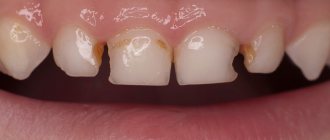
Any problems with the baby's health cause concern among parents. But, when it comes to baby teeth, many do not attach importance to their defects and diseases. Experts strongly recommend promptly consulting a doctor at the first unwanted symptoms, since advanced cases threaten the development of serious complications. Pathological processes in the milk range can negatively affect the buds. If a tooth has darkened, be sure to show your child to the dentist - this is not only an aesthetic problem.
It is not always possible to restore the previous whiteness of a tooth. But in most cases, after several visits to the doctor and teaching the child to take proper oral care, the smile returns to its former attractiveness.
Bruise is the most common cause of tooth defects and discoloration.
More often, darkening of the tooth is observed after an impact. Young children are active and explore the world through play. Often their excessive activity leads to falls and, consequently, bruises. The greatest number of visits to the doctor with this problem occurs between the ages of 1–3 years. A child’s tooth can become damaged even after it has been replaced, since children reach their peak physical activity at 8–9 years of age. In addition to an accidental fall, other possible causes of tooth injury:
- An accident in which there was a blow to the jaw;
- bad habits, such as biting nails or the tip of a pen;
- playing sports;
- leisure;
- hitting a utensil - glass, spoon, etc.;
- biting into super hard food.
The structure of the primary occlusion is similar to the permanent one. Not everyone realizes that the first teeth also have roots, thanks to which they receive calcium and other necessary microelements from the periodontium. The pulp and network of nerve plexuses are responsible for the sensitivity and healthy condition of the tooth. This fragile system can be damaged by a strong impact.
Mechanical impact with a hard object on a tooth provokes damage to periodontal tissues. If the integrity of the neurovascular bundle is disrupted, hemorrhage may occur in the dentinal tubules and pulp tissue, which manifests itself in the form of staining or darkening of the tooth. Enamel also becomes dull due to a lack of nutrients supplied through damaged fibers and tissues.
Prevention
To prevent dental injuries, you must:
- Observe safety precautions at work, arrange the workplace and carry out potentially hazardous work in accordance with established rules.
- Properly equip playrooms for children and supervise children while playing.
- Follow traffic rules and use seat belts when traveling, as even minor emergency braking of the car carries a high risk of injury.
- Avoid conflict situations that lead to fights.
- Ensure the safety of sports games using special equipment (helmets, masks, dental guards).
- Carefully select sports grounds: they must comply with safety requirements.
Why else can a tooth darken?
Other possible causes of the defect:
- caries;
- improper diet – predominance of carbohydrate foods;
- lack of calcium in enamel;
- incorrect treatment;
- violation of microflora in the oral cavity;
- taking certain medications;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- Excessive ingestion of fluoride into the body during the formation of dental tissues - stains appear, merging into large darkened areas.
Parents may notice that the entire row of teeth near the gum line has darkened. This should raise suspicion of Priestley's plaque. This bacterial film appears during dysbacteriosis. If it stains, it becomes even darker.
Even if parents do not understand why their child’s tooth has darkened, it is important to visit a doctor on the first day after symptoms are detected. You especially shouldn’t put off a visit to the dentist’s office if you have a bruise.
Why do a one-year-old child's teeth turn black?
Many children aged 1-1.5 years are diagnosed with so-called “bottle caries” or “night caries”, which develops against the background of a lack of calcium and weakness of the enamel. The disease occurs due to night feeding of the baby from a bottle and lack of oral care. Milk formulas and juices for children contain a lot of carbohydrates. By processing them, microorganisms in the child’s mouth release acids that wash away minerals and calcium from the enamel and lead to tooth decay and pigmentation.
To avoid such a devastating effect on the first baby teeth, it is advisable to stop nightly bottle feedings as early as possible and carefully care for the baby’s oral cavity. Instead of a brush, you can use a silicone attachment or a sterile gauze swab soaked in clean water or chamomile solution.
Features of baby teeth
The first teeth of babies have porous, thin enamel, which cannot effectively resist the attack of harmful microorganisms. The pulp cavity is wide. Once bacteria gets inside, they spread quickly. If a child has a weakened immune system, the pathogenic process affects the “neighbors.” Carious lesions are possible even in a one-year-old baby. We are talking about the so-called “bottle” caries, when the baby falls asleep while feeding. The sweet mixture remaining in the mouth creates favorable conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora.
Since caries in children progresses quickly, after some time the dentin is damaged. A carious cavity forms inside. But there is not always a visible stain on top. Blackening of the tooth from the inside may occur. Various factors contribute to the development of caries:
- insufficient hygiene is a common occurrence in children;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition, including excessive consumption of sweets;
- the influence of negative factors during the formation of teeth in the embryo - previous illnesses of the pregnant woman, taking certain medications.
Saliva has antibacterial properties and helps neutralize bacteria. In children this function is not as pronounced as in adults. She is also depressed by non-compliance with hygiene rules and a large amount of sweets in the diet.
Why is this happening?
Sometimes treatment allows you to regain lost whiteness, and sometimes the changes are irreversible, but this process still cannot be ignored. The main thing is to correctly determine the cause.
- Poor or lack of oral hygiene. Plaque of food debris on the surface of the enamel thickens over time and absorbs dyes, which leads to blackening.
- Regular consumption of drinks and foods containing dark food pigments.
- Unhealthy diet, vitamin deficiency and the predominance of sweets in the diet.
- Development of caries. A small dark spot quickly increases in size, and if the carious cavity deepens inward, the internal affected areas turn black.
- Due to trauma, the vascular bundle inside the pulp is sometimes damaged. The hematoma gives the tooth a characteristic dark shade.
- Taking certain drugs, for example antibacterial ones from the tetracycline group, also leads to blackening of the enamel. The medicine accumulates in the tissues - even the first tooth may be black.
- Also, teeth turn black after silvering - applying a solution with silver ions to the caries-affected surface.
Symptoms accompanying tooth darkening
If the cause of the defect is a bruise, then the symptoms will be pronounced. More often, the impact damages the upper or lower front teeth. At the same time, the baby feels pain, which only increases over time. Pain is especially evident when pressing on a sore spot or chewing food. In addition to pain and staining, other symptoms may occur:
- poor tooth mobility;
- swelling of the gums;
- hyperemia;
- deformation of individual areas of the mucosa;
- formation of hematomas;
- increase in temperature (in some cases).
If the blow to the jaw was strong, the ligaments at the site of the injury may be torn, the joint may be damaged, or the alveolar process may be fractured. When trying to open or close the jaw, the child will experience pain.
Symptoms
External signs will also differ depending on the strength of the impact. Externally, a bruise manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- The tooth hurts after a blow. Any mechanical injury leads to pain, but if it is intense and does not go away for a long time, severe injury can be suspected.
- The crown has darkened. This indicates that the blood vessels are damaged and hemorrhage has occurred in the soft tissue.
- Numbness of the face, swelling. These signs indicate severe damage to the nerve endings.
- Mobility of teeth after bruise. They begin to wobble, the gums swell.
Even if your teeth don’t hurt much after the blow, the pain goes away quickly and there are no other external manifestations, you should consult a dentist. It is possible to speak accurately about possible complications only after examination and x-rays.
Consequences of a tooth bruise
Darkening of the dentition provokes psychological discomfort, especially if these are the front teeth. Any injury does not go away without a trace. The tooth can be dislocated, cracked, broken, or sometimes embedded in the gum. Even if at the time of treatment the determination of the vital activity of the pulp gave a positive result, after the end of therapy it can still gradually die. This process is accompanied by damage to nerve endings, which provokes inflammation. More serious complications are also possible:
- cyst formation;
- manifestation of periodontitis;
- stopping root development.
These unpleasant consequences are possible in both baby and permanent teeth. Advanced pathology can even lead to tooth loss.
The rudiment of a permanent tooth often suffers from injury to a baby tooth. His enamel may develop poorly, and the risk of hypoplasia formation increases. The rudiment sometimes even dies.
Treatment
- For mild bruises, treatment consists of resting the tooth for 3-4 weeks by reducing the load during chewing: the menu includes soft and semi-liquid foods, and a blender is used to grind hard foods.
- To ensure rest for baby teeth, temporary bite separation with the help of mouth guards is used; if a permanent tooth is bruised, splinting is performed. The splint allows you to immobilize an injured tooth and redistribute the load during chewing onto healthy teeth.
- If the pulp dies due to an impact, the tooth cavity is opened and the pulp is removed, after which the root canals are filled and a permanent filling is installed. If the crown of a tooth darkens, it can be whitened.
- When a baby tooth is bruised, grinding of the cutting edge of the crown of the antagonist tooth is used to prevent tooth contact and reduce pain. This method is not used for permanent teeth.
- To relieve pain, it is recommended to take an anesthetic tablet (ibuprofen, ketorolac, nimesulide) and apply an anesthetic gel (Dentol, Kamistad) to the gums around the tooth.
- When swelling of the soft tissues of the face accompanies a bruise, cold compresses are applied: a plastic bottle with cold water (not lower than +4°C) is wrapped in a cloth and held on the area of swelling for 15-20 minutes.
- A course of magnetic laser therapy is carried out - a combined effect on injured tissue of a magnetic field and low-intensity laser radiation. The method helps improve healing processes, relieves swelling and inflammation. The course consists of 10 daily procedures lasting 5 minutes.
- UHF therapy is indicated to accelerate tissue regeneration.
How to diagnose
At the diagnostic stage, it is important to determine why the tooth has darkened. The doctor will perform palpation and visual examination. But in order to make an accurate diagnosis, assess the degree of damage or carious lesion, one cannot do without radiography. Based on its results, the doctor determines what to do to eliminate the problem. In some cases, consultation with other specialists, such as a gastroenterologist or endocrinologist, may be necessary.
X-rays can also be used to rule out a fracture of the root or alveolar process due to a bruise. If the periodontal area is damaged, the defect will definitely be visible on the image. After the impact, the dentist should monitor the condition of the pulp for several days. For this purpose, electroodontodiagnostic methods are used. If even initial signs of death are detected, the affected areas will be removed so that an inflammatory process does not develop.
Diagnostics
- Patients with a tooth injury are referred for x-ray diagnostics to exclude a root fracture. To obtain information using targeted radiography, it is sometimes necessary to take several images from different angles, which is undesirable for the patient.
The most accurate information about the condition of the roots is provided by computed tomography - an x-ray examination method that allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the tooth. The examination results are displayed on the computer screen and must be transferred to a CD or USB flash drive.
An X-ray examination of a tooth bruise reveals a slight widening of the periodontal fissure.
- The condition of the pulp after injury is monitored using EDI - electroodontodiagnosis. The method consists in determining the reaction of the nerve endings of the pulp to the influence of electric current. The level of electrical excitability of the pulp depends not only on its condition, but also on the degree of formation of the tooth root.
The examination is carried out 2 or 3 days after the injury, since on the first day the pulpal response may be reduced due to traumatic neuritis. Be sure to perform an electrical test on adjacent healthy teeth to compare sensitivity levels. 3-4 weeks after the injury, EDI is repeated.
- Another method of examination for a tooth bruise is transillumination, the essence of which is to pass a beam of cold light through the tooth and evaluate shadow formation. If there are cracks in the enamel after an impact, they will be clearly visible in the stream of light; The technique also helps to detect pulpitis. In modern clinics, all dental units are equipped with light guides for transillumination examination.
What is the treatment
If the darkening of dental tissues is associated with dental diseases, the doctor will act according to the protocol. It is important to eliminate negative factors and carry out correct treatment. In case of caries, the dentist will remove the damaged tissue and install a filling. If the disease is advanced, endodontic treatment may be necessary, in which pulp removal is performed and the canals are filled. When pigmentation is caused by a general disease of the body, to eliminate it you need to cure the disease itself.
It is worth considering the situation in more detail if the tooth has darkened after an impact. What to do in this case? It all depends on the force of the impact and damage. If the bruise is not severe, most often only medical supervision is required (even up to 2-3 months) without any treatment. The tooth is provided with rest, excluding chewing and pressure on it. You need to remove solid food from your child’s diet for several days. To remove the load from baby teeth, their cutting edge is ground off. This technique is not used for indigenous people.
If the bruise is severe, the first thing you can do is give your child painkillers. The doctor’s actions depend on the clinical picture. If the pulp is damaged, they are gradual:
- tooth opening and pulp removal are carried out;
- the dental cavity is thoroughly disinfected;
- The channels are tightly filled with filling material.
If a permanent tooth has darkened as a result of a bruise, you can whiten it. After the procedure, the enamel will acquire a more or less natural color. To quickly restore oral health after injury, the dentist additionally prescribes physiotherapy and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Complete dislocation requires tooth extraction, after which the child’s condition returns to normal. In some cases, they may try to save the integrity of the dentition. To do this, the tooth is splinted using ligatures, caps, staples and other structures. The last steps are possible if the roots are sufficiently developed. Children aged 2–3 years often have to undergo removal.
Treatment of tooth trauma
After a thorough examination and questioning of complaints, a diagnosis is prescribed. Treatment of dental injuries in children depends on the age and condition of the child. The dentist's actions are aimed at preserving the rudiments of permanent units. Therapy of temporary organs requires rest. Solid foods are excluded from the diet. If the cutting edge protrudes, it is ground off. Wearing a mouthguard is recommended; a release plate may be needed. Sometimes the pulp dies and periodontitis or pulpitis develops, which requires trephination of the dead pulp and filling.
If a child hits his teeth, but the color of the temporary units does not change, the molars will grow correctly. In case of darkening of the crowns, bone resorption is observed. These baby teeth are most often removed. Therapy can last from several days to 1-2 weeks. The treatment period is divided into several stages.
- Initial treatment and diagnosis of pathology.
- Emergency care: the sooner it is provided, the lower the risk of complications.
- Specialized treatment with specific clinical methods.
- Restoration of injured organs and tissues, clinical observation.
For preventive purposes, you need to show your child to the dentist at least once every 3 months for 12 months. If your baby complains, you need to visit the doctor more often.
Causes
Like any other injury, a tooth bruise can have a wide variety of causes. This could be an accidental hit in the jaw with a ball or other sports equipment, an unfortunate fall, a strong blow in a fight, or the consequence of a road accident or riding a bicycle. All these reasons have one thing in common - a strong blow of a mechanical nature.
Children and athletes are the most vulnerable to such injuries. It is these two categories of patients with a similar diagnosis that are the most frequent visitors to dental clinics. However, household injuries, as a result of which a person accidentally or recklessly hits a tooth, can cause a bruise. In this case, the most unprotected and weakest anterior and lateral incisors on the upper jaw most often suffer due to the anatomical structure and overhang of the upper jaw over the lower jaw.
Providing first aid for broken, knocked out and dislocated teeth
One of the most common injuries is a fracture. The types of fracture are as follows:
- Chipping of the enamel of a tooth crown.
- Partial tooth destruction without exposing the pulp.
- Chipped crown exposing dental pulp.
- Tooth root injury.
Additionally, the mouth and gums, the jaw itself and the bone nearby can be damaged. If this happens, the first thing you need to do is calm down - the accompanying injuries create additional stress, which significantly interferes with the doctors and the victim himself. In addition, you should try to find broken fragments and leave them in the water until you see a doctor. The situation does not require an urgent visit to the dentist, so you can make an appointment a little later, for example the next day, but try not to involve the damaged tooth until it is restored.
As for diagnosis, everything is simple - the doctor will first conduct an examination. To detect the risk of root injury, the victim is sent for x-rays and electroodontometry. In this way, the condition of the pulp (tooth pulp) is checked. The goal of treatment is to restore the crown of the tooth. If the fracture led to pulpitis, the patient will be treated with subsequent restoration of the pulp. If an x-ray shows that there has been root trauma, complete extraction of the tooth and subsequent placement of a post is often recommended.
The second most common injury is dislocation. This is a partial or complete loss of connection between the tooth and the socket. Dislocation occurs:
- Partial. The tooth moves greatly or slightly, but does not fall out completely.
- Full. The tooth falls out.
- Impacted, in which the dental crown is driven into the gum.
If a temporary tooth has been completely dislocated (falls out of its socket), do not under any circumstances try to return it to its place - you may damage the new permanent one or its rudiment. And in order to look for and insert a molar into place, you will have only 20 minutes. If you manage to do this, the chance of re-engraftment becomes much greater. What is the procedure? As soon as you have discovered the lost tooth, take it with clean hands (it is also advisable to wash it) by the white part, without touching the root, and return it to the hole, orienting parallel to the neighboring teeth. When you return the lost item to its place, bite on a gauze pad or a piece of cloth, such as a scarf.
There are situations when the tooth cannot be inserted back, for example, if the victim is unconscious or the socket is severely damaged. In this case, place the found tooth in milk or saline solution. You cannot put it in water or any other liquid; you can hold it in the victim’s mouth, but there is a risk of swallowing.
Unlike a fracture, in a situation with complete dislocation, it is necessary to urgently visit a specialist for examination and subsequent treatment.
For partial dislocation, the procedure is slightly shorter. It is important to try not to spit (or do it as little as possible) and under no circumstances take out the tooth. If it prevents your mouth from closing, carefully insert it back in with clean hands, focusing on the adjacent teeth. To hold it in place, bite down on gauze or any other piece of tissue.
In the case of an impacted dislocation, first aid is practically useless; the only option is an emergency visit to the dentist.
Panoramic radiography
How are dislocations identified and treated? The doctor first examines and records the complete absence or displacement of a tooth. Next, the victim is sent for an X-ray and radiovisiographic examination, where the location and condition of the alveoli are clarified. In case of incomplete dislocation, the patient is recommended treatment aimed at preserving the tooth and fixing it with the help of special mouthguards and other structures. In addition, medications are recommended to prevent inflammation and infection in the socket, for example antibacterial ones.
If, after complete dislocation, the tooth does not take root, the specialist is forced to resort to prosthetics and implantation. In case of impacted displacement, you can either remove the affected tooth and replace it with an implant, or perform immobilization using local anesthesia.
A knocked out tooth is a dislocated or broken crown due to a mechanical injury. For example, a blow to the jaw caused the victim to completely dislocate or chip the dentin, exposing the pulp. Depending on the injury detected, you can provide first aid as described above. That is, if a tooth falls out, find it, try to put it back in, or place it in saline before visiting a doctor.