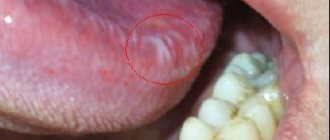
Leukoplakia - what is it?
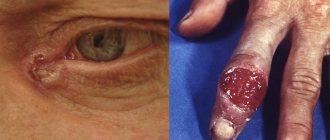
Leukoplakia refers to the presence of small areas of altered mucosa. This nonspecific process can be found in any organ where there is a mucous membrane, but most often it occurs in the oral cavity and on the genitals.
We can talk about the problem as a precancerous condition, since it has the potential to develop into a malignant tumor.
With this nonspecific process, the appearance of an area of dense cells of the surface epithelium is observed. In a normal state, there is a regular process of death and exfoliation of the upper layers of the skin and mucous membrane. As the pathology develops, it disrupts it, thus the cells that have died do not disappear and form a multilayered whitish island.
Uterus and reproductive organs
The female reproductive system is represented by the mammary glands and pelvic organs.
The main function of these organs is procreation. The gonads produce regulatory substances that affect the development of the reproductive system and other organs. The most important structures are the ovaries, in which the maturation of female germ cells occurs. During ovulation, the reproductive cell leaves the ovarian follicle and enters the fallopian tube. The fusion of male and female reproductive cells in this organ leads to the formation of the rudiment of a new organism. The remaining stages of embryo development occur in the lumen of the uterus. The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located next to the rectum, vagina, ovaries and bladder. The uterine cavity is connected to the external environment through the cervical canal and the vaginal opening. The fallopian tubes allow the fertilized egg to migrate to the uterus. Attachment of the embryo to the inner layer (endometrium) of the organ is necessary for the formation of embryonic organs.
The main part of the cervix is the narrow cervical canal, which connects the vaginal opening to the uterine cavity. This anatomical structure is necessary for the transport of sperm into the fallopian tubes. The mucous membrane of the cervical canal contains a large number of glands that secrete a special fluid. Gynecologists include the functions of cervical mucus as protection against pathogenic microorganisms and ensuring the transportation of sperm. Smooth muscle and elastic fibers of the cervix provide expansion of the cervical canal during childbirth.
Etiology of oral leukoplakia
The etiology of oral leukoplakia includes some external (exogenous) irritants that act for a very long time, that is, they have already entered the chronic stage.
- Mechanical factors:
- Rough food;
- Poorly fitted removable dentures;
- Poor quality fillings;
- Anomalies of teeth position;
- Bite abnormalities;
- Destroyed tooth crowns;
- Galvaniz;
- Bad habits
- Chemical irritants:
- Household factors (passion for spices, smoking, ethyl alcohol);
- Production factors (exposure to bromine, iodine, acids);
- Temperature irritants;
- Meteorological factors;
- Special attention is also paid to the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Pathological conditions such as gastritis, ulcers, enteritis and colitis lead to a decrease in the resistance of the mucous membrane to the action of pathogenic factors
- Anemia;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Anatomy - physiological factors;
Causes
The exact causes of leukoplakia are unknown. Gynecologists associate the etiology of this disease with pathological external and endogenous influences. Thus, a significant increase in estrogen production against the background of progesterone deficiency can trigger the development of the disease. Hereditary factors play an important role in the formation of leukoplakia: certain genetic mutations can cause epithelial changes.
Possible reasons:
- Diseases of the endocrine system. The endocrine glands regulate the development of all organs, including the structures of the reproductive system. The greatest risk of developing cervical leukoplakia is associated with a disorder of the pituitary gland and ovaries. Diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands can also be complicated by damage to the cervix.
- Chronic infections and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic cavity. In particular, human papillomavirus infection directly affects the condition of the cervical epithelium.
- Sexually transmitted infections including chlamydia, gonorrhea and herpes. Sexually transmitted diseases affect the condition of the external and internal genital organs.
- Mechanical damage to the cervical epithelium that occurs during trauma, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Artificial termination of pregnancy leads to tissue trauma.
- Mutation of the gene responsible for suppressing the growth of tumor cells. According to research, a mutation in the p53 gene, which controls cell development, leads to impaired tissue growth.
Normally, the outer lining of the cervix is represented by stratified non-keratinizing epithelium. Certain diseases can affect the internal structure of epithelial cells. Changes in the regulation of epithelial cells lead to keratinization and thickening of the outer layer of the membrane. It is assumed that one of the mechanisms of cell changes is the expression of a mutant gene.
Causes
Medicine cannot give a definite answer as to what causes the nonspecific process. It can be assumed that there is a cause-and-effect relationship with local inflammation over a long period.
Long-term trauma can be identified as the main causes:
- Mechanical injury;
- Chemical injury;
- Physical injury;
- Operating trauma.
The development of the process against the background of a form of chronic trauma to the mucous membrane occurs due to:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Infection with papilloma virus, caries;
- Generalized process of infection;
- Decreased immunity;
- Metabolic diseases.
Hereditary predisposition to degenerative processes also initiates the development of the process of keratinization disorders.
Risk factors
In addition to the direct causes of cervical leukoplakia, gynecologists recognize the importance of certain forms of predisposition to the disease associated with heredity, individual history and a woman’s lifestyle.
Known risk factors:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities;
- drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- radiation therapy of the pelvic organs;
- insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements from food;
- metabolic diseases;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- detection of leukoplakia or cervical carcinoma in a close relative.
Eliminating some of the risk factors listed above is an effective method of preventing the disease.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia
| We start by organizing feelings and thoughts and achieve success with the help of natural medicines and spa factors. There is EXPERIENCE, there are RESULTS, there are ways to ACHIEVE stable remission. |
CLINIC FOR TREATMENT OF LEUKOPLAKIA - this is the name of the Resort Clinic for Women's Health in Pyatigorsk by satisfied patients from many cities of Russia, near and far abroad, who have achieved a state of stable remission of leukoplakia.
TREATMENT OF LEUKOPLAKIA OF THE VULVA is one of the priority areas of scientific and practical activity of our Clinic.
For more than 20 years, we have been SUCCESSFULLY TREATING VULVAL LEUKOPLAKIA, achieving STRONG REMISSION and a clear improvement in the quality of life.
In the treatment of leukoplakia, we do not use painful and traumatic methods and give PREFERENCE to physiological, effective and time-PROVED treatment METHODS.
At the Women's Health Resort Clinic, TREATMENT OF LEUKOPLAKIA begins with psychometric testing.
PSYCHOMETRIC TESTING allows us to identify the underlying psychological causes of leukoplakia.
Based on the results of psychometric testing, we carry out PSYCHOLOGICAL CORRECTION in order to normalize the processes of excitation-inhibition in the cerebral cortex and hormonal levels.
Normalization of the psycho-emotional state based on the experience of doctors at the Women's Health Resort Clinic is the pathogenetic basis for the successful treatment of vulvar leukoplakia.
The study of immune status (IMMUNOGRAM) allows you to IDENTIFY and individually correct DISORDERS of the immune system (immunity) using natural medicines.
Modulation of brain rhythms restores the physiological (correct) alpha rhythm of brain activity and persistently SENSORS the effect of psychological and immunological correction. About the modulation of brain rhythms in detail...
For the purpose of comprehensive correction of psycho-emotional, immune and hormonal disorders in the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia, the Women's Health Resort Clinic uses herbal medicine and modern physiotherapeutic procedures.
Medicines made from mineral and herbal raw materials according to the prescriptions of doctors at the Women's Health Resort Clinic have a tranquilizing effect on the state of the cortex (the "mental" part) of the brain, NORMALIZE metabolism at the cell and tissue level, "gently" CLEANSE the liver, kidneys, intestines, and normalize the immune system. and metabolic processes in the body, STIMULATE ovarian function and STABILIZE (normalize) hormonal levels, regular and timely ovulation, thickness and structure of the endometrium during the ovulation period, have a general sanogenic effect (promote self-healing of the body), reduce the drug load on the body and significantly increase the EFFECTIVENESS of treatment .
The use of rectal suppositories in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetophoresis, laser phoresis, sonophoresis, darsonval) allows the delivery of drugs to the basal (deep) layers of the skin and mucous membrane of the vulva.
| This modern technique significantly slows down the activity of degenerative processes in the skin and mucous membrane of the vulva and actively regenerates (restores) altered tissues. About homeopathy in detail... |
Our experience in spa treatment shows that the use of medicines based on natural raw materials is an important physiological (corresponding to human physiology) component of the treatment of leukoplakia.
REGENERATING MICROINJECTIONS of the skin and mucous membrane of the vulva relieve (stop or significantly reduce) unpleasant sensations and itching in the vulva area, which arise in some cases as manifestations of a degenerative process in the skin and mucous membrane.
In addition to the above, regenerating microinjections RESTORE the structure of COLLAGEN and cells of the deep (germ) layers of the skin and mucous membranes. Thus, regenerating microinjections restore damaged or lost ELASTICITY of vulvar tissue.
| The technology of regenerating microinjections with natural medicines for vulvar leukoplakia is a successful scientific development of the Women's Health Resort Clinic. |
Modern physiotherapeutic procedures (modulation of brain rhythms, elective regulation of the menstrual cycle, transcranial immunocorrective magnetic therapy, percutaneous laser blood treatment, ILBI) correct biological rhythms and psycho-emotional state, normalize metabolism, i.e. have a SYSTEMIC sanogenic EFFECT (normalize the constancy of the internal environment - “the secret wisdom of the human body”) and HELP consolidate the effects of psychological and immunological CORRECTION.
All physiotherapeutic procedures at the Women's Health Resort Clinic are performed painlessly, psychologically comfortably and carefully by professionally trained midwives.
Contraindications to physiotherapeutic procedures are general contraindications to physiotherapy: stage III hypertension, oncological processes in the body, severe somatic (therapeutic) diseases in the stage of decompensation. Contraindications to each specific physiotherapy procedure are discussed in detail in the article “Physiotherapy”.
A PRIMARY APPOINTMENT with a gynecologist, examination and treatment of leukoplakia is possible on ANY DAY of the menstrual cycle, except for menstrual days.
In the absence of menstruation in the premenopausal and menopausal periods, an initial appointment with a gynecologist, examination and treatment of vulvar leukoplakia is possible on any calendar day.
There are no RESTRICTIONS or peculiarities of nutrition and physical activity during the period of resort treatment of vulvar leukoplakia.
During spa treatment of vulvar leukoplakia, the best physical activity is a health path (dosed walking taking into account the natural landscape). About the health path in detail...
Clinical and laboratory examination includes
- consultations with a gynecologist-endocrinologist;
- extended vulvoscopy (colposcopy);
- 3D ultrasound of the pelvis;
- microscopic examination of smears from the vagina, cervical canal and cervix for flora and atypical cells;
- PCR examination of smears for human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk;
- clinical blood test;
- immunogram.
The examination can be performed at the Clinic on the day of the initial appointment or at your place of residence.
The survey results are VALID for 6 months from the date of completion.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia begins on the FIRST DAY of treatment (arrival) at the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk.
THE DURATION of an intensive course of TREATMENT for vulvar leukoplakia is 12-14 days.
| THE COST of a 14-day course of treatment for vulvar leukoplakia is 54,240 rubles. THE COST OF TREATMENT for vulvar leukoplakia is adjusted (downward) taking into account the individual characteristics of the severity of the process. |
*The cost of treatment of vulvar leukoplakia is current since the last update of the price list (November 2022).
In case of EXTENSIVE LEUKOPLAKIA of the vulva, observation and correction of the state of the immune system is carried out once every 3 months.
AT THE COMPLETION of the course of treatment for vulvar leukoplakia, based on the dynamics (changes) of the condition against the background of intensive treatment, we prescribe individual maintenance therapy for 6 months.
Maintenance therapy with natural medicines allows you to CONSTAIN the achieved positive RESULTS of intensive treatment of leukoplakia.
The resort clinic for women's health operates on a paid basis and in the voluntary health insurance system.
Each doctor at the Clinic has long-term experience, several specializations and is able to comprehensively assess the situation.
Classification
There are two main types of cervical leukoplakia, differing in morphological and functional features. Determining the specific type of disease is possible only with the help of histological examination. Different morphological forms of leukoplakia differ in the risk of malignant degeneration.
Forms of the disease:
- Simple leukoplakia, characterized by coarsening of the outer layer of the epithelium and excessive cell division. Significant morphological changes in the cells of the basal layer are not detected.
- Proliferative leukoplakia. This form of the disease is characterized by a violation of cell specialization and the appearance of specific morphological changes. Proliferative leukoplakia is considered a precancerous condition.
Determining the form of the pathology is necessary to select treatment.
Types of leukoplakia
How to treat leukoplakia depends on its type. The disease is dangerous because pathological processes in the epithelium can become malignant and provoke oncological tumors.
Today, medicine distinguishes three categories of leukoplakia.
- Simple. The formations are located flush with the epithelium. They are usually white in color and the changes are benign.
- Proliferative. It is expressed in dense growths rising above the epithelium. There are warty and scaly forms.
- Erosive. Characterized by cracking and bleeding lesions. This form is the most dangerous because the structures contain atypical cells.
Symptoms
In most cases, the disease does not manifest itself symptomatically. In itself, the coarsening of the outer epithelium of the cervix does not lead to dysfunction of the organ, so the pathology can remain undiagnosed for a long time. Typically, leukoplakia becomes an incidental finding during a gynecological examination.
Possible symptoms:
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- pain during menstruation;
- bloody issues;
- excess vaginal discharge.
The appearance of frequent uterine bleeding not associated with menstruation and pain may indicate the transformation of leukoplakia into a malignant tumor.
Clinical manifestations
Treatment of leukoplakia of the vagina or uterus is prescribed depending on the manifestations and symptoms. Women with this pathology may complain of the following types of discomfort:
- insufficiency of vaginal secretion;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during urination;
- cracks on the labia;
- spots on the mucous membrane;
- warts;
- erosion;
- genital discharge;
- scales.
Often the lesions do not cause discomfort, remaining unnoticed by the patient. This is why regular visits to the gynecologist are necessary. You can find a doctor you can trust at the Dr.AkNer clinic. We employ the best specialists with extensive experience in the treatment of women's diseases.
Diagnostics
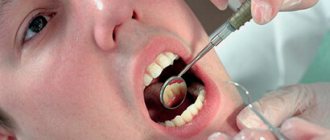
If risk factors for the disease are detected, you must make an appointment with a gynecologist. During the consultation, the doctor will ask the woman about her complaints and examine her medical history. Then an initial examination of the genital organs is carried out, including palpation examination and the use of mirrors to assess the condition of the cervix. If suspicious changes are detected, the gynecologist prescribes instrumental and laboratory tests.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- Colposcopy is a method of visual examination of the cervix. The doctor asks the patient to sit in the gynecological chair. A colposcope equipped with optics and a light source is carefully inserted into the cervix through the vaginal opening. The gynecologist studies in detail the condition of the epithelium of the organ. Treatment of suspicious areas with iodine solution makes it possible to detect pathological changes in tissues. If necessary, the optics are replaced by a video camera, allowing the specialist to see a clear image of the organ tissue on the monitor. Colposcopy is a reliable and safe examination that does not require anesthesia.
- Scraping of cervical epithelial cells. During a colposcopy, the doctor inserts a special instrument into the organ cavity to collect cells from the suspicious area. Cytological examination of the obtained material in the laboratory makes it possible to evaluate morphological changes and determine the form of leukoplakia. Cytology is a reliable method for excluding malignant tissue degeneration.
- Cervical biopsy. If the epithelium is severely coarsened, the doctor cannot obtain cells from the lower layers of leukoplakia by scraping. In this case, a knife biopsy is the optimal diagnostic procedure. Using a special instrument, the specialist excises the required amount of tissue. Cytological examination of the biopsy is also necessary to exclude the growth of malignant cells. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. If necessary, the gynecologist prescribes complete curettage of the epithelium of the cervical canal.
- Microbiological examination of the material. Tissue obtained by scraping or smear can be used to rule out infection. Special nutrient media give a specialist the opportunity to identify the causative agent of the disease.
- Blood analysis. In the treatment room, a nurse collects venous blood from a patient. Laboratory examination of the material is carried out to detect signs of inflammation and infection. Serological tests aimed at searching for specific immunoglobulins are necessary to exclude sexually transmitted diseases. If an HPV infection is suspected, sections of the DNA of the virus are searched using polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
The scope of diagnosis depends on the results of colposcopy and general examination. The main goal is to eliminate the risk of malignant tissue degeneration.
Leukoplakia of the cervix
The article was checked by an obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D. Sazonova Yu.M. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Visit your gynecologist regularly for preventive care. Leukoplakia is asymptomatic. — At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, experienced doctors will conduct a comprehensive examination to identify cervical leukoplakia, including simple and extended colposcopy, cytological, bacteriological, and morphological examination. — When identifying leukoplakia, we use the most effective and safe treatment methods (radio wave surgery and laser treatment of leukoplakia). This will minimize the risk of complications and will not interfere with future pregnancy and childbirth.
- The frequency of cervical leukoplakia in the population is not very high and amounts to just over 1%, and in the structure of cervical diseases it is about 5%.
- Despite the fact that this pathology is not very common, in almost 32% of cases in patients with cervical leukoplakia, malignant transformation of stratified squamous epithelium is observed.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment make it possible to cope with the disease and preserve the life and health of a woman even if the process becomes malignant.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a nonspecific process in which thickening and keratinization of the squamous epithelium covering the vaginal portion of the cervix occurs. As a result of this process, a spot of white plaque forms on the surface of the cervix, visible to the naked eye when examining the cervix.
Causes of cervical leukoplakia
All causes of the disease can be divided into two groups:
- Internal - changes in hormonal levels.
- External - infectious, including diseases caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), traumatic - abortion, childbirth, inadequate treatment of cervical diseases (intensive drug treatment), surgical interventions on the cervix (in particular, diathermocoagulation).
- In the group at increased risk of developing cervical leukoplakia are patients with menstrual irregularities, recurrent pseudo-erosion of the cervix, and inflammatory gynecological processes.
Leukoplakia is a benign formation, but can sometimes develop against the background of malignant processes caused by damage to the cervix by the human papillomavirus.
Symptoms of leukoplakia
The disease is practically asymptomatic, even in advanced cases, and is detected during a gynecological examination. In some cases, vaginal discharge and bleeding are possible. Leukoplakia with such symptoms raises concerns about a malignant process.
Diagnosis of leukoplakia
Gynecologists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital make a diagnosis after a detailed conversation, gynecological examination, colposcopic, cytological, histological, and bacteriological examinations.
Foci of altered mucosa, visible to the naked eye during a gynecological examination, are a clinically pronounced form of leukoplakia. Spots detected only during colposcopy are a colposcopic form of leukoplakia.
Colposcopy - examination of the cervix with high magnification - is the most informative method for identifying leukoplakia in women. It makes it possible to clarify the nature of leukoplakia, the size of the mucosal lesion, and assess the condition of the epithelium.
Subtle, questionable lesions appear when performing the Schiller test . It involves treating the cervix with special solutions, in which the normal mucosa is stained (positive Schiller test, normal), but the pathologically altered mucosa due to leukoplakia is not (negative Schiller test, pathology).
Bacteriological examination - detects the presence of pathogenic microflora, including high-risk HPV strains. Helps select drugs to which the identified microflora is sensitive.
A cytological examination of a scraping of the cervix reveals pathological ones, including atypical cells in the epithelium, and if detected, a tissue biopsy is indicated.
Histological (morphological) examination of a small sample of cervical tissue taken during a biopsy is aimed at excluding tumor processes. In addition, if necessary, histological examination is carried out in conjunction with histochemical analysis to identify markers of the malignant process and individual selection of pharmacotherapy.
Forms of leukoplakia
Simple leukoplakia without atypia is considered a benign underlying disease. Leukoplakia with cell atypia is already a precancerous process. Divided depending on the severity of cell atypia.
Treatment of leukoplakia at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Stage 1. If inflammation is detected in the vaginal area, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out.
Stage 2. Then one type of surgery is performed to remove foci of leukoplakia. The operation is performed on days 4-7 of the cycle so that the wound heals before the next menstruation begins.
Important! With severe widespread leukoplakia after surgical treatment, the formation of cicatricial deformation of the cervix is possible, which can lead to miscarriage due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency and problems during childbirth. Therefore it is very important:
- promptly detect the disease and carry out treatment in the early stages,
- correctly assess the indications for surgery;
- use modern medical technologies when choosing surgical treatment methods.
Specialists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital, trying to avoid unwanted trauma to the cervix and associated consequences, carry out surgical treatment of cervical leukoplakia only according to strict indications, when there is a significant risk of developing a malignant process. We use modern effective methods such as radio wave surgery and laser exposure.
Laser. The effect of a laser beam is painless and non-traumatic, the recovery period proceeds almost unnoticed by the patient. The risk of recurrence of leukoplakia after laser treatment is much lower than after electrosurgery. Healing occurs without the formation of a rough scar.
Radio wave. Radio wave surgery is practically bloodless, according to patients, it is painless, does not cause the formation of scabs and scars after the operation, and does not interfere with future pregnancy and natural childbirth.
Stage 3. After surgery, patients are recommended to have sexual rest for 1 month. To speed up regeneration, vaginal suppositories with methyluracil can be prescribed. Control examinations are carried out after 1, 3 and 6 months.
Make an appointment
You can see prices for services
Treatment
The treatment method depends on the form of leukoplakia and the patient’s individual medical history. Due to the high risk of transformation of the pathology into carcinoma, it is recommended to remove the focus of the changed tissue. In some cases, the gynecologist prescribes drug therapy. Prescribed medications may include antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. Treatment of the root cause of the disease helps prevent relapse.
Pathology removal methods:
- Cryosurgery is the use of cold to destroy the affected epithelium. During the procedure, the patient is in a gynecological chair. After inserting the dilator into the cervix, the surgeon uses a special probe, the tip of which is cooled with liquid nitrogen. Destruction of leukoplakia takes 5-10 minutes. Cryosurgery is not accompanied by tissue trauma or severe pain.
- Radio wave destruction. A special device inserted into the cervix affects the tissue. This is a safe and fast treatment method with a low risk of complications.
- Other methods of minimally invasive removal of the disease, including chemical cauterization and argon plasma coagulation. The duration of rehabilitation after such interventions does not exceed 2 months.
If the gynecologist detects signs of malignant degeneration of leukoplakia, radical methods of surgical treatment are prescribed. The doctor needs to remove not only the pathological focus, but also the cells surrounding it. This is important to prevent abnormal cells from migrating into neighboring tissues.
Other methods of surgical treatment:
- Conization of the cervix. Using a special instrument, the specialist applies radio waves to the organ and removes the affected part of the cervix. This is a low-traumatic procedure that allows you to preserve reproductive function.
- Amputation of the cervix - removal of the affected segment of the organ. The disadvantage of this method is the high degree of tissue trauma, but the operation allows you to preserve the integrity of the reproductive system.
During treatment of the disease, the doctor asks the patient to abstain from sexual intercourse and taking hormonal contraceptives.
Classification of oral leukoplakia
There are many classifications of oral leukoplakia, which mainly take into account the clinical manifestation of oral leukoplakia. I will present one of them. Classification of oral leukoplakia according to A.L. Mashkilleyson:
- Simple or flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity;
- Verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity;
- Erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia of the oral cavity;
- Tappeiner's leukoplakia;
- Soft leukoplakia.
Most often, leukoplakia of the oral cavity is localized along the line of closure of the cheeks, in the area of the mouth, on the front of the tip of the tongue, on the floor of the mouth, on the hard palate, and sometimes on the alveolar process. The clinical picture of oral leukoplakia will depend not only on the location of the lesion elements, but also on the stage of leukoplakia. So the process of leukoplakia begins with the pre-leukoplastic stage - a slight inflammation of the mucous membrane, which quickly succumbs to keratinization. The area acquires a cloudy white tint, sometimes bluish, easily taken into a thick fold, painless on palpation. With further progression of the disease, the focus of leukoplakia will seem to become higher than other areas of the oral mucosa, at this moment the focus most often becomes malignant (metaplastic changes occur). Thus, all clinical forms of leukoplakia are a single pathological process.
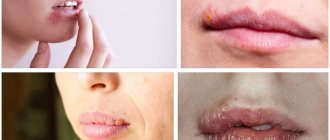
Oral flat leukoplakia
Complaints with flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity
Complaints with flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity are most often absent. Some patients note a cosmetic defect, a whitish tint on the mucous membrane or on the red border of the lips. No other subjective features are noticed.
Symptoms of flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity
The main symptom of flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity is the appearance of a whitish spot with clear contours on the oral mucosa. The spot can be of various shapes, but is often large. The stain is covered with a coating that does not come off even when scraped.
If flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity is located along the line of closure of the teeth, then it looks like an uneven strip. In the retromolar region, the lesion has a star shape. On the mucous membrane of the lips, flat leukoplakia is compared to tissue paper or individual strips (like wood).
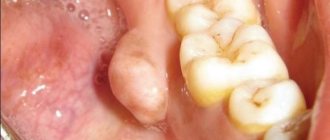
Verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity
Verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity is a continuation of the progression of flat leukoplakia of the oral cavity.
Complaints with verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity
Complaints with verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity are reduced to subjective sensations when talking or chewing food. Patients note dryness and flaking, and are constantly thirsty due to dry mouth.
Symptoms of verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity
Verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity occurs in two forms.
The plaque form of verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity is characterized by multiple foci in the form of plaques rising above the oral mucosa. They have an irregular shape and a rough surface.
The warty form of verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity is more common than the plaque form of verrucous leukoplakia. The lesions have the appearance of tuberous formations, which are sometimes found in the form of growths that rise above the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity most often becomes malignant, this is associated with constant trauma to the keratosis areas. Since areas of verrucous leukoplakia are often located next to carious decayed teeth, incorrectly installed crowns/dentures, etc.
The color of the areas of verrucous leukoplakia varies from milky white to yellow; if the color changes to brown, it means that the process has become malignant. The mucous membrane surrounding the lesion is hyperemic, but only slightly. Regional lymph nodes are not palpable.
Erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia of the oral cavity
Erosive - ulcerative leukoplakia most often occurs in middle-aged and elderly men.
Complaints with erosive and ulcerative leukoplakia of the oral cavity
Complaints with erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia boil down to a burning sensation, itching, and sometimes pain, which intensifies when eating food or water, and sometimes there may be bleeding.
Symptoms of erosive and ulcerative leukoplakia of the oral mucosa
The main symptom of erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia of the oral cavity is the appearance of an erosion site on the oral mucosa, the size of which reaches up to 0.5 cm in diameter. Several areas of erosion may be observed, which are separated from each other by healthy oral mucosa. Around the erosions there are foci of inflammation of the oral mucosa, such as simple or verrucous leukoplakia of the oral cavity. Most often, such erosions do not heal, but progress and become malignant. A sign of malignancy of erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia is a sudden thickening at the base of the lesion (most often on one side), bleeding and papillary growths may be observed.
Soft oral leukoplakia
Soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity is the only form of leukoplakia of the oral cavity, which is identified as a separate nosological disease.
Causes of soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity
The causes of soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity are considered to be neuro-emotional overexcitation, stress, psychosis, neuroses, and overwork.
From the anamnesis it turns out that the patient smokes heavily, has bad habits such as biting or licking lips, drinking strong and hot drinks, a large number of carious teeth, and dental plaque.
Soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity is more common in men aged 17 to 45 years; in women, soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity is observed less frequently.
Complaints with soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity
There are no complaints with soft leukoplakia. Most often, soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity is discovered during professional examinations or during oral sanitation. With mild leukoplakia of the oral cavity, there may be complaints about the feeling of peeling of tissue, the appearance of excess tissue, and changes in taste sensitivity. Patients most often bite down areas of keratinized tissue without feeling pain.
Symptoms of soft oral leukoplakia
A symptom of soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity is the appearance of an area of keratosis, that is, keratinization. The area may be limited or diffuse. If the area is limited, then it is localized on the mucous membrane of the cheeks along the line of closure of the teeth).
An area of soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity of a whitish hue, without signs of inflammation, is removed with a spatula.
There are two forms of soft oral leukoplakia. Typical or atypical.
Most often, the typical form of soft leukoplakia of the oral cavity is represented by a focal form, and it can be differentiated from the atypical form due to complaints of peeling and dryness in certain areas. In the atypical form, areas of soft leukoplakia of the oral mucosa are diffuse in nature, with no peeling or dryness noted. Sometimes this form of soft leukoplakia is represented only by a raised line above other areas of the mucous membrane on the cheeks along the line of closure of the teeth.
Prevention and prognosis
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. The absence of human papillomavirus infection and dysplasia indicates a low risk of malignant tissue degeneration. Surgical intervention not only eliminates the risk of organ malignancy, but also preserves reproductive function. After treatment, the gynecologist regularly conducts examinations to eliminate the risk of relapse.
Simple medical recommendations can reduce the likelihood of leukoplakia and other diseases of the reproductive system. Prevention methods are aimed at changing lifestyle and eliminating negative external factors.
Basic methods of prevention:
- use of hormonal drugs only under the supervision of a physician;
- regular gynecological examinations;
- keeping a calendar of the menstrual cycle and contacting a doctor if disorders occur;
- refusal of alcoholic beverages and cigarettes;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases of the genital and endocrine organs;
- using a latex condom;
- sexual intercourse only with a trusted partner (HPV infection can be transmitted even when using a condom).
A consultation with a gynecologist or oncologist will help a woman learn more about the risk factors for leukoplakia and treatment methods for this disease. If necessary, the doctor immediately conducts an examination and excludes the presence of suspicious changes in the cervix.
Prevention of leukoplakia
The key measures for the prevention of leukoplakia are basic rules of personal hygiene and strengthening the immune system:
- regular hardening;
- sufficient physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of any disorders;
- regular preventive examinations;
- giving up bad habits, heavy and spicy foods that irritate the esophagus;
- careful intimate hygiene and visiting a gynecologist;
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations during a preventive examination.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Causes of oral leukoplakia
- taking strong medications (in particular, antibiotics, as well as constant use of drugs of various spectrums of action in large quantities);
- smoking, as harmful components penetrate through cigarettes and deplete the mucous membrane;
- poor nutrition and abuse of spicy, salty and sour foods;
- chronic gum disease in an advanced stage;
- abundant carious lesions of teeth;
- incorrectly placed fillings;
- incorrectly selected dentures that cause an allergic reaction;
- alcoholism;
- hormonal changes;
- bite problems;
- diabetes;
- HIV infection;
- avitaminosis;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- stress;
- hereditary predisposition;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- harmful production activities.
Typically, at the initial stage, oral leukoplakia can be completely asymptomatic. That is why it is very important for people who are susceptible to risk factors to undergo regular dental examinations for prevention. The 32 Dent dental network will help you, even if the disease is in an advanced stage.
Leading specialists in the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in the Southern Federal District
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna is a well-known and recognized specialist in the North Caucasus in the treatment of leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix, diagnosis and treatment of kraurosis, lichen sclerosus, Keir's erythroplasia and other diseases of the vulva. One of the authors of the method of regenerating microinjections for the treatment of leukoplakia. Desperate people turn to her and women exhausted by suffering. Experienced gynecologist, physiotherapist-health resort specialist, ultrasound doctor.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-endocrinologist with 25 years of experience and successful experience in the treatment of dysplasia, kraurosis and leukoplakia of the vulva Able to see relationships that elude others
About the doctors of the Clinic in detail...
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
The resort women's health clinic is open 7 days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk by appointment no later than 3 days in advance by multi-channel phone number 8 (calls within Russia are free), or (for foreign calls).
| ONLINE information about the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk can be found at REGISTER ONLINE for leukoplakia treatment here. REGISTER online for leukoplakia treatment here. You can buy a COURSE for treatment by phone or here. |
Booking a course
The doctors of the Women's Health Resort Clinic have gained EXTENSIVE EXPERIENCE in treating vulvar leukoplakia, vaginal leukoplakia, cervical leukoplakia using natural medicines and resort factors.
We accept women from all cities of Russia, near and far abroad.
The spa clinic for women's health facilitates the accommodation and accommodation of women, women with children and couples during examination and treatment.
ACCOMMODATION in Pyatigorsk is NOT INCLUDED IN THE PRICE of the treatment course and is paid separately.
About living conditions and transfer from Mineralnye Vody airport and Pyatigorsk railway station in detail in the article “Accommodation”.
If you need to book accommodation, please coordinate your arrival date no later than 7 days in advance.
We are at your complete disposal if you have any doubts or wishes.
What it is
It is believed that leukoplakia occurs against the background of chronic irritation of the oral mucosa and is a kind of protective reaction of the body. This is a local reaction and is not transmitted through contact with a sick person.
The disease is not so harmless, since it most often occurs shortly before the development of oral cancer. Many people mistakenly believe that leukoplakia itself is cancer, however, this opinion is incorrect. This disease affects the epithelial covering of the oral cavity in response to constant external irritants; vitamin deficiency, a decrease in the level of immunity and the presence of chronic foci of inflammation in the oral mucosa serve as an additional impetus for its development.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity is a significant lesion of the mucous membrane of the lips, tongue, cheeks, upper and lower palate, manifested by keratinization (hardening) of the epithelial cover to varying degrees. Doctors usually classify leukoplakia as a disease that precedes the development of a tumor.
The greatest risk of developing this disease are men in the age group from 30 to 70 years, who abuse alcohol, smoke and wear dentures. Leukoplakia does not occur overnight, and its development can last for years.
Reasonable restrictions for leukoplakia
For leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix, it is extremely UNADVANTABLE to take hot general baths, stay in the sun for a long time and sunbathe (regardless of the activity of the Sun, the presence/absence and type of bathing suit).
HEAT TREATMENTS and insolation (sunbathing in natural conditions and solariums) increases the production of estrogens (female sex hormones), the excess of which stimulates oncological processes.
- Reviews about the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in our Clinic
- About the Clinic
- Clinic team
- Prevention of female diseases
- What is homeopathy?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a gynecologist?
Our specialized clinic for the treatment of leukoplakia is open 7 days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk by appointment no later than 3 days in advance by multi-channel phone number 8 (calls within Russia are free), or (for foreign calls).
| ONLINE about the treatment of leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk at BOOK ONLINE for leukoplakia treatment here. BOOK online for leukoplakia treatment here. Buy coursework for treatment by phone or here. |
Booking
Subsections
- Program No. 1. Treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the pelvis
- Program No. 2. Treatment of urinary incontinence, prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina
- Program No. 3. Treatment of female infertility of endocrine (hormonal) and mixed origin
- Program No. 4. Treatment of erosion, endometriosis, leukoplakia, dysplasia, polyps, cervical cysts (uterine cysts)
- Program No. 5. Treatment of uterine fibroids
- Program No. 6. Treatment of cervicitis and endocervicitis
- Program No. 7. Postpartum rehabilitation and wumbling
- Program No. 8. Treatment of chronic cystitis
- Program No. 9. Treatment of severe menopause
- Program No. 10. Treatment of mastopathy
- Program No. 11. Treatment of endometriosis
- Program No. 12. Treatment of hydrosalpinx
- Program No. 14. Comprehensive treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
- Program No. 15. Preconception preparation for IVF, ICSI
- Program No. 16. How to remove belly fat
- Program No. 17. Treatment of kraurosis
- Program No. 18. Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia