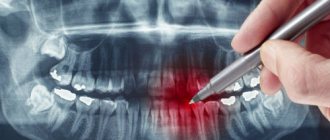
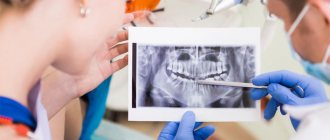
X-ray examinations in dentistry are divided into two types: traditional two-dimensional radiography and 3D computed tomography. The advantage of the latter is that it allows you to examine each tooth from literally all sides - in all conceivable sections and sections. As a result, the doctor receives the most complete and reliable information about the condition of the patient’s dental system.
What is dental computed tomography?
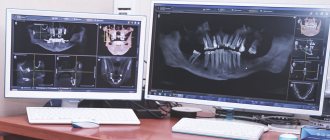
In modern clinics, 3D photographs of teeth are taken using cone beam tomographs. The design of such devices is based on a C-shaped arc, on one side of which there is an X-ray source, on the other - its detector. During the examination, the arc makes a full revolution around the patient's head, scanning his jaw from different angles. During this time, the detector manages to take about 200 two-dimensional images, which are then converted by software into a three-dimensional model of the jaw.
On a computer, the doctor can study the created 3D model in the way that is convenient for him: rotate, enlarge individual fragments or make sections of potentially suspicious teeth, take bone measurements necessary for implantation. Digital images are high resolution and clear. Therefore, with their help, it is possible to identify features of the dental system that cannot be seen on a regular x-ray.
Which is better - multislice or cone-beam CT?
Multislice MSCT
The device scans the area under study in a spiral, the examination is carried out in a horizontal position. Most often used in maxillofacial surgery. Layer-by-layer visualization occurs, soft and bone tissues are examined. The results are indispensable for TMJ dystrophy and jaw injuries. But for traditional implantological treatment, MSCT has some disadvantages:
- results may be inaccurate
due to the horizontal position of the patient - distortion of jaw closure occurs; - high degree of radiation
up to 1000 μSv - such radiation exposure is impractical, since after the operation more than one control examination is carried out in the first year.
Cone beam CBCT
This is a newer method, used in our clinic before implantation. The device rotates around the patient's head, the procedure is performed in a vertical position. Scanning of the area under study occurs in different planes. CBCT is important when planning dental implantation and has advantages over MSCT:
- radiation exposure is less - 25–50 μSv, can be carried out several times a year;
- fast diagnostics;
- wide range;
- cheaper than MSCT.
Indications for computed tomography
- Upcoming orthodontic or orthopedic treatment
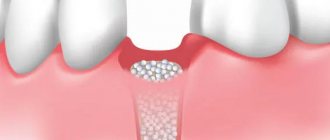
- Planning for dental implantation (in this case, photographs are taken with markings of missing teeth)
- Diagnosis of hidden dental pathologies
- Diagnosis of cysts, tumors of the dental system, diseases of the temporomandibular joint
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Acute respiratory infections
How is the preparation carried out?
Computed tomography of teeth does not require special preparation. Before the examination, the radiologist will ask you to remove items that may interfere with the operation of the tomograph: earrings, hair clips, piercings, glasses, hearing aids. If you have removable dentures, you will need to remove them from your mouth. Before the procedure, the patient must wear a protective lead apron.
Advantages of the MRI method
Magnetic tomography is a safe, painless and most informative type of diagnostics for a wide range of diseases:
- blood vessels;
- brain;
- thyroid and mammary glands;
- joints;
- internal organs;
- soft tissues;
- spine;
- tumor processes.
MRI eliminates radiation exposure to the body, does not require special preparation, and has only the presence of metal implants in the body as contraindications. This type of study can be carried out during pregnancy and at a very early age. There are no restrictions on the frequency of tomography repetitions. It is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
How is the research going?
The examination is carried out in 1-3 minutes:
- The doctor takes the patient to the CT scanner and helps fix the head in the desired position. Depending on the design of the tomograph, the examination takes place while sitting or standing.
- A small plate covered with a disposable cover is placed in the mouth, which fixes the position of the jaws.
- The scanning arc of the tomograph makes one revolution around the patient's head. The exposure time to X-ray radiation does not exceed 20 seconds.
The specialist writes the obtained data onto a CD and, if necessary, prints it onto film.
What is a 3D dental image?
If you visit an orthodontist, maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, or even a plastic surgeon for a consultation, most likely one of his first appointments will be to do a computed tomography (CT) scan of the jaw, or a 3D dental scan. This is a modern and very accurate diagnostic technique that allows the doctor to view an image of the patient’s jaw from any angle and in any projection, even when the patient has already left his office. CT, unlike an orthopantomogram, provides a three-dimensional image of the jaw without distortion and allows you to look into any layer of tissue, making a kind of virtual section, without the need to perform unnecessary traumatic procedures on the patient live. The efficiency and safety of diagnosis and treatment are thus significantly increased.
How much does it cost to take a dental photograph in Moscow?
The cost of a 3D dental photo in Moscow depends on a number of factors: the clinic, the type of equipment and the size of the area being examined. The price of the service usually already includes recording images onto a CD. Printing of photographs is paid separately.
We compared the cost of dental CT scans in two well-known Moscow dental chains: “All Yours”, “Novadent” and in the clinic of the Open Association of Dentists ROOTT.
Dental network “All Yours”
- Cost of initial examination at the clinic: Free.
- Cost of CT scan: The clinic only takes a picture of both jaws for orthodontic or periodontal treatment. The cost of 3D tomography for new clients is 3,700 rubles, for regular clients - 2,700 rubles. The clinic’s website does not indicate the cost of a CT scan with image markings (for patients planning implantation).
- The cost of deciphering the results: 1000 rubles.
- Cost of printing photos: No information on the website. More information about the clinic.
Dental network "Novadent"
- Cost of initial examination at the clinic: Free.
- Cost of CT: Only the lower price threshold is indicated - from 4050 rubles. The minimum shooting area is 10X10 cm (i.e., both jaws are scanned at once).
- Cost of interpretation of results: Included in the cost of CT.
- Cost of printing photos: No information on the website. More information about the clinic.
Clinic of the Open Dental Association ROOTT
- Cost of initial examination at the clinic: Free.
- Cost of CT: In the area of 3 teeth - 1300 rubles, for two jaws - 4000 rubles, for two jaws + sinuses + temporomandibular joint - 5000 rubles. Marking for the implantation of 3 teeth with printing on film costs 1000 rubles, for implantation of one or both jaws with printing on film - 2500-4500 rubles. When receiving treatment at the ROOTT clinic, image marking is performed free of charge.
- Cost of decoding results: Included in the cost of the service.
- Cost of printing photos: Included in the cost of the service. More about the clinic
In our opinion, performing computed tomography in ROOTT clinics is most beneficial for patients, especially for those planning implantation. In addition, this is one of the few clinics in Moscow where you can take three-dimensional photographs of not only both jaws, but also individual segments of the oral cavity, jaw joints, maxillary sinuses and lacrimal canals. Such images are often required by therapists (when treating root canals) or surgeons (when planning an operation). Computed tomography of teeth allows patients to further save on treatment and reduce radiation exposure.
Equipment of centers and cost of services
We use modern PHILIPS ACHIEVA tomographs, expert-class equipment with a power of 1.5 Tesla. This makes it possible to make scanning as accurate and effective for diagnosis as possible. Our prices are truly affordable - at least 25% lower than the average market price for MRI in Moscow.
Approximate image quality at 0.3-0.5 Tesla.
Image quality is 1.5 tesla. Higher quality means lower probability of error.
Contraindications for 3D dental imaging
The radiation exposure of CT scans ranges from 0.045 to 0.06 mSv. This is relatively little, given the recommendations of SanPiN, which indicate the upper possible threshold of radiation exposure for research purposes equal to 1 mSv per year. However, if you compare a CT scan with a dental x-ray, where radiation occurs in the range of 0.002 - 0.003 mSv, a 3D photograph of teeth no longer seems so harmless. In this regard, there are a number of contraindications to CT scanning. If we are talking about simple tomography, then, as a rule, it is not done during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester. The doctor will always consider the need for radiation exposure for a pregnant patient based on the balance of benefit to the mother and risk to the fetus. If tomography with contrast is necessary (for better visualization of soft tissues and blood vessels, it is rarely used for CT of the jaw), then the number of contraindications expands. It should not be given to pregnant women, nursing mothers, or to persons suffering from thyroid disease, severe diabetes mellitus, renal failure, or an allergy to iodine. If you have any allergies or have ever experienced drug intolerance, be sure to tell your doctor.
3D computer X-ray diagnostics for TMJ diseases
Complaints from patients in the dental office have long spread beyond the dental system - these include headaches, drowsiness, chronic fatigue, tinnitus, hearing loss, poor posture, numbness in the fingers and even wrinkles and dull complexion.
The dentist is not limited to just examining the oral cavity. He is interested in whether you snore in your sleep, whether you have flat feet, whether nasal breathing is difficult, and will definitely pay attention to the relative position of your facial bones and the symmetry of skeletal landmarks. The doctor will try to collect as much information as possible, seemingly completely unrelated to the main problem, in order to draw up the most competent treatment plan.
The initial examination almost always includes computed tomography (CT) of the maxillofacial area and, if necessary, teleradiography (TRG). After carrying out a standard analysis of radiological data (determining the condition of dental tissues and periodontal tissues), we conduct further examination of bone structures
for the presence of abnormal growths and calcification of ligaments and tendons. This usually happens as a compensatory (response) reaction of the body in response to hypertonicity of a particular muscle. Being in constant spasm, the muscle seems to pull the bone behind it, forming bone growths at the site of its attachment.
Manifestations of anomalies
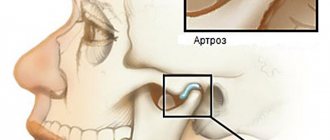
Condition of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
computed tomography is one of the first to signal us about possible disturbances in occlusion and the need to restore muscle balance.
With increased or physiological (age-related) abrasion, loss of a group of teeth, a decrease in the bite occurs, a shortening of the lower third of the face, nasolabial folds, “puppets”, and wrinkles near the lips appear. In this case, the lower jaw moves back, and the articular heads move towards the posterior wall of the joint, bordering the auditory canal. In this condition, pain in the joint may occur, since the articular head will compress the so-called bilaminar zone, in which the neurovascular bundle is located. In this case, tinnitus and headaches are possible.
Often, with an unstable position of the lower jaw, the lateral pterygoid muscle, which is fixed at one end to the articular head and articular disc, is in a spasmodic state. Under the influence of this traction, the disc moves out of its place and no longer absorbs shock when opening/closing the mouth (manifests itself in the form of clicks in the joint, pain, limited mouth opening), and the articular head is deformed, which gives the doctor a hint about the need to manage the patient in the neuromuscular concept .
Kimmerly Anomaly
This is the formation on the posterior arch of the first cervical vertebra of an abnormal bone bridge (ponticulus posticus) in the form of a ring or semi-ring above the vertebral artery supplying the brain. According to recent studies, this condition is attributed to the body's compensatory mechanisms to protect the vertebral artery during bruxism (involuntary grinding of teeth, mainly during sleep), as well as postural deformities of the spine, which are caused by the distal position of the lower jaw (its displacement back), which occurs with the loss of chewing teeth, increased abrasion, incorrect orthodontic treatment.
Clinical manifestations are associated with compression of the vertebral artery: headaches, migraines, tinnitus, loss of consciousness when throwing the head back, impaired coordination of movements, numbness of the fingers, tremor of the limbs, etc. This anomaly is easily diagnosed by CT or teleroentgenogram (TRG).
Also in our practice, we often encounter other changes in the spine associated with musculoskeletal imbalance. Such as:
- Deformations of the odontoid process
of the second cervical vertebra.
- Ossification (ossification) of the cruciate ligament of the atlas
(first cervical vertebra).
- syndrome
.
On CT it appears as an elongation of the styloid process. In fact, this is a calcification of the stylohyoid ligament, which starts from the styloid process, passes between the external and internal carotid arteries and is attached to the hyoid bone. The ossification process is caused by chronic tension of the ligament, which in turn is a consequence of the position of the lower jaw in a forced, pathological bite. All symptoms and manifestations of this syndrome can be divided into two subtypes depending on the proximity of this growth to the branches of the carotid arteries or to the nerves (hypoglossal, glossopharyngeal) and muscles.
- When the nerve endings of these nerves are irritated (stylopharyngeal syndrome
) there may be pain in the pharynx, tonsils, soft palate, root of the tongue, sensation of a foreign body in the pharynx, as well as impaired taste perception in the posterior third of the tongue.
- If this growth irritates or compresses the branches of the carotid artery in certain positions of the head (awl-carotid syndrome
), then the face will have vascular (vascular) symptoms associated with impaired blood supply to the carotid artery of the brain, orbital area, and face. This manifests itself as headaches, pain in the orbital region, frontal, parietal and in the ears. This option is the most unfavorable, since it can cause acute cerebrovascular accidents, cerebral infarctions and lead to disability of the patient. Therefore, timely diagnosis of this syndrome may be vital.
- Proliferation of the angles of the lower jaw.
Formed in the area of attachment of the masticatory muscle (m. masseter). Observed with parafunction (increased activity) of the masticatory muscles, clenching (involuntary strong clenching of the jaws) or bruxism.
When something is wrong with the body, it always gives clues. The main thing is to be able to read them in time. To maintain your health and recognize diseases on time, make preventive visits to the doctor.
Megastom clinics are equipped with the most modern equipment, and our doctors will unravel the most complex diagnostic tangle and will certainly offer solutions to the problem for each patient.
In the next article we will continue to introduce you to 3D computer X-ray diagnostics for TMJ diseases.