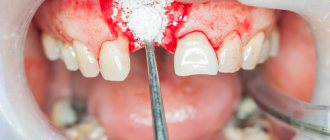
Any surgical intervention is serious and the implantation of artificial tooth roots is no exception. The procedure requires attentiveness and concentration not only from the attending physician, but also from the patient. Proper preparation will reduce the likelihood of unpleasant and undesirable consequences. Detailed tips and recommendations will help you understand what you need to know before dental implantation, how to behave and what to prepare for.
Before surgery, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene.
If the operation is performed with an anesthesiologist, you must come with an accompanying person, or the operation will be cancelled.
Recommendations for surgical treatment
After surgery, you may experience pain, which will go away as the tissue heals. Postoperative swelling or hematoma can also occur in areas adjacent to the surgical site, which is a natural consequence of surgery. There may be a slight increase in body temperature.
Please follow our recommendations!
Contraindications for dental treatment under anesthesia
In a situation where a patient needs surgery for health reasons, it can be performed under anesthesia, so there are no absolute contraindications for general anesthesia.
The anesthesiologist should be especially attentive to the following patients:
- with heart rhythm disturbances;
- with heart disease and heart failure;
- have had a myocardial infarction or stroke less than six months ago;
- with severe diseases of the endocrine system;
- with functional pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
- with bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- recently suffered from a severe infectious disease.
During planned anesthesia, a full stomach is also an absolute contraindication. The patient should not eat for at least 6 hours before anesthesia, and drink for 4 hours. In addition to general contraindications to anesthesia, it should be understood that any drug used for its administration also has its own indications and contraindications.
Before surgery
- Prepare an ice pack at home.
- On the day of surgery, eat a light meal 2-3 hours before your scheduled time.
- The day before surgery, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
- Be sure to inform your dentist about all the individual characteristics of your body and any allergic reactions, in order to accurately select an anesthetic that is safe for you.
- Visit the toilet before surgery.
- It is better to come to the operation in loose clothes without a collar.
Sanitation at home
Those people who take care of their health will be required to follow all the dentist’s instructions and carry out a set of hygiene procedures.
These measures can be carried out at home, but no more. Oral hygiene is important for dental health, but in addition, it is the prevention of dental diseases. It should be remembered that full oral sanitation cannot be performed at home. After all, there is no special equipment for this at home, and this research is distinguished by its complexity.
After operation
— To avoid severe swelling and bleeding during the first 24 hours after surgery, it is necessary to apply an ice pack to the cheek on the side of the operation for 15-20 minutes with breaks of 30-40 minutes.
- Rinsing your mouth when bleeding is unacceptable!
— After sinus lift surgery, you should not drink through a straw, blow your nose vigorously, or puff out your cheeks.
- To reduce the likelihood of nosebleeds (after upper jaw surgery) and reduce post-operative swelling, you should sleep with your head elevated (add an extra pillow) for several days after surgery.
— It is not recommended to use tobacco products 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery.
— It is prohibited to drive a car on the day of surgery with premedication.
- It is not recommended to eat until the anesthetic wears off. In the first days after surgery, it is recommended to eat soft, non-hot foods.
— It is not recommended to drink alcohol, coffee, or strong tea to avoid the negative effects of these drinks on blood circulation and wound healing.
Validity of tests for hospitalization
All tests that the patient undergoes before going to the hospital should be as recent as possible so that the current state of his health is fully reflected.
Therefore, you should not delay hospitalization after receiving all the results. If any of the available tests are out of date, the patient is not allowed to undergo surgery/hospitalization. In this case, samples must be resubmitted.
Expiration date of laboratory tests:
- clinical (general) blood test 7-10 days;
- biochemical blood test 10-30 days;
- blood test for sugar 7-10 days;
- coagulogram 1 month;
- HIV test 3-6 months, depending on hospital requirements;
- express diagnostics for syphilis (Wassermann reaction) 3-6 months;
- blood test for markers of viral hepatitis groups B, C, D, E
- up to 3-6 months;
- analysis for fungal and parasitic infections up to 6 months;
- clinical urine test 7-10 days;
- blood type and Rh factor indefinitely.
At the MedicCity multidisciplinary clinic, you can take all the necessary tests and undergo all the necessary examinations at a convenient time, without queues and stress.
We care about your health and value your time!
Additional Tips
Avoid lifting heavy objects, bending over, playing sports, or taking hot baths for 5 to 7 days after surgery.
Within a few days, performance and the ability to drive may be reduced.
Remember to take medications prescribed by your dental surgeon after surgery.
We kindly ask you!
Appear for examination and removal of stitches 5-7 days after surgery, in agreement with your surgeon. You must immediately notify your surgeon or clinic administrator of any changes in your health.
Recommendations for caring for dental implants
The service life of the implant depends on:
- The correctness of the surgical and prosthetic stages carried out in the dental clinic.
- The patient's compliance with the recommendations given by the dentist immediately in the postoperative period and the period after implant prosthetics.
- Careful hygienic care of the “implant-crown” structure.
- Blood supply to bone tissue and gums in the area of implantation. (Smoking cigars and cigarettes has a very, very negative effect on peripheral blood circulation, which can even interfere with implant implantation.!!!)
Stages of preoperative measures
The preparation stage is aimed at studying the patient's health status. It is necessary to exclude contraindications for intervention, to cure acute and chronic diseases that increase the risk of complications (including rejection of the artificial root). The implantologist needs to know all the characteristics of the soft and hard tissues that will surround the implant.
History taking
The doctor asks the patient questions, finds out complaints, and asks the patient to fill out a questionnaire. It is important to identify chronic diseases, allergies, and immune diseases that can affect implant healing. The medical history is used as a basis for ordering an examination.
Visual inspection
An in-person examination involves assessing the condition of the entire maxillofacial system. The implantologist studies the oral cavity, the condition of the gums and teeth, the tongue, the frenulum of the lips and tongue, the function of the maxillotemporal joint, the degree of mouth opening, and changes in bite. Sometimes consultation and examination by other doctors (orthodontist, orthopedist) is required. If implantation has already been performed, the doctor takes into account its results and the condition of the artificial teeth.
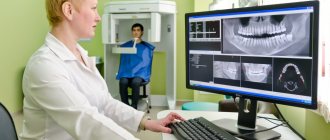
Diagnostic process using a computed tomograph
X-ray diagnostics
Before implantation, you need to collect as much information as possible about the condition of the bone tissue, its thickness and height, density, position of the roots of the teeth, which are located next to the implantation zone. To do this, an examination is carried out:
- Sight X-rays. They reflect the condition of the bone in the area of the planned implantation of titanium rods and neighboring areas.
- Orthopantomogram. Provides information about the condition of teeth, blood vessels, nerves, and bones. A necessary examination, the results of which the doctor uses to plan the operation.
- Computed tomography. A radiation diagnostic method that provides a three-dimensional image of the jaw determines the condition of the bone and nearby structures. Based on the results, the condition of bone and soft tissues is assessed and hidden diseases are identified.
Oral hygiene
Regardless of the size or number of implants, they must be cared for as if they were regular teeth. Brush and floss your dental implants twice a day. Use special fluffy dental floss (for example, Oral-B superfloss or ultrafloss).
When brushing your teeth, pay special attention to the back teeth and between teeth. Use a soft or medium-hard brush. In addition, use an irrigator for additional deep cleaning of the interdental spaces with water irrigation.
There are special brushes that can be used to clean interdental spaces - dental brushes. Ask your dentist about them - in some cases they are not recommended.
Visit your dental hygienist twice a year; they are the only ones who can clean your implants as thoroughly as necessary. Regular visits to the dentist are very important. Your dentist will check the condition of your gums, jaws and implants.
Smoking is bad for your health and for dental implants, too. To have a good prognosis for the lifespan of your implants, it would be a good idea if you stopped smoking.
3D planning for dental implant installation
The results of a CT scan and other measurements of the jaw are entered into a special computer program to visually reconstruct the jaw.
The implantologist calculates the location for the implants and draws up a detailed surgical plan. In difficult situations, the doctor models the jaw visually and then creates a 3D model of the patient’s jaw (using a 3D printer). The model is made of special plastic that imitates the jaw with the patient’s bone density. Using a lithographic model, the implantologist reproduces the operation, studies the structure of the jaw and the nuances of installing implants.
Eating
Avoid chewing hard candy, ice, or other hard foods (such as hard chocolate or dry fish) as they may loosen or break the abutment screw.
Avoid foods such as caramel or toffee, as they may stick to the crown and cause the abutment screw to loosen.
Do not open bottles or crack nuts with your teeth for the same reasons.
Wear protective sports mouth guards when participating in sports and avoid direct blows to the face.
Refrain from grinding your teeth. If creaking occurs unintentionally or during sleep (bruxism), notify your dentist and he will make you a thin night guard.
The length of their service depends on the quality and regularity of care for implants.
Before and after implantation
Our Center has digital equipment for detailed 3D studies
By adjusting the scanning volume, we obtain maximum information about a local area of bone or the entire maxillofacial apparatus with minimal radiation exposure. We examine the bone tissue, the temporomandibular joint, the roots of the teeth, the nasopharynx and even the upper parts of the spine.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Information from the images is used to select a treatment protocol, shape and size of implants, and draw up a detailed surgical plan.
Consultation with relevant specialists
At the first consultation with an implantologist, you need to inform about health problems and chronic diseases. Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs increase the risk of complications during and after surgery.
If a patient complains about health, the doctor prescribes a consultation with a specialized doctor. Most often this is an endocrinologist, cardiologist, or therapist. Surgery is not denied, but treatment will be required to bring the disease under control, adjust treatment and minimize risks.
Analyzes
Laboratory diagnosis is required for older people with a history of severe illness. For patients at risk, the doctor will prescribe tests at the first meeting. Laboratory examination is not carried out against the background of complete health.
Sanitation of the oral cavity
Sanitation involves measures to treat teeth and gums. Necessary to reduce the risks of complications after implantation. Foci of caries or inflammation act as chronic sources of infection and can cause adverse consequences after surgery. Sanitation of the oral cavity before intervention includes treatment:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- stomatitis;
- periodontitis.
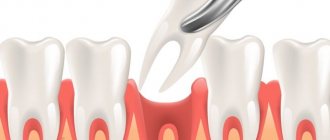
Tooth extraction
The condition of the remaining teeth is assessed by the doctor. The patient is unable to give an objective assessment. Even if in his opinion the teeth are healthy, the doctor may recommend removing them. The reasons are mobility, periodontitis in various forms. These conditions increase the risk of implant failure.
Professional cleaning
Before installing implants, professional teeth cleaning is performed. Remove supra- and subgingival deposits (stone), plaque. This ensures the sterility of the oral cavity.
Orthopedic training
Consultation with an orthopedist before restoring teeth is mandatory if the patient already has orthopedic structures. The doctor evaluates their shape, quality, condition, impact on nearby areas, possible impact on implants, compatibility of materials of already installed and implanted structures.
Bone tissue augmentation
Related articles:
- Bone grafting during implantation
- Bone tissue augmentation
- Guarantees
After tooth loss, bone tissue quickly atrophies. The thickness of the jaw bone decreases, as does the height of the ridge. Since the implant must be firmly anchored in the bone, sufficient bone tissue is necessary. If a tooth is lost more than 3 months ago, implantation cannot be performed without bone augmentation.
The procedure involves increasing the width or height of the ridge of the jawbone. If there is a slight deficiency of bone tissue, one-stage bone augmentation is possible, simultaneously with implantation.
When augmenting with your own material, a bone block is transplanted from another part of the jaw. It takes time to engraft, so most often such operations are performed preliminary (before implantation). We do not recommend this method. We use guided bone regeneration (GBR) technology.
A sinus lift is performed on the upper jaw in the area of the chewing teeth. The operation involves increasing the height of the maxillary bone by raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus. Such interventions are carried out in advance or simultaneously with the implantation of implants.
Photometry
Photometry is the taking of photographic parameters of the face. This is a diagnostic procedure that optimizes the work of the implantologist and orthopedist and helps correct defects in appearance. The patient is photographed from the front, profile, with and without a smile, with his mouth open and closed. The photographs are used by the orthopedist during the modeling of an individual denture. With its help you can improve the lower third of your face, correct your bite and even get rid of wrinkles. The photographs show the difference in the smile before and after implantation.
Occlusion assessment
In order to properly make a prosthesis, it is necessary to identify the characteristics of the bite and the degree of closure of the jaws. For this purpose, condylography is performed - functional diagnostics of the temporomandibular joint. An examination is mandatory in case of multiple or complete edentia, since in these conditions the bite changes. Condylography parameters are needed to create a prosthesis that will correct the bite and relieve the load on the temporomandibular joint.
The procedure is performed using a HIP plane analyzer, articulators, and face bows. Repeat twice (before implantation and before taking impressions of the prosthesis).
Before surgery:
Prepare several days off after the date of the planned operation.
Do not smoke or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke.
If you are sick on the eve of the operation, please notify the implantologist.
Ask your implantologist about the medications you will need immediately after surgery.
Patients suffering from compensated diabetes mellitus must follow a strict diet 2 weeks before surgery and 2 weeks after it.
Get a good night's sleep the night before surgery.
Make sure you are accompanied if you plan to undergo anesthesia, sedation or a complex operation, do not plan to be behind the wheel.
If you have herpetic rashes on the mucous membrane, the operation should be rescheduled.
After operation:
If you have had dental implants, you may experience some of the typical discomforts associated with any type of dental surgery. These may include:
- Swelling of the gums and face.
- Gum injury.
- Mobility of adjacent teeth.
- Pain at the implantation site.
- Minor bleeding.
- Bruises and bruises.
You may need painkillers and antibiotics. Follow the recommendations of the implantologist.
What must be observed after implantation:
- Brush your teeth with a soft brush before removing sutures
- Eat soft foods for 5-7 days. Do not eat hot, spicy or salty foods.
- Starting from the third day after surgery until the sutures are removed, you should rinse your mouth with a chlorhexidine solution twice a day (after brushing your teeth).
- Do not overheat in the sun or in a sauna.
- Do not engage in active sports.
- Do not smoke or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke.
- Do not fly on an airplane, do not swim, do not dive for 2 weeks (especially important after sinus lift surgery).
- Do not blow your nose or sneeze with your mouth open (especially important after sinus lift surgery).
- If swelling, discomfort or other symptoms increase within a few days after surgery, or the temperature rises, contact your implant surgeon.
- After tooth extraction
- If you have had a tooth removed, you must take care of your oral cavity. By following certain recommendations, you will feel better and healing time will speed up.
The drug "Sevoran" in modern pediatric dentistry
It is difficult to imagine modern pediatric dentistry without anesthesia - young patients cannot always tell what exactly is hurting them, and do not allow the doctor to do a full examination. Until recently, young children did not receive dental treatment, which was fraught with damage to baby teeth, and as a result, permanent teeth could form incorrectly. Treatment and removal of teeth under anesthesia is an excellent option for pediatric dentistry.
The drug Sevoran (sevoflurane), produced by Abbott Laboratories, is often used as dental anesthesia in children's clinics. It is believed that Sevoran is one of the safest drugs for anesthesia today.
The main active ingredient of Sevoran is sevoflurane. The drug is supplied in liquid form, packaged in dark 250 ml bottles. Before use, Sevoran is poured into an evaporator, where it turns into a gaseous state and provides the child with inhalation anesthesia.
Kon is adjusted using an anesthesia machine, which helps influence the duration and depth of dental anesthesia. Using Sevoran, you can perform not only treatment or tooth extraction, but also other surgical procedures such as removal of a defect in the frenulum of the lip or tongue.
“Sevoran” has established itself as a safe drug with minimal side effects, and although it is used quite rarely for adults, in pediatric dentistry it is indispensable for the treatment and removal of teeth under anesthesia.
Stopping bleeding:
To control bleeding, it is necessary to bite down on a gauze pad placed by the dentist in the oral cavity. The pressure promotes the formation of a blood clot in the socket. If you have heavy bleeding that has not stopped within an hour of tooth extraction, you should bite into a regular tea bag. Tannin in tea helps in the formation of blood clots. Hold the tampon or tea bag until the bleeding stops.
Additionally, cool the extraction area, apply a cold compress to the face in the area of tooth extraction for 10-15 minutes. at one o'clock. A slight bleeding on the first day after removal is normal.
Consultation with an implantologist before surgery - when and why it is done
Before implantation, the patient visits the doctor at least 2 times. If there are health problems, the implantologist prescribes consultations with specialized doctors in order to comprehensively prepare the body for surgery. Each of them prescribes their own treatment. The operation is carried out after removing the obstacles.
Initial consultation
At the first meeting, the implantologist conducts a survey and examination, collects anamnesis, and sends the patient for x-ray diagnostics. Based on the results obtained, he prescribes:
- laboratory diagnostics (tests);
- consultations with specialized doctors;
- sanitation of the oral cavity (treatment of teeth and removal of those that cannot be treated);
- correction of already installed orthopedic structures;
- bone grafting, if indicated as a separate stage.
At the initial consultation, the approximate time frame for solving the problem is assessed. The final terms and cost of treatment are calculated after drawing up a detailed plan, taking into account additional procedures and identified obstacles.
On the eve of the operation
After preoperative measures, the doctor checks the patient’s readiness for implantation. If all obstacles are eliminated, a surgery date is set. The doctor explains in detail the sequence and duration of the procedure and how to prepare at home. A contract for the operation is drawn up.