A sore throat
14.07.2017
52.8 thousand
35.4 thousand
6 min.
4
Sore throat when swallowing is the most common symptom of colds and signals the development of an inflammatory process.
The organs of the mouth, throat, and nose are closely interconnected and the development of the inflammatory process in one focus quickly spreads to the entire group of organs. This is facilitated by the unification of the oro- and nasopharynx with the help of the pharyngeal ring, which acts as the main immune organ.
Pain in the throat area, extending towards the ears, can be caused not only by inflammation, but also by the development of an infectious process.
Diseases with sore throat radiating to the ears:
- Otitis.
- Eustachite.
- Pharyngitis.
- Tonsillitis.
- ARVI.
- Angina.
- Infectious diseases: diphtheria, chicken pox, scarlet fever, measles.
- These diseases have different etiologies, so the clinical picture may differ significantly.
Otitis is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the middle ear; as a rule, with otitis, the throat and ear hurt on one side. Otitis media can occur in several forms:
- Spicy. The disease begins with the appearance of acute pain in the area of one ear, the spread of the process to nearby tissues leads to a feeling of discomfort when swallowing. In the absence of timely treatment, it can develop into subacute, chronic or purulent forms.
- Subacute. It has no clear boundaries and easily develops into an acute or chronic course. In this case, an increase in temperature is not observed or does not differ significantly from normal.
- Chronic. In this case, the temperature rises above normal only in the evening or does not rise at all. The patient complains of weakness, painful sensations when swallowing, which radiate to the ear.
- Purulent. The most dangerous form can lead to partial or complete hearing loss. The purulent form is accompanied by acute pain and fever.
This disease is most often the reason why the throat hurts when swallowing, radiates to the ears, but there is no fever.
The cause of pain in the ear in this case is inflammation of the Eustachian tubes. The Eustachian tube is involved in the process of inflammation in diseases of the throat: tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, etc. Swelling of the inflamed tissues causes compression of the Eustachian tubes. Because of this, the patient begins to experience a sore throat, which radiates to the ear when swallowing.
In this case, ear pain is not the main symptom of the disease, and an increase in temperature is noted depending on the course of the inflammatory process in the throat.
In this case, the disease is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharyngeal cavity, which easily spreads to the hearing organs.
Pharyngitis is usually not accompanied by fever; a slight increase in body temperature may be observed. Acute pharyngitis can cause a sharp and prolonged increase in temperature, general weakness and depression of the body.
Inflammation in the mucous membrane of the pharynx causes irritation of the nerve endings, which lead to a reflex cough. Coughing irritates the pharyngeal cavity even more, which leads to painful sensations in the throat, which can radiate to the ear. In this case, painful sensations when swallowing spread to both ears at the same time.
Another common disease that is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the tonsils.
The chronic form of tonsillitis is accompanied by periodic remissions of the disease associated with a decrease in the body's resistance.
In this case, pathogenic organisms are constantly located in the crypts and on the surface of the tonsils. Decreased immunity and stress lead to the body being unable to suppress the growth of microbes.
The disease is accompanied by a sore throat and can radiate to the ears.
Acute forms of tonsillitis occur with a high increase in body temperature.
The development and intensity of the disease largely depends on the aggressiveness of the pathogen. As a rule, it is accompanied by fever, but in rare cases, painful sensations in the throat, radiating to the ears when swallowing, pass without a clear increase in body temperature.
This disease most often occurs in children and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. The clinical picture of the infectious disease depends on the pathogen itself and may differ depending on the age of the patient.
A sore throat that radiates into the ear when swallowing and occurs without an increase in body temperature should be taken seriously. The tissues of the hearing aid are very sensitive and the most harmless infection can cause the development of irreversible processes in them. As a result, hearing may be permanently lost.
A sore throat that radiates to the ear or ears at normal body temperature does not mean there is no reason to worry. In some cases, the body does not respond with an increase in temperature to the development of a pathological process in the pharynx, but the hearing organs are already involved in it.
When the first signs of hearing impairment appear, it is recommended to seek help from an otolaryngologist; it is almost impossible to independently find out the cause of the pain and make an accurate diagnosis. Using a mirror, the specialist will assess the condition of the patient’s pharynx, determine the involvement of other organs in the process and the severity of the disease.
Treatment should begin immediately after the first symptoms appear, this will help stop the development of the process and avoid possible complications.
To prescribe the correct treatment regimen, it is necessary to have an accurate diagnosis; the effectiveness of treatment measures will depend on this. Incorrectly prescribed treatment can aggravate the course of the disease and make it much more difficult to get rid of the problem.
Rinse. The effectiveness of gargles for throat diseases is due to the fact that a large amount of mucus accumulates on the surface of the mucous membrane involved in the inflammatory process. Mucus contains dead microbial cells, which lead to additional irritation of the throat.
It is recommended to rinse several times a day; folk remedies and traditional medications may be suitable for this. With the help of rinses, the mucous membrane is cleansed of pathogens and the passages are cleared.
Often it is the accumulation of large amounts of mucus that causes stuffy ears or unpleasant sensations in them.
Table salt, baking soda, and iodine are suitable solutions for gargling at home. Solutions of Chlorphyllipt and Chlorhexidine are suitable medications for rinsing. Medicinal herbs are good for relieving inflammation in the throat; chamomile, sage, eucalyptus, etc. can be brewed for this.
Before rinsing, you need to clean your mouth with toothpaste. Rinsing is carried out for 5-7 minutes, after which it is not recommended to eat.
Nasal rinsing. The nose is washed with saline solutions or vasoconstrictors. This will reduce swelling of the nasopharynx and reduce pain in it.
Irrigation of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions. The irritated mucous membrane has microscopic damage, into which microorganisms living on it easily penetrate. This leads to aggravation of the patient's condition. The use of aerosol antiseptics has a detrimental effect on microorganisms, which makes it possible to reduce the intensity of the disease.
Antihistamines. Taken in tablet form, they reduce swelling of the mucous membrane. This allows you to reduce pressure on the auditory tubes and relieve pain radiating into the ear. Antiallergic therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
Antibiotics or antiviral drugs. Prescribed by a doctor after making a diagnosis and determining the nature of the pathogen.
Diet. If you have a sore throat, you should avoid eating hard, spicy, hot or cold foods. These products irritate the mucous membrane and aggravate the inflammatory process.
It is recommended to eat liquid, warm food. To soften the mucous membrane of the throat, you should take warm drinks at intervals of several hours.
Maintaining the body's resistance. It is difficult for a weakened body to fight pathogens; to maintain it, it is recommended to take immunostimulating drugs and vitamins.
Peace and warmth. Stress and hypothermia negatively affect health; for a speedy recovery, the patient must avoid hypothermia and adhere to a normal regimen.
A sore throat that radiates to the ear is a symptom of the initial stage of a serious disease that can lead to complete or partial hearing loss. When the first signs of hearing damage appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What to do if you feel pain
Most obviously, it is difficult to find a person on the planet who would never complain of a sore throat.
Each person's position is individual in how his body will react to pathology.
Some patients can restore the healthy state of their organs in a short time.
Others may experience worsening and the addition of other symptoms, including ear pain, head pain, and aching joints.
And for some, perhaps, some time after the signs of the disease disappear, it turns out that complications have appeared in some organs.
Practice shows that the ears experience the consequences of diseases most often. And hearing loss is one of the first sad consequences of not taking painful body signals seriously.
This means that you should not delay visiting the doctor. Determination of the cause of the illness and subsequent treatment will be carried out after a thorough diagnosis.
Unilateral pain in the throat and ear is observed in various otolaryngeal diseases
Lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory process that affects the tissue of the lymph nodes. In most cases, it occurs as a syndrome of various bacterial or viral pathologies; in some cases it can be caused by exposure to toxins on the body, including the use of cytostatics. Damage to the lymph nodes in the neck or behind the ears leads to the appearance of a rather intense pain syndrome that radiates to the throat and ear canal.
With lymphadenitis, patients are concerned about symptoms characteristic of the inflammatory process:
- enlargement and pain of the lymph node;
- possible hyperemia in the affected area;
- pain in the head and ear on one side;
- increased discomfort when tilting or turning the head;
- it is possible to form an abscess at the site of the node;
- low-grade fever, chills.
In children, lymphadenitis can occur in a severe generalized form, in which the patient feels a sharp deterioration in health, he experiences severe hyperthermia to critical levels. In the absence of timely treatment, there is a risk of developing sepsis.
Pathology therapy includes the mandatory use of antibacterial drugs: Ampicillin, Doxycycline, Cefazolin
etc. The doctor prescribes a broad-spectrum antibiotic or selects the most appropriate drug after identifying the causative agent of the pathology. The patient is also indicated for UHF therapy and vitamin and mineral complexes.
Sore throat and pain in the ear: what to do? First aid
When a sore throat when swallowing radiates to the ear, you should immediately start using antiseptics. They will help to quickly alleviate the condition and eliminate pathogenic microflora.
To eliminate discomfort in the throat, rinsing using solutions is ideal:
- Furacilina;
- Chlorophyllipt alcohol;
- Angilexa;
- Givalexa;
- Tantum Verde.
If these or similar drugs are not at hand, you can thoroughly rinse your throat with saline solution. To prepare it, take 1 tsp per glass of warm boiled water. regular table or sea salt and 1 drop of iodine.
In order to eliminate discomfort in the ears, antiseptics will also be required.
It is advisable that the drug contains lidocaine or other painkillers, which will literally eliminate the pain in a matter of minutes, which is extremely important if there is a shooting in the ear. These include:
- Otipax;
- Anauran;
- Otinum;
- Ototone;
- Candibiotic.
To normalize the outflow, it is recommended to use vasoconstrictor drugs. They are instilled into the nose, even if there is no runny nose. These medicines include:
- Eucazoline;
- Nazik;
- Knoxprey;
- Rinazoline;
- Galazolin;
- Xylo-Mepha.
Such manipulations for purulent otitis media will speed up the process of pus production and its spread to the surrounding tissues. And, as you know, the brain is in close proximity to the ear structures.
If you experience an elevated body temperature, you should not bring it down immediately. It is recommended to take antipyretic drugs only when the thermometer readings exceed 38.5°C. In such situations, you can drink:
- Panadol;
- Nurofen;
- Has;
- Rapimig;
- Paracetamol;
- Nise.
It is also advisable to stop smoking, thoroughly wipe away dust and pay attention to the level of humidity in the room. Normally, it should fluctuate between 50–65%
To achieve the necessary air humidity, you can install a special device or place wide-necked containers of water around the house.
It's important to drink a lot. Any warm drinks are ideal for these purposes, but not hot ones.
Ear pain relief, first aid
Doctors usually recommend Otipax drops.
bury it in the ear, traditional medicine - there are many ways to warm it up. It is absolutely unacceptable to do all this before visiting a doctor. There are a number of reasons for this ban.
In case of a purulent inflammatory process, hot compresses on the area of the ears and nearby will provoke the activation of pathogenic bacteria and increase the rate of their reproduction. As a result, the patient’s condition will worsen as much as possible due to the spread of inflammation to all nearby tissues of neighboring organs.
If the eardrum has ruptures, punctures, drops will not bring relief. They should not be used without a doctor’s recommendation if there is acute pain in the ear.
To calm the pain before visiting a doctor, you are allowed to take Ibuprofen, but only a tablet. Doctors' recommendations:
- Place vasoconstrictor drops inside the nasal openings: Nazol, Galazolin, Naphthyzin.
- The drops will reduce the swelling of the mucous membranes of the eustachian passages, help equalize the pressure, and stop the development of inflammation.
- The pain syndrome is partially reduced if you cover the ear with a napkin, protecting it from contact with hair, clothing and wind.
- To prevent the development of infection, a sore throat should be rinsed with Miramistin, Chlorophyllipt or saline solution.
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Ibuprofen | From 15 rub. | |
| Nazol | From 160 rub. | |
| Galazolin | From 37 rub. | |
| Naphthyzin | From 23 rub. | |
| Miramistin | From 218 rub. | |
| Chlorophyllipt | From 115 rub. |
Causes
There are many factors that lead to the appearance of such symptoms. These include sore throat, chickenpox, and diphtheria. Often the cause is measles, pharyngitis, otitis media, scarlet fever. Only a doctor can identify the exact cause of the disease.
Ear diseases
Otitis media is considered the main cause of problems.
Unilateral or bilateral ear inflammation usually results from infections. It also leads to damage to the respiratory tract. This pathology is the result of a weakened immune system, chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx, and abnormalities in the structure of the nasal septum.
The main cause of inflammation is infection entering the Eustachian tube. This provokes blockage of air access to the middle ear. First, the pressure increases in it, and then liquid accumulates. In this case, the following signs appear:
- a serious increase in temperature - up to 39 degrees;
- heaviness in the head;
- headaches that are pulsating in nature;
- purulent discharge from the ears;
- the appearance of an echo in the hearing organ during a conversation;
- ear congestion;
- shootings in the ears;
- hearing impairment.
If lumbago occurs with otitis media, this indicates complications. This means that pathogenic bacteria have entered the ear cavity. The purulent form of inflammation develops extremely quickly - within 1-2 days. At the same time, pain increases when swallowing.
When purulent discharge appears, it can be judged that the eardrum is damaged. In particularly difficult cases, there is a risk of complete hearing loss. If the pus cannot come out, this allows the infection to enter the brain, which can lead to an abscess, meningitis and other disorders.
How to recognize otitis media by symptoms:
Throat
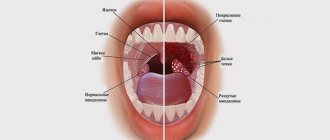
Pathologies of the throat include disorders such as tonsillitis, laryngitis and pharyngitis. The last anomaly is the most common and is an acute inflammation that is localized on the back wall of the pharynx.
Pharyngitis rarely occurs on its own. It is usually combined with inflammatory lesions of the upper respiratory tract. During the examination, redness of the mucous membranes and tonsils can be visualized.
Sore throat is an acute process characterized by inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils. Laryngitis is commonly understood as inflammation of the larynx.
Throat diseases have the following manifestations:
- dryness and soreness in the mouth;
- pain when swallowing;
- hoarseness in the voice;
- dry cough;
- weakness;
- increase in temperature;
- pain on palpation of lymph nodes;
- local redness and swelling in the throat;
- headache;
- purulent plaque.
What to do if your throat hurts, watch our video:
How to relieve the condition
Treatment is selected depending on the cause of the disease. So, with purulent otitis media there is a need to take antibiotics. Tonsillitis requires the use of local antibiotics for the throat and means to strengthen the immune system. Ear drops may be used to relieve this.
In addition to traditional methods, traditional medicine is used. Gargling with herbal infusions is especially effective. Warm compresses can help relieve ear pain.
To reduce discomfort, the following measures are recommended:
- Gargling with anti-inflammatory agents or antiseptics. You can use saline or soda solution.
- Rinsing the nasal cavity. To do this, you can use saline solution or pharmaceutical preparations. These include aquamaris and no-salt.
- Instillation of nasal vasoconstrictors. This category includes substances such as naphthyzine and galazolin.
- Taking antihistamines. It is necessary to use such remedies in case of severe swelling of the throat.
All these medications help cope with swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa. This helps restore the patency of the hearing organ.
How to quickly cure a throat with gargles, says Dr. Komarovsky:
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is a disease in which the mucous membrane of the larynx becomes inflamed. In most cases, pathology is caused by various viruses, leading to hyperemia and swelling of the inner layer of the respiratory tract. If left untreated, laryngitis, especially in preschool-age patients, can lead to the development of false croup, a disease during which the movement of air masses in the larynx becomes difficult or impossible.
Acute laryngitis rarely occurs as an independent pathology; in most cases it develops against the background of a severe form of acute respiratory viral infection, measles, scarlet fever, etc. The chronic form of the disease is formed due to improper treatment of acute laryngitis or as a result of prolonged harmful effects on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract of various pathogenic factors: dust, chemicals, smoke.
The disease manifests itself as a dull pain and burning sensation in the throat, while the unpleasant sensations can be localized on one side of the larynx. Patients often also complain of discomfort in the ears, difficulty swallowing, and dry mouth and throat. When diagnosing laryngitis, you should pay attention to other symptoms of the disease:
- hoarseness or hoarseness of the voice;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- dry cough in acute laryngitis or wet in chronic.
A patient with uncomplicated laryngitis does not require hospitalization, so treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. In this case, bed rest is necessary only for patients whose pathology has developed against the background of ARVI. Other patients can lead their normal lives, but try not to talk or whisper to reduce the strain on the vocal cords.
Patients are prescribed ultraviolet treatment, magnetic therapy, quartz procedures, alkaline or oil inhalations. To relieve pain and stop coughing, it is recommended to drink plenty of warm drinks and use lozenges with eucalyptus, sage or chamomile extract.
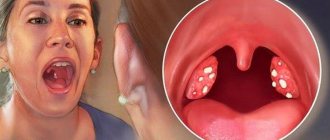
Angina
Sore throat is a whole group of acute diseases that arise due to the development of an infectious process on the tonsils of the pharyngeal ring. In this case, pathology can be of both endogenous and exogenous nature. In the first case, the pathogen enters the throat from the sinuses, ear canals, or teeth destroyed by caries. With exogenous inflammation, pathogens are transmitted by airborne droplets or nutrition.
Signs of a sore throat
With angina, patients are concerned about the characteristic symptoms of the infectious process:
- Hyperthermia up to 38.5-39.5°C.
- Plaque on the tonsils, the appearance of ulcers.
- Intense pain in the throat and ears, which gets worse when swallowing. In this case, the pathology often affects the tonsils only on one half of the pharynx, in which case the pain syndrome is also one-sided.
- General deterioration in health.
- Severe hyperthermia of the palate, tonsils, and uvula.
- Decreased appetite.
- Weakness, lethargy, drowsiness.
- Attacks of sweating.
- Myalgia and arthralgia.
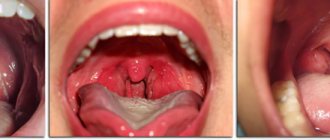
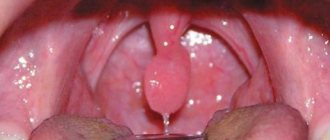
Throat with follicular sore throat
There are several main types of sore throats, each of which has specific manifestations.
Typical types of sore throats
| Symptoms | Catarrhal – acute inflammation of the tonsils or acute catarrhal tonsillitis | Lacunar - damage to the tonsils with involvement of the lymph nodes in the pathological process | Follicular - a purulent inflammatory process in which the lesions are located in the form of separate points |
| Hyperthermia | Up to 38°C | Up to 39°C | Up to 40°C |
| Patient's condition | Satisfactory | Moderate | Moderate |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | Not expressed | Expressed | Expressed |
| Soreness of the lymph nodes | Moderate | Strongly expressed | Strongly expressed |
| Plaque on tonsils | Absent | Expressed | Absent |
| Pain when swallowing | Moderate | Expressed | Strongly expressed |
Types of sore throat
In most cases, sore throat is treated on an outpatient basis. The exception is severe or atypical forms of the disease. The patient is advised to take local and general antibacterial agents: cephalosporins, macrolides and sulfonamides. The average course of treatment is about 7-8 days. Tonsils are treated with Chlorophyllipt, Stopangin, Ambazon, etc. Irrigation with products containing chlorhexidine or streptocide is possible. During the period of treatment and rehabilitation after illness, the patient is recommended to follow a gentle diet.
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammation of the middle ear that can spread to the inner and outer ears. It occurs due to the penetration of bacteria from the nasal cavity through the Eustachian tube. Causes fluid accumulation in the ear, resulting in pain, headache, discharge from the ear canal, tinnitus, congestion, and soreness of the tragus.
Otitis is a dangerous disease, as if not treated correctly it can lead to a number of complications, including paresis of the facial muscles, meningitis and abscess of brain structures.
When diagnosing otitis, there are three main types of this disease:
- Otitis externa
- affects the external auditory structures; middle-aged and elderly people most often suffer from this form of pathology. - Otitis media
, in which the inflammatory process is localized in the middle ear and usually affects children under the age of 5-7 years. - Internal otitis media
. Develops against the background of a severe infection, such as meningitis. With this pathology, the patient's labyrinth, the internal structure of the ear, becomes inflamed. The disease has an extremely high risk of complications.
The external form of the disease is divided into local and diffuse. In the first case, a boil forms in the patient’s ear - purulent inflammation in the soft tissues, which has clear boundaries. The doctor opens the pathological formation and drains the cavity.
Diffuse otitis usually develops against the background of chronic otitis, when pathogenic microflora persists in the ear canals for a long period. In this case, the inflammation spreads to the tissues of the ear structures, including the eardrum.
If left untreated, the pathological process moves to the middle ear. The disease can spread through the eustachian tubes to the pharynx. In this case, tubo-otitis or eustachitis develops - a disorder in which the infection affects the mucous membrane of the ear canals.
With otitis media, the pathological process involves the nerves passing through the canals of the skull and connecting the throat and ear. As a result, inflammation and compression of the ganglia occurs, which causes severe pain both in the ear canal and in the pharynx on the affected side. Also, with otitis media, the patient is bothered by other symptoms:
- hyperemia of the epidermis of the ear with external otitis;
- sharp discomfort when touching the entrance to the auditory canal;
- decreased hearing, especially when discharge appears;
- discharge from the ear canal, usually greenish or yellowish in color;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness, cephalgia;
- sore throat on the affected side, sometimes pain can also affect the jaw;
- low-grade or febrile fever.
Otitis externa is treated by introducing turundas soaked in alcohol or antiseptics into the ear canal: Otipax
,
Anauran
. The patient is also advised to undergo physiotherapy, warm compresses and take multivitamin complexes.
For more severe forms of the disease, the otolaryngologist prescribes antibacterial drugs: Ampicillin, Cefazolin, Augmentin
etc.
Drops with an anti-inflammatory effect are instilled into the ear: Otinum, Sofradex
.
If conservative treatment does not bring effect, then paracentesis is performed - a puncture of the eardrum, which ensures the outflow of purulent exudate. After the procedure, the patient must take antibacterial drugs, neuroprotectors and medications to stimulate blood circulation. Treatment in this case is carried out in a hospital setting.
Diagnosis
It would be a great misconception and self-deception for a person if he independently diagnoses himself, relying on his intuition, experience of past illnesses or the advice of friends.
It is possible to choose treatment wisely only after establishing the exact cause of the ailment. Indeed, often, medications against one ailment turn out to be powerless against another.
Moreover, “shots” or heaviness in the ear with pain in the pharynx should already indicate a connection between inflammatory processes in these organs.
The doctor will make a diagnosis primarily based on the patient's complaints. He will carefully examine the patient's nasopharyngeal area.
Often, you have to turn to laboratory readings. This will require taking a smear for bacterial culture from the almond inflammatory surface.
And after this, the specialist determines the cause of the ailment, the severity of the inflammatory process and prescribes adequate treatment.
After establishing the exact cause of the ailment, you can choose the right treatment
Sinusitis
A disease in which one or more sinuses become inflamed is called sinusitis. The pathology is inflammatory in nature and develops as a complication of various bacterial or viral infections. Most often, this disorder is diagnosed in children and adolescents aged 4-15 years. Sinusitis is a whole group of diseases that are classified according to the location of the inflammatory process:
- Sinusitis
is inflammation of the epithelium of the nasal sinuses of the upper jaw. - Frontitis
is a lesion of the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus. - Ethmoiditis
is sinusitis of the ethmoid bone cells. - Sphenoiditis
is a pathological process in the sinuses of the sphenoid bone.
With sinusitis, the patient experiences characteristic symptoms indicating the development of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses:
- There is an unpleasant sensation in the nose. Depending on the location of the lesion and the number of sinuses involved in the pathological process, the pain can be localized in the bridge of the nose, above the eye or between the eyebrows. In this case, the discomfort increases sharply when pressing on the inflamed area or when tilting the head.
- Cephalgia. The headache is dull or aching and gets worse in the evening.
- With sinusitis, there is often discomfort in the throat and ear area on the affected side.
- Impaired nasal breathing. Due to nasal congestion, the patient's voice acquires a characteristic nasal sound.
- With normal outflow of pus from the sinuses, the patient experiences yellowish-green or brownish discharge with an unpleasant putrid odor from the nose.
- Low-grade or febrile fever, weakness, chills.
Treatment for sinusitis should be aimed at stopping the inflammatory process and ensuring the free outflow of purulent exudate from the sinuses. For this, various antibacterial or antiviral drugs are used: Amoxicillin, Meropenem, Ceftriaxone
etc.
If conservative treatment does not have an effect, then surgical drainage is performed. It is performed to cleanse the sinuses of pus and collect material to identify the pathogen. After the analysis, the specialist can select the most effective drug for the treatment of sinusitis.
Pain in the throat and ear on one side is a fairly common symptom, which may indicate the development of various diseases of the upper respiratory tract, hearing organs or lymphoid system. If any signs of pathology appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
Antiviral agents
With the help of traditional medicine, it is possible to reduce ear pain and improve the effect of drug therapy.
Garlic
Use the product as drops, sending them into the ear in case of severe pain. You can do without oil if you drip garlic juice into your ear. This article explains how to use onions and garlic for colds.
This budget option effectively relieves ear pain. At the same time, onions also have an antiseptic and antibacterial effect. During therapy, it is possible to stop the inflammatory process.
You need to take one onion, remove the husk and crush it. Wrap the pulp in gauze. Apply the compress to the affected ear for 20 minutes. This procedure can be performed 2-3 times a day. You can take onion juice in an amount of 20 ml, heat it and add 2 drops.
You need to fill a plastic bottle with thermal water. Place it on the affected ear and place a towel on top. The duration of the thermal procedure will be 5 minutes. This therapy option can relieve pain when swallowing in the ear.
Ginger root
With the help of this plant it is possible to have an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, ginger root perfectly relieves pain. It is necessary to extract the juice from it and then send it to the affected ear. You can also combine 20 g of fresh ginger juice and combine with 50 ml of warm sesame oil. Apply the resulting mixture to the affected ear when it has cooled. This article explains how to use ginger against flu and colds.
Bishop's weed
To relieve ear pain, use the oil of this plant. You need to combine 20 ml of bishop oil with 40 ml of sesame oil. Place 3-4 drops of the product into the affected ear. Be sure to warm the mixture before use.
Camphor oil
This product can be used in the treatment of ear pain in two ways:
- Compress. You need to take 20 ml of the main product, warm it and dip gauze in it, folded in several layers. Apply the compress to your ear for 30 minutes. Then place a cotton swab in your ear.
- Drops. You can drip 4 drops of camphor oil into the affected ear, and then apply a cotton swab. Lie like this for 10 minutes and leave the tampon overnight. But this article will help you understand how to use oil for dry throat.
Pain in the ear when swallowing is an unpleasant symptom that may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. Most often this occurs with otitis and injury to the eardrum. Each case is assigned its own treatment regimen, the essence of which is to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and the underlying factor.
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Arbidol | From 162 rub. | |
| Kagocel | From 212 rub. | |
| Teraflu | From 161 rub. | |
| Tsitovir | From 242 rub. | |
| Remantadine | From 71 rub. | |
| Anaferon | From 206 rub. | |
| Coldrex | From 192 rub. | |
| Amiksin | From 593 rub. | |
| Tamiflu | From 1276 rub. |
They destroy viruses, reduce throat swelling, and increase the body's immune defense. Release forms for children are syrups, for adults - capsules, tablets.
Plant decoctions have an analgesic effect:
- mint,
- oregano,
- fragrant rue,
- bloodroot,
- caraway,
- meadow lumbago.
A teaspoon per 150 ml of water, leave for 15 minutes in a thermos.
If you have a sore throat, or if there is pain in the hearing organs, you need to prepare drinks from medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, and sedative properties for gargling:
- chamomile,
- elecampane,
- calendula,
- St. John's wort,
- oak bark,
- sage.
To gargle and gargle in case of purulent inflammation of the throat, teeth, or if the ear hurts when swallowing, it is necessary to use solutions with salt; it, by changing the osmotic pressure of the cells, draws out all pyogenic bacteria from them. Mix a teaspoon into half a glass of water.
After a cold, tea, rose hip drink, black currant, and lemon are useful to boost immunity.
Treatment of tubootitis: disinfection of the ear cavity at home is done with hydrogen peroxide 3%.
- mint;
- oregano;
- fragrant rue;
- bloodroot;
- caraway;
- meadow lumbago.
- chamomile;
- elecampane;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort;
- oak bark;
- sage.
Traditional healers recommend gargling with a solution of salt and iodine, decoctions of chamomile and calendula. Warming up is possible (if the body temperature does not exceed 37 degrees) - vodka or alcohol compresses on the neck. Inhalation is the procedure of inhaling steam from solutions of medications, herbs or just potatoes.
Diagnosis of the disease
You should not overuse self-medication and adopt the experience of friends. Medical statistics show a huge number of examples of premature disability due to incorrect use of medications.
Groups of pharmaceuticals effective for inflammatory infectious diseases of the throat:
- antiseptic drugs;
- antiviral;
- combined agents - antiseptic and anesthetic.
- antiseptic drugs,
- antiviral,
- combined agents - antiseptic and anesthetic.
To determine what caused the condition to worsen, you should consult a doctor. You should not diagnose yourself at home, since you can make an incorrect diagnosis and prescribe inappropriate treatment, which will cause your health to worsen.
The doctor will interview the patient and find out his complaints. An external inspection will then be carried out. The doctor will look at the throat and examine the patient by palpation. Tests will be ordered if necessary.
To avoid the occurrence of pathology, it is recommended to carry out preventive measures on a regular basis.
Immunity should be strengthened. Hardening, daily exercises, and taking vitamins with food or in the form of special complexes will help with this. It is recommended to give up bad habits: smoking, alcohol, consuming various substances that are toxic to the body. Healthy sleep and sufficient rest time are important. It is necessary to walk in the fresh air. To prevent pathological conditions, you can drink herbal decoctions in courses. It is recommended to consult a doctor to select appropriate medicinal plants.
During the cold season, the head and neck should not be allowed to become hypothermic. It should be remembered that you can get sick not only in winter, but also in summer. During the hot season, you should not drink too many cold drinks or consume excessive amounts of ice cream and fruit ice. During epidemics, public places should be avoided. It is recommended to spend as little time as possible in large stores, public transport and other locations where infection is likely to occur. To reduce the risk, you need to wear a special face mask
It is important to change it promptly: if you wear a mask for too long, it will cease to be an effective means of protection against infection.
It is important to wash your hands with soap. Unwashed hands are especially dangerous after visiting a hospital, where there are often a large number of infected people.
When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a therapist. This will help avoid the development of the pathological process and facilitate treatment.
Causes
There are a number of pathologies in which similar symptoms occur. Other symptoms help determine what a person is sick with.
In children, similar symptoms occur with chickenpox, measles, and scarlet fever. These diseases are rarely diagnosed in adults.
Tubootitis can cause pathology. This is an inflammatory process in the mucous membranes of the eardrum and eustachian tube. The patient notes tinnitus, decreased hearing acuity, and a slight increase in temperature. When you move your head, you feel like water is pouring in your ears.
Another disease that causes unpleasant symptoms is eustachitis. Inflammation occurs in the Eustachian tube. Most often there is no temperature. Soreness occurs due to the fact that the inflamed tissues, which have increased in size, compress nearby organs.
Angina
With a sore throat, the tonsils and throat become inflamed. A characteristic symptom is a strong increase in body temperature. However, most patients do not have a runny nose. A white or light yellow coating appears on the surface of the larynx. Patients report bad breath. Weakness appears, the patient quickly gets tired. Swallowing is painful and difficult.
The pain may radiate into the ears due to the accumulation of pus. This symptom does not always occur; it often appears when treatment is delayed. The localization of pain in the throat can also be different: sensations can be localized on the left, right, or in the middle.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammatory process in the pharynx. This disease is characterized by dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa, sore throat, and dry cough. Sore throat, raw, scratching; spread to the ear area. There is swelling, hyperemia of the palatine arches and the posterior wall of the inflamed organ. The cervical, occipital and submandibular lymph nodes become larger in size, and pain appears on palpation.
There is general weakness, high fatigue, and headaches. Possible fever and chills. Localization may vary. Often discomfort occurs only on the right or only on the left side.
Otitis
This inflammatory process affects the inner ear. There is a pain in the throat area that radiates to the ear, the intensity of which increases in the evening and reaches a peak at night. Body temperature rises, fever and chills occur. Appetite disappears, weakness occurs. If the pus ruptures the eardrum and leaks out, the shooting sensation in the ear becomes less intense.
The disease often turns out to be a complication of a cold that is not completely cured.
Laryngitis
If you have a sore throat, a person may have laryngitis, an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the larynx. A barking cough appears. Gradually it turns into wet, the sputum released contains inclusions of blood. The size of the submandibular lymph nodes increases; palpating them is unpleasant and painful. Swallowing is difficult and speaking also becomes difficult.
As the inflammatory process progresses, other symptoms arise. The patient's body temperature rises to 37-40 degrees, and a lump is felt in the throat. If swelling is present, the person will feel difficulty breathing. Nasal congestion, weakness, and pain in the muscles appear.
Lymphadenitis
A sore throat can also appear due to inflammation of the lymph nodes. This pathology is manifested by an increase in damaged structures, pain when palpating, high body temperature, drowsiness, headaches, and weakness. Advanced stages are characterized by changes in the skin: the skin turns red and swelling occurs. Local temperatures are 1-2 degrees higher than in undamaged areas. If the disease was caused by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, the lymph nodes will fester and become dense.
Sinusitis
When the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses becomes inflamed, heaviness in the nasal area, thick discharge from it, and high temperature appear. It hurts when moving the head. Adults often develop a cough, runny nose, and discomfort in the throat.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is a disease in which the epithelial lining of the back wall of the pharynx becomes inflamed. Pathology can be non-infectious, bacterial or viral in nature. The disease in most cases is combined with tonsillitis, accompanied by lacrimation and a feeling of congestion in the nose and ears.
Non-infectious pharyngitis develops due to the patient inhaling excessively hot or cold air, toxic vapors, prolonged contact with substances that irritate the mucous membranes: coal, chalk, wood or stone dust, etc. The infectious form of the disease occurs when a streptococcal, staphylococcal, pneumococcal, fungal or viral infection develops in the human body. In this case, pharyngitis is usually caused by a pathology that has spread beyond the source of inflammation: sinusitis, otitis media, etc.
In case of infectious pharyngitis, it is necessary to identify the nature of the causative agent of the disease. Otherwise, treatment may not be effective.
With pharyngitis, patients experience characteristic signs of the disease:
- Pain
. The pain syndrome is dull and localized in the throat. When swallowing, the discomfort increases, causing unilateral discomfort in the ear area. - Sore throat
. The patient constantly has a desire to cough; patients often complain of a painful dry cough. - Hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx
. In rare cases, upon examination, small papules or ulcers may be noted on the surface of the epithelium. - Low-grade fever
with an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38°C.
Pharyngitis therapy is aimed at relieving the symptoms of the pathology and eliminating the factor that caused the disease. The patient is prescribed antibacterial or antiviral agents: Doxycycline, Ampicillin, Acyclovir
etc.
Taking these drugs is necessary in the treatment of infectious pharyngitis. It is also recommended to use sprays with local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects: Hexoral, Strepsils, Chlorophyllipt
.
To treat a disease of a non-infectious nature, the patient should stop smoking, use personal protective equipment when working with irritating substances, and avoid eating spicy or excessively hot foods.