Tooth loss is a disease in which, under the influence of negative factors, the integrity of the dentition is disrupted (due to the loss of one or more teeth). This disease is called edentulism.
Teeth are an important element of the human body. We lose them starting from childhood: healthy, strong teeth grow in place of lost milk teeth. Losing permanent teeth is a serious problem because a new tooth will not grow in the vacant space.
Causes of tooth loss
It is clear that teeth do not fall out on their own; this process is facilitated by various diseases of the periodontal tissue and gums. The reasons why a person may lose one or more teeth can be divided into objective and subjective. The first group includes phenomena that depend little on us or do not depend at all, the second group includes our erroneous actions or deliberate inaction.
Objective reasons
Chronic diseases are the main objective reason why seemingly healthy teeth begin to loosen and fall out: diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, stomach ulcers or duodenal diseases seriously affect the health of the oral cavity.
To better understand the nature of tooth loss, we will briefly talk about the negative effects of some chronic diseases. For example, diabetes is a disorder of blood sugar levels. Excess glucose leads to impaired blood supply to the gums, and due to impaired mineral metabolism, the enamel becomes thinner. A person with heart disease often takes medications that cause dry mouth, interfering with the normal functioning of the oral mucosa. Taking calcium antagonists (hypertension medications) can cause gum overgrowth.
One of the reasons leading to tooth loss is injury (as a result of an accident, while playing sports, during incidents). Often, after receiving a blow to the lower or upper jaw, you can lose one or more teeth.
Heredity is an important factor influencing the formation of a baby’s dental tissue in the mother’s womb. Poor nutrition and bad habits of the expectant mother can also affect the buds of teeth.
Subjective reasons
Failure to maintain oral hygiene leads to diseases of the gums and teeth. Lack of habit of regularly brushing your teeth to prevent pathogenic bacteria that penetrate under the gum tissue, forming tartar and plaque on the teeth.
The main enemies of the oral cavity are carbonated water and sugar, which, when combined, destroy tooth enamel and provide food for bacteria that destroy gums and dental tissue. They cause tooth decay and periodontitis, the most common diseases that occur in people who consume candy and soda.
Bad habits also make a destructive contribution to tooth loss - tobacco smoke contains a long list of toxic substances that do not add health to teeth and gums.
People cause some injuries to their teeth quite deliberately, for example, by opening bottle caps with their teeth. The fact that a tooth did not break due to such abuse does not mean that it will pass without a trace for him: in combination with other factors, everything can end in tooth loss.
Unfortunately, fears and worries about visiting the dental office and possible pain often repel patients from the opportunity to protect their teeth. No money? If a tooth falls out, the prosthesis will be much more expensive.
When do baby teeth start falling out?
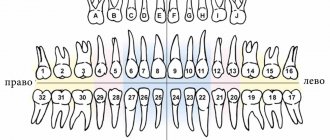
Baby teeth begin to form while the baby is still in the mother's womb. Moreover, their number is not 32, as in an adult, but only 20. Baby teeth usually fully erupt by the age of 2. At the age of approximately 6 years, the replacement of baby teeth with permanent teeth begins to occur. In this case, 20 existing teeth fall out, and the remaining 12 erupt. This usually happens in the following order:
- The deciduous incisors are usually the first to fall out. The roots of the teeth begin to thin out, and when the baby reaches a certain age, the incisor falls out. For central incisors it is 6 years, for lateral incisors - 7 years.
- Then the molars begin to fall out. These baby teeth are divided into first and second teeth. Loss of first molars occurs between 7 and 10 years of age. The second molars are the last to fall out, between the ages of 9 and 13.
- In the interval between the loss of the first and second molars, loosening and loss of the upper and lower canines occurs. This occurs between the ages of 9 and 11 years.
It should be remembered that the process of replacing baby teeth with molars is individual, and the indicated timing is not necessarily suitable for all children.
Diagnosis of tooth loss
If the first signs of disease are detected, and even more so of loose teeth. If the problem is ignored, the tooth will be lost forever. The doctor will ask you to take the necessary tests, take pictures, make a diagnosis, taking into account information about previous or existing diseases, and prescribe treatment. The main diagnostic methods are x-rays and, in some cases, dental computed tomography.
In the case when a patient suffers from a chronic disease, tooth loss is a consequence, the elimination of which will be an insufficient measure. The solution is comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease together with a specialized specialist.
Treatment of tooth loss
There are few methods for treating tooth loss: therapeutic and surgical intervention. In the first case, when the first symptoms are detected, the dentist removes tartar, eliminates the consequences of caries, prescribes antibiotics, antiseptics, and medications that strengthen the general immune system. Together with constant and proper oral hygiene, this method will help to cure most diseases associated with tooth loss.
To save the tooth, surgical intervention may be necessary - an incision in the gum, removal of tartar and dead tissue. The incision is sutured; the operation takes from 40 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the complexity and volume of work.
If a tooth is lost or the dentist was forced to remove it, the patient will need dental prosthetics. This work is performed by a highly specialized specialist - a prosthetist dentist. In place of a missing tooth, you can place an implant - an artificial tooth root with a crown, implanted into the jaw, or a bridge - a ceramic crown attached to adjacent teeth.
Replacing baby teeth with permanent ones: what should parents pay attention to?
The process of replacing children's milk teeth with permanent ones requires increased attention from parents. It is necessary to monitor the child’s adequate nutrition and oral hygiene, and if there are deviations from the norm, immediately contact a dentist
Every person in childhood goes through a period when temporary teeth are replaced with permanent ones. In most cases, this process does not cause any problems. However, parents should still know what exactly to pay attention to when a child’s baby teeth fall out and permanent teeth appear.
Causes of loss of baby teeth
There are very specific reasons for the process of changing a set of teeth after a certain age. The fact is that children erupt their first teeth before they reach the age of one, when more dense foods than milk appear in the diet. However, the child’s jaws at this time are still quite small, and the first teeth that grow have a corresponding size. And milk teeth themselves, which have weak enamel, are not very strong.
Gradually, as the baby grows up, the chewing load on the teeth increases due to the intake of increasingly solid foods. This requires the formation of an appropriate masticatory apparatus. By this time, the growing child's jaws are just large enough to accommodate the entire set of permanent teeth. Therefore, the process of loss of milk teeth and the appearance of stronger molars, necessary for a full future life, begins.
At what age do baby teeth change?
Parents often mistakenly believe that the process of changing primary teeth begins with the loss of the first milk tooth. As a rule, this occurs at the age of 6-7 years. However, doctors take as a starting point the appearance of the first permanent teeth - third molars, which are absent in the “deciduous bite”. This process is observed at the age of 5-6 years. It is at this time that the process of resorption of the roots of temporary teeth begins, which lasts approximately 2 years. Gradually, baby teeth begin to loosen, and by the time the molars appear, they fall out.
The age at which teeth change varies from person to person, and the time difference is sometimes up to 2 years. Experts note that this factor may also depend on the region of residence: in warmer climates, permanent teeth appear earlier. It is also known that girls replace their baby teeth with molars a little faster than boys.
What to pay attention to during the period of teeth change?
Proper nutrition
The process of final formation of enamel during the eruption of permanent teeth takes several years. And during this period, proper nutrition becomes extremely important, thanks to which the child must receive all the substances necessary for the body.
Parents should pay attention to the following points:
- the child’s daily diet should include foods with a good calcium content - milk, cottage cheese, cheeses;
- the diet should be supplemented with fresh fruits and vegetables to obtain the required amount of vitamins and microelements;
- at least 1-2 times a week, to obtain a sufficient amount of phosphorus, you need to include fish dishes in the menu;
- Until the final formation of the enamel of the molars, it is advisable to give up sweets, chocolate and sweet pastries. Sweet soda is also extremely dangerous for young enamel;
- The child should eat some food, such as fruits and vegetables, in solid form. The load on the teeth will stimulate the resorption of the roots of baby teeth, helping the eruption of molars;
- in some cases, for example, if a child does not eat dairy products well, the baby’s diet should be supplemented with a multivitamin complex with calcium.
It is better to exclude the hardest or most chewy foods, such as nuts or toffees, from the diet completely during the period of teeth change. Their use can lead to injury or early loss of primary teeth, which will interfere with the proper growth of permanent teeth.
Oral hygiene
As already mentioned, permanent teeth appear with weak, not yet fully formed enamel. Therefore, oral care to prevent tooth decay is very important.
Proper oral hygiene in a child involves morning and evening brushing of teeth using children's toothpastes that have an optimal content of calcium and fluoride. To avoid injury to the gums, it is better to choose a toothbrush with soft bristles. It can also be helpful to teach your child how to use children's dental rinses. Ideally, it is advisable to rinse your mouth every time after eating - this will optimally prevent the formation of plaque.
Visiting the dentist
Special attention should be paid to the medical prevention of dental diseases during the period of teeth change. For preventive purposes, dentistry for children should be visited at least 2 times a year. And if there is a need to treat a child’s teeth, then you need to go to the doctor as quickly as possible. After all, caries in children with teeth with still weak enamel can develop very quickly.
Early and late change of primary teeth
Sometimes situations arise when the replacement of temporary teeth with permanent ones in children occurs in violation of the deadlines. Let's consider what parents should do in such cases.
Early tooth loss
The loss of baby teeth can be called early if it occurs before the age of 6 years. As a rule, such situations arise due to injury, dental disease, or intentional loosening of a tooth. The main problem here is that when a baby tooth disappears, free space appears in the dentition. And if the permanent tooth does not begin to grow after the loss of the temporary one, then gradually the neighboring milk teeth will begin to move, filling the resulting volume. In the future, this will lead to the fact that the molars will not have enough space for normal eruption, and the dentition will be uneven.
With the early loss of a temporary tooth, pediatric orthodontics comes to the rescue. Currently, modern techniques are available to doctors to prevent the displacement of adjacent teeth. Therefore, in case of early loss of a baby tooth, it is advisable to immediately go for a consultation with an orthodontist. After all, correcting cosmetic defects and correcting the bite will bring much more trouble in the future.
Late replacement of primary teeth
There are two possible scenarios here. The first is when molars do not appear in a timely manner, even if the milk teeth have already fallen out. There may be several reasons for this anomaly, from a physiological delay in the appearance of new teeth to incorrect positioning of the tooth inside the jaw apparatus. The second scenario is when the molars began to erupt before the baby teeth fell out. The result can also be the formation of bite defects.
If a child shows signs of a delayed change of teeth, it is necessary to contact a dentist to identify the causes of the deviations. As a rule, the doctor will be able to tell about the causes of the anomaly after an X-ray examination, after which appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
Prevention of tooth loss
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it - this truism is remembered more often when the disease has progressed far and complex treatment is required. Tooth loss can be prevented by following these recommendations:
- Maintain personal oral hygiene: brushing your teeth should be done at least twice a day, morning and evening;
- use dental floss to clean the spaces between your teeth from food debris;
- Visit your dentist regularly, even if your teeth are not causing concern;
- strictly follow your dentist’s recommendations for dental care and disease prevention;
- take care of chronic diseases (if any);
- protect your teeth from injury.