Why does my tongue sting?
Physiological reasons
In healthy people, a short-term tingling of the tongue is observed after eating certain foods: tomatoes, onions, garlic, herbs, spices, hot seasonings, pickles, marinades.
Often provoked by berries, sour fruits (lemon, kiwi, pineapple). Drinks that can cause the development of symptoms include kefir, some juices, strong tea, coffee, alcohol, primarily wine. Sometimes hot drinks or food cause superficial burns of the mucous membrane. In this case, the tingling is intense, complemented by tingling and burning. The sensation is also typical for heavy smokers and is associated with constant irritation of the tongue from tobacco smoke. Sometimes the disorder occurs while taking antidepressants, antibiotics, antiemetics, sedatives and hormonal drugs.
Glossalgia
It is a functional disorder, often develops against the background of gastrointestinal diseases, endocrine and neurological pathologies. Pinching, burning and rawness of the tongue during glossalgia can be periodic or constant, causing rapid fatigue when speaking, and is accompanied by dry mouth. Mostly it occurs in the area of the tip and side surfaces. The symptom intensifies against the background of excitement, disappears or weakens when eating. External changes, as a rule, are absent.
Glossodynia
Along with tingling and tingling, patients may complain of a hairy sensation or “crawling sensation.” The symptom is more pronounced in the tip area and can spread throughout the entire tongue. The root rarely suffers. Characteristic is the spread of the affected area and an increase in the duration of discomfort as glossodynia progresses. Manifestations increase in the evening, sometimes bother you all night, and disappear during meals. The disorder is observed in the following diseases:
- Lesions of the digestive system:
gastritis, gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis. - Endocrine pathologies:
diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction. - Cardiovascular problems:
hypertension, atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease. - Neurological dysfunction:
vegetative-vascular dystonia, functional disorders due to stress, neuroses, psycho-emotional exhaustion.
Tongue tingling
Desquamative glossitis
In most cases, the pathology is asymptomatic, however, some patients complain of changes in taste sensations, tingling, and pinching of the tongue. Diction problems are possible. Upon examination, multiple whitish areas are revealed, which, after peeling off the epidermis, turn into red spots. Desquamative glossitis can accompany the following conditions:
- Gastroenterological problems:
gastritis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis, hepatitis. - Autoimmune diseases:
rheumatism, systemic scleroderma, SLE. - Chronic dermatoses:
psoriasis, exudative diathesis. - Hypovitaminosis:
deficiency of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B12.
Sometimes it develops during pregnancy and worries patients with pathologies of the hematopoietic system and autonomic disorders. Some patients have a hereditary predisposition.
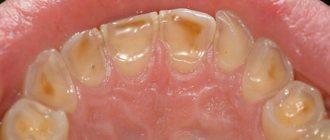
Dental diseases
A common cause of tingling, pain and burning are dental diseases: caries, tartar deposits. The symptom occurs when the edge of the tongue is damaged by a tooth fragment, prosthesis or crown; the damage is local in nature. Sometimes the cause of development is an individual reaction to the prosthetic material. In such cases, itching, irritation and redness of the mucous membranes are observed.
Xerostomia
Due to an insufficient amount of saliva, the tongue dries out, and a feeling of tingling, tightness, and tingling occurs. The disorder is aggravated by eating hard, dry foods or talking for a long time. Over time, the changes progress, and the discomfort becomes permanent. To reduce the severity of symptoms, patients often drink water or rinse their mouth. Taste sensations are reduced or distorted. Xerostomia can be diagnosed in the following cases:
- Endocrine pathologies:
hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus. - Diseases of the salivary glands:
tumors, mumps, calculi. - Dehydration:
fever, increased sweating, repeated vomiting or diarrhea. - Infectious diseases:
HIV, some other viral infections. - Other reasons:
condition after radiation therapy, frequent or prolonged stress.
Oral candidiasis
Pinching, discomfort, tingling are detected in the chronic form of the disease. Acute candidiasis is often manifested by pain and burning. The unpleasant sensations are widespread, covering the tongue and oral mucosa. The affected areas are covered with a dense gray coating, which, when removed, reveals a bright red inflamed epithelium. With hyperplastic candidiasis, the mucous membranes become painful and rough. Atrophic candidiasis is localized, the lesions are located next to the dentures and are areas of erythema with clear boundaries.
Allergic reactions
The most common etiological factor for tingling is food allergy. The symptom can also be observed in a reaction to pollen, house dust, animal dander and other allergens. Severe itching predominates, which forces the patient to “scratch” the affected area with his teeth, may be supplemented by tingling of the tongue, and is accompanied by sneezing and lacrimation.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of tongue swelling are its increase in size and swelling. In difficult cases, the patient has difficulty breathing, and there is a sensation of a foreign object in the mouth. The mucous membrane becomes loose, with prominent papillae, and tooth marks become noticeable on the lateral surfaces. Blood vessels become clearly visible on the lower part of the tongue.
Swelling is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Change in taste sensations.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane.
- The appearance of heaviness when swallowing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swelling of lips.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
- Paleness of the skin.
If the problem is not detected in a timely manner, the tongue continues to swell, does not fit in the oral cavity, and falls out. The help of a doctor cannot be neglected. If the tongue is swollen and this process persists for several days, it is dangerous to self-medicate or wait until the problem goes away on its own.
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of tongue tingling is the responsibility of a dentist. If the presence of provoking diseases is suspected, patients are referred to therapists, gastroenterologists, neurologists, and other specialists. The survey program includes activities such as:
- Dental examination.
Depending on the etiology of the symptom, tartar, poorly fitting dentures, carious teeth, dry mucous membranes, focal or diffuse changes in the tongue, cheeks and gums may be detected. Additionally, the acidity of saliva is determined and the potential difference is measured. - Neurological examination.
Informative for glossodynia. The results reveal the absence of curtain and pharyngeal reflexes, rhythmic trembling of the tongue. The submandibular and upper cervical vegetative nodes are painful when touched. According to electromyography, the prevalence and duration of paresthesia is determined. - Examination of the salivary glands.
Recommended to clarify the causes of xerostomia. Based on the results of ultrasound of the salivary glands, congenital anomalies, cysts, tumors, stones, and inflammatory processes are detected. During sialography using a contrast agent, neoplasms and signs of inflammation are detected. - Lab tests.
A general and biochemical blood test is performed to exclude B12-deficiency anemia and hypovitaminosis. If candidiasis is suspected, microscopy of the scraping is indicated. Identification of pseudomycelium is a reason for conducting a microbiological study. - Other techniques.
For secondary diseases that cause tongue tingling, fibrogastroscopy, colonoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, electrocardiography, echocardiography, and tests for specific markers to determine autoimmune pathologies may be prescribed.
Oral examination
Dangerous symptoms
Typically, cracks in the tongue do not cause any discomfort; their appearance is often discovered at a doctor’s appointment. But this is not always the case. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms may appear that indicate health problems:
- pain;
- burning, change in taste;
- itching or swelling;
- pain when chewing, problems with speech;
- temperature increase.
If cracks appear on the tongue, there are several of the listed symptoms, then perhaps the cause is an inflammatory process in the oral cavity - glossitis. If the tongue becomes covered with cracks and ulcers, the cause is ENT diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis). In any case, professional treatment is necessary.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Patients are advised to stop smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking foods that cause tongue tingling. Food should be steamed, stewed or boiled. Food should be soft, not traumatic to the tongue and oral mucosa. You can reduce the severity of the symptom by regularly rinsing with clean water. It is not recommended to use elixirs and other liquids that irritate mucous membranes.
Conservative therapy
At the initial stage, professional hygiene is carried out and the oral cavity is sanitized. If crowns or dentures are the cause of your symptoms, they may need to be replaced. When pinching another etiology, the following measures are taken:
- Glossalgia.
Psychological factors play a significant role in this disease, so patients are recommended to undergo a course of psychotherapy or hypnosis sessions. Light tranquilizers, sedatives of plant origin, and iron supplements are effective. To eliminate discomfort, oral baths with anesthetics are prescribed. It is possible to carry out therapeutic blockades and reflexology. - Glossodynia.
Local treatment does not bring the desired result; therapy for the causative disease, a special diet, and pathogenetic measures are necessary to normalize the functioning of the vagosympathetic part of the nervous system. The list of medications includes B vitamins, antispasmodics, and antihypertensives. To reduce the severity of paresthesia, neuroleptics and sedatives are prescribed, and blockades are performed. - Xerostomia.
The effectiveness of treatment largely depends on the cause of the pathology. Dry mucous membranes caused by medications, diseases of the teeth and salivary glands can be easily eliminated after treatment of the underlying disease. As part of symptomatic treatment, the mucous membrane is lubricated with various solutions, blockades are performed, vibration massage, electrophoresis, and galvanotherapy are performed. - Candidiasis.
If possible, discontinue corticosteroids and hormonal drugs. Antimycotic agents, alkaline applications and rinses are used locally. The oral cavity is first treated with antiseptics, and subsequently with keratoplasty preparations. General antimycotics, antihistamines, laser therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, and electrophoresis are prescribed.