water. Glossalgia is sometimes caused by diseases of the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, diabetes mellitus, and diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
Symptoms of illnesses
When complaints arise from the baby, parents begin to look for an answer to the question “why does the child’s tongue hurt?” Various obvious and hidden reasons contribute to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Young children experience discomfort in the oral cavity quite often. Unpleasant sensations appear suddenly, immediately affecting the baby’s general well-being. Children experience irritability and lethargy. They refuse to eat.
The way a baby’s tongue hurts can be characterized by three main symptoms. Among them:
- tingling;
- itching;
- burning.
Visually, pain manifests itself in the form of pimples, spots and blisters appearing on the organ of speech. This happens in 99% of all requests.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
Pediatricians do not recommend parents to independently diagnose their baby’s condition. If they have symptoms of the disease, they should consult a doctor. Only he can make the correct diagnosis.
Antiviral drugs taken orally are used to treat herpes stomatitis. Acyclovir is a fairly effective remedy, according to pediatricians. It should be given to the child for a week 4-5 times a day, 200 mg. In particularly severe cases, this drug is prescribed for intravenous drip administration.
Such treatment should be accompanied by local treatment of ulcers. For this purpose, drugs such as Zovirax and Oxolin are used. You can also lubricate the sores with sea buckthorn oil applied to a cotton swab. To reduce the level of intoxication in the body, pediatricians recommend taking immunoglobulins in the form of “Viferon” and “Anaferon”.