Like any part of our body, our gums can also become injured. The tactics of the planned treatment depend on the volume and nature of the damage received. Only with properly organized treatment will trauma to the gums not leave serious consequences. When any oral disease appears without the necessary treatment, manifestations of a weakened body and complications are possible.
Despite the fact that the gums are protected from the outside by the muscle tissue of the lips, they are easily exposed when talking, eating, or laughing. This is facilitated by the fact that facial muscles in humans are quite well developed. Therefore, gums can easily suffer injuries of varying severity.
Dental periodontitis - what is it?
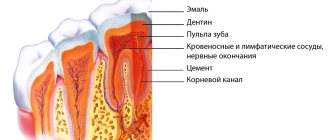
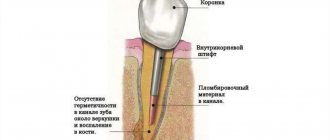
Periodontium refers to the whole complex of tissues responsible for tooth retention: connective fibers, blood vessels, periodontium, gums, canals and jaw bone. Periodontitis is an inflammation of the gum tissue, which quickly affects the rest of the complex. As a result, the dentogingival connection is disrupted and the tooth falls out. Periodontitis is a very common disease that affects more than 95% of the world's inhabitants in various stages: from the rudimentary form of periodontitis to advanced, untreatable.
It is believed that most often the pathology manifests itself in men and women aged 30 to 40 years and in adolescents 16-18 years old. However, the disease can affect anyone, regardless of gender and age, if you do not monitor the condition of your oral cavity and postpone a visit to the dentist. Periodontitis can be treated only in the early stages; when it becomes chronic, no dentist, even the most modern, can cope with it, since the tissues have undergone irreversible changes.
Etiology of periodontitis
Periodontitis can be caused by various factors.
- Microbes.
The oral cavity of any person is inhabited by pathogenic microorganisms that do not cause harm if proper nutrition and hygiene are observed. But, if the patient constantly consumes carbohydrates and neglects to use dental floss, bacteria actively develop and gradually affect the enamel, dentin and reach the periodontal tissues. - Genetic predisposition.
If for many generations all family members have suffered from this disease, there is a high probability of adopting this predisposition. Heredity plays a big role in the development of gum periodontitis, even if a person carefully monitors hygiene and eats right. - Mechanical damage to the gums.
Tissue bruise due to negligence, an incorrect bite, in which increased pressure is applied to a specific area of the gum, or an oversized filling, due to which the tooth puts increased pressure on the gum and damages it. - Systemic diseases.
Dental diseases and periodontitis can cause pathologies not related to the oral cavity, such as vegetative-vascular dystonia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and gastrointestinal diseases. - Autoimmune diseases.
Reduced immunity, disruption of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances during pregnancy. - Poor quality dentist work.
Tissue damage during treatment, an unsuitable crown, incorrectly installed braces and other tissue injuries due to the fault of the doctor can provoke periodontitis.
Among the given factors are microbial causes of the development of periodontitis, and microbes are known to be transmitted from one person to another. So is periodontitis contagious? No, directly, for example, by airborne droplets or through saliva, it is impossible to become infected with the pathology, and every person has microbes that provoke the disease - even if periodontitis bacteria are transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, the microbes will not develop without additional favorable circumstances: poor oral hygiene, gum injuries, predisposition or concomitant diseases.
Symptoms
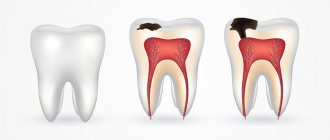
Recession of the adjacent gum edges and a noticeable increase in the length of the teeth are obvious symptoms that do not stop growing and worsening the problem over time. The pathological process begins its journey with one or several units, and if the diagnosis is not determined in time and treatment is not started, then the next stage will be damage to the entire oral cavity. Also, an increased reaction of teeth to temperature and food stimuli will be a warning sign. In the area of the roots of neighboring units, gaps may appear where food will get stuck. The corresponding conditions for the manifestation of the disease will be exposure of the root cement (an area darker in color than the enamel is noticeable) and its damage by caries, bleeding, mobility and loss of units. Therefore, it is important to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as the manifestation of the pathology becomes noticeable.
Symptoms of periodontitis in adults and children
Typically, the signs of periodontitis vary depending on the stage of development of the disease, but there are also general symptoms characteristic of the entire period of pathology:
- unpleasant constant bad breath, plaque and tartar are associated with the active activity of bacteria;
- bleeding and brighter gum color due to tissue inflammation;
- increased sensitivity of teeth, pain when chewing;
- thick viscous saliva;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- headache, weakness and lethargy.
Stages of periodontitis
With each stage, dental periodontitis develops more strongly. Unfortunately, most often patients consult a doctor already with a severe form of the disease.
Mild periodontitis
There is bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth, small periodontal pockets up to 3 mm deep, slight swelling of the gums and discoloration - the tissues look loose and slightly blue. The initial stage is almost painless and can be treated in just a couple of visits to the dentist.
Moderate periodontitis
The gums bleed almost constantly, and small purulent discharge appears. Gum pockets enlarge and expose the roots of the teeth, and the interdental spaces widen. The patient feels the tooth bursting and increased pressure on the gum tissue. It is difficult to cure moderate periodontitis, but it is quite possible if you make an effort and follow the doctor’s instructions.
Severe periodontitis
The gums are completely weakened, the tissues are loose, there is no swelling. Severe tooth mobility and even tooth loss. Bone tissue with severe periodontitis becomes thinner and atrophies. The entire complex is affected - ligaments, muscles, periodontal tissues and blood vessels, and nutrition of the tooth stops. The only thing a specialist can do at this stage is to relieve gum inflammation and recommend tooth extraction for prosthetics.
Varieties
There are several classifications of pathology. According to the degree of damage, the process is divided into local (affects 1 unit) and generalized (from several units to the entire oral cavity).
According to Miller, there are 4 classes:
- The pathology spreads over the entire area of the gum tissue, but the roots are not exposed.
- The process with the periodontal ligament (attachment of the unit to the gum) and exposes the roots up to 0.5 cm.
- The level of the interdental papillae is greatly lowered, the necks of the teeth are exposed.
- The roots are exposed, part of the bone tissue has resolved, interdental papillae are absent.
In specifying the clinical picture of gum recession, its index helps, thanks to which a classification is compiled according to the severity of the process as a percentage.
The index is calculated using a special formula:
Recession index = number of units with exposed neck/number of units per patient × 100%
The index value is based on 0 to 100%. Easy Art. - up to 25% (exposure of roots by 3 mm), medium grade - 26%-50% (up to 5 mm), and severe - over 51% (from 5 mm).
Forms of periodontitis
Types of periodontitis are classified into groups according to different criteria.
By place of development:
- localized - a small lesion affecting only one tooth, and sometimes part of the tooth, for example the root; most often occurs due to mechanical damage to tissue;
- generalized - the damage spreads to a group of teeth, gum and bone tissue, so it seems that half of the jaw hurts; A common cause is the development of bacteria and reduced immunity.
According to the nature of the course:
- acute - pain during periodontitis occurs suddenly, symptoms develop rapidly;
- chronic - advanced periodontitis of the acute stage becomes chronic, pain and other symptoms practically disappear, but the disease continues to progress and destroy tissue.
Exacerbation of periodontitis
The disease does not occur in isolation; periodontitis affects the condition of the entire organism. Even if the pathology has passed from an acute form to a chronic one and it seems to the patient that the pain has gone away and the illness has receded, the destructive effect of the inflammatory process still continues. And the advanced chronic stage can not only worsen, but also cause severe complications of periodontitis:
- osteomyelitis - inflammation of bone tissue;
- abscess and phlegmon - the formation of abscesses and the spread of pus through the tissues;
- lung diseases - pathogenic bacteria from the oral cavity enter the lungs when breathing;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels - a long-term inflammatory process affects the functioning of the heart.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Diagnostics includes a visual examination to determine the presence of problems and analysis of complaints to make a preliminary diagnosis. Then the patient is sent for additional examination:
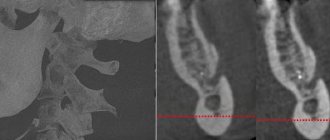
- orthopantomogram - a circular image of the entire jaw;
- X-ray - X-ray of periodontitis on a specific tooth using a targeted image;
- periodontogram - measuring the depth of periodontal pockets;
- urine and blood analysis - determination of infections and diseases in the body.
The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of other dental pathologies; the doctor’s task is to make an accurate diagnosis for effective treatment.
- With periodontal disease, there is no bleeding, swelling of the gums and periodontal pockets, there is no inflammation, since the main cause is age-related changes, diabetes mellitus and cardiac dysfunction. Read more about periodontal disease in a separate article.
- With gingivitis, periodontal pockets and tooth mobility are not observed, there is no exposure of the roots, and inflammation affects only the gum tissue. Find out about the symptoms of the disease here.
- Stomatitis is accompanied by plaque on the tongue and ulcers on the mucous membrane, bleeding and inflammation of the gums, tooth mobility and exposure of the roots are absent. About the types and signs of the disease in a separate article.
Gum recession
Gum recession (ICD-10 code K 06.0) - drooping of the cervical gum tissue and exposure of the root - is a decrease in the level of the gingival margin around one or a group of units relative to others in the oral cavity. At first, gum receding does not cause any discomfort and does not manifest itself in any way, which is why many patients ignore this condition (this approach entails various consequences). Recession provokes the development of aesthetic problems when smiling or talking, and the roots of the teeth are not covered with a protective layer in the form of enamel, so when they are exposed, caries and sensitivity develop. Modern dentistry has accumulated a wide variety of methods for treating recessionary pathology, which means there are opportunities to avoid complications and violations of aesthetics.
To help patients treat gum recession and prevent severe consequences, our specialists from various fields will provide advice at an attractive price. Dentists from the branches of the West Dental family clinic in Yanino-1 and Vsevolozhsk are always ready to perform professional and effective defect closure at a more reasonable price than in St. Petersburg.
Our dentists treat on the latest equipment, using a Leica M320 operating microscope and Pax-i3D panoramic CBCT.
Treatment of periodontitis
Treatment of periodontitis in the early stages consists of removing plaque and tartar, cleaning periodontal pockets and drug therapy: local treatment of tissues with anti-inflammatory drugs, taking antibiotics and strengthening the immune system.
Moderate to severe disease requires complex therapy for periodontitis. In addition to sanitation of the oral cavity and taking medications, it includes splinting teeth to keep them from moving, surgery to remove pus and affected tissue, consultation with a therapist, immunologist and gastroenterologist to prevent relapse; in the case of an advanced form of the disease - examination by a prosthetist and subsequent restoration of lost teeth using crowns. Read more about the treatment of periodontitis in our article.
Dentists always aim to preserve the patient’s natural teeth, but in cases of severe periodontitis, often the only solution is tooth extraction. You shouldn’t let your oral cavity reach this state; seeing a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease gives you a 100% chance of recovery—the early stages of periodontitis can be treated quickly and without complications. And regular visits for preventive examinations completely exclude the occurrence of any dental diseases.
Diagnostics
Carrying out differential diagnosis to determine the treatment method, the doctor identifies the pathogenesis of the disease. The origin of gum recession is classified to select the appropriate treatment:
- Traumatic. The pathology affects the vestibular surface of the units. The level of gingival tissue decreases by 1–2 mm and it does not become inflamed, but reactivity to irritants increases.
- Symptomatic. All dental surfaces of the teeth are affected and the cause is lack of proper hygiene. Therefore, there are symptoms in the form of inflammation and swelling of the gums, mobility of units.
- Physiological. It is a consequence of age-related changes and decreased tissue tone. It is asymptomatic.
Also, the specialist performs a temperature test (specifying the degree of sensitivity) and an x-ray (the condition of the hilar bone tissue).
Methods of treating and correcting the defect
Basically, a periodontist, a specialist in mucous membranes and gingival tissue, knows how to stop gum recession. If, during a diagnostic examination, he identifies the cause of the pathology that needs correction by a related specialist, he will be referred to an orthodontist, orthopedist, surgeon, or therapist.
Methods for eliminating and correcting pathology:
- Selecting the right dental care products at home. Active actions of the patient during brushing can lead to damage to the gums, which means you should choose the right brush and paste. To help, you need to purchase a super-floss and irrigator.
- Correction of braces. Gum recession will go away after the traumatic factor is eliminated and the braces are fixed, taking into account all individual nuances. The interdental papillae and adjacent gums will be restored.
- Prof. cleaning the oral cavity. Ultrasound cleaning and Air Flow will remove soft plaque and stones. There will be no favorable conditions left for the development of pathology, which will allow one to avoid pathological symptoms.
- Drug therapy. Applications and dressings with NSAIDs and healing drugs, administration of vitamins and antibiotics, application of self-absorbing membranes. Possibly a herbal rinse.
- Filling. When there is a combination of cervical caries and slight exposure of the neck of the tooth, as well as non-inflamed gums, it is possible to apply a filling material. Aesthetic rehabilitation and sensitivity reduction are achieved.
- Plasmolifting. A composition of the patient’s own blood (plasma with platelets and growth factors) is injected into the patient’s gums. Tissue restoration occurs quickly.
- Hyaluronic acid. The drug interacts with water molecules, saturating and regenerating soft tissues. In combination with plasma lifting, an effective result is achieved.
- Collagen treatment. Natural collagen implants are implanted, which dissolve on their own over time. For age-related pathology, this treatment for gum recession in St. Petersburg is very effective.
- Surgical intervention. Flap operations and curettage remove excess deposits from under the gums, and also increase the volume of the patient’s healthy mucous tissue. It is performed under local anesthesia.
- Tunnel method. The most atraumatic technique for increasing gingival volume. The graft for transplantation is taken from the patient's palate, where regeneration of the area will occur quickly and painlessly.
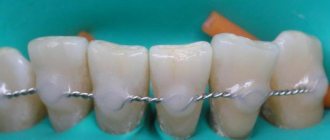
- Splinting is the bonding of units with fiberglass tape. Such manipulation will strengthen the mobile units for some time.
- Plastic surgery for gum recession (gingivoplasty). One of the mechanisms in the field of surgery is to grow tissue. A gingival flap is transferred to the pathological area using the method of a free connective tissue graft (plastic) from the tubercle of the upper jaw or the hard palate.
- Physiotherapy. Tissues are supported by magnetic current, laser, and UV radiation. Blood supply, functioning, nutrition and metabolism in the area of soft tissue structures improves.
- Implantation with immediate loading. A radical solution to a problem in an advanced stage. Damaged units are removed and complex implantation is carried out with the installation of a temporary prosthesis.