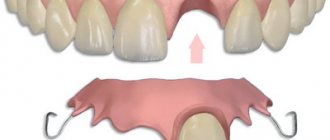
Temporary fixation technology
At the preparatory stage, the surgical field and orthopedic structures that are to be fixed are dried and isolated from saliva. Degreasing of working surfaces is not required. Temporary cement is mixed taking into account the manufacturer's recommendations. In the future, the fixation technique - using the example of temporary acrylic crowns on eugenol-free cement - looks like this.
- Temporary cement is applied with a spatula to the cervical part of the temporary crown.
- Under bite control in habitual or central occlusion, the orthopedic structure is fixed in the oral cavity.
- After the time specified by the manufacturer, the temporary cement is removed.
- If work is carried out in support of a dental implant, a rubber dam is used to protect the latter.
- The final stage is x-ray control to check the effectiveness of cement removal.
- Fixation is completed by control of occlusal contacts.
- The patient receives recommendations on the rules for caring for the structure (they are practically no different from the case of installing fixed structures on permanent cement, with the exception of replacing dental floss with a dental brush).
Compound
Glass ionomer cement is a combination of powder and liquid. The powder contains fine-fractal elements of aluminum fluorosilicate glass containing silicon oxides and dioxides, metal and calcium fluorides, aluminum phosphate, radiopaque salts, as well as precious metal alloys. A copolymer solution of tartaric and carboxylic acid is used as a liquid component, providing polymerization of the composition.
Operational characteristics
The degree of fixation depends on the characteristics of the temporary cement. One of its important properties is the retention force, which allows you to hold the structure and remove it if necessary. The optimal characteristics of temporary cements include:
- good adhesion of indirect restoration;
- ease of mixing and application;
- ease of removal after fixation of cement residues from prepared structures and outer surfaces of the crown;
- adequate working hours;
- optimal viscosity for comfortable use;
- easy removal of the structure without damaging nearby tissues;
- biocompatibility with abutment tooth structures and soft tissues;
- long shelf life;
- no effect on the adhesion of permanent cement.
To identify and remove excess cement, it must be radiopaque. Today, none of the temporary cements on the market have absolutely all of the above properties. It is advisable to use each of them for a specific purpose due to the lack of a single universal solution.
Production of filling material
When developing a high-quality mixture for use in dentistry, manufacturers strive to ensure that its composition closely resembles the natural, inherent component of the tooth. For this purpose, additives are used that divide dental cement.
into several types:
- phosphate;
- polycarboxylate;
- polymeric;
- silicophosphate;
- glass ionomer.
Each subtype of cement is used in certain cases of oral treatment. The phosphate type is used for filling teeth with increased chewing load; polycarboxylate solution is characterized by rapid hardening. Polymer cement does not leave gaps between the gums; the silicophosphate type is good for its increased plasticity properties, and the glass ionomer solution is hypoallergenic and color resistant.
From the family of dental cements: Silicin Plus, Cemilight, Cemion, Uniface-2...
When contacting your dentist, ask him what materials are used to treat your tooth.
You can also choose the type of cement yourself, having previously studied its features and consulted with your dentist about the advisability of using it. Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
Complications
Due to temporary fixation, the following complications are possible:
- de-cementing;
- damage to the supporting structure;
- breakage of the orthopedic structure during removal;
- development of gingivitis or peri-implantitis due to insufficient removal of temporary cement from the gingival sulcus.
The most severe complication is peri-implantitis, in the event of which it is necessary to remove the structure as quickly as possible, remove excess cement and carry out anti-inflammatory measures.
Breakage of the prosthesis or supporting structures is possible due to too much retention force of the temporary cement. Most often, temporary crowns made of plastic or composite materials break. Correcting the situation is quite simple - the damage is glued together with plastic or composite right in the office.
When permanent structures are removed, the ceramic veneer often chips, which requires the manufacture of a new denture. Therefore, it is undesirable to fix ceramic or metal-ceramic prostheses with temporary cement. The least common cases in orthopedic dentistry are cases of breakage or fracture of the crown of a tooth and other damage to supporting structures. Also considered quite rare is the case of excessive load on the implant with the development of peri-implantitis.
General overview
From the point of view of the current classification, glass ionomer cement belongs to the category of materials based on the combined structure of a silicate system and a polyacrylic polymer of the thermoplastic group. The functional properties of the composition determine the rapid growth of its popularity - GIC can be considered as the next stage in the evolution of cement materials, replacing traditional zinc-based phosphate and polycarbonate compositions.
Differentiation of glass ionomer cements involves the use of three criteria:
- By area of application, they are divided into compositions for fixing prosthetic and corrective systems, treating and restoring the structure of dental tissue, securing fillings and onlays, as well as ensuring tightness and adhesion;
- Based on the form of release, there are powder materials, capsule modifications, as well as photopolymer cement paste that does not require pre-mixing;
- According to the mechanics of hardening, the already mentioned photopolymer compositions are divided, as well as materials that harden as a result of a chemical reaction with water.
Conclusion: what to choose?
Based on the results of everything said above, we can conclude that there is no ideal method of fixing crowns, but the optimal one will be the one that best suits a particular patient, provided that it is chosen by a professional based on objective factors. In addition, competent and careful adherence by the orthopedist to the technology will help mitigate any shortcomings and avoid negative consequences.
The VivaDent dental clinic employs just such professional dentists - qualified, experienced and competent, which means that no matter how the crowns are installed on your implants, it will be implemented flawlessly.
Glass ionomer cement for fixation of crowns and fixed dentures
The liquid part of glass ionomer cement is represented by polyacrylic acid, and the powder part is not similar to those described in this material.
Aluminosilicate glass contains a high fluorine content.
Application
- Ideal for cases where the risk of developing caries due to the release of fluoride is increased.
- It has proven itself excellent among patients with moderate tooth sensitivity.
- Time is not a very useful factor when fixing long bridges.
Properties
- Excellent prevention of caries.
- Very thin film.
- Low risk of developing allergies and pulp damage.
- With not very high strength, high adhesion.
PLEASE NOTE : This material cures slowly and is very dependent on moisture.
How are cementum, tooth sensitivity and periodontitis related?
Loss of cementum contributes to a number of dental problems, such as tooth sensitivity, loss of enamel, and gum recession . When cementum is lost, the dentin underneath is exposed, and this, in turn, can cause tooth sensitivity. The latter manifests itself as short-term or acute pain in the area of one or more teeth. If you've ever winced and winced painfully after taking a sip of cold water or juice, you know the feeling!
While cementum loss can trigger the development of some dental diseases, other dental diseases can trigger cementum loss. Such diseases include, for example, periodontitis. Cementum loss occurs when there is irreversible damage to the bone and connective tissue fibers that hold the tooth in place. Such damage to bone tissue and cement is characteristic of progressive periodontitis and leads to tooth mobility, which in some cases even has to be removed.
How to choose the right dental cement - dentists advise
You should not judge cement by such standards as the best cement for fixing crowns. Experts say that this concept does not exist. Each has its own pros and cons.
Against this background, it would be more correct to say that you need to make a choice regarding each individual situation.
How to choose the best cement for crowns?
When making this choice, you need to focus on a number of parameters in the form:
- Strength: i.e., how a frozen substance compresses and unclenches during eating or closing teeth for other reasons.
- Adhesiveness: here we are talking about how artificial cement bonds with natural dental tissues.
- Irritability : namely, whether the cement will cause an allergy, whether it will lead to rejection of the remaining natural teeth and gum mucosa.
- Removal difficulties : this parameter is important in a situation where there is a need to remove a permanent prosthesis, replace it with another, or if the doctor allows it to be defective at the stage of fixing it - and then quickly eliminate it.
- Aesthetics: when a prosthesis is installed in the smile area, both the retainer layer and its exact match to the shade of the product are taken into account.
Rate
—
general information
Glass ionomer cements (hereinafter referred to as GIC) are a category of dental materials obtained by combining thermoplastic polyacrylic masses with silicates present in them.
Unique performance properties have made this group of compounds indispensable in dental practice - in their popularity they are far superior to cents, the basic part of which is zinc and phosphate compounds.
Classification of mixtures is carried out based on the following criteria:
- functional purpose – prosthetics, filling, sealing;
- release form - in the form of powders, capsule filling, ready-to-use, pastes;
- the principle of solidification is the initial and final phase of the process.
Flaws
There are also negative aspects that arise during the process of prosthetics:
- increased sensitivity to a humid environment at the stage of final hardening of the mixture.
The salivary secretion washes out a certain part with aluminum ion, which provokes a fragmentary violation of the spatial structural content of the composition. The result is cracking of the surface relief. This is why it is necessary to maintain a dry environment during the first 60 minutes after fixation of the prosthesis; - the ability to overdry during the final hardening of GIC - this negatively affects polymerization, can cause physical discomfort during the recovery period, and lead to increased sensitivity in the area where the structure is placed.
To reduce the risk of developing this manifestation to a minimum, the final step during restoration is to cover the working area with a special insulating varnish; - poor resistance to mechanical damage the first day after the procedure. This concerns the distribution of pressing force when chewing food.
The intensity of the negative impact of the described disadvantages is determined by the modification of cement - innovative developments in the process of their production have made it possible to reduce these disadvantages to a minimum.
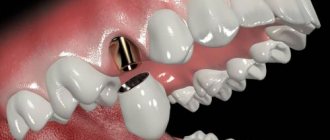
How to glue a dental crown
It should be noted that the stage of fixing the crown is as important as all other stages of prosthetics. Incorrect fixation can cost the patient a tooth and will simply nullify all the efforts of the doctor and the patient. Therefore, one of the main tasks when installing a crown will be reliable sealing of the crown, stability and long-lasting results. The doctor will need to ensure that the fixation holds the result of the prosthesis for as long as possible without any discomfort for the patient.
How is the crown fixed?
A special cement is used as an adhesive for crowns. There are different types of cement, which are selected depending on whether the crown is temporary or permanent, and what material it is made of. The cement must have the same optical characteristics as the prosthesis in terms of its structure. In each specific clinical case, the dentist selects the optimal material. The cement used to fix the prosthesis is absolutely safe for the tissues with which it comes into contact.
To secure the crown with cement, the tooth must be ground down to the desired thickness. The crown is then carefully treated with cement and inserted into the tooth. In this case, the prosthesis should stand in the same way as in previous fittings. Excess cement that appears at the base of the prosthesis must be removed before hardening occurs. Insufficiently thorough treatment of cement residues leads to gum trauma. Upon completion of the procedure, the cement is irradiated with a special light to harden and finally secure the crown. The patient may feel tightness in the teeth, this feeling goes away after 40 minutes. Discomfort and whitening in the gum area will also disappear after 10 minutes.
After proper fixation, the cement protects against moisture and food getting under the crown. It is highly durable and protects teeth from caries by releasing fluoride. Proper fixation allows the crown to last for decades. Permanent cement holds the prosthesis so tightly that removal of the crown is only possible using a special device or sawing.
What to do if the crown falls out
The question of how to glue a dental crown is more pressing than ever if the denture suddenly falls out. This can happen for various reasons, for example, due to a loose fit of the crown to the tooth. Often the crown falls out when eating food. In such cases, you should not panic. The first thing to do is save the crown. It needs to be washed and placed in a cool, safe place. After this, you should contact your dentist to report the problem and schedule an appointment. It is important not to delay your visit to the doctor, as if the denture is not put back in as soon as possible, the tooth may break or move.
Before seeing a doctor, it is recommended to try to insert the crown back. If the prosthesis does not fit securely, there is dental cement available at the pharmacy that will help in this matter. To insert a crown, you need to carefully clean it along with the tooth using a toothbrush. Next, you need to dry the tooth and denture by wiping them with sterile gauze. A small amount of dental cement is then applied to the crown. After fixing the crown, gently squeeze the jaw. The denture should not interfere and be higher than the rest of the teeth. If everything is done correctly, the crown will feel the same as before it fell out. After this, you will need to remove excess cement from the gums and tooth and wait for it to harden.
Under no circumstances should you use household glue to glue the crown. If a denture is lost, the patient can apply dental cement to the top of the tooth to relieve discomfort. But it’s better to quickly see a doctor, he will install the crown in place.
French dentists at French Dental Clinic will help you even in the most delicate situation. If a patient addresses the problem of a fallen crown, he will very soon have an appointment with an experienced and attentive orthopedist who will solve this problem without unnecessary difficulties.
Healthy teeth and good health
FDC will be a pleasant find for you and your family on the path to impeccable aesthetics and good health.
Reviews
In the process of fixing crowns using glass ionomer cements, the risk of complications, allergic intolerance and rejection is minimal.
This explains the demand for the material and its wide range of applications.
If you are interested in the topic of this article, you can leave your comment in the appropriate section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags crowns prosthetics glass ionomer cement for fixation of crowns
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
What other problems are associated with dental cement?
In addition to the loss of cementum, which can be the result of periodontitis and at the same time cause tooth sensitivity, there are several other dental problems directly related to the condition of this tissue.
Cementoblastoma
This long word refers to a rare benign tumor on the root of a tooth. It occurs when specific cells, cementoblasts, grow in the area of the root apex. Typically, cementoblastoma affects one tooth root, but sometimes it can develop on several roots and spread to the surrounding bone. The growth of cementoblastoma is sometimes accompanied by dull pain, but often the disease is asymptomatic. Being a benign tumor, cementoblastoma, however, is constantly increasing in size; Over time, it can begin to interfere with the normal functioning of the teeth and affect the patient's appearance.
Adolescents and young adults under 30 years of age are at higher risk of developing cementoblastomas. Treatment of cementoblastoma involves surgical removal of the tumor and the affected tooth, which most often turns out to be a premolar or molar of the lower jaw. Sometimes several teeth have to be removed. Although tooth extraction is by no means the optimal solution, the risk of tumor regrowth makes it necessary. Although cementoblastoma is a rare condition, it is best to make sure that pain or strange thickening in the area of the tooth roots is not associated with it. To do this, you should contact your dentist.
Exposure of the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)
The cemento-enamel junction is a special zone around the perimeter of the tooth where the enamel covering the crown meets the cement protecting the root. In most cases, the cement partially extends onto the enamel, covering it, but in some people there is a thin strip of unprotected dentin between the hard enamel and the less mineralized cement.
sensitivity to cold and hot foods may occur The exposure of the CEJ is associated with recession, that is, drooping of the gums.
To confirm that the sensitivity is caused by gum recession, the dentist will need to measure how much the gums have receded. To do this, use a special tool, a periodontal probe, which the dentist inserts between the gum and tooth. This examination will determine whether the periodontal ligament is in good condition or whether there is a risk of infection, inflammation and further gum recession.
Hypercementosis
Hypercementosis is the process of formation of an excessively thick cement layer on the roots of teeth. Local thickening of the cement leads to a change in the size and shape of the root, which in some cases even begins to interfere with neighboring teeth.
Although the exact causes of hypercementosis are unknown, dentists typically diagnose it in patients with certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acromegaly, and Paget's disease. Researchers have also associated hypercementosis with vitamin A deficiency. Hypercementosis also occurs in patients with periodontal disease or dental trauma caused by occlusal disorders. For the most part, hypercementosis occurs in adults, and the risk of developing it increases with age.
That's how many new words you learned today! Of course, this amount of information is difficult to digest at once, but understanding the important role of cement will help you take a more responsible approach to protecting your teeth. Start with proper oral care to avoid lost or damaged cementum. By regularly brushing your teeth and using dental floss, an interdental brush or irrigator, and an antiseptic mouthwash, you can maintain the health of your teeth and all their tissues.
Manufacturers' offers
GICs are considered today one of the most effective means for fixing orthopedic structures. Sufficient strength, ease of mixing, increased fluidity and other positive properties of glass ionomer cements ensure their high demand among dentists all over the world.
The market responds with an appropriate offer. Many international and domestic companies are engaged in the production of GIC for various purposes, including for fixation of orthodontic structures. Among them are such famous ones as Fuji i (GC, Japan), (3M ESPE, USA).
Arde Kwik Tsem
The German drug Arde Quick Cem is a dual-curing microhybrid cement intended for fixation of dental structures in the form of veneers (both light-conducting and non-light-conducting), intracanal pins, bridges, crowns, etc.
Mixing cement can be done either automatically (in cannulas and syringes) or manually. The main advantages of Arde Quick Cem:
- increased fluidity (with the help of intraoral attachments, good filling of small posterior and anterior carious cavities that are difficult to access is ensured);
- high radiopacity;
- possibility of automatic mixing without the formation of air bubbles;
- relatively low price.
Arde Fix
Chemically cured German (Ardenia) glass ionomer cement is designed primarily for fixation of various dental structures - bridges, crowns, intracanal pins, onlays, orthodontic rings.
Arde Fix provides:
- high adhesion to dental tissues and orthodontic structures;
- guaranteed (chemical) polymerization, which ensures reliable fixation of internal structures, in particular intra-channel pins;
- non-oxidation and practical insolubility in oral fluids.
Fuji Plus
Fuji plus is a Japanese glass ionomer cement reinforced with a composite, and according to its main purpose it is classified as a fixing material.
With its help, various metal-composite, metal and metal-ceramic orthodontic structures are attached - inlays, dentures, bridges, crowns, intracanal pins.
The combination of a glass ionomer with a composite provides Fiji Plus a wide range of indications.
The material has:
- mechanical characteristics close to composite cements;
- high chemical adhesion to dental tissues, good adhesion to polymers, metals, ceramics;
- precise and easy fitting due to the thin film thickness;
- radiopacity, which makes diagnosis accurate;
- constant fluoride release.
Ketak Tsem
Ketac Cem is a hand-mixed GRC intended for the cementation of bridges, crowns made of various materials, and onlays.
Ketac Cem:
- has high chemical adhesion to orthodontic structures and tooth tissues;
- non-toxic, biocompatible with dental tissues;
- releases fluoride for a long time;
- does not require an absolutely dry surface;
- close in thermal expansion to dental tissues;
- provides high-quality edge fit and high wear resistance;
- has 5 color shades.
The only disadvantage of cement is its relatively high price. But given the 25-year documented history of successful international application, this disadvantage cannot be considered so significant.
Tsemion F
Cemion F Russian is a two-component material designed for fixation of various endodontic structures - crowns, inlays, intracanal pins, bridge prostheses.
The delivery set includes powder, which is a material based on polyacrylic acid and fluorosilicate glass, conditioner and solvent.
The advantages of Tsemion F include:
- abrasion resistance;
- high strength;
- good adhesion to tooth tissues and materials of endodontic structures;
- radiopacity;
- anti-carious properties due to the long-term release of fluoride;
- low cost.