Treatment
How to treat pemphigus in a child? The main drugs today are hormones from the group of glucosteroids. In this case, systemic therapy is carried out without age restrictions.
Treatment of pemphigus has several main directions:
- preventing the appearance of new blisters and erosions;
- healing of affected areas of the skin.
Glucosteroids are administered in increased dosages. Due to this technique, the intensity of the formation of new foci decreases and the restoration process begins in existing erosions. This process takes about 2 weeks. Subsequently, the patient is transferred to maintenance hormonal therapy. The drug does not change, but the dosage is significantly reduced.
Viral pemphigus in children treatment is aimed at suppressing the virus. Pemphigus vulgaris requires the administration of a larger volume of drugs than foliaceus. The transition to maintenance therapy is carried out gradually. Moreover, the vast majority of patients are forced to take daily injections of maintenance doses of glucosteroid drugs throughout their lives.
Children should take hormonal medications simultaneously with calcium and vitamin D. The effectiveness of treatment increases due to the use of immunosuppressive drugs from the first days of treatment. These drugs have a depressing effect on the activity of the body's immune system.
Early stages of treatment often involve the use of procedures aimed at clearing the blood of aggressive antibodies. Such procedures include hemodialysis and plasmapheresis. The skin must be treated with antiseptics and special ointments to reduce the risk of infection.
Treatment of pathology is daily and lifelong. Sometimes there may be breaks between relapses of the disease.
Baby care
The diagnosis of pemphigus requires special, attentive and daily care for the child. The organization of a baby’s life directly affects his life expectancy. The initial stage of treatment takes place within the walls of the hospital. After discharge, the child should receive all necessary medications in the prescribed volume and time of administration. Parents must learn how to give injections, because the daily services of a hired nurse will negatively affect the family budget.
Every day your child needs to treat blisters and eczema on the skin. Processing is carried out using aniline dyes. This group of agents has the widest spectrum of action on various microbes, including staphylococcus. Erosion and crusts formed are treated with corticosteroid-based ointments.
The presence of infectious signs in the form of pus, inflammation, swelling means the start of using antibiotic ointments. Large affected areas require the use of sterile dressings to help avoid further injury. Dressings are changed at least 2 times a day. For small affected areas, the relevance of bandages is associated with the child’s high motor activity.
The appearance of pain requires taking painkillers and consulting a specialist. The presence of damaged areas in the oral cavity is associated with mandatory rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic agents. A useful and effective means of care is taking baths with antiseptic agents. It is mandatory to take vitamin and mineral complexes consisting of vitamin E, calcium, magnesium and folic acid.
The diet also requires enrichment with vitamins and minerals. Meals are provided on a fractional and frequent basis, at least 6 times a day. This diet plan is especially important when the esophagus and mucous membranes in the mouth are affected. Diet therapy is based on the complete exclusion of salt and increasing the amount of protein. Registration at a dispensary and systematic visits to a dermatologist are required - at least twice a year and urgently in case of relapse. The use of immunosuppressive therapy imposes restrictions on vaccinations.
Causes of occurrence and development
The pathology begins its development after the development of autoimmune antibodies aggressive to desmoglein proteins. These proteins act as an adhesive base used to connect skin cells. In the process of protein destruction, the skin is destroyed. At this point, bacteria from the environment begin to penetrate the skin layers, causing the formation of blisters.
The factors that trigger the pathological process still remain unclear. Some of them are established by science:
- genetic predisposition to autoimmune processes;
- malfunctions of the central nervous system;
- the presence of viruses, infections or other pathogens in the body - a connection has been identified between infection with endogenous bacteria and the appearance of an autoimmune reaction.
Russian official medicine identifies the following reasons causing an inadequate immune response:
- taking medications of the thiol group - strong antibiotics, immunomodulators and others;
- burns;
- herpes virus types 1, 2 and 8;
- tactile contact with pesticides;
- severe stress or nervous overload.
It is almost impossible to establish the true cause of the disease. In fact, in laboratory conditions only the presence of aggressive antibodies is determined.
Symptoms and signs
The early stages of the disease have virtually no dangerous signs. The child’s health remains normal, and skin changes have not yet appeared. The condition worsens as the area of the affected skin gradually increases.
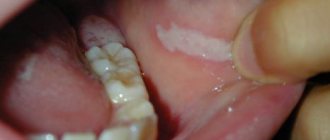
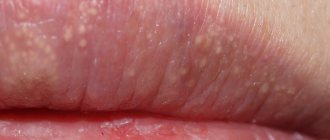
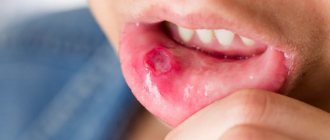
The bubbles themselves have a number of distinctive features - lethargy, easy to open, sagging skin under the liquid inside the bubble. Primary rashes are always localized in the mouth and mucous membranes of the lips. There are no painful sensations. Opened blisters form skin crusts or wet eczema, which take a long time to heal.
Gradually the affected area increases. Infection with bacteria leads to the appearance of suppuration and foci of inflammation, in place of which eczema and large erosions subsequently appear. Another distinctive feature is the lack of healing of the skin at the site of the blister rupture. Gradually, the erosions expand and unite into a single lesion.
All forms of pemphigus have a wave-like manifestation of symptoms. In the absence of a timely response, intoxication syndrome begins - nausea and headaches. Ultimately, the death of the little patient inevitably occurs. Viral pemphigus in children has symptoms similar to the true disease, and there is a pronounced viral infection.
When to see a doctor
Baby rash appears frequently and rarely poses a real threat to the child's life. Basically it becomes a reactive feature to allergens and infections. It is important for parents to know which rashes pose a mortal danger to the child. If signs of such a rash appear, you should seek help from a dermatologist.
The pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) has been guarding children's health for many years. You can make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist by phone. The clinic has a convenient location, a two-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station, as well as the possibility of placement in a hospital for examination and treatment.
Prevention and prognosis
Medicine has not proposed any specific measures to prevent pemphigus due to the fact that the true causes of its occurrence have not been established. A set of preventive measures is aimed at strengthening the health of a little person:
- formation of strong immunity;
- hardening and walking in the fresh air from the moment of birth;
- proper nutrition;
- avoidance of excessive use of drugs and medications.
Forecasts depend on the speed of contacting a doctor - for symptoms of pemphigus in children, treatment should begin as early as possible. Therefore, you should not self-medicate under any circumstances. In order not to miss the appearance of signs of pathology, it is necessary to examine any skin problems with a dermatologist.
The prognosis of true pemphigus is a priori conditionally unfavorable. Even with adequate and timely treatment, the likelihood of death cannot be eliminated. Any form of pathology is considered chronic.
At the same time, the introduction of hormonal drugs into therapy made it possible to reduce the mortality rate from 65% to 7%. The disease requires constant maintenance therapy. Otherwise, 91% of cases experience acute exacerbations and sudden progression, and consequently an increase in the likelihood of death.