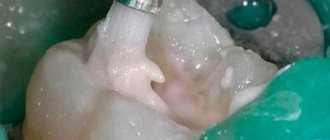
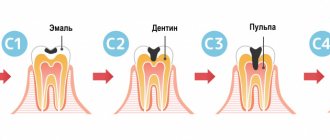
Healthy teeth are the key to the health and beautiful smile of every person. However, as a result of neglecting the rules of oral hygiene, caries often occurs, which causes holes in the teeth.
When visiting a dentist, a specialist suggests filling with Silidont cement.
Properties
Silidont is a filling material belonging to the silicophosphate group. Available in powder form, consisting of 20% phosphate (visphate) and 80% silicate (silicin) cement. It is intended for filling carious cavities:
- in children on temporary teeth (premolars) with carious cavities of class I, II, V;
- in adults on permanent molars and premolars with carious cavities of class I, II, V.
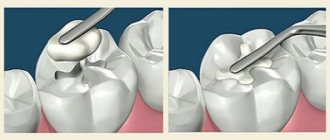
For permanent teeth, before filling, it is necessary to make a spacer that will isolate the pulp.
Silidont is available in the form of a container with powder; liquid orthophosphoric (H3PO4) acid is added to it in a glass jar for mixing.
Silidont was previously called Erkodont mixed type and included zinc-phosphate and silicate powder. Currently, an improved Silidont-2, which is less toxic, is being produced for dental practice.
Silidont-2 is used to fill any carious cavities in all teeth, except those that do not extend to the labial and buccal surfaces. Available in powder form in a 50 g plastic jar, in 3 colors (from light yellow, yellow-gray to light yellow-gray) and 30 g. glass bottle with liquid for mixing it.
Silicophosphate cement Silidont is used for filling permanent, temporary chewing and anterior teeth and their contact surface. Medium and deep caries are filled with this product only when an insulating lining is created.
Silidont-2 - silicophosphate filling cement - 50 g + 30 g (Polymer-Dentistry)
at room temperature
All product characteristics
St. Petersburg: free from 3000 ₽
in Russia: free from 30,000 ₽
Krasnodar: free from 5,000 ₽
Rostov-on-Don: free from 6,000 ₽
- Description
- Characteristics
- Reviews (0)
- Delivery
Composition, properties
The powder consists of 5 parts silicate and 4 parts phosphate cement, which are made.
The liquid is orthophosphoric acid, which has been partially neutralized with aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) and zinc oxide (ZnO).
Properties of the drug:
- high mechanical strength;
- high chemical resistance;
- sets quickly;
- plastic;
- radiopacity;
- ensures the tightness of the filling, which reduces the risk of complications or relapse;
- bactericidal effect;
- high compatibility with biological tissues.
A significant advantage of the product is its low cost and the ability to purchase at any pharmacy chain.
Indications, contraindications, side effects
Indications for use of Silidont:
- Filling of permanent and temporary teeth of molars and premolars in children.
- Filling in adult small and large molars, superficial type of caries, medium and deep, in the presence of isolation with other cement (containing zinc, phosphate).
- Fixation of fixed dentures.
Contraindications to the use of the composition are individual intolerance, allergy to one of the chemicals.
Side effects may occur due to non-compliance with the rules of mixing and applying the composition:
- Development of secondary caries.
- Filling falling out.
Choosing temporary filling material: proceed without mistakes
- Login Registration
- Home →
- News and articles on dentistry →
- Therapy →
- Choosing temporary filling material: proceed without mistakes
Every practicing dentist knows how important the correct selection of filling material is for effective treatment. Modern dentistry offers a huge selection of materials, which are divided into classifications depending on composition, properties, time of use, purpose, etc. A fairly large place among them is occupied by a group of filling materials for temporary fillings, as well as insulating and therapeutic pads.
Materials for temporary fillings
Based on the time of action, they are divided into bandages and temporary fillings. Inexpensive materials are used for dressings. The most common option: water-based dentin or dentin-paste. The period of use of these materials should not exceed 14 days. At the same time, the bandages do not differ in aesthetics and durability. All temporary fillings are cements : zinc phosphate, zinc eugenol, polycarboxylate, glass ionomer, etc. The period of their use in the patient’s oral cavity ranges from several weeks to six months.
1) Zinc sulfate cements (“artificial dentin”)
The main components of the composition are zinc sulfate and zinc oxide. Adding water helps the mass harden. The most famous materials of this group: “Dentin for dressings”, Dentine paste, Vinoxol, etc.
The basis of the composition is zinc oxide and eugenol. According to Smith's classification (1996), this subgroup includes three main types of cements: simple zinc oxide eugenol; reinforced zinc oxide eugenol with filler and cements based on orthoethoxybenzoic acid (EBA). The materials consist of zinc oxide powder, into which 1-2% zinc acetate, acetic anhydride or rosin are added, which accelerate hardening. Purified eugenol or clove oil is used as a solvent. Additionally, to speed up the hardening process of cement, acetic acid or 1% ethyl alcohol, as well as a small amount of water, can sometimes be added. The most popular representative of this group is Cariosan. Zinc-eugenol cements are used not only for temporary fillings , but also for therapeutic linings. It is important to take into account that eugenol disrupts the polymerization process of composites, so experts do not recommend using this type of cement in combination with them. That is why today zinc-eugenol cements are practically not used for therapeutic linings in commercial clinics, but they are still in demand in pediatric dentistry and in municipal clinics for the treatment of deep caries in two visits.
75-90% of the cement base is zinc oxide with the addition of other modifying oxides. The liquid part is an aqueous solution of 38-44% orthophosphoric acid containing phosphates of zinc, aluminum, magnesium, etc. Among the most famous zinc-phosphate cements presented on the Russian market are: Phosphate cement from Raduga-R, Uniface ( “Medpolymer”), Adgesor (“Dental Spofa”), DeTreyZinc from “DeTrey/Dentsply”, etc. As a rule, metals containing silver are added to these compositions to impart a bactericidal effect. As an example, we can o), Phosphate with silver and bactericidal Foscin (“Rainbow-R”), as well as cements containing bismuth oxides: Visphate cement and Dioxyphosphate (Medpolymer).
The undoubted positive properties of these cements are: ease of use, low thermal conductivity, good X-ray contrast, and impermeability to acids and monomers. However, they have quite a lot of negative characteristics. Among them: weak adhesion, low resistance to the aggressive effects of saliva, shrinkage, low mechanical strength, the presence of free acid and lack of aesthetics.
Most often, zinc-phosphate cements are used as an insulating spacer for filling baby teeth and permanent crowns, fixing cast stump inlays, pins, crowns and bridges.
The basis of cement is thermochemically treated zinc oxide with the addition of magnesium oxide, which reduces the reactivity of the first component. Aluminum is also often added to powders. The solvent is represented by a 32-42% aqueous solution of polyacrylic acid. During the hardening process, cement turns into an amorphous zinc-polyacrylate gel, which contains zinc oxide particles.
The positive properties of these cements include: satisfactory chemical adhesion to enamel and dentin, strong bond with metals, weak toxicity to the pulp compared to phosphate cement and high biocompatibility with tooth tissues. Negative properties: high solubility under the influence of saliva, short formation time in the oral cavity and insufficient fluoride adhesion.
Polycarboxylate cements are used as insulating spacers when filling teeth under artificial crowns, for fixing orthopedic and orthodontic structures, and in the treatment of baby teeth (1-2 years before their replacement).
All materials for temporary fillings must be:
- harmless to the pulp;
- have high plasticity;
- inactive for other drugs;
- insoluble under the influence of saliva;
- sealed for at least two weeks;
- have a certain strength;
- easily removed from the dental cavity using an excavator, probe or drilling.
Insulating and healing pads
The purpose of these materials follows from their name. Despite the fact that they can be conditionally classified as filling materials, the application of gaskets is an integral step in the treatment of medium and deep caries. spacers when treating medium and deep caries . They contain calcium hydroxide, which has an anti-inflammatory effect on the pulp and stimulates the deposition of replacement dentin. Among the most popular materials are: “Calmecin”, “Dycal”, “Calcimol” and “Alcaliner”, as well as modern insulating gaskets made from glass ionomer cements, such as: “Fuji 2”, “Chelon Fil”, “Base Line” and etc.
How to use
To mix a mixture of liquid and cement, the surface should be prepared; it should be:
- smooth;
- dry;
- clean;
- room temperature.
You also need a spatula made of plastic or stainless steel.
In this case, it is necessary to maintain the temperature in the room from 18°C to 21°C.
Stages:
- For one scoop of powder (0.22 g) two drops of liquid (0.11 g).
- Pour half a measuring spoon onto the surface and add all the liquid.
- Stir thoroughly with a spatula and gradually add the second part of the powder.
Mixing should take place for 1 minute. The cement must be quickly mixed to a homogeneous gel-like mass. You can check the quality of the prepared material using a spatula - the composition should stretch behind it.
If the room temperature is more than 22°C, the dental surface must be cooled in water for 2-3 minutes.
If the temperature is less than 16°C, then it is necessary to add a larger amount of powder than during normal mixing.
If the filling material turns out to be very dense, then you need to prepare a new one: you cannot add liquid, due to the possible disruption of chemical reactions in it.
For better fixation of cement, it must be protected from premature wetting with saliva in the mouth; for this, it is covered with wax.
Silidont cement for fillings
Silicophosphate cement (silidont) is a mixture of powders of two cements: 20% visphate powder and 80% silicine.
For 1 g of silidont powder, 0.25 - 0.30 ml of liquid is required. The quality of silydont is determined by the positive and negative properties of phosphate and silicate cements.
In silydont, the binding of phosphoric acid occurs more vigorously and completely than in ordinary silicate cement, due to the content of zinc oxide in sufficient quantities. However, when applying a silidont filling to a tooth with living pulp with a diagnosis of “deep caries,” a phosphate cement lining is also required, which protects the pulp from the action of incompletely bound phosphoric acid.
The optimal temperature for mixing is 18 - 20 °C. When working in a cold room (below 16 °C), in order to achieve the hardening time of cements, an excess of powder should be used when mixing compared to the recommended ratio. If the room temperature is above 20 °C, the glass plate must be cooled with a cotton swab soaked in ether before mixing. The glass plate for mixing the filling mass must be clean and dry. Do not mix on a warm or hot plate removed from the sterilizer. Mixing silicate cement (silicin) and silydont should be done with a plastic spatula. It is not recommended to use a metal spatula due to possible staining of the filling material.