Facial injuries are quite common. A jaw bruise is an injury without violating the integrity of the skin and bone tissue.
The main difference between it and a fracture is that the victim is able to close and open his mouth, although this causes serious pain. Only an experienced specialist can identify the problem and carry out differential diagnostics.
Most often, such injuries have a favorable prognosis, but it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive study to exclude possible complications. In addition, you should strictly follow medical recommendations and appear in a timely manner for preventive examinations if necessary.
Pain is the main symptom of injury
Causes of bruises in the maxillofacial area
Most injuries occur unexpectedly and to varying degrees of severity.
Most often they are observed in the following cases:
- falling onto a hard surface;
- due to collision with objects;
- various impacts (road traffic accidents, domestic fights, contact sports).
Falls are the most common causes of injuries to the maxillofacial area
The severity of such injuries largely depends on the affected area, the type of object that affected the bone tissue and age-related changes in facial tissue.
Fracture of the zygomatic bone and arch, signs, consequences and methods of treating injury
Fracture of the zygomatic bone and arch is one of the most common injuries of facial bone tissue. In this case, the pathology almost immediately becomes noticeable visually. And the effectiveness of treatment and the risk of complications vary depending on the timing of seeking medical help.
Anatomical features of the zygomatic bone
The zygomatic bone is a paired facial segment. It consists of thick fabrics, porous in structure. Conventionally, the bone is divided into 3 parts:
- Lateral, or buccal. The site has a convex quadrangular shape. The anterior edge below is located next to the zygomatic process of the upper jaw. The upper section connects with the zygomatic process of the frontal bone. The posterior section is located in close proximity to the wing of the sphenoid bone. The lower angle is formed from the process of the temple, forming the zygomatic arch with it. The zygomaticofacial nerve passes through the existing hole.
- Orbital. Participates in the formation of the floor of the orbital wall. In this part there is an opening through which the zygomatic nerve passes.
- Temporal. Located next to the infratemporal fossa. The symotemporal nerve passes through its opening.
When the zygomatic bone is fractured, the nerve endings running in this part of the face are often damaged.
Causes
There can be a huge number of causes for injuries. All of them can be divided into the following types:
- Sports and household;
- Production;
- Transport (road accidents).
Most often, a fracture of the zygomatic bone occurs due to a strong blow to this area.
This can be either a deliberate blow to the face with a fist or a hard object, or an unsuccessful fall of the head on a hard surface.
Classification and types of zygomatic bone fracture
Damage is classified according to several parameters. However, the main characterization of injury is the analysis of the damage present. According to this classification, damage occurs:
- Fracture of the zygomatic bone. The pathology can occur without complications, and can also be accompanied by displacement of the damaged area of the bone and disruption of the integrity of the walls of the maxillary sinuses.
- Violation of the integrity of the zygomatic arch. Damage occurs with or without displacement.
- Simultaneous fracture of the zygomatic bone and arch. Damage may occur without complications, with displacement of debris, or accompanied by injuries to the maxillary sinus.
When prescribing treatment for a fracture, not only the main, but also secondary characteristics of the injuries received are taken into account.
Minor injury classification
When the zygomatic bone is broken, the severity of the injury is determined by the nature of the injury. According to this classification, fractures are divided into:
- Open. Damage to the skin is observed. A piece of broken bone protrudes from the wound;
- Closed. There are no deep damage to the integrity of the skin on the face;
- Linear. There is a fracture running along the bone and looking like a deep crack;
- Splintered. When a fracture occurs, a large number of fragments are formed.
The most difficult thing to treat is damage to the integrity of the tissue, as a result of which the bone is crushed into small fragments.
There is also a classification of fracture duration:
- Fresh. No more than 10 days passed from the moment of injury to the visit to traumatology;
- Obsolete. From the moment of formation of the pathology, from 10 days to 1 month passed;
- Malunited and non-united fracture. More than 30 days have passed since the fracture appeared.
This classification is taken into account when the victim seeks medical help and determines the likelihood of complications occurring in the future.
Symptoms
The main signs of a fracture of the zygomatic bone have their own distinct symptoms. The pathology manifests itself as follows:
- Unbearable sharp pain when trying to open your mouth;
- It is difficult to move the jaw not only up and down, but also to move it to the sides;
- Nose bleed;
- Hemorrharia of the eye white;
- The clarity of vision decreases, often the victim begins to see double;
- Swelling of the tissues around the eyes and cheekbones;
- Formation of hematomas on the face in the cheekbones and under the eyelid;
- When palpating the site of injury, the protrusion of the broken bone is clearly felt.
Sharp pain and nosebleeds are signs of a fracture of the zygomatic bone.
When the infraorbital nerve is damaged, numbness of the skin in the cheekbone area, under the eye and on the nasal wing is added to the general symptoms of a fracture. It is also possible to develop Purtscher syndrome. With this pathology, 2 days after the injury, the patient’s vision sharply deteriorates, retinal dystrophy occurs, and in some cases the optic nerve dies.
In case of displaced fractures of the zygomatic bone, the main signs of pathology are supplemented by a sharp change in the shape of the face on the side of the injury.
First aid
First aid is to alleviate the patient’s condition, and in the case of an open fracture, also to prevent infection of the wound. To do this, you need to take the following measures:
- If there is an open fracture, wash the resulting wound with a medical disinfectant solution. Chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, and ethyl alcohol are suitable for these purposes. It is important to ensure that the liquid does not get into the victim’s eyes. You should also not rub the damaged area. Only lightly dabbing the edges of the wound with a clean cloth or gauze, generously moistened with a disinfectant, is allowed. After this, the wound is carefully closed loosely with a sterile gauze bandage.
- Sit the victim down and calm him down.
- Apply cold by first wrapping the source of cold in a clean cloth. This is necessary to prevent frostbite and infection of the skin in the presence of minor damage to its integrity. For a closed type fracture, cold is applied directly to the site of injury. To alleviate the condition of a victim with an open fracture, you can periodically apply a source of cold at a distance of 3-5 cm from the edge of the wound.
Transportation of the victim to a medical facility should be carried out in a sitting position or on foot.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of fractures of the zygomatic bone and arch is carried out in 2 stages:
- Visual examination by a traumatologist with recording of the victim’s complaints;
- Carrying out radiography.
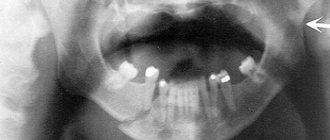
An x-ray determines a fracture of the zygomatic bone, as well as the presence of fragments and shifts. If there is pathology on an x-ray, the lower and outer edge of the orbit has a continuous outline, and the maxillary sinus is not transparent.
Methods and methods of treatment
Treatment of injury is selected depending on the nature and severity of the injuries suffered. Therapy can be carried out in the following ways:
- Conservative treatment;
- Surgically.
In most cases, these fractures are treated with surgery, and the type of surgery depends on the location and complexity of the injury.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment is carried out for linear fractures and damage to the integrity of bone tissue without displacement. Therapy consists of the following activities and procedures:
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and drugs with an analgesic effect. The choice of drug is made individually and depends on the general health of the patient and the severity of pain. Typically used are injections of Ibuprofen, a combination of Analgin with Diphenhydramine, Ketoprofen, Ketanov and Dicloberl;
- Taking vitamins in injections;
- Ensuring complete peace;
- Attendance at physiotherapy treatments. This can be laser therapy, quartz treatment, electro- and phonophoresis, shock wave and magnetic therapy.
Until complete fusion of bone tissue, nutrition should be only liquid. Food intake is carried out through a straw.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of fractures of the zygomatic bone and arch is carried out in the presence of bone fragments, as well as displacements. During manipulation, the bone is placed in its natural position, and the existing fragments are removed.
The operation can be performed using one of the following methods:
- Malarchuk-Khadarovich;
- Dubova;
- Kazanyan;
- Limberg;
- Duchant;
- Kina.
The selection of a specific method for bone reduction and fracture treatment is carried out based on the nature of the damage.
Malarchuk-Khadarovich method
It is used for both fresh and old fractures. Manipulations are carried out with a special hook. The end of the hook is carefully inserted under the cheekbone and grabs it. Using a special lever, the bone, along with the fragment, is pulled to its natural position.
Dubov method
Used for damage to the walls of the maxillary sinuses. To carry out manipulations in the oral cavity, a dissection of the mucous membrane is performed along the upper arch from the central tooth to the second molar. After this, the maxillary sinus is exposed and the damaged bone is placed in its natural position. The fragments are fixed using an artificial anastomosis.
During the procedure, a cotton swab thoroughly soaked with iodomorph is inserted into the nasal passage. Its end must be brought out. After suturing the mouth, the tampon is left in place for 2 weeks.
Kazanyan method
It is used in especially severe cases when the fracture is accompanied by the appearance of many small fragments. Under general anesthesia, an incision is made in the lower eyelid area. In this case, it is necessary to expose part of the cheekbone and the edge of the eye socket.
Channels are made in the damaged bone through which a metal wire is pulled. Its outer end is bent into the shape of a loop or hook and secured in the rod of a special plaster cap. These manipulations make it possible to fix the crushed zygomatic bone in the position required for fusion.
Limberg method
The technique is used very often for mild injuries. During the procedure, the victim lies with his head turned so that the injured area is on top. A special hook is used to puncture the skin in the area of injury, and the hook is deepened to the bone. The device is placed under the damaged bone and hooked. Next, the hook is rotated 900 so that its sharp edge is located on the inside of the bone. In this position, the broken part of the zygomatic bone is pulled up to a characteristic click. In this case, it is necessary to pull the broken element in the direction opposite to its displacement.
Duchant method
Used for uncomplicated fractures. Under general anesthesia, special sharp forceps are used to puncture the skin at the site of injury. The same forceps grasp the bone and place it in the correct position.
Keen method
It is used for injuries accompanied by complete separation of the zygomatic bone from the rest of the bone tissue. Using a special zygomaticalvelar ridge, the tissue surrounding the bone is cut. A Karapetyan elevator is inserted under the torn bone, and with its help, moving forward and outward, the torn element is established in its natural position.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is carried out only after the existing fracture of the zygomatic bone and arch has completely healed.
During the rehabilitation period, you need to forget about solid and tough foods.
The restoration method consists of following the following rules:
- The diet should be balanced and contain a large amount of dairy products and foods rich in calcium;
- In the first 1-2 months, food should be soft and mostly liquid;
- To develop the jaw, it is recommended to periodically chew soft chewing gum;
- Attendance at physiotherapy treatments. Magnetic therapy, quartz treatment, and electrophoresis are used. During quartzing, it is extremely important to protect your eyes with special glasses. Otherwise, there is a huge risk of getting a retinal burn.
With proper rehabilitation measures, almost all the consequences of fractures of the zygomatic bone and arch can be eliminated in 1.5-2 months. Only retinal detachment cannot be treated.
Complications
The consequences of a cheekbone injury, in which there is a fracture of bone tissue, are the following complications:
- Changes in the shape of the cheekbone, which leads to distortion of the face;
- Development of inflammatory processes of bacterial and purulent type;
- The occurrence of pathological contraction of the lower jaw, or contracture. With complications of this type, the patient’s ability to move the jaw is significantly limited or completely absent;
- Blindness or inability to move the eyeball. Occurs due to damage to nerve endings;
- Development of chronic sinusitis.
Complications from a fracture of the zygomatic bone develop mainly when seeking medical help is delayed. Sometimes unpleasant consequences, in the form of inflammatory processes, can occur as a result of surgery.
nettravm.ru
Damage to the lower jaw
This injury is the most common. It occurs in both children, adults and the elderly. The important point is to identify the type of damage as soon as possible and provide first aid. The further prognosis and duration of treatment will depend on this.
A mandibular contusion is a soft tissue injury in the lower parts of the face. As a result, an internal hematoma is formed due to the rupture of small blood vessels.
In the event of a bruise, the bone tissue remains intact and the teeth and gums are not injured. Usually occurs as a result of impact on the maxillofacial area with a blunt object.
Bruise of the jaw after a blow to the lower parts of the face on the left side
The severity of the injury is largely influenced by the moment of impact. Severe consequences are observed with highly tense muscles. In this case, they rupture, forming an extensive hematoma with a pronounced pain reaction.
Main symptoms
Any disease has its own fundamental signs. Symptoms of a bruise of the lower jaw are usually quite striking. The main sign is sharp pain, abrasions, damage to the cheek or lip.
If the blow falls on the area of the dental arch, then gaping wounds form on the soft tissues on the side of the oral cavity. The lower lip looks swollen, sagging and hyperemic.
To make a correct diagnosis, differential diagnosis is necessary. It is important to exclude fractures of the bone areas of the jaw, eye socket and nose.
After a strong blow, the victim should not be left unattended. It is imperative to monitor his general condition. Together with complaints and external examination, a preliminary diagnosis can be established.
In addition to local signs, general manifestations should also be taken into account:
- damage in the form of scratches and hyperemia in the jaw area;
- swelling in the lower part of the face;
- the presence or absence of hematoma of varying volume;
- malaise and swollen lymph nodes;
- sharp or constant pain even at rest;
- impairment in mouth opening, eating and speaking;
- increased pain response from touching the damaged area, as well as movement of the jaw to the left or right side.
Attention!!! The main differential diagnostic sign of a bruise from a fracture is that the jaw bones do not change their anatomical structure. In addition, the line of bone integrity violation can be determined by palpation.
If the injury is severe, the victim must in any case be taken to a doctor for examination to clarify the condition. It is important to carry out rapid transportation with preliminary first aid.
Fractures of the zygomatic bone - symptoms and treatment
In the structure of facial bone injuries, a fifth is occupied by fractures of the zygomatic bone and arch. There are two of them in the skull. The bone has three surfaces - buccal, temporal, orbital and two processes - frontal and temporal. It forms the lower-lateral edge of the orbit and borders the maxillary sinus. The zygomatic arch is the zygomatic process of the frontal bone and the frontal process of the zygomatic bone. A zygomatic bone fracture is a skull injury. And this means the proximity of the brain, the most important vessels and nerves. This facial injury is in second place after a fracture of the nasal bones.
Causes and classification of fractures
The reasons why a fracture of the zygomatic bone occurs, in descending order, look like this:
- blow to the face;
- sports injury;
- traffic accident;
- falling from height;
- work injury.
Unfortunately, gunshot injury has recently become another cause.
There are several classifications. By localization:
- fracture of the zygomatic bone;
- zygomatic arch fracture;
- fracture of the bone and arch at the same time (combined fracture).
According to the ratio of bone fragments:
- no offset;
- with offset.
Trauma to the zygomatic bone may be accompanied by damage to the walls of the maxillary sinus.
By time of injury:
- fresh - the injury was no more than 10 days old;
- old - older than 10, but up to 30 days;
- unfused or incorrectly fused - more than 30 days old.
In addition, there are:
- linear;
- splintered;
- open;
- closed.
Useful: What causes leg muscles to cramp?
Symptoms
The victim's complaints are quite specific and depend on the presence or absence of displacement.
The main symptom is severe pain when trying to open the mouth, while jaw mobility is impaired.
When the infraorbital nerve is damaged in the area of the eye, wings of the nose, and cheekbones, numbness is observed. When an injury is accompanied by penetration into the sinus of the upper jaw, nosebleeds occur. There is swelling around the eyes until the eye closes with swelling; double vision (diplopia) may be observed. When the fragments are displaced, deformation of the face occurs, and upon palpation it is possible to feel the bony protrusion.
On the 2nd day after injury, serious eye complications may occur. A sharp decline in vision, changes in the retina up to detachment, atrophy of the optic nerve is called Purtscher syndrome.
When an arch is fractured, the deformity may not be immediately detected due to swelling of the soft tissues. Opening the mouth causes pain, as does lateral movement of the lower jaw. The patient cannot chew food. This is not only because the fragment of the arch moves inward, but also because of damage to the masticatory muscles.
First aid
First aid is provided by those who are near the victim before transporting him to a medical facility. Under no circumstances should you try to reduce fragments protruding from the wound. Help consists of applying a sterile bandage and applying cold through a clean cloth or towel for 20 minutes, repeat after 10 minutes.
Useful: Chronic prostatitis: symptoms and treatment
Diagnostics
An indication of an injury in the zygomatic region, examination of the patient, and palpation of the affected area suggest a diagnosis. To clarify the nature of the injury, it is necessary to perform radiography in 2 projections.
In the image you can see a defect in the zygomatic bone, a change in the airiness of the maxillary sinus, and unevenness of the inferolateral edge of the orbit. In the future, x-rays are used to monitor the consolidation of the fracture.
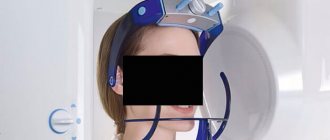
A modern diagnostic method is computed tomography. It is advisable to consult a neurologist to assess the condition of the cranial nerves and the presence of brain injury. Accurate recognition of the nature of the fracture determines treatment tactics.
Treatment
The simplest in terms of treatment choice is a fresh fracture of the zygomatic bone or arch without displacement. This allows the use of conservative treatment tactics.
It is as follows:
- rest, limitation of mouth opening and lateral movements of the lower jaw for 10-12 days;
- local fractional application of a cold compress to the area of injury in the first 2 days for 15 minutes up to 6 times a day;
- from the 2nd day you can move on to physiotherapy;
- eating only liquid food.
Painkillers are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections, depending on the severity of the pain syndrome. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Voltaren, Brufen, Nurofen) are recommended. Calcium supplements speed up consolidation, as do physiotherapy procedures. Fresh fractures of the zygomatic bone with displacement, old fractures, regardless of displacement, are subject to surgical treatment. The age of the victim matters for the timing of bone restoration. Fractures in children heal much faster than in older people.
Surgical treatment
The goal of surgical treatment of displaced fractures is reposition (comparison) of fragments.
There are several proprietary methods of surgical treatment.
The Limberg method is used for minor damage to the maxillary sinus. A single-prong hook is inserted through the skin under the displaced fragment and, with a movement opposite to the displacement, is reduced until it clicks.
If the zygomatic bone is separated from all three adjacent bones, then the Keene method is used. Access is made through an incision in the mucous membrane in the area of the transitional fold of the upper jaw. A special elevator is inserted under the displaced bone and moved upward and forward into place.
If there is significant damage to the maxillary sinus, surgery is performed using the Dubov method. Access to the sinus occurs through an incision in the vestibule of the mouth. After the fragments have been reduced, a tampon with iodoform is left in the cavity, the free end of which is removed through the nose. The wound is sutured and the tampon is removed after 2 weeks.
The Gillis-Stone method provides external access to the displaced zygomatic bone through an incision in the skin in the temporal region, after which the fragments are put in place using an elevator.
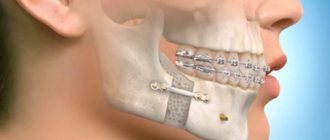
It is possible to perform osteosynthesis at the joints of bones (sutures) with polyamide thread or metal plates on screws.
There are methods for fixing fragments with metal wire or special hooks to an external splint or rod built into a plaster cap. The connection of the fragments can be done with a thin metal thread inserted through the tendon of the temporal muscle. This is the Matas-Birini method.
If the arch is fractured with a slight displacement, a small incision is made above the arch, holes are drilled in the fragments, through which the integrity of the arch is restored using a polyamide thread. The incision is closed tightly with skin sutures. You can use plates made of quickly hardening plastic. They are removed after 8-10 days.
Complications
If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, severe complications requiring surgical treatment are possible:
- deformation of the facial skeleton;
- chronic inflammatory process, osteomyelitis;
- chronic sinusitis;
- contracture of the lower jaw.
Ununited or improperly healed cheekbone fractures, resulting in deformation of the facial skull, require the patient to make a decision about the need for surgery. He may decide to remain with a cosmetic defect or undergo facial plastic surgery.
If improper consolidation of the fracture occurs, a series of surgeries may be required. First you need to destroy the malunion, then perform plastic surgery. This work is carried out by maxillofacial surgeons.
Post-traumatic sinusitis has a long course and is difficult to treat; it is dangerous due to progressive bone resorption. The most fatal complication is Purcher's syndrome - loss of vision. The person remains disabled for life.
The risk of postoperative complications is reduced due to timely intervention and antibiotic therapy. Neuroprotectors are prescribed to improve nutrition of injured nerves.
Is it possible to prevent zygomatic bone fractures? To some extent, yes.
Avoid drunken fights, be careful while driving, driving while intoxicated is simply unacceptable. Follow safety regulations at work.
Remember that when you receive a facial injury, it is possible to underestimate its severity immediately; serious symptoms may appear later. It is in the best interests of your health to seek medical attention immediately.
plannt.ru
Damage to the upper jaw
The nature of injury in this area is more complex. Its danger lies in the fact that serious complications may occur. It is quite easy to distinguish a bruise of the upper jaw from the lower one.
This is determined by the location of the pain and the consequences of trauma. However, it should be taken into account that unpleasant sensations can radiate to the lower part of the face. But the main difference here will be the absence of impaired mobility of the lower jaw.
The symptoms of a bruise of the upper bone tissues are very similar to the previous problem. There is an inflammatory process and pain, swelling, and sometimes enlargement of regional lymph nodes. Even if there are no obvious signs of bruises, you need to go to the clinic.
The photo shows fractures of the upper jaw with severe bruises
The doctor must first rule out a fracture. In the upper jaw, such injuries are dangerous for brain damage.
For example, a Le Fort 3 fracture is a separation of the bones of the skull and face. Without professional medical care, death can occur in this case.
First aid for a fracture of the zygomatic bone and its treatment
The zygomatic arches are a complex formed by the temporal and zygomatic processes. A fracture of the zygomatic bone is a common injury that can occur not only during a blow during a conflict, but also in a dangerous situation at work, at home, during an accident or at sports competitions. Such injuries are quite life-threatening due to the proximity of the brain and increased blood supply.
Types and characteristic symptoms of injury
According to its characteristics, a fracture of the zygomatic arch can be:
- open isolated with or without offset;
- closed with or without offset;
- combined fracture with or without displacement;
- combined fracture with damage to other facial bones and the maxillary sinus;
- traumatic defect of the zygomatic arch and bone with impaired mobility of the lower jaw and facial deformation.
Depending on the time elapsed after the injury, fractures are divided into fresh, which were received within the last 10 days, old - from 11 to 30 days, non-united and improperly fused - after 30 days. Signs of a fracture are as follows:
- Pain in the middle third of the face, intensifying when opening the mouth.
- Deformation of the facial bone due to tissue damage and displacement of fragments.
- Nosebleeds due to violation of the integrity of the maxillary sinus.
- Restricted mobility of the lower jaw.
- Damage to the masticatory muscles, which manifests itself in the form of swelling of the zygomatic region, swelling, hemorrhages, and wounds.
- Numbness in the area of the wings of the nose, upper lip, infraorbital region.
- Hemorrhage in the retina, blurred vision as a result of damage to the eyeball, double vision.
- 2 days after the injury, Purtscher syndrome may occur, which is expressed in a sharp drop in vision, changes in the retina, its detachment, even atrophy of the optic nerve.
First aid
First aid provided immediately after an injury is quite important because it eliminates the risk of possible complications. It consists of applying cold to the damaged area, administering an anesthetic injection and transporting the victim to the emergency room in a side-lying position. If debris is visible from the wound, it cannot be reduced. A bandage should be applied and the patient taken to a medical facility.
In case of severe bleeding, it is necessary to clamp the artery, which is done by the victim himself. If the condition of the injured person does not allow this, then the person providing assistance fixes the lower jaw with a bandage, using a bandage or a piece of fabric. This fixation will prevent the debris from moving and reduce pain.
Treatment methods
At the medical center, the patient is given a preliminary palpation, then an x-ray is taken, which shows the degree of destruction of bone tissue and the possible consequences of the injury.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist is also recommended, since damage may affect the area of the eye orbits.
Treatment methods for a zygomatic arch fracture can be conservative or surgical. For minor injuries to the facial bone or minor displacements, a conservative method is prescribed, the use of which involves rest and the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, which also have an analgesic effect. For severe pain, medications are administered intramuscularly. An ice pack is placed on the affected area. For the first 2 days, the cold is used 6 times a day for 20 minutes, on the 3rd day the patient is sent for physiotherapy.
Surgical treatment can be non-operative and operative. Non-operative, or bloodless, intervention is indicated for fresh, easily reduced fractures, when the surgeon reduces the zygomatic bone using the thumb or index finger. In another case, a special spatula or medical spatula wrapped in gauze is used, with the help of which the arch, zygomatic bone or its fragments are set. This option is most effective in the first 3 days after injury.
For old fractures (more than 10 days), surgical intervention is used when the zygomatic bone is reduced through an incision made behind the zygomatic-alveolar ridge. Using a strong short elevator advanced under the displaced bone, it is reduced to its original position. In severe cases, several operations are required to install a plate or a special fixator.
After reduction and fixation of the zygomatic bone, rest and restriction of solid food intake are ensured. Cold is applied to the affected area, anti-inflammatory drugs, neuroprotectors and a course of physiotherapy (electrophoresis, ultrasound, pulsed and magnetic therapy, UHF) are prescribed, which complement the treatment and relieve swelling.
Rehabilitation and recovery
For mild injuries, bed rest is not required. During the recovery period after a fracture, the diet includes chicken broth, yogurt, kefir, milk, and mashed potatoes. If there is difficulty opening the mouth, feeding through a tube is allowed. With surgery, rehabilitation is delayed. If a plate has been installed, then the adaptation of the surrounding tissues to the foreign material plays an important role.
In difficult cases, fixation lasts up to 12 days. The recovery period can last up to 1.5 months. After removing the retainer, the jaw must be developed. It is recommended to use chewing gum for this. Strengthens bones by taking calcium supplements.
Possible consequences
If you do not seek help in a timely manner and the necessary measures are not taken, the consequences of a fracture can be quite negative. With an old injury, deformation of the facial bones of the skull occurs and a stable asymmetry of the face is formed, which reduces the aesthetic appearance of the injured person. Left untreated, it can lead to an infection in the sinuses. Maxillary sinusitis often occurs, which is poorly treated and leads to gradual resorption of bone tissue.
The most dangerous consequence of a fracture of the zygomatic orbit may be Purcher's syndrome, which affects the eyes, which threatens complete loss of vision and lifelong disability. Therefore, after a head injury, it is important to consult a surgeon as soon as possible to exclude the possibility of deep damage to the bone tissue.
It is also worth visiting a doctor if, after some time after the fracture, the pain in the cheekbone area does not go away.
ortocure.ru
Diagnostic measures
If minor injuries to the maxillofacial area occur, they do not require contact with a dentist or surgeon, or urgent hospitalization. If there is severe and prolonged pain, the area of damage should be examined by a specialist.
The following are used as diagnostics:
- taking anamnesis;
- general examination by a surgeon, orthopedic dentist, traumatologist;
- special examination by an otolaryngologist, neurologist and other specialized specialists as necessary;
- X-ray examination of the maxillofacial area;
- CT scan;
- analysis of blood, urine, saliva.
Based on the data obtained, a general picture of the victim’s health is formed and a specific treatment is recommended.
The main therapeutic direction will be the following:
- taking painkillers;
- applying a pressure bandage;
- ensuring maximum peace for the victim;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic procedures;
- local and general anesthesia;
- elimination of hematoma and infiltrate.
First aid and treatment of bruises
Ice pack on problem area
Once the location of the damage has been identified, it is necessary to begin simple manipulations. Of course, they will depend on the nature of the damage. If there are open wounds, first of all they must be washed and treated with antiseptic.
Suitable products for this include hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Bepanten. Before applying the antiseptic, the wound can be washed with soapy water. The bleeding area must be covered with a clean cloth or, if available, a sterile bandage.
Then apply cold to the affected area through the cloth. This can be an ice pack or a regular towel soaked in cold water, which is applied through a waterproof film.
Elements of treatment and means used
Immediately after injury, first aid must be provided. Usually, all bruises of the upper and lower jaw can be treated quite well without medical intervention. However, in case of severe lesions, it is still worth contacting specialists for examination.
Table No. 1. Painkillers:
Name of the drug Active substance Additional action Directions for use
Ketonal
Ketoprofen. Anti-inflammatory and decongestant. Apply a thin layer to the skin 2-3 times a day.
Fastum gel
Ketoprofen. Anti-inflammatory, improves blood circulation. Rub in the gel until completely dry 2 times a day.
Dolgit
Ibuprofen. Relieves swelling and inflammation. Apply with gentle massage movements, 3 times a day, up to 3 weeks.
Finalgon
Nonivamide, Nicoboxil. Improves blood circulation, recommended on the 3rd day after injury. After application, it is recommended to cover the affected area with a warm cloth.
Indomethacin
Indomethacin. Anti-inflammatory. Children apply no more than 1 cm of gel, adults no more than 15 cm, 2 times a day.
First of all, cold is applied to the lesion. Low temperatures will help not only relieve swelling and stop bruising, but also provide partial pain relief.
For the most effective elimination of unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to take analgesics internally or apply special ointments externally. Modern drugs are available in the form of gels. They are easy to use, absorb quickly and do not stain clothes.
It is good to use products that contain Heparin. It helps to quickly get rid of infiltration and eliminate the phenomenon of swelling. Heparin-based drugs should not be used by persons with bleeding disorders.
If the gel contains horse chestnut extract, it is contraindicated for people suffering from kidney disease and pregnant women. To prevent side effects from using the gel or ointment, the attached instructions should be studied in any case.
Table No. 2. Coolants:
Name of the drug Active substance Additional action Directions for use
Ben-Gay
Menthol, methyl salicylate. Painkillers, anti-inflammatory Apply in large quantities 3-4 times a day.
Flexall
Aloe vera extract, menthol, camphor, vitamin E. Quickly relieves pain and has an anti-inflammatory effect. Apply in a thin layer without rubbing.
Bystrum gel
Ketoprofen, Trometamol, essential oils. Decongestant and painkillers. Rub in with smooth movements until completely dry.
Reparil gel
Escin, salicylic acid. Decongestant, anticonvulsant, painkillers. Apply with light massage movements, 3-4 times a day, no more than 14 days.
The price of medications in the form of gels and ointments ranges from 220 rubles to 350 rubles. One package is completely enough for a course of treatment.
It is difficult to predict when a particular injury will occur. To reduce the risk of bruises and other injuries, precautions should be taken. In winter, move carefully on slippery sidewalks; in summer, when engaging in active sports, think through the possible consequences.
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of cheekbone fracture
One of the most serious types of injuries is a fracture of the cheekbone, which can occur as a result of domestic, industrial or sports injuries. The clinical picture of this type of injury is severe, and the patient himself needs immediate assistance from surgeons and traumatologists. In order to understand how serious this type of injury is, you need to briefly familiarize yourself with the structure of the zygomatic bone, which is paired and consists of three surfaces: temporal, orbital and buccal, and also connects with the zygomatic processes of the frontal, temporal and upper jaw bones. The zygomatic bone is one of the strongest in the human body, therefore, if you receive an injury or a fracture of the cheekbone, treatment is quite long and requires a professional approach. In traumatology, there are two main types of cheekbone fractures - with and without displacement. The injury can be open or closed, and linear or comminuted. Regardless of the type of injury, specialists in the field of traumatology recommend seeking medical help immediately after receiving an injury, since with old injuries, the zygomatic bone may not heal properly, which will entail not only a noticeable facial defect, but also more severe consequences.
Symptoms
Clinical signs of a cheekbone fracture with or without displacement are quite pronounced and are present immediately after the injury. The most characteristic signs are the following symptoms:
- Acute and sharp pain in the jaw and face, which intensifies when turning the head or opening the mouth.
- Lack of skin sensitivity in the eyelid area and wings of the nose. Basically, such symptoms are characteristic of damage to the infraorbital nerve.
- A noticeable deformation of the facial bone is a sign of a displaced cheekbone fracture.
- Nosebleeds – present when the maxillary sinus is damaged.
- Bleeding in the conjunctiva or lower eyelid.
- Double vision.
- Fainting due to painful shock.
- Decreased vision, double vision, “floaters before the eyes.”
The appearance of the above symptoms cannot go unnoticed, therefore, if a person is injured, they must be taken to the traumatology department as quickly as possible.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing a cheekbone fracture is quite simple and it is enough for a qualified traumatologist to examine the patient. Externally, with a fracture, there is no integrity of the zygomatic bone, the edges of the orbit are damaged. In order to get a clearer picture, the doctor prescribes an x-ray, MRI or CT scan. The results of these studies will allow the doctor to determine the slightest changes and disturbances caused by the fracture. After receiving all the results of the study, the doctor decides on treatment tactics, which can be carried out conservatively or surgically. The main task of the doctor in case of a cheekbone fracture is to restore the integrity of the bones. For displaced fractures of the zygomatic bone, an operation is performed to remove or realign the bone fragments. If the injury occurs without displacement, then treatment can be carried out conservatively using bone fixation, physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as taking analgesics to relieve pain.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment consists of complete rest, fixation of the bones and muscles of the face, taking painkillers, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures. Considering that the pain during a fracture is quite severe, the doctor most often prescribes drugs based on ketorolac (Ketanov, Ketorol) or nimesulide (Nimid, Nise). In case of severe pain, it is possible to administer analgesics intramuscularly. In the first days after the fracture, an ice pack is applied to the injury site. A few days later, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. The duration of treatment directly depends on the severity of the injury.
Cheekbone fracture surgery
In case of a displaced cheekbone fracture, the only treatment option is surgery. There are several ways to perform surgery, but the choice always remains with the doctor, as well as the capabilities of the clinic itself. The operation can be performed using the following methods: Malarchuk-Khadarovich method. Used for both early and late cheekbone fractures. In the process, a special hook is used, which is placed under the cheekbone, and with the help of a lever, it is pushed outward, without affecting the nerve endings and other bones of the skull. Keen method. A more complex operation is performed when the cheekbone is completely torn off and not attached to other bones. The procedure consists of dissecting the mucosa, inserting a Karapetyan elevator under the displaced bone, with the help of which an upward and then outward movement is made. Dubov's method. It is carried out if the sinuses of the upper jaw were damaged due to a fracture of the cheekbone. During the operation, the upper arch of the jaw is cut, exposing the maxillary sinus. The bones are fixed using an artificial anastomosis. Limberg method. Used for damage to the walls of the jaw sinus. This method is the most common and consists of using a special hook, which is inserted into the displaced part of the cheekbone, then rotates the displaced bone using rotation. Duchant's method. This method of surgical intervention is used for minor injuries. During the operation, special forceps with sharp teeth are used to grab the damaged bone and put it in place.
Any of the methods of surgical treatment is carried out under general or local anesthesia, has its own risks and complications and can only be performed by a surgeon or traumatologist under completely sterile conditions.
Consequences
The consequences of a cheekbone fracture can occur if medical care is not provided in a timely manner or in cases where a person completely refuses surgery or treatment. The most common consequences of a cheekbone fracture are the following:
- Deformation of the cheek bone.
- Osteomyelitis is inflammation of the bones and surrounding muscle tissue.
- Chronic sinusitis.
- Jaw deformation.
- Damage to the facial nerve.
In order to avoid complications and various consequences, treatment should be carried out immediately after the injury. Only a doctor will be able to determine the degree of damage, prescribe and carry out appropriate treatment with subsequent rehabilitation of the patient.
travmoff.ru
Folk remedies
There are several proven, simple and at the same time effective ways to have the positive effects of alternative medicine. They are indispensable products for pregnant women, children, as well as people who have a severe allergic reaction to medications. You can make a choice based on personal preferences or doctor’s recommendations.
Treatment at home for bruises can be carried out using the following means:
- Table salt solution. Compresses are prepared from it, which are used for any complexity of bruises. To prepare, a tablespoon of salt is dissolved in 150 ml of boiled water. Then take a sterile bandage, soak it in the solution and apply it to the problem area. The compress is covered with a thick cloth on top. The gauze pad with salt can be left overnight.
- Grated potatoes. The tubers should be washed and cleaned first. Grate one tuber on a coarse grater, place in linen cloth and wrap several times. After applying the bruise, cover the top with a thick towel. Compressor exposure time is 30-40 minutes. For best results, make 3-4 applications in a row.
- Cabbage leaf. Before applying it, you should knead it a little or make cuts on it to let the juice out. The sheet is applied to the sore spot 2-4 times a day until it dries completely.
- Onion and garlic. The two ingredients are ground and mixed together. The resulting slurry is added with half a tablespoon of salt; it is recommended to wrap the mixture in gauze and place it in the area of the bruise.
- Beetroot and liquid honey. Finely grated root vegetables are mixed with a tablespoon of natural honey. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a day for 2 hours.
- Laundry soap. This remedy helps reduce the pain response. The soap is grated and mixed with raw chicken yolk. I apply a compress every half hour up to 6-8 times a day. You can also rub a damp cloth with laundry soap and apply an application to the bruised area.
- Apple vinegar. This is one of the most effective remedies. To prepare the solution, you need to take 2 teaspoons of vinegar and dilute it in 1 liter. water. Soak a clean cloth in the solution and apply 3-4 times a day for half an hour.
Popular folk remedies for bruises
The video in this article shows how to properly apply a warm and cold compress for bruises.