Today we will talk about orthodontic structures such as temporary crowns .
We will discuss their features, types, indications for use, functional characteristics, materials from which they are made and installation steps.
We will also pay attention to the service life of these prostheses, why they are needed and much more on this topic.
Temporary crowns are a separate type of dental elements that are installed in place of a permanent crown while it is being manufactured.
Review of plastic dental crowns – stages of their manufacture, indications for installation and current prices
Article navigation
- Short description
- What types of plastic crowns are there?
- Materials
- Manufacturing methods
- Indications and contraindications
- Pros of crowns
- Flaws
- Stages of dental restoration
- Installation Features
- How long can you wear it?
- Life time
- Price
Question for a specialist
Today dentistry has a variety of materials for prosthetics. Among others, plastic stands out, which has fairly good aesthetic characteristics and low cost. Should I wear plastic crowns permanently? Of course not. But some types can be used for quite a long time. Next, we will talk about the features of dental crowns made of plastic, the pros and cons of these orthopedic structures, their service life and prices.
Brief description of products
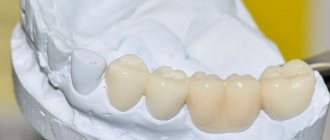
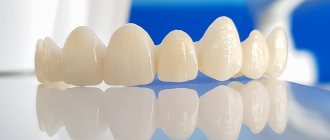
Plastic crowns are artificial dental crowns in the form of single caps made from dental plastics. They are used to protect a tooth when it is severely damaged, as well as to restore the aesthetics of a smile. The “cap” is attached to the abutment tooth, core inlay or implant (more precisely, to the abutment on the implant). Externally, it imitates a natural tooth quite well, because plastic can be easily painted to the desired shade. What the prosthesis looks like is shown in the photo below. Plastic crowns are classified as non-removable. To restore several teeth in a row, plastic crowns are combined into a bridge.
Operational characteristics
The degree of fixation depends on the characteristics of the temporary cement. One of its important properties is the retention force, which allows you to hold the structure and remove it if necessary. The optimal characteristics of temporary cements include:
- good adhesion of indirect restoration;
- ease of mixing and application;
- ease of removal after fixation of cement residues from prepared structures and outer surfaces of the crown;
- adequate working hours;
- optimal viscosity for comfortable use;
- easy removal of the structure without damaging nearby tissues;
- biocompatibility with abutment tooth structures and soft tissues;
- long shelf life;
- no effect on the adhesion of permanent cement.
To identify and remove excess cement, it must be radiopaque. Today, none of the temporary cements on the market have absolutely all of the above properties. It is advisable to use each of them for a specific purpose due to the lack of a single universal solution.
Materials for production
Plastic dental crowns are usually made from materials obtained by mixing two components - liquid and powder. As a result, a plastic mass is formed from which the prosthesis is already made. But some manufacturers produce ready-made paste in small dispensers. There are acrylic monomer and non-monomer materials - for example, Tempron from GC (Japan). As well as plastic composite non-monomer compositions - for example, DentaCrown from Itena (France), Protemp 4 from 3M ESPE (USA). There are also initially solid PMMA (thermoplastic plastic) blocks. Telio CAD from Ivoclar Vivadent is also such a material.
There are plastic crowns in which the plastic is specially reinforced at the production stage - for greater strength and wear resistance of the structure. For example, this could be reinforcement - strengthening a plastic cap with a metal or fiberglass mesh. There are also metal-plastic products - they are based on a metal cap, which is covered on top or only on the side with a layer of light synthetic material1.
Dental bridge: general characteristics
With the help of prosthetics, a number of visual and functional dental problems are solved. The name for the installation was not chosen by chance, because the principle of the device is reminiscent of engineering structures. Artificial crowns are held on a base, and adjacent intact incisors, canines and molars act as supporting elements.
The choice of the appropriate type of construction depends not only on the financial capabilities and personal preferences of the patient, but also on his medical history. That is why a full restoration is impossible without a thorough diagnosis, medical examination and adjustment of the finished system, created from casts, to the required parameters.
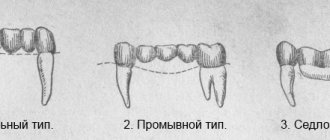
Types of Dental Bridges
Modern dental clinics offer many options for restoring lost units using prosthetic bridges. They differ according to different criteria:
- by manufacturing method - solid cast, adhesive, stamped, pressed, combined;
- by material - metal, metal-ceramic, ceramic, plastic, zirconium dioxide and aluminum oxide;
- according to the method of fastening - locking, adhesive, on healthy teeth, on implants.
There is also a classification according to purpose. For example, artificial prostheses are restorative, splinting, temporary and permanent.
Manufacturing technology
The main selection criterion is the amount of time spent on creating a design according to the individual standards of a particular patient. There are 3 main groups:
- Solid cast. Ideally adjacent to hard and soft tissues, airtight. In this way it is possible to reproduce the natural shape with high precision. They are strong and durable. The disadvantages include the need to grind healthy teeth, as well as the use of high-precision casting and the high cost of production.
- Adhesive. Modeling takes place directly in the oral cavity. This is a gentle alternative to the previous method when only one element is missing. There is no need to grind the adjacent crowns; the plates are glued to them using a special cement composition.
- Stamped. An outdated option that most doctors refuse because the product weighs a lot and often leads to injury to the supports.
Material for production
The type of raw materials from which products are made determines their durability, practicality and care. Modern clinics offer many options to suit every taste and budget. Types of bridges and their features (photos are presented in the article):
- Metal. They were actively used decades ago, cast from precious metals, gold and silver. They are distinguished by high strength and affordable price. However, this type has a significant drawback: the dentition looks unattractive. Damage to the supporting elements is also possible.
- Metal-ceramic. The base consists of an alloy, which is complemented by ceramic inserts. This option is considered ideal with an optimal ratio of cost and high quality. The color is matched to the shade of the enamel.
- Ceramic. There is no all-metal cast frame. These teeth look quite natural, but do not tolerate strong mechanical stress due to their fragility. You need to be very careful when wearing it.
- Plastic. They are used primarily as temporary substitutes for permanent products while they are being manufactured in the laboratory. They are produced very quickly, do not cause allergic reactions, weigh little, look attractive, but do not last long.
- Made from zirconium dioxide. All-ceramic combined dental bridges on this basis are among the most modern. They absorb all the advantages of their predecessors: light weight, reliability, aesthetic appeal, hypoallergenicity, long service life.
- Made from aluminum oxide. They are not widespread enough because they have an exorbitant price. In terms of durability, strength, beauty and other characteristics, they have proven themselves exclusively on the positive side.
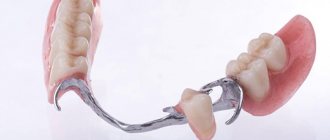
Mounting type
The structures are attached in different ways, the most common in dentistry:
- Consolidation on healthy units. The product consists of crowns with holes intended for teeth and bridges that connect them. For strength, the elements are made solid. When choosing this type, preliminary grinding and depulping will be required. Dentists are resorting to the latter procedure less and less; modern technologies make it possible in some cases to skip this stage.
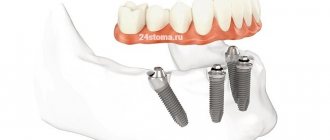
- On implants. When choosing this method, intact incisors, canines and molars remain intact. They will not be ground or depulped. However, the cost of treatment increases significantly.
- Adhesive method. The bridge is not put on supports, but is attached to the rear surface using special composite compounds.
- Lock fastening. This is a removable bridge, which, if necessary, can be detached and returned to its place. Grinding of the abutment crowns is also not carried out.
Methods for making dentures
The production of plastic dental crowns can be carried out in two ways:
- direct: in the dentist's office, i.e. in the presence of the patient. Very fast method of prosthetics,
- indirect: in a dental laboratory based on previously taken impressions of the patient’s dentition. It takes longer, but as a result the product “sits” more accurately on the support and adheres to it without gaps.
Plastic crowns can be made using cold or hot polymerization (hardening of plastic compounds). There are also stamped and milled plastic "caps". The latter are distinguished by the highest production accuracy, because are cut on computerized machines, which eliminates any errors.
Another option is standard, that is, templated plastic crowns. These are used in removable or adaptive dentures on implants. Essentially, these are just ready-made teeth that are inserted into an acrylic base.
A laboratory technician performs the following manipulations:
In addition to the traditional manufacturing method, there is also the so-called milling from ready-made blocks on a computer-controlled machine (CAD/CAM technology, for example CEREC, EVEREST). Using an optical system, an impression is taken (essentially scanned) either of the prepared area directly in the oral cavity, or of a model, then the data is transferred to a computer, where the image is processed by a special program, a model of the future restoration is built, which can be corrected, and then sharpened and finalized ( painted and glazed to give a shine comparable to natural). Now this is the most accurate way to create structures of various sizes and lengths (up to the entire dental arch), because human involvement and therefore possible inaccuracies are reduced to a minimum. The next step will obviously be the development of 3D printing technologies.
Indications and contraindications
Plastic crowns are suitable for installation on both chewing and front teeth. And also for implants. But, we repeat, this will be temporary prosthetics. However, you cannot do without it in the following cases:
- it is necessary to preserve or restore the aesthetics of the smile while a permanent prosthesis is being made: this becomes especially important when the upper front teeth are prosthetic - after all, the entire smile depends on their appearance,
- it is necessary to protect the ground teeth from infection from outside or from injury,
- you need to maintain the level of the gum before installing a permanent prosthesis: the point here is that the layer of enamel on the stump can be worn down quite strongly, plus the stump is ground down with a slight ledge near the gum. And if the permanent crown takes a long time to be made - more than 2-3 weeks, then the gum tissue will simply grow onto the ledge (bottom of the stump). Therefore, permanent installation will be painful, there will be bleeding, inflammation of the gums, pain and discomfort in wearing.
There are practically no contraindications to installation. But one can highlight the risk of allergies, especially if conventional plastics are used rather than composite monomer-free compounds. It is the monomer that most often causes allergies. At risk are children, people of retirement age and those who are already allergic to anything. Another contraindication is the inability to wear prosthetics at a given time. For example, if you have recently suffered a serious illness or in the coming weeks it will not be possible to maintain good oral hygiene.
Dental laboratory
The FDC clinic has its own dental laboratory, equipped with the latest technology, so even the most labor-intensive orthopedic work is performed in the shortest possible time.
Laboratory in France
Exclusive work, if necessary, can also be performed in the most prestigious dental laboratory in France, Bourbon Atelierd' Art Dentaire (Nice)
Temporary crowns can function for a short time; they last from a week to a month. This period should be enough to create a permanent structure. As for the appearance of such crowns, they are quite capable of maintaining the aesthetic appeal of the oral cavity.
When planning prosthetics, the doctor and the patient discuss methods for making temporary crowns, choosing the optimal one. This means you don’t have to worry about this; specialists at the French Dental Clinic always provide clear and competent advice before starting treatment.
Advantages of plastic crowns
The advantages of plastic crowns lie in the characteristics of the material. After all, it is inexpensive, easy to process and has the color of natural enamel. The positive aspects look like this:
- you can quickly restore a damaged tooth: literally in 1 hour, maximum in 1 day,
- good aesthetics: plastic does not stand out from the dentition,
- low cost,
- allows you to protect the ground tooth, adjacent gums or tissue around the implant: while a permanent prosthesis is being made or while the implant is taking root,
- prevents neighboring teeth from moving towards the defect (“holes” in the row).
As for the ground teeth, if you leave everything as it is (and do not put a temporary plastic crown on the stump), then the remaining layer of dentin without enamel will be attacked by microbes, destroyed by acids or trauma. Since in general dentin is much weaker than enamel. This is reflected in pain throughout the tooth. The shape of the stump may be disrupted - i.e. the prosthesis being manufactured simply will not fit.
What shortcomings can be found
There are few disadvantages (in number) of plastic crowns on teeth, but they are quite significant. See for yourself:
- fragility of the material,
- a high probability of gum inflammation during long-term use due to a not very tight fit to the gum and support (this does not apply to milled dentures made using CAD/CAM technologies),
- there is a high probability of caries appearing under the prosthesis if the period of wearing it is exceeded,
- risk of allergies,
- rapid loss of color, darkening, pigmentation from food and other dyes: due to the presence of micropores on the surface.
Afterwards, the plastic prosthesis is replaced with a more durable, aesthetic, durable one - for example, ceramic, metal-ceramic, zirconium dioxide, ceramic composite. That is, a permanent one that will last for many years.
Only until December 25 South Korean implant Osstem - from 18,500 rubles.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and lock in promotional prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Advantages and disadvantages of dental bridges
Advantages of bridges in prosthetic dentistry:
- There is no need to wait for the installed structure to take root. That is, there is no need for osseointegration, which can last up to six months. It turns out that the adaptation process lasts quite quickly (up to 12 hours).
- This is the most economical option for restoring rows when individual units are lost than implantation.
- Modern technologies make it possible to obtain aesthetically attractive artificial teeth with full functioning. Hidden elements (fastenings, etc.) are not visible to others, so no one will even notice the medical intervention.
- The procedure has virtually no contraindications. A bridge is also placed in cases where implantation of an implant is not possible.
- Normal diction is maintained.
Weak sides:
- It is necessary to grind down the adjacent crowns remaining in the mouth. Very often, dentists resort to depulpation (removal of the nerve, cleaning and cementing of the canals).
- The normal load on the jaw bone is not fully restored. When a person chews food, the supports are loaded; the central part is practically not involved in this. As a result, the risk of bone tissue atrophy increases.
What is included in the stages of dental restoration?
Making plastic crowns is not a very complicated process. However, the dentist and dental technician must observe all the nuances of production in order for the product to cope with its function. Prosthetics consists of the following stages:
- the best method of prosthetics is selected: first, the patient undergoes an examination by a doctor, then an X-ray diagnosis follows, then the option of a permanent prosthesis is selected and/or implantation is discussed,
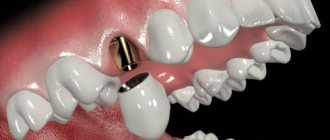
- preparation: diseased teeth or their roots are removed, the enamel surface is cleared of plaque and stone, root canals are prepared, the enamel is ground, an implant or pin is installed (stump inlay),
- impressions are taken,
- making a plastic crown in the office or in a dental laboratory,
- installation of a temporary plastic prosthesis for the patient.
Read on the topic: what is better to choose – implantation or prosthetics, and why?
General sequence of clinical and laboratory stages of manufacturing artificial crowns
Several specialists take part in their creation:
- Orthopedic dentist (carries out diagnostics, design planning, consultation, preparation of teeth for prosthetics - odontopreparation, taking impressions, quality control of the construction at all stages with correction if necessary, fitting, temporary and permanent fixation, dispensary observation - periodic examinations);
- Dental technician (together with the doctor, plans the future design and carries out its direct production on models (plaster analogues of teeth and jaws, obtained from impressions) in the laboratory, makes adjustments, if any);
- Dental assistant – performs auxiliary manipulations in the oral cavity and office during treatment.
Stage 1:
- Diagnostic – basic (questioning, i.e. medical history, examination) and additional (usually one of the types of x-ray examination) examination methods, drawing up and agreeing on a treatment plan, impressions for diagnostic models and temporary crowns , preliminary determination of color, bite registration . If necessary, auxiliary measures are carried out - a complex of professional hygiene (removal of dental plaque), treatment or re-treatment of caries (replacement of old restorations), endodontic (pulp removal, re-treatment of the root canal system) or surgical (lengthening of the clinical, i.e. visible crown with insufficient height). In a difficult clinical situation, total prosthetics, a special device is used - a face bow , which fixes the position of the upper jaw in the space of the skull and makes it possible to transfer it to a device that reproduces the natural movements of the lower jaw - an articulator. A dental photography protocol is also used - registration of images of the patient’s face in front and in profile, dentition in a closed and open state in the anterior and lateral sections. This manipulation helps the technician in choosing the visual characteristics of the future restoration (building a color scheme for the restoration, determining its size and shape).
Stage 2
- Preparatory – odontopreparation – grinding of hard tissues to create the shape of the tooth stump, providing the possibility of applying and subsequent fixation of the structure, as well as ensuring the correct relationship between the edge of the crown and the soft tissues of the gums. During this manipulation on living teeth, water-air cooling in order to prevent overheating of the hard tissues of the tooth. Taking working impressions, final color determination. Fitting, correction (relining) and temporary fixation of temporary crowns.
Stage 3
- Final – delivery of the work (trying on and, if necessary, correction of the structure, agreement with the patient on the coincidence of the existing and desired results regarding color, shape, size, convenience, temporary (for combined) or permanent (for metal-free structures) fixation; subsequent replacement of the temporary fixation with a permanent one) .
Installation features - how to install and how to remove
The plastic crown is fixed using special cement, which quickly hardens after installation. But, at the same time, the cement is not as strong as that of fixed permanent dentures. Therefore, sometimes the plastic crown falls off - if there is no damage, the doctor will be able to put it back. Before permanent prosthetics, the dentist will easily remove the temporary cap and clean the support from excess “glue” using ultrasound or special compounds.
When using prosthetics on implants, screw fixation can be used; in this case, the prosthesis will be conditionally removable (since the dentist will be able to remove it without damage). Here a small hole is created in the crown, a small screw is screwed through it, and the groove is closed on top with a filling. If necessary, the filling is removed, the screw is unscrewed, and the prosthesis is removed, changed, cleaned, and put back.
Removing temporary crowns
Temporary crowns can be removed quite easily. Over time, the cement on which they were installed becomes loose.
So, it will not be difficult for the dentist to quickly and painlessly remove it.
You can ask your treating dentist how temporary crowns are removed; he will explain this simple procedure to you in detail.
If the crown slips, you must visit the dentist to re-fix it with temporary cement. In the meantime, it is not possible to get to the dentist, it is better to return the structure to its original place.
At night and during meals, it is better to remove such an orthodontic element from the mouth. You can store it in a glass of water.
The COST of these prostheses ranges from $10-30. Their prices are low, so anyone can buy or order their installation.
Service life
The service life depends on the manufacturing method and the characteristics of the materials used. Thus, for those manufactured by the direct method, the service life is 1-2 months. For laboratory ones – up to 1 year. For those models whose walls are reinforced with fiberglass or metal thread, as well as those made by milling, the service life can be 1.5-2 years. But, of course, if you take good care of the prosthesis - clean it regularly and do not subject it to heavy loads.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS ON 4 IMPLANTS - from RUR 170,000.
The price includes all procedures for installing Osstem implants (South Korea), including anesthesia and diagnostics.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and fix your prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
How much does prosthetics cost?
The cost also depends on the manufacturing method, the quality of the plastic and its quantity, and the method of fixation. An ordinary plastic crown made in a doctor’s office costs from 1,000 rubles. The laboratory price is already higher - from 2000 thousand. The most expensive ones are milled ones; they can cost 3500-5000 rubles.
1Vyazmitina A.V. Materials science in dentistry, 2002.
Your questions and answers
QUESTION Hello, how long can I wear a temporary plastic crown on a tooth? Svetlana
ANSWER Hello, Svetlana. It all depends on what your dentist told you and what type of prosthetic treatment you are having. Ideally, if prosthetics are on your “native” tooth, then wearing a temporary plastic crown is not recommended for longer than 2-3 weeks. It is less common to walk with her for up to 12 months. For example, if you were given an implant with a temporary crown, and now it is healing. This is a slow process that requires some time. And after engraftment, it is necessary to change the temporary crown to a permanent one - made of ceramics, metal-ceramics or zirconium dioxide.
Author: Sambuev B. S. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
The main functions of such prostheses:
- protection of the pulp from the negative influence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- preventing displacement of treated and adjacent teeth;
- formation of the gingival margin and prevention of gum growth when treating teeth with a special ledge;
- reconstruction of occlusion during therapy for increased wear of chewing elements;
- continuation of the full functionality of teeth;
- acceleration of adaptation to the modernized chewing element, which will take the place of the affected one after installation;
- maintaining the aesthetic appearance of the oral cavity.
Many people are concerned about the question: how long can temporary crowns be worn? The answer is simple - the entire period allocated for the manufacture of permanent dentures.
This may even take a couple of months. When these orthodontic structures are worn for a long time, they wear out, which will lead to the displacement of adjacent teeth.
Inflammation of the gingival margin also occurs due to bacterial contamination of the plastic. Sometimes the crown breaks, followed by gum growth and pain.
The production of such crowns is much faster than their permanent counterparts.
Regardless of what material modern crowns are made from, they are fixed with temporary cement. Such material gradually dissolves under the influence of saliva.
Sometimes it becomes necessary to attach temporary dentures after implantation. This is because it is important for the gums to return to the desired shape after this type of intervention, and non-permanent crowns can help with this.
Before installing a permanent prosthesis, the implant must take root. The average period of its integration in the upper jaw is about six months, and in the lower jaw – 4 months.
The lower jaw is better supplied with blood, and it is larger and stronger, since it bears more chewing load.
While it takes root, the patient wears a temporary crown, which imitates a regular tooth, protecting the gums from inflammation.
Dentures are placed on an implant when the dental nerve is removed and it is not possible to restore the chewing element.