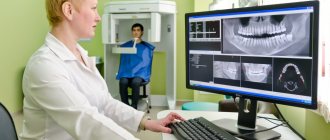
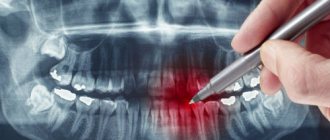
Computed tomography (CT) allows you to most accurately diagnose the condition of the patient’s oral cavity. That is why this procedure must be done before implantation. Only based on the results of such diagnostics can the dentist make a conclusion whether implantation is indicated or, conversely, contraindicated for a particular patient.
CT allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the jaw, and in great detail. This is a kind of successful alternative to an x-ray. In dentistry, spiral or multispiral dental tomographs specially created for this purpose are used. They scan tissues and transmit data to a monitor.
Advantages of computed tomography
The results of computed tomography make it possible to detect any pathologies in the oral cavity at the earliest stage of their development. Thanks to this, treatment can be prescribed on time and, accordingly, proceed faster than with an advanced problem. For successful dental implantation, three-dimensional photographs are simply necessary for the dentist; this is the only way to choose an error-free option for installing implants. Statistics show that in 65% of cases of implant failure, dentists did not have three-dimensional photographs of the patients’ jaw bones. On the other hand, if such images are available, successful implantation is observed in 98% of cases.
Types of CT in dentistry
Modern dental and diagnostic centers use different types of tomographs:
- cone beam,
- spiral,
- apparatus for sequential processing of layers.
Modern dental centers use different types of tomographs.
The choice of a specific technique remains at the discretion of the specialist. So, for example, for dental implantation using one-stage technology, a computed tomography scan is a prerequisite. If you plan to implant zygomatic implants, you will additionally need to undergo multislice tomography. And here you need to understand that even modern clinics for the most part do not have professional diagnostic equipment with the required level of detail. Therefore, to obtain better and more informative images, the patient is sent to specialized medical institutions.
Benefits of CT
- Minimum X-ray exposure. CT scan is indicated even for young children.
- Diagnostics takes from 8 seconds to 5 minutes.
- There is no need to decipher the diagnostic result.
- The highest quality and resolution of images.
- Adjustable image contrast allows you to reveal the smallest details.
- The ability to study the problem area in three planes.
- Ability to change the scale of the image or part of it.
- The ability to see the location of nerves and thereby optimally select places for bone drilling.
- The ability to quickly make copies of a photo.
- The ability to detect complications invisible to the eye.
Computed tomography is a completely painless procedure. It does not even cause the slightest discomfort in the patient. Depending on the type of tomograph, diagnostics can be performed while the patient is sitting, lying, or standing. No preliminary preparation is required to carry it out. A computed tomography scan can be done even when the patient comes only for a consultation. Pictures can be received instantly. Computed tomography is important for both the patient and the dentist; there is no more accurate diagnosis.
What is a 3D photo?
A 3D image or computed tomography of teeth is an x-ray that is performed using a special device - a tomograph (CBCT). The picture is a three-dimensional image that demonstrates the entire dental system in detail. The resolution of the image is high, which means that even the smallest details can be seen in it. The doctor, using a computer program, will be able to thoroughly examine absolutely any part of the patient’s jaw, moreover, at any depth and at any angle. The snapshot is provided on disk, where it is stored. If you need to view the disc, you can insert it into your computer and see everything you need on the monitor. Moreover, sometimes this diagnostic option saves the patient from a number of unpleasant manipulations on the part of the doctor.
On a note! The scanning volumes of such an image vary from 5x5 to 13x15 cm.
An orthodontist, implantologist, maxillofacial surgeon and other doctors can give a referral for such a plan. The technique is very accurate, and often without it, doctors simply will not do most of the manipulations. And the effectiveness of treatment thanks to this image increases significantly.
The advantages of taking a 3D photo are as follows:
- high image accuracy and detail;
- the ability to view all parts of the mouth - the image is three-dimensional;
- errors are excluded when identifying the location of pathology development, since there are no distortions in the image;
- the ability to assess the condition of the jaw from any side;
- the picture is taken quickly - a few seconds are enough to get a detailed image;
- taking a picture is safe for health, since the radiation exposure experienced by the patient’s body is extremely small. Especially if you compare its level with the level with the same x-ray.
Disadvantages of Computed Tomography
Alas, this seemingly completely harmless procedure has its drawbacks. They consist in the fact that CT has a number of contraindications. These include the following reasons:
- an allergic reaction to a contrast agent that is used to pre-treat the patient’s oral cavity;
- pregnancy at any stage;
- breastfeeding a baby;
- the impossibility of diagnosing excessively active young children;
- panic fear of closed spaces;
- diabetes;
- kidney diseases;
- thyroid diseases.
The introduction of a contrast agent into the oral cavity allows you to obtain the highest quality image of the oral cavity. However, as a last resort, you can do without this, which experienced dentists sometimes do.
A CT scan of the oral cavity can be done no more than twice a year. Moreover, over the next year it is necessary to refrain from this procedure.
Features of irradiation during CT and not only
The operation of the tomograph is based on the effect of x-rays. Without knowing all the features of the procedure and equipment, some still believe that dental CT is harmful to health, since the body is exposed to radiation. At the same time, few people remember from a school physics course that a person is exposed to radiation everywhere, even outside the X-ray room, for example:
- Outdoors on clear days. The sun is the largest natural source of radiation.
- At home, being near switched on household appliances: TV;
- refrigerator;
- various kinds of gadgets, etc.
To understand what kind of radiation exposure a person receives during a CT scan of the jaw and whether it is harmful, it is worth learning a little more about the radiation itself. It is measured in sieverts (Sv), millisieverts (mSv) and microsieverts (µSv). According to SanPiN standards, the following are safe for a person undergoing preventive medical examinations:
- 1000 μSv per year for an adult;
- 300-400 µSv per year for children under 15 years of age.
Taking into account the fact that one x-ray examination is performed with a radiation dose from 2-3 μSv (sighting shot) to 16-18 μSv (panoramic shot of the jaw), it is permissible to take 300-500 targeted shots or 60-70 shots of the jaw per year. These figures reflect average data without reference to any specific type of equipment. But they also show that it is not harmful to the body to receive only a few microsieverts for a detailed diagnostic picture.
You might be interested in:
Dental diagnostics
Computed tomography of teeth and jaws
Orthopantomogram of teeth
How is a tomographic image taken?
A three-dimensional dental tomograph consists of a scanner and a computer. Scanning of the oral cavity is performed using very weak x-rays.
Currently, the industry produces two types of tomographs for dentistry. Tomographs of the first type have a scanning device in the form of a cylinder, through which a table with the patient moves. Tomographs of the second type are equipped with a head stand. The stand is installed on the rotating part of the device. If the first type of tomograph is universal, then the second is designed specifically for the needs of dentistry.
Both types of tomographs work on the same principle. The scanner takes from two hundred to six hundred images of the patient’s oral cavity within one hundred seconds. All of them are sent to the computer in electronic format. The program installed on it analyzes the images and produces an accurate image of the area under study. A three-dimensional image is formed by superimposing layers of different thicknesses on top of each other. Each such layer is separately saved as a DICOM file and can be examined separately.
The tomographic diagnostic procedure itself is not at all burdensome and is done in the following sequence.
- The patient is freed from all metal objects that he has with him.
- The patient places his chin on a support.
- The patient remains completely motionless for several seconds.
That's the whole procedure. If the diagnosis requires the administration of contrast, the patient must not eat or drink anything for 4 hours before the diagnosis.
How long does it take to do a CT scan?
The duration of tomography depends on the type of diagnostic equipment used. Before doing a CT scan of the jaw and teeth, it is better to ask what kind of tomograph is used in the clinic. Modern devices allow you to carry out the necessary manipulations as quickly as possible with minimal radiation. If you are offered a procedure that will last more than 15 minutes, then you should refuse. Only innovative equipment allows you to carry out the required research in just a few minutes, guaranteeing highly detailed images.
On average, everything is done in no more than 10 minutes, taking into account the instruction time and the preparatory stage. Please note that 3Shape is also used for 3D diagnostics, but this intraoral scanner is not suitable for all types of diagnostic studies. The attending physician will be able to determine which scan is required for you after collecting a general clinical picture and based on the reason why you came to the dentist.
What exactly does CT help with successful dental implantation?
Computed tomography is not a mandatory procedure when preparing a patient for dental implantation. You can do without it by trusting the experience of the dentist. However, in this case, there is a high probability of unsuccessful implantation. Simply put, there is no complete guarantee that the implant will grow into the bone safely.
Computed tomography allows the dentist to obtain:
- comprehensive information on jaw bone density;
- a complete picture of existing foci of inflammation and defects in the oral cavity;
- an accurate picture of the location of the maxillary sinuses, nerves and blood vessels;
- the ability to accurately calculate the size of implants and the optimal depth of their immersion into the bone;
- the ability to accurately determine the optimal angle of inclination of the implant in relation to the dentition;
- the ability to calculate the maximum permissible mechanical load on the implant.
Agree, each of the listed points is extremely important for successful implantation. Under no circumstances should any of these points be neglected.
What is dental tomography?
When performing any type of CT scan, the principle of different conductivity of X-ray rays by different tissues of the body is used: cavities, bones, muscles, ligaments, etc. In this case, the rays penetrate through any tissue of the body and are captured using a special detector. After a series of layer-by-layer images, a 3D computed tomography model is built using a computer.
Most often, dental tomography of teeth is prescribed before prosthetics, dental implantation, or surgical intervention on the jaw.
The X-ray method does not provide all the advantages that modern computed tomography can provide. Dental CT allows you to study various features of dentofacial anatomy: the structure of teeth and canals, the condition of the jaw bones.
CT results are indispensable for orthopedists, pediatric dentists, orthodontists, and surgeons. For example, for the most accurate production of any prosthesis, the doctor often needs data on the exact dimensions of the jaw anatomy and the most detailed location of the teeth. Only in this case can the prosthesis be manufactured with maximum comfort for the patient.
If, when using implants, the artificial root is implanted incorrectly (inaccurate dimensions or in the wrong location), then the prosthesis will be uncomfortable for the patient or will quickly fail.
Therefore, CT in many clinics is a mandatory preparatory procedure for any type of dental prosthetics (removable or dentures).
Dental tomography is also indispensable for orthodontists, as it ideally shows the exact location of the teeth. In case of surgical pathologies, this method allows you to fully examine the existing dentofacial injuries in all projections.
Individual application
Dental implantation is not some cookie-cutter procedure. On the contrary, it requires an exclusively individual approach, since no two identical jaw bones exist in nature.
The key to successful implantation is the complete surrounding of the implant surface with bone tissue. The implantation should be completed without the slightest gap between the bone and the artificial root. This process occurs differently for each person.
The dentist’s task, among other things, is to choose the right place to drill a hole for the implant. In this place, the density of bone tissue should be maximum, but it is far from being the same throughout the entire volume of the jaw.
No less important is the choice of the angle of inclination of the implant. If there is an error, the crown will not fit into the overall shape of the remaining dentition.
The drilling depth must also be calculated as accurately as possible to avoid damaging the nerve.
Without computed tomography data, it is extremely difficult to do all this.
Read also
What is dental restoration
If the aesthetic properties of teeth are lost, a person experiences certain discomfort.
What to do if your tooth aches
Sometimes aching pain in a tooth can appear for no apparent reason at first glance.
Risks and dangers of dental implantation
The most risky is dental implantation in the lateral parts of the upper jaw. This is due to the presence of the maxillary sinuses in this area. The trouble is that after the loss of teeth, these sinuses tend to increase in size. It is almost impossible to find out their size without a computed tomography scan. Problems in the maxillary sinuses can significantly complicate dental implantation in the upper jaw, and therefore diagnosis of the sinuses is done as carefully as possible.
If there is chronic inflammation, tumors, polyps or cysts, dental implantation is not performed until all these problems are eliminated. If this is not done, then the implants in the bone tissue simply will not take root and will be rejected by the body. An opinion on the readiness of the upper jaw for implantation is given by two specialists - a dentist and an otolaryngologist. This approach minimizes the likelihood of implant failure.
Is special training needed?
The preparatory stage includes an initial consultation with a dentist, who conducts a survey to identify possible contraindications. Further preparation depends on what type of research needs to be carried out:
- Normal (without contrast injection). Such a CT scan will not require additional preparation, except for the general requirements: it is recommended to remove all metal objects from the head - earrings, hairpins, etc. if present, remove the hearing aid and removable dentures; warn the radiologist if there are non-removable orthopedic structures in the mouth (this will allow the specialist to adjust the device in a special way).
The lack of serious preparation before taking a CT scan of two jaws or teeth allows diagnostic studies to be carried out immediately after receiving an order from a doctor.
What are the consequences of not having a three-dimensional image?
Refusal to conduct a computed tomography scan can lead to very sad consequences. The fact is that without a three-dimensional image, the dentist makes a decision almost intuitively, and this, of course, is a risk. The consequences may be as follows:
- nerve damage;
- inflammation of the gums due to uneven load on the implants;
- premature wear of the structure;
- the likelihood of resorting to treatment for problems with the oral cavity;
- risk of re-installation of the implant.
Where is the best place to get a dental MRI?
ABC-Medicine, a network of medical clinics for the whole family, offers to visit MRI diagnostic rooms in Balashikha and near the Park Kultury metro station. If necessary, you can make an appointment with a dentist or any other specialist. These two clinics have adult and pediatric departments, modern diagnostic equipment, as well as operating rooms with short-stay wards. If an MRI reveals the need for surgical intervention, you will be able to get all the necessary help right on the spot and at an affordable price. Pay attention to special dental programs - for example, “Annual oral hygiene for children”, which at a low cost will help you save on visits to the dentist and maintain dental health since childhood.
CT scan after implant placement
Many patients have questions about whether a CT scan can be performed after implants, crowns or pins have been installed. This question is asked for a reason. Many people know that when performing an MRI, artificial materials present in the oral cavity create a “phonic” sound and thereby confuse dentists. Nothing like this happens with a CT scan. Moreover, it is advisable to do a computed tomography scan before and after dental implantation. This will allow, firstly, to verify the success of the operation, and secondly, to notice in time possible problems with implantation.
However, if there are metal crowns in the oral cavity, it is better to refuse computed tomography. The fact is that metal interferes with the normal operation of the scanner. As a result, the picture turns out to be of poor quality. The same applies to metal pins.
Situations when taking photographs is strictly prohibited
Such situations practically never occur. On an individual basis, X-rays are considered in cases where the patient receives radiation in other areas of life: for example, in hazardous work, while undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy. But again, when X-raying the state of the jaw system, the radiation is so small that it will not affect the overall picture.
Thus, you should not be afraid to take photographs - in single quantities they are quite acceptable and will not affect your health at all.
It is important to understand that such diagnostic procedures allow for better treatment, especially with dental implantation, the results of which will last not a couple of years, but for many years of life. 1 Sanitary rules and regulations (SanPiN) 2.6. 2.6.1.1192-03 for the design and operation of X-ray rooms, devices and the conduct of X-ray examinations.
Preparatory stage
CT scan of the upper and lower jaw according to the basic (native) protocol does not require special preparation. If a CT scan of the jaw with contrast is prescribed, the diagnosis is usually carried out with a break in food for 2 hours. If the patient suffers from renal failure, tests to determine the level of creatinine in the blood are preliminarily prescribed before contrast tomography. This way, the doctor can assess the possible risks of developing nephropathy after administration of a contrast agent. Before entering the CT room, it is better to change into comfortable clothes and remove all jewelry.
Indications
Determining whether a patient has indications for this tomography is usually determined by a dentist, oral surgeon or orthopedist-traumatologist. Computed tomography of the jaw is primarily intended to identify bone diseases and pathologies of the maxillofacial area, including:
- injuries of the upper and lower jaw
- dislocations and subluxations;
- osteomyelitis
- osteonecrosis
- osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis.
Computed tomography data will additionally be able to show some dental defects and dentition anomalies, bone cysts. Tomograms can be used to first approximate the condition of the temporomandibular joint, but its pathologies are better visible on MRI of the temporomandibular joint. In the field of maxillofacial surgery, MSCT is used to create implants and maxillofacial structures.