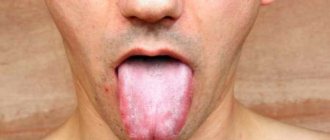
What should a healthy tongue look like?
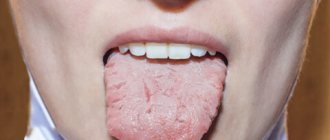
Dentists explain that a healthy tongue is pink in color and evenly covered on top with small seals called taste buds. The appearance of the tongue changes with certain diseases, sometimes very dangerous. If your tongue has become a different color, is swollen and painful, or has permanent plaques or ulcers, contact your dentist or physician to find out what is causing this.
Changing tongue color
A change in the color of the tongue and the appearance of streaks or bumps on it may be a sign of a dental or systemic disease. According to the MSD Manual, a white coating or whitish patches on the tongue can occur due to oral thrush, leukoplakia associated with alcohol or tobacco use, fever, dehydration, and skin conditions such as lichen planus. Another reason for the appearance of a white coating on the tongue is the habit of breathing through the mouth.
The tongue becomes smooth, red and sometimes swollen due to anemia and vitamin B3 deficiency. The tongue acquires a characteristic strawberry color during scarlet fever and in young children with such a serious illness as Kawasaki disease. If you suspect scarlet fever and Kawasaki syndrome, you should immediately seek medical help. In case of anemia, the tongue may not become red, but, on the contrary, pale.
Experts note that the tongue can also take on a “hairy” appearance and turn brown, greenish or even black. In most cases, this does not pose a threat to health: such a change in the color of the tongue is often associated with the accumulation of dead skin cells on the taste buds. According to the MSD Manual, a black tongue can also be caused by taking medications that contain bismuth.
Coated tongue
Light white
Such tongue indicates problems with the liver or gastrointestinal tract. Since it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis based on this symptom alone (it could be either low acidity or a stomach ulcer), it is better to consult a doctor.
Thick layer of white plaque
If your tongue is covered with a thick layer of white coating, this is not a good sign that some systems in the body cannot fully perform their physiological functions in maintaining health. It may also indicate the presence of a viral infection.
Yellow
This type of plaque indicates liver or gallbladder disease. It can also be a sign of stagnation of food in the body and poor digestion.
Unevenly colored, grooved tongue
“Geographical” tongue is a sure sign of gastrointestinal diseases. If the grooves are so deep that they look like cracks, this indicates increased blood sugar. A doctor will help you establish an accurate diagnosis.
How to keep your tongue healthy
The tongue, like teeth, is visible to others, and if it looks unhealthy, you may feel self-conscious. If your dentist or therapist has already determined that the discoloration of your tongue is not due to disease, you can improve its appearance by gently brushing your tongue twice daily during your normal oral hygiene routine. Use a toothbrush with a special scraper or pad to clean your tongue and cheeks.
Also, get into the habit of sticking out your tongue and examining it after brushing your teeth, this will allow you to immediately notice changes in its color or detect other problems. However, you need to understand that a healthy tongue color does not guarantee good dental health. Remember to visit your dentist regularly to check the health of your teeth, gums, and overall mouth.
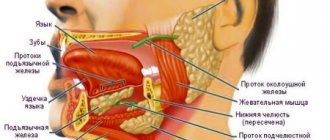
Language: its structure with photos
The description of what the tongue consists of includes the following information. The human tongue does not contain bones and consists of muscle tissue, which is covered with a mucous membrane. It makes movements using striated muscles. In this case, in order to fix the position of the tongue, protrude it and return it to the oral cavity, skeletal muscles are used (see also: what functions do the muscles of the floor of the mouth perform?). Raising, thickening and shortening of the organ becomes possible thanks to its own muscles.
From an anatomical point of view, the circuitry of the nervous apparatus is finely structured. The innervation scheme involves 5 out of 12 cranial nerves. The structure of the tongue can be seen in the photo accompanying the article. There are several main parts of the tongue (the photograph shows where they are located) - the root, the body, the groove and the frenulum. The parts of the language are:
READ ALSO: cut tongue in a person: symptoms with photos and treatment
- The body is part of the tongue, which consists of muscles characterized by mobility and rounded ends, the anterior 2/3, a vertical line divides the body in the middle.
- The root accounts for 1/3 of the length and has minimal mobility.
- The bridle is located below. Needed to connect the lower fascia with the floor of the mouth.
- Furrow - if you look at the diagram of the tongue, you can see a kind of demarcation between the body and the root (we recommend reading: what to do if grooves form on the tongue?).
The dorsum of the tongue is its upper surface. The lower part of the tongue is called the fascia. It is indicated on the tongue diagram. The submucosal layer is absent. For this reason, the organ does not form folds. If you examine its structure under a microscope, you can see that the body is covered with papillae, which are divided into 4 types.
Stages of tongue cancer
There are several stages of the disease, each of which has its own distinctive features.
Initial stage of tongue cancer (first)
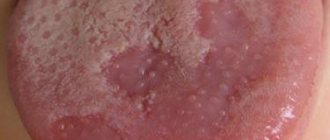
Photo: this is what the initial stage of tongue cancer looks like
It is characterized by an asymptomatic course - practically nothing bothers patients. It appears as whitish spots on the mucous membrane, the so-called papillary growths. They are often mistaken for plaque, which is located on the lateral surface of the muscular organ.
When examined, doctors often mistake these formations for manifestations of other diseases: glossitis or stomatitis. There is no pain at this stage.
Stage of clinical manifestations (second)
As the disease progresses, the “plaque” gradually turns into a lump on the tongue, which, if left untreated, transforms into a tumor on the tongue. At this stage, a pain syndrome appears; the pain is diffuse or local in nature, very often radiating to nearby organs (neck, temple, ears).
Patients at this stage often complain of bad breath, which is caused by infection and suppuration of the tumor. The clinical picture is accompanied by difficulty swallowing, articulation disorder, swelling and numbness of part of the tongue. Metastasis to surrounding tissues and nearby lymph nodes - submandibular, cervical - is possible.
Advanced degree (third)
It is possible to bring the disease to this stage if you completely ignore the symptoms of the initial and second stages of tongue cancer. It manifests itself as aggressive invasive (penetrating into the thickness of the organ and surrounding tissues) growth, accompanied by tissue decay.
Terminal stage (fourth)
In this phase, distant metastases occur - in the bones, liver, lungs. Treatment of advanced tongue cancer is not very successful and the prognosis is very doubtful. Patients who progress the disease to the terminal stage rarely live more than a year.
Treatment is only palliative - the fight against pain and cancer intoxication.
Prevention methods, prognosis of tongue cancer
You can reduce the likelihood of developing the disease by giving up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol and chewing tobacco. If there is dental pathology that contributes to chronic injury to the mucous membrane, the oral cavity is sanitized: dentures are reinstalled, fillings are treated, and the bite is corrected.
Maintaining basic oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer. In terms of prognosis, regular preventive examination by a dentist is important, during which the first signs of cancer can be noticed, which allows a person to be referred to an oncologist in a timely manner.
With radical combined treatment of tongue cancer in the early stages, the five-year survival rate approaches 90%; in advanced cases it drops to 60%. If treatment is started at the metastatic stage, the five-year survival rate is less than 35%, even in Moscow.
Treatment methods for tongue cancer
Regardless of the cause of tongue cancer, combination therapy is used to treat it, including the following methods:
- Surgery. The operation is aimed at radical removal of a malignant tumor: either partial resection (excision) of the tongue or its complete removal (glossectomy) is performed. In advanced cases, when the tumor has grown into the surrounding tissues, they are resected down to the bones of the lower jaw.
- Radiation therapy. There are remote therapy, when the tumor is irradiated at a distance with X-rays, and contact therapy (brachytherapy), when the radiation source (radioactive isotopes) is placed deep within the organ. Radiotherapy is performed both before and after surgery. The doctor determines how many sessions are needed.
- Polychemotherapy. It is used in advanced cases in the presence of distant metastases, when other methods cannot be used, or their effect is insufficient. Patients are treated with Cisplatin, Methotrexate and other drugs.
Surgeries in the later stages of the disease are often mutilating in nature - in some cases it is necessary to remove almost the entire lower jaw. After surgery, patients live with some restrictions. In order to create a satisfactory quality of life, they undergo reconstructive medical operations.
All the colors of the rainbow in your mouth
Everyone knows that by the color of the tongue one can easily determine that something is wrong with the body, since some diseases are “reflected” on it by the characteristic color of the plaque. The most common of them:
- measles or flu, high fever - burgundy coating;
- lack of nutrition, anemia, heart failure - pale tongue;
- diseases of the blood or respiratory tract - purple plaque;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract, smoking, jaundice - yellow or gray plaque;
- diseases of the liver, spleen, dysentery, abscesses, advanced viral diseases - black plaque;
- kidney disease - blue plaque;
- blood circulation disorders, heavy metal poisoning, scurvy - blue plaque;
- dehydration, fungal infection - white tongue;
- diseases of the oral cavity - dark brown plaque.
That is why it is important to pay attention to details, as they can tell more about health than the person himself.
Is it worth diagnosing by tongue?
Doctors have been studying the question of what diseases can be identified by language for several hundred years. The results of research by ancient and modern scientists show that this connection exists, but it must be properly understood and assessed. If a healthy person has irregularities or the color of the plaque has changed, this phenomenon may be the very first symptom of a disease that will manifest itself in the future with other abnormalities.
There is an assumption that the imprints of the disease appear on this organ several days before its clinical signs, but you should not use diagnosis by a person’s tongue for further self-medication. This is a whole science, and only a good specialist can understand it. Treatment can begin only after a full examination and establishment of a correct diagnosis.