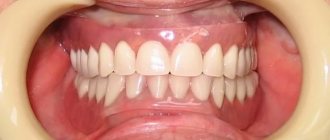
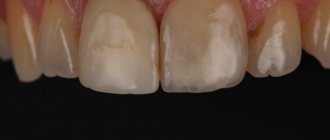
Features of using glass ionomer cement for fixation of crowns
The quality of dental treatment and restoration is largely determined by the characteristics of the materials used.
No matter how highly qualified a dentist is, if he uses materials with low performance properties, achieving a good result is impossible.
The development of glass ionomer cements (GICs) marked a significant step forward in improving the quality of dental treatment and restoration.
The content of the article:
Photopolymer – light-curing materials
Photopolymer filling is considered the highest quality. Lighting composites represent the latest generation of materials that provide excellent results. They are produced in the form of a paste that hardens under the influence of UV radiation from a special lamp. They are applied in layers (about 2 mm), which makes it possible to form the shape of the tooth as accurately as possible. Other advantages of the material:
- a wide selection of shades - allows you to choose the desired color, which makes the filling invisible to others;
- strength;
- application for restoration of anterior and lateral teeth;
- low toxicity;
- the highest aesthetic properties compared to other materials;
- slight shrinkage.
A photopolymer filling has virtually no disadvantages. If the restoration technology is followed, it will last for many years. The only negative is the higher price when compared with plastic and cement materials. But the expenses are justified, because the patient receives high quality. Today, dental clinics often work with photopolymers.
Permanent cements
The purpose of using such materials is the final fixation of finished prostheses. After mixing and applying to the internal surfaces of the crowns, they harden fairly quickly. Therefore, excess cement must be removed in a timely manner. Permanent cements are classified depending on the composition of the components.
Zinc phosphate
Zinc phosphate cements were the first to be used in dental practice for the installation of orthodontic structures. The material is imperfect and can irritate the pulp. But such clinical manifestations are observed quite rarely. Occasionally, patients experience discomfort in the first days, and then disappear on their own. Zinc phosphate cements are valued by dentists for the following positive properties:
- plastic;
- good adhesion;
- low thermal conductivity;
- long working hours;
- the ability to obtain a thin, uniform layer;
- radiopacity.
There are also significant disadvantages. Zinc phosphate cements are not strong enough
chemically unstable to saliva, porous, do not match the color of tooth enamel, and shrink during the hardening process.
Adhesive and synthetic cements
In dental materials stores, including the largest Dental Market, adhesive and synthetic cements are presented in a wide range and it is constantly being replenished. Fixing materials vary significantly in their characteristics, and their use requires certain skills from the doctor. Modern cements have many advantages:
- Universal, compatible with almost all dental materials.
- Resistant to loads, provide durable bonding with tooth tissues.
- Compensate for stress that occurs due to shrinkage of composite materials.
- Provide good adhesion to the wet dentin surface.
- Biocompatible, do not lead to tissue irritation.
- Insoluble upon contact with saliva.
- Durable.
Practicing dentists consider poor hardening as a result of contact with oxygen to be a disadvantage of adhesive and synthetic cements. They often have difficulty removing excess material.
Sealers-Endogermetics in Dentistry
No high-quality endodontics is complete without a sealer. In simple words, a sealer is a material, in this case cement, paste, that fills the space between the wall of the root canal and gutta-percha. Sealers not only provide tight sealing of the root canal, but also prevent the development of infection inside the root canal and outside its apex, so it is very important to know and understand what, why and how to use a sealer. Indeed, for each clinical case it is necessary to choose a specific chemical and physical composition of the sealer. There are many types of sealers on the dental market; in this article I will try to introduce you to some of them.
Requirements for the sealer
The requirements for the sealer are quite logical and meet the requirements of quality patient treatment. First of all, the sealer must be biologically compatible and not have a pathological effect on periodontal tissue or the general health of the patient. In addition, a high-quality sealer should not change the color of the tooth some time after filling the root canal. The next requirement for the sealer is its resistance to moisture and gingival fluid; the sealer should not dissolve in them. For a doctor, the requirements for a sealer are as follows:
- Convenient working hours;
- The material must be plastic, tightly seal the teeth canals;
- Possess adhesion to tooth dentin;
- Do not shrink;
- Do not form pores;
- Be radiopaque;
- Teeth filled with sealer should be easily refilled if necessary;
In addition, the sealer must influence the microflora of the root canal and have either a static/cidal effect in relation to microbial agents.
Unfortunately, most sealers are not 100% insensitive to moisture or gingival fluid. As a result, the formation of microspaces, micropores, microleakages at the border of gutta-percha and the wall of the root canal. And any space is filled with pathogenic microbes, which causes the development of a pathological process.
Compound
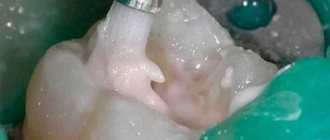
The standard component type of GIC is two main components (powder and liquid). As a result of mixing until homogeneous, a mass is obtained, ready for use as a fixing agent when installing crowns.
Powder is the smallest granules containing, in addition to silicate glass, aluminofluoro:
- oxides and dioxides of silicon;
- calcium fluorides;
- additional calcium-metallic elements;
- aluminum phosphate – increases strength and resistance to excessive surface abrasion;
- barium, zinc strontium salts - due to their filling, the mixture is radiopaque;
- alloys of precious metals - silver, tin, palladium (improves performance).
Liquid should be understood as solutions of organic nature of formations and tartaric acid, which allow achieving high-quality polymerization.
Related products
Dental tray LMS for 8 instruments with lid
Endogel No. 2 syringe - material for chemical-mechanical expansion, cleaning, shaping and antiseptic treatment of tooth root canals (gel 3 ml)
Viedent set - material for filling root canals of teeth (20 g + 10 ml)
Two-component argenate - material for silvering infected and difficult-to-pass canals, carious milk teeth (4ml+3ml)
Dental tray with lid and storage for LSKB burs
Rectangular tray LMPr 400x300x45
Stomaflex Light/Stomaflex light-C-Silicone impression material of low viscosity and higher fluidity (paste 130 g)
Dental tray with lid and storage for endocanal instrument LSCE
Viedent - material for filling root canals of teeth (paste 4 g + paste 4 g)
Polident No. 4 - paste for final processing of fillings (paste 6 g)
Rectangular tray LMPr 300x220x30
Cotton Rolls/Dental cotton rolls Medicom (1000 pcs.)
Attention! FREE delivery of goods applies!*
Using cement for crowns at home
There is no need to despair if the prosthesis falls out, because you can temporarily glue it on yourself. Dental adhesive cement can be purchased at a pharmacy. It is worth saying that its composition is much different from professional cement used in dentistry. With these steps you can temporarily fix the crown until your next trip to the dentist.
Many people believe that by gluing a prosthesis at home, you can walk with it for a long time, but this is not so. The thing is that the dentist must first treat the tooth socket with special means and securely secure the crown. Only in this case can you count on the correctness and effectiveness of prosthetics.
Retreatment prognosis
The prognosis depends on the specific clinical situation.
- With timely treatment, if there is no severe inflammation, and the structure of the hard tissues is relatively intact, it is possible to unfill the root canals, re-treat them, and direct composite restoration.
- If the inflammation is severe, it needs to be removed, and this may require several visits to the dentist. The prognosis will depend not only on the preservation of dentin and roots, but also on the condition of periodontal tissues.
- If the hard tissues have retained their strength, prosthetics are possible. In this case, the roots must be unsealed and properly treated, making sure that they will be a reliable basis for an artificial crown.
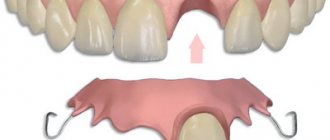
- If the condition of the dentin and tooth roots is poor, there are several ways to restore such a tooth: using a removable, conditionally removable or bridge prosthesis, using implantation.
Dentists at the DentoSpas clinic recommend regularly visiting the dentist to monitor the condition of teeth filled with resorcinol-formalin paste, even if they do not bother the patient.
vote
Article rating
Attaching a crown at home
Their composition differs from professional glue, which is used in dentistry, so after fixing them at home, the patient still needs to see a dentist. The algorithm for self-fixation of prostheses includes the following steps:
- Cleaning of old cement. Before you begin gluing, you should clean the crown from the old substance using a special dissolving liquid, which can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- Drying. After cleaning, the crown should be thoroughly rinsed with running water and dried thoroughly.
- Applying glue. The inner surface of the crown should be glued to the tissue using a thin strip of adhesive.
- Putting the crown in place. For a strong fixation, the patient needs to clench his teeth tightly for several minutes.
Types of crowns
Popular materials include metal, plastic, metal ceramics, pure ceramics or glass ceramics, and zirconium dioxide.
The most affordable option is plastic. Most often it is used as a temporary option due to its low strength.
Another affordable and popular option is cermet. Ceramic is applied in layers onto a metal frame that perfectly follows the shape of the front tooth. The product is fired for special strength. This type of crown is reliable and quite aesthetic.
Among its disadvantages:
- possible allergy to metal;
- negative impact on the natural tooth and gums;
- slight external difference from natural teeth.
To avoid the last unpleasant moment, metal ceramics are placed along the entire smile line. Then the difference is not noticeable at all.
Metal crowns for the front teeth are very durable, but not aesthetically pleasing. Because of this defect, they are now almost never used.
An excellent option for front teeth is all-ceramic crowns. They are practically indistinguishable from real teeth and have maximum biological compatibility with them.
Plastic and ceramic types are used mainly for aesthetic purposes. Due to their high fragility, such crowns are installed only on the front teeth. They will not withstand the load on chewing ones.
Zinc phosphate cement unitsem
- Product catalog Microscopes Microscopes
- Anesthetics
- Healing materials
- Adhesive systems
- Fiberglass pins
- Light curing
- Disobturation of root canals Materials
- Tools
- Tools
- Materials for relining the prosthesis
- Plasters
- Auxiliary means (eg conalor, reinforcing mesh)
- Compressors
- Equipment and consumables for sterilization Equipment for sterilization
- Densim Tools
- Visiographs
- Desensitizers and sealants
- DIO implants (DIO implants Korea)
- Sets
- Physiodispenser Saeshin
- DIO (Korea)
- home
- Restoration
- Cements for permanent fillings
- Chemical curing
- Unicem bactericidal set - zinc phosphate two-component bactericidal cement (50g+30g)
About DentMed
is one of the leaders in the dental market of Uzbekistan, selling a full range of equipment and consumables for dental clinics and dental laboratories. The main activity of the company is the sale of high-quality materials, tools and equipment for dentists and dental technicians from the world's leading manufacturers.
Our phones
+998 (71) 278 07 80 (Call center) or +998 (97) 704 49 00 (Technical support).
Root canal filling
One of the most popular methods of dental treatment after pulp removal is root canal filling.
The procedure is necessary to strengthen the teeth and prevent infection from entering the root canals. Dentists at the Berezka clinic use new technologies when performing fillings and use reliable innovative materials as fillings. We offer our patients the best and safest methods to restore the integrity of the tooth.
Hoffmann' S Germany
Hoffmann ́s Cement normalhärtend Normal-curing phosphate cement Area of application: Fixation of crowns, bridges and inlays, fixation of orthodontic rings, fixation of pins and screws, temporary fillings Release form: Powder: 100 g Liquid: 40 ml Set: 35 g powder and 15 ml liquid B assortment in 15 different colors
Hoffmann’s Cement schnellhärtend Zinc phosphate cement, fast curing Area of application: Fixation of crowns, bridges and inlays, fixation of orthodontic rings, fixation of pins and screws, temporary fillings Release form: Powder: 100 g Liquid: 40 ml Set: 35 g powder and 15 ml liquid Available in 15 different colors
Hoffmann's Universal Cement Universal zinc phosphate cement Used with Hoffmann's zinc phosphate cement normal-curing, rapid-curing and carboxylate cement fluids. Area of application: Fixation of crowns, bridges and inlays, fastening of orthodontic rings, temporary fillings, fixation of pins and screws, linings for all filling materials (only with normal curing liquids and carboxylate cement) Release form: Powder: 100 g Available in 15 different colors
Hoffmann's Provisorischer Cemen Zinc oxide based cement Area of application: Temporary fillings. Release form: Powder: 50 g Liquid: 40 ml
Hoffmann ́s FARBTÖNE Set of colored cements for fixation Area of application: Try-in and permanent fixation of crowns and bridges made of oxide ceramics (zirconium oxide and aluminum oxide), as well as lithium ceramics with a bending strength of more than 200 MPa Capabilities: 1. Correction of the color of the structure for adjustment to the remaining teeth: - Lightening (Color 01 and mixed tones from 01) - Darkening (Colors 07, 10, 11) - Color correction of the structure (All colors and mixed tones) 2. Adjustment of differently colored stumps 3. Imitation of living pulp (Color 15) Release form: Fixing liquid 40 ml Test liquid 40 ml Powder 1 x 100g, 4 x 30g
Hoffmann ́s Glass mixing Mixing glass, crystal Area of application: Professional base for mixing all Hoffmanns cements. During the entire mixing process, the glass maintains a constant temperature, even when heat is generated. The glass has a sufficiently large surface for stretching, is resistant to scratches, also from metal spatulas, and is easy to clean. The solid design ensures stable and reliable use. Size: 150 x 75 x 20 mm Weight: 596 g
Modern materials for filling teeth
The following groups of dental cements : zinc phosphate (phosphate cement, visfat cement, uniface), bactericidal (phosphate cement with silver, dioxyvisfate), zinc-xide eugenol cements (Kariosan), silicate (silicin, silicin-2, alumodent) , silicophosphate (silidont, lactodont, infantid), polycarboxylate cements, glass ionomer cements. Zinc phosphate cements . Powder and liquid are available as a set. Powder components: 75-90% zinc oxide (providing adhesion), with the addition of silicon oxide (giving glassiness, transparency, shine), magnesium oxide (increasing ductility and mechanical strength), calcium oxide (accelerating setting, viscosity), aluminum oxide (increasing strength and hardness). The liquid is an aqueous solution of orthophosphoric acid. Phosphate cement. The powder is yellow or light yellow in color and consists of 90% zinc oxide, 60/0 magnesium oxide, 4% calcium oxide. Liquid - 35% aqueous solution of orthophosphoric acid, with the addition of phosphates: zinc, aluminum, magnesium to reduce the rate of interaction between powder and liquid.
Kneading technique . Powder and liquid are separately applied to the smooth surface of the glass in a ratio of 4:1. The powder is divided into approximately 4 parts, added sequentially to the liquid and thoroughly ground. The mass is considered correctly mixed if it does not reach behind the spatula when it is torn off, but breaks off, forming 1 mm teeth. If the mass turns out to be thick, you cannot add liquid; you need to prepare it again. The maximum adhesive period of the filling test is 4-8 minutes. Positive properties : good adhesion, coefficient of thermal expansion is close to the coefficient of thermal expansion of tooth tissue, does not irritate the pulp, impermeable to acids and monomers of permanent fillings , has low thermal conductivity, radiopaque. Negative properties : absorbs in oral fluid, low mechanical strength, does not have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects, does not have aesthetic qualities. Indications for use: as an insulating gasket under a permanent filling ; for permanent filling under an artificial crown or for filling baby teeth; Root canal filling according to indications; fixation of orthopedic structures. Uniface. Unified phosphate cement. Due to the ammonium molybdate-based matrix, it has good adhesion to both metal and tooth tissue, is more durable and chemically resistant. Visphat cement (bismuth cement). The powder has the same composition as phosphate cement, but with the addition of 3% bismuth oxide. Available in 3 shades: light yellow, golden yellow and dark yellow. Liquid - 37% aqueous solution of orthophosphoric acid. It has good adhesion, hardens faster, is more durable and radiopaque, less soluble, has bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties, but is capable of changing the color of hard tooth tissues. The maximum adhesive period of the filling test is 3-3.5 minutes. The mixing technique is similar to mixing phosphate cement. Indications for use : as an insulating gasket under a permanent filling ; for permanent filling under an artificial crown or for filling baby teeth; fixation of orthopedic structures. Bactericidal . Phosphate cement with silver, Argyl, Unitsem. Foscem is a phosphate cement with the addition of silver. Has pronounced bactericidal properties. The preparation method and application are similar to phosphate cement, but it cannot be used as a spacer under a filling on frontal teeth, since silver stains the tooth gray. Dioxyvisfate with the addition of dioxidine. Cement also has bactericidal properties, is mechanically strong, slightly soluble, and does not stain tooth tissue. Silicate. Silitsin, Silitsin-2, Velatsin. Available in powder-liquid kits. Powder components - silicon oxide (29-47%), aluminum oxide (15-35%), calcium (up to 14%), fluorides (up to 15%), a small amount of magnesium, iron, phosphorus salts. Available in 7 colors. Positive properties : the color is close to enamel, fluoride compounds impart anti-cariogenic properties, reduce the solubility of enamel, and reduce the possibility of secondary caries. Disadvantages : toxic, therefore used on living teeth only with an insulating gasket, weak adhesion (no zinc oxide), low mechanical strength (fragility and brittleness), relatively high solubility in the oral cavity. Kneading technique . Apply 1 g of powder and 5-7 drops of liquid to the smooth surface of the glass. The powder is gradually added to the liquid and mixed with a plastic spatula, since the metal changes the color of the filling. Indications for use : filling the frontal group of teeth in the presence of cavities of classes 3, 4, 5 according to Black. Silicophosphate cements are silicate cements modified with zinc phosphate cements. Silidont, Veladont . Available as a powder-liquid kit. Powder - 80% silicine powder and 20% phosphate cement. The liquid is a solution of orthophosphoric acid. Positive properties : good adhesion, mechanical strength and chemical resistance are higher than that of silicine. Negative properties : toxic, not aesthetic (white, opaque), not strong enough and resistant compared to modern filling materials. The mixing technique is similar to silicine. Indications for use : filling the chewing group of teeth, grades 1,2, 5 according to Black. Filling with phosphate, bactericidal, silicate, silicophosphate, and polycarboxylate cements should be carried out under conditions of isolating the tooth from saliva and thoroughly drying the cavity to be filled. Glass ionomer cements. Glass ionomer cement (polyalkene cement) consists of components typical of dental cements - powder and liquid, which harden due to an acid-base reaction. Conventional glass ionomer cements use aqueous solutions of polycarboxylic acids (polymers of alkene acids), for example, polyacrylic acids and their copolymers with itaconic or maleic acid. The carboxyl group of the polymeric acid interacts with calcium ions and a strong polymer matrix is formed. The same acid provides chemical adhesion to calcium of enamel and dentin. Available in chemical, light curing and double curing. Because of freeze-drying, acids can be added directly to the powder, increasing the accuracy of liquid and powder dosing. The liquid component of water-hardening glass ionomer cements consists of distilled water or tartaric acid. The powder component consists of calcium-aluminum-silicate glass containing crystallized droplets saturated with calcium fluoride. Fluoride, after applying the filling, is released into the oral cavity for a long time, providing organic anti-caries protection in the marginal area of the filling. The binding reaction of both main components occurs in 3 stages. The acid releases calcium and aluminum ions from silicate glass. Since calcium ions are released faster, they are the first to react with the acid. After wetting the calcium bridges with polyacrylate acid, a carboxylate gel is formed, which is sensitive to moisture and drying. When moisture initially enters, the binding time increases, strength and hardness decrease, loss of transparency, porosity and roughness of surfaces, and increased erosion of the filling . As glass ionomer cement dries, it becomes opaque, cracks, and does not fully bond. Therefore, protection through varnishes, bonding or matrices is necessary. Aluminum ions penetrate the matrix within a few hours, forming a water-soluble calcium-aluminum-carboxylate gel. The sintering method can be used to fuse metal into glass particles. Used for this purpose in most cases, silver serves as a shock absorber and increases bending strength and abrasion resistance. Glass modified in this way is called cermet cement (ceramics-metal-glass ionomer cement). The third group includes light- and dual-curing glass ionomer cements, the liquid components of which, in addition to acid, contain, for example, hydrophilic monomers (hydroxyl methacrylate - HEMA), Bis-GMA and photoaccelerators. Due to light copolymerization of methacrylate with polyacrylic acid groups, covalent and ionic bonds are formed, which contribute to the hardening of the material. Method of application. Before taking, the powder is thoroughly mixed. Mix in a strict powder-liquid ratio specified by the manufacturer. After taking the powder, you should carefully and tightly close the lid of the bottle, since the powder is hygroscopic. It is necessary to apply cement to a slightly moistened, not overdried surface, since the high concentration of ions promotes the diffusion of dentinal tubule fluid outward. In addition, glass ionomers are hydrophilic, they absorb small amounts of liquid from the surface of dentin and dentinal tubules, which improves adhesion. Therefore, immediately after adding the material, the filling is covered with protective varnishes (they are supplied as a set) to prevent the penetration of liquid from the oral cavity. The final finishing of the filling is carried out after 24 hours. Positive properties : chemical adhesion that does not require acid etching; biological compatibility with dental ; no toxic effect on the pulp; gradually released fluorine enters the tooth tissue and increases the tooth’s resistance to demineralization (anti-carious effect); low polymerization shrinkage; the coefficient of thermal expansion is close to the coefficient of thermal expansion of tooth tissue ; radiopaque. Disadvantages: insufficient mechanical strength; satisfactory aesthetic qualities. Indications for use: filling cavities mainly of classes III and V, filling non-carious lesions of teeth (hypoplasia, wedge-shaped defects, erosions); filling cavities of primary teeth of all classes; as insulating gaskets; as a sealant; creating the basis for the restoration (the main part of the cavity is filled with ionomer cement, and the surface layer is filled with a composite material); restoration of the tooth crown under an artificial crown, inlay; restoration of the crown stump before taking an impression; fixation of orthopedic structures; filling .
The canal is sealed with phosphate cement
+7
- home
- Services
- Therapeutic dentistry
Unsealing a root canal previously treated with phosphate cement/resorcinol-formaldehyde method.
Removing old fillings from root canals is called disobturation. During this manipulation, cleansing is carried out from the crown of the tooth to its apical part. In this case, expansion is carried out first with special devices of smaller diameter with their gradual increase in order to achieve complete and effective cleansing of the root canals.
severe pain in the treated tooth;
development of an inflammatory process in the tooth;
lack of filling of additional root canals;
unsatisfactory condition of the filling.
Disobturation is a rather complex procedure that can be carried out by two methods: chemical and mechanical.
With the mechanical method, special equipment is used. The filling is crushed into several fragments, drilled out, and its remains are removed by rinsing or other devices.
The chemical method uses special substances: pastes, gels, solutions. When they are applied to the filling, it softens. Then cleaning is carried out with special tools.
How is deobturation performed with phosphate-cement/resorcinol-formaldehyde fillings?
First, a special solvent is placed into the opened dental canal and left there for several days.
mechanical processing of the chamber and the entrance to the tooth canals;
placing a cotton swab soaked in a special sealing liquid into the cavity;
placing a temporary filling.
A few days later, during the second visit to the doctor, the temporary filling is removed and the remaining filling is removed from the root canals. At the end, the cavity is washed, dried, degreased and subsequent filling is carried out.
Properties
Unicem is a universal, improved zinc phosphate dental cement with high mechanical compressive strength: 90 MPa with a powder to liquid ratio of 1.5:1 (for fixation), 121 MPa with a powder to liquid ratio of 2:1 (for filling).
Cement is formed by mixing a powder containing zinc oxide with modifying additives with a liquid that is orthophosphoric acid of reduced activity. The thickness of the cement film for fixation does not exceed 25 microns.
The presence of silver in bactericidal cement prevents the development of secondary caries and reduces the likelihood of primary caries in primary teeth.
Dental cement Unitem meets the requirements of GOST R 51744-2001.