Lip cancer is a severe, progressive oncological disease during which a malignant tumor forms on the upper or lower lip from epithelial cells located in the red border area. As the tumor grows, it penetrates other anatomical structures, causing the patient to have difficulty eating. Often the course of the disease is complicated by infectious inflammation. In the absence of timely medical care, tumor tissue begins to disintegrate over time, and the patient’s face becomes disfigured. Metastases spread most often through the lymphatic system.
Kinds
According to localization they distinguish:
- cancer of the lower lip, accounting for about 95-98% of all cases;
- Cancer of the upper lip, which occurs in no more than 2-5% of patients, but has a more aggressive and rapid course, affects mainly women.
According to histological classification, lip cancer is a squamous cell tumor, represented by two types:
- keratinizing – the most common, accounting for up to 95% of cases, which is characterized by a slow course with moderate germination into other tissues and slight metastasis;
- non-keratinizing - rarer and significantly more malignant, quickly growing into nearby tissues (usually into the anatomical structures of the jaw), forming ulcers and metastasizing relatively early through the lymph and blood flow. Metastases usually affect the lymph nodes under the jaw, in the chin and jugular vein, as well as lung tissue.
In addition, there are four clinical forms of the tumor: ulcerative, ulcerative-infiltrative, papillary and warty. The first two have a more malignant course.
Statistics
In relation to all cancers, lip cancer in Russia ranks 15th in terms of prevalence among men (1.5%) and 20th among women (0.53%). According to data for 2014, 1,958 new cases of this disease were identified in Russia. In the vast majority of cases (85-90%), cancer affects the lower lip.
In 2015, 398 people (2.99%) died from cancer of the oral cavity, lip, and pharynx in St. Petersburg.
In general, statistics for St. Petersburg indicate that the incidence of lip cancer is decreasing: in 1980, 811 cases were registered, and in 2009 – 416.
Symptoms
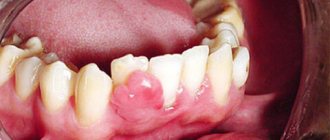
Many patients mistake the first signs of lip cancer for a rash characteristic of an exacerbation of herpes: a small seal forms on the lip, in which a slight itching is felt. At the same time or even a little earlier, the lymph nodes of the chin enlarge. As the tumor develops, the following appear:
- small painless ulcers, covered with a crust, with a bleeding, tuberous base;
- cracks and crusts along the red border of the lip;
- a compaction that grows in size over time and becomes crusty;
- pain in affected soft tissues;
- increased secretion of saliva;
- difficulty eating, deterioration of diction.
If left untreated, the tumor penetrates the tissues of the jaw and begins to destroy them. Simultaneously with the local symptoms of lip cancer, manifestations common to all types of cancer develop: general weakness, decreased performance, decreased appetite, unmotivated weight loss.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of lip cancer is a malignant modification of cells located at the border of the transition of the skin epithelium to the mucous membrane. As a result, cells begin to actively divide, which leads to tumor growth and displacement of healthy tissue. What becomes the trigger for the reformatting of the original healthy cell into a cancerous one has not yet been established, but the factors that increase the likelihood of developing pathology are well known:
- prolonged exposure to the open air, due to which the lips are constantly chapped and cracked;
- diseases of the digestive tract, metabolic disorders;
- habit of biting lips;
- unbalanced diet, chronic vitamin deficiency;
- regular consumption of strong drinks that burn the mucous membrane of the lips;
- smoking and microburns of the lips caused by it, the habit of chewing tobacco;
- irritation due to poorly fitting dentures or broken edges of a tooth;
- poor oral hygiene.
Among patients with lip cancer, rural residents who constantly work outdoors predominate. Men get sick two to three times more often than women; the main age group at risk is people over 60 years of age.
Benefits of onco
For more than 30 years, onco has been working for the health and comfort of patients with oncology. During this time, we have developed an ideal efficiency formula, which includes:
- maximum safety;
- exact compliance with domestic and international standards and protocols;
- experienced and competent oncologists, diagnosticians, laboratory technicians and consultants;
- modern and high-tech medical equipment;
- uncompromising comfort and support for patients at every stage of therapy.
The high level of service and quality of services has been repeatedly confirmed by numerous certificates and awards. Most of the doctors working for us have trained in medical institutions in the USA and Europe, learning from the invaluable experience of their foreign colleagues.
In our work, we achieve amazing results not only thanks to modern equipment and a staff of true professionals. Our patients feel safe and comfortable, as all rooms of the oncology center are beautifully designed. The furnishings and interior are imbued with a favorable atmosphere, far from a hospital one. Also available to patients and those accompanying them is a pharmacy, a cozy cafe and a rooftop restaurant with panoramic views.
Two onco buildings have extensive territories; The buildings themselves house many offices, departments and treatment rooms. To prevent you from getting lost, our employee will guide you to the right door. Finding a place for your car will also not be a problem: we have a large parking lot.
Stages
There are four stages of lip cancer.
- The size of the neoplasm is small and does not exceed 2 centimeters; the malignant tissue is concentrated within the lip. Lymph nodes are not affected, there are no metastases.
- The pathological tissue increases in size up to 4 centimeters, but the lymph nodes are not affected and there are no metastases.
- The tumor exceeds 4 centimeters in diameter and affects one or two regional lymph nodes.
- Malignant tissue spreads to the jaw bones, tongue, maxillary sinus, or penetrates the masticatory muscles and pterygoid process, reaches the carotid artery and grows into the base of the skull.
Diagnostics
External signs of lip cancer, as a rule, are not enough to accurately determine the diagnosis, so the oncologist prescribes a series of laboratory and instrumental tests for the patient.
- A smear or scraping from the surface of the ulcer to perform a cytological analysis of cells and determine the type of cancer.
- Tissue biopsy followed by histological examination of the removed sample to confirm malignant changes.
- Ultrasound of the neck to identify affected lymph nodes.
- X-ray of the lower jaw, chest to identify metastases or ensure their absence.
- CT scan of the facial skeleton to detect metastases in them.
Attention!
You can receive free medical care at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the program of State guarantees of compulsory medical insurance (Compulsory health insurance) and high-tech medical care.
To find out more, please call +7, or you can read more details here...
Diagnostic procedures
The diagnosis is made to the patient taking into account complaints, data from physical methods of examining the lip, oral mucosa using a magnifying glass, as well as the results of instrumental diagnostics. Review the results:
- Ultrasound of the lips and neck area;
- X-rays of the lower jaw;
- cytological examination of fingerprint smears, punctate and scrapings from the primary tumor and nearby lymph nodes.
An extremely informative diagnostic method is the innovative PET-CT (positron emission tomography) method. It is based on the use of radiological methods and the capabilities of the latest computer technologies. This makes it possible to identify micrometastases and assess the response to therapy already administered, and, if necessary, choose the optimal treatment route.
Differential diagnosis should also be carried out with candidiasis, syphilis, and herpetic manifestations. In most cases, identifying a neoplasm is not difficult.
Treatment
After diagnostic confirmation of lip cancer, treatment must begin immediately, since the sooner it is carried out, the less traumatic and more organ-preserving the methods used will be.
- Surgery. At the first and second stages, in the absence of metastases, surgery, as a rule, serves as the main method of treatment. The affected tissue is removed, and reconstructive lip surgery is performed at the same time. Patients in the third and fourth stages can be operated on depending on the local spread of the tumor and the expected volume of tissue to be removed. At the same time, the affected lymph nodes in the neck must be removed. If the tumor has spread to vital organs, surgical treatment is not performed.
- Radiation therapy. As an independent method, irradiation is used for small tumor sizes and few metastases; chemotherapy can be used to enhance the effect. After surgery, radiation exposure is necessary to avoid relapse of the disease and destroy residual cancerous foci.
- Chemotherapy. For inoperable cancer and distant metastases, chemotherapy is prescribed to inhibit the growth of malignant tissue and prolong the patient's life. Courses are prescribed, depending on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the tumor, simultaneously or alternately with radiation.
- Cryogenic method. Low-temperature destruction of tumor tissue is in some cases used in the initial stages to avoid surgery and chemoradiotherapy.
- Photodynamic method. Therapy for limited superficial oncological pathologies consists of the introduction of a photosensitizer and subsequent laser treatment.
Pathogenesis
The spread of the oncological process on the lower lip is due to its anatomical and physiological characteristics, as well as its injury to teeth affected by caries and exposure to carcinogens.
The condition, which is defined as obligate precancer, includes papillomas and focal dyskeratoses . In addition, malignant transformation can occur in diffuse dyskeratosis and keratoacanthoma .
Diagnosis and treatment of lip cancer in Moscow
If you find signs of lip cancer, contact the Meditsina clinic for a comprehensive examination and confirmation or refutation of suspicions. At your service:
- exclusive diagnostic equipment;
- own laboratory performing all types of analyses;
- oncologists of the highest category who will conduct treatment;
- a well-equipped inpatient department;
- medical service of international level.
Call us to find out the details you are interested in and schedule a consultation.
Diet
Diet during radiation therapy
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: lifelong / until recovery
- Groceries cost: 2300 - 3800 per week
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
During the treatment of the disease, it is necessary to follow the doctor's advice regarding nutrition. It is important to practice gentle nutrition: it is recommended to eat dishes warm, preferring soft and easily digestible foods.
- It is important to avoid hot drinks, broths, and soups.
- Alcoholic drinks should be excluded.
- It is also not recommended to eat spicy, fried, smoked foods.
- It is necessary to reduce sweets and dairy products to a minimum.
The diet should consist of boiled vegetables, boiled meat, fermented milk dishes, and cereals. Drinking should be plentiful.
Questions and answers
What does lip cancer look like?
In terms of external signs, lip cancer at the initial stage resembles a herpetic rash: a small swelling appears, which later turns into one or several ulcers covered with crusts. A thickened area with redness of the skin may form. Unlike a herpetic infection, ulcers do not heal after two to three weeks, but on the contrary, increase in size.
How to recognize lip cancer?
If a lump or swelling appears on one of your lips and does not go away within two to three weeks, you should definitely contact an oncologist to check for lip cancer. It is impossible to independently determine cancer by external signs; laboratory tests are required - histological and cytological examination of tumor tissue, biochemical blood tests, examinations using a tomograph and other types of medical equipment.
How long do people live with lip cancer?
A malignant tumor on the lip is one of the least aggressive oncological pathologies and is most often detected at an early stage. More than 90% of people who develop it live after diagnosis for more than 10 years, i.e. are completely cured of cancer.
Attention! You can cure this disease for free and receive medical care at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the State Guarantees program of Compulsory Medical Insurance (Compulsory Medical Insurance) and High-Tech Medical Care. To find out more, please call +7(495) 775-73-60, or on the VMP page for compulsory medical insurance