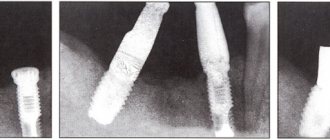
The restoration of damaged or removed teeth is carried out by an orthopedic dentist.
This specialist can offer only one, but very effective way to solve the problem - installation of prosthetic structures. At the same time, one or two visits to the clinic will not be enough: the recovery method involves a multi-stage approach. Let's look at the main stages of dental prosthetics, which consistently bring the patient closer to the main goal: gaining a beautiful smile and the ability to chew food normally.
What is dental prosthetics?
This is a set of therapeutic measures aimed at restoring the appearance, aesthetics of a lost tooth or the entire dentition, chewing function and speech. Dental prosthetics is also necessary to preserve the remaining teeth in the dentition, to prevent deformation of the lower, upper jaws and temporomandibular joints. Correctly installed modern structures can completely replace lost teeth. You just need to choose a dental clinic with a good reputation.
About the technique
Dental prosthetics involves restoration of dental tissue, replacement of lost teeth, restoration of structure and chewing function. Dentures in modern times are one of the most popular ways to restore tooth enamel. Dentures are manufactured using special modern high-precision equipment. Denture manufacturing is constantly improving due to new developments in the dental industry.
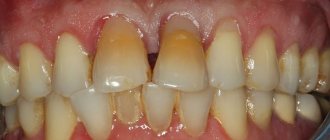
The absence of teeth or one of them is a problem of both aesthetic and medical nature. This can cause inconvenience to a person in his everyday life. Due to incomplete dentition, healthy teeth may become displaced, the bite may be disrupted, and other oral diseases may occur. To avoid these problems, you should contact an orthopedist or specialized specialist to get prosthetics installed. This method of restoring dental tissue will help to avoid a number of problems and return a person to a healthy smile.
Indications for prosthetics
Dentures are installed:
- when one or more teeth are lost in one row - if this is not done in time, nearby teeth begin to gradually shift, taking the place of the removed one; this leads to an imbalance in the dental system;
- with the loss of several teeth in opposite rows, there is a high risk of dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, chewing and speech;
- with complete loss of teeth (edentia);
- after surgery for partial removal of jaw bones due to tumors or severe purulent-inflammatory processes.
Pros and cons of dental prosthetics
Various methods of installing dentures have both advantages and disadvantages. But there are more benefits, since orthopedic treatment significantly improves a person’s quality of life.
Advantages
The advantages of prosthetics are obvious. This:
- improvement of appearance; in case of problems with the front teeth, problems of eliminating stress and social adaptation are also solved;
- preservation of jaw bone tissue is a very important function, since when a tooth is absent for a long time in a cell, the bone is resorbed and the dentition shifts, disrupting the function of the dentofacial system;
- correct distribution of the load when chewing;
- elimination of speech defects - dentures in the complete absence of teeth contribute to its restoration;
- prevention of dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
Flaws
The disadvantages of installing dentures for teeth are not so noticeable, but they are:
- discomfort in the first days, sometimes the process of getting used to the structure is delayed due to the individual characteristics of the patient’s soft tissues (abrasions and irritation of the gums);
- in some cases, the patient is contraindicated for prosthetics using the method he has chosen and has to choose another method, which does not always suit him for various reasons;
- fixed bridge products require pre-treatment of the supporting teeth and can overload them, leading to loosening;
- improperly installed removable models can place uneven pressure on the jaw, contributing to partial atrophy of its bone;
- a crown or inlay can make root canal treatment difficult for secondary caries.
A good dentist takes into account all the pros and cons, smoothing out the latter and avoiding complications.
Diagnostics
At this stage, the quality and thickness of the jaw bone, the condition of the roots and canals of the dental elements, the identification of hidden anomalies, and the study of the maxillary cavities are determined.
As a result of the diagnosis, limitations and contraindications to the operation are identified. A comprehensive study of the dental system prevents potential complications.
Research methods:
- CT. Obtaining an accurate three-dimensional image of the human dentofacial apparatus. Allows you to identify anomalies, determine the quality of bone tissue, the condition of the alveoli, and pathologies of the root system.
- Orthopantomogram. The panoramic image displays a reliable picture of the condition of the dentofacial apparatus.
- MRI. A clear 3D image, free of distortions and errors, allows you to study in detail the area of the proposed restoration.
- Radiovisiography. Study of individual elements and the root system and diagnosis of the jaw bone and tissue surrounding the teeth.
The diagnostic method is selected by the doctor. The duration of the clinical stage is determined by the client’s age, health status and duration of research.
Types of dentures
There are different types of dentures. The dentist decides which dental prosthetics is suitable for a given patient, coordinating this issue with his aesthetic needs and financial capabilities.
Removable dentures
The patient removes, puts on, and cleans dentures of this type independently. Removable dentures are divided into plate and clasp.
Plate prosthesis
Plate dentures for teeth
Plate dentures are classic removable dentures, consisting of a plastic plate that follows the relief of the gums and palate to which it is applied (base) and artificial crowns. Plate (plate) models are divided into complete dentures (for complete edentia) and partial dentures (for incomplete edentia). Modern designs of lamellar removable dentures made from soft hypoallergenic materials are very popular.
Installation of lamellar removable dentures: if the patient has teeth left, the structure is fixed to them using special clasps; with complete edentia, it is fixed by clenching the jaws - thus removing air and the structure sticks to the mucous membrane. Special fixing adhesives and creams are also used.
The advantages of complete removable dentures: low cost, easy care, ease of manufacture, and the possibility of repair. Disadvantages: relative fragility and the need for replacement every three years, tissue atrophy due to uneven load, inflammatory processes of the periodontal tissues, insufficient fixation in the oral cavity. Contraindications to complete removable dentures: mental illness, allergic reaction to plastic, significant malocclusion.
Clasp denture
Bugel prosthesis for teeth
Bugel dentures are more modern partial removable dentures. They consist of support clasps (they fix the prosthesis on the remaining natural crowns and can have a different design), a connecting arch (clasp) and a saddle, located in places where teeth are missing and holding the structure in the desired position. Installation is possible only if the patient still has his own dental crowns on both sides of the jaw, that is, these are dentures with partial absence of teeth.
The advantages of clasp removable dentures: they stay well in the oral cavity and take up minimal space, fully perform the chewing function (the chewing load is distributed evenly), do not have a negative effect on speech, and remain in working condition for a long time; repairs are possible during operation. The disadvantages of clasp removable dentures include a more complex manufacturing process, which results in a higher cost, since these are the best removable dentures. Clasp dentures are not installed in the absence of teeth, due to the impossibility of fixing the structure on both sides of the jaw.
Conditionally removable dentures
Conditionally removable dentures all-on-4 and all-on-6
This type of prosthetics is performed on implants - artificial titanium roots. First, implantation is carried out, and then the plate prosthesis is installed and tightly attached to the implant. This design is called conditionally removable because the dentist can remove it, clean it and reinstall it.
Installation of a conditionally removable dental prosthesis is carried out using the all-on-4 and all-on-6 methods (all on four or all on six implants). Implantation and prosthetics are carried out simultaneously or at intervals of 2–3 days. The advantages of this technique are its reasonable price, strong fixation in the oral cavity and complete restoration of the patient’s chewing and speech functions. There are practically no downsides; a prosthesis can be installed even with a long absence of teeth and atrophy of the jaw bone tissue. Many people consider these dentures to be the best.
Read more about dental implantation in this article.
Fixed dentures for teeth
This is the most popular type of dentures for teeth with incomplete edentia. The structure is installed in place of the missing tooth (or part of it) and is firmly fixed. There are several subtypes of fixed models. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications.
Fixed dentures
Bridges are a structure consisting of two crowns on supporting teeth and artificial crowns firmly connected to them. A bridge usually contains 1-3 artificial crowns, rarely more - this compromises the strength and reliability of the structure. A bridge is the most common and popular type of permanent structure. The indication for installation is the absence of one or more teeth in a row. Contraindications: absence of 4 or more teeth in a row. Pros: quite durable, reliable and not very expensive design. Disadvantages: installing a bridge requires grinding down healthy supporting crowns; at the site where the artificial crown is installed, the jaw does not receive load, so the tissue may atrophy.
Veneers are thin, durable ceramic or composite plates used to hide defects in the front teeth. Veneers are made of ceramics or composites and are glued to the front surface of the crown, hiding defects such as chips, slight curvature, changes in color or shape of the tooth. The advantages of veneers are: high strength, aesthetic appearance (beauty of a smile), biocompatibility with tissues. Cons: high cost, need to grind down a healthy crown.
Inlays are orthopedic structures made from individual patient impressions in a dental laboratory. Inlays are installed mainly on chewing teeth with significant destruction of the crown. They replace a filling, but are more reliable and aesthetically pleasing. They are made from different materials; ceramic and metal inlays are widespread. Nowadays, tabs are used more and more often. Pros: durability, no depressurization, aesthetic appearance, full functionality. Cons: More expensive than fillings.
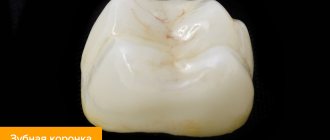
Crowns are artificial caps that are installed on a destroyed natural crown, repeating its shape. Before installing a crown, treatment, filling, and grinding for the crown are carried out. If the crown is completely destroyed, a stump tab is first installed in the root canals - it serves as a support for subsequent prosthetics using an artificial crown. These dental prostheses are made from different materials - metal, ceramics, composites, zirconium dioxide, etc. The advantage of these designs is the preservation of chewing and speech function, preservation of the natural load on the jaw bone tissue, and aesthetic appearance. Cons - artificial crowns made of plastic often change their color under the influence of food coloring.
Dentures for teeth on implants - artificial crowns are attached to implants - titanium roots. The method is used when the natural crown is completely destroyed and removed along with the root. There are methods of immediate and delayed prosthetics on implants. In one-stage procedure, a titanium root is inserted immediately after tooth extraction, after which prosthetics are performed. The delayed technique requires complete implantation of the implant and only after this (several months) prosthetics are performed. Pros: all functions of the dentition are almost completely preserved. Cons: the procedure is quite expensive.
Features of dentures
Dental prosthetics, based on the area where the dental element is installed, has its own characteristics:
- When denture replacement of anterior incisors, special attention is paid to the aesthetic side. Dentists try to restore the dental tissue of the incisors as soon as possible, because this can lead to psychological discomfort. Discomfort arises due to the fact that a person is embarrassed to smile and is not confident in himself. When replacing the anterior incisors, all-ceramic structures are used. Thanks to such designs, it is possible to eliminate the transmission of metal through artificial enamel or its exposure.
- When restoring chewing teeth, close attention is paid to chewing function. Here, metal-ceramics are most often installed to increase the strength indicator, because these teeth are largely responsible for the chewing function.
- When replacing dentures in the upper jaw, there may sometimes be a need for a sinus lift, since the maxillary sinuses are located close to the roots of the upper lateral teeth. A sinus lift is a plastic procedure that lifts the bottom of the maxillary sinus and fills the resulting space with bone tissue. It is this tissue that will fix the titanium root.
Types of prostheses by material
Dentures are made from a variety of dental materials. All of them have advantages and disadvantages, indications and contraindications for use. The orthopedic dentist must take all this into account. Basic requirements for materials: strength, biocompatibility with human tissues, lack of toxicity, allergenicity, effects on taste and olfactory receptors. The following types of materials are distinguished:
- metal – used for the manufacture of crowns, inlays, bridges; These are mainly precious metals, their alloys and hypoallergenic types of steel; titanium, as well as a nickel-cobalt alloy, are suitable for the manufacture of clasp dentures;
- zirconium dioxide is the most durable material; it looks beautiful in appearance, so it is used to make crowns of any teeth; The disadvantages include its ability to erase the surface of natural antagonist teeth;
- ceramics (dental porcelain) is a very fragile material in its pure form, so today it is rarely used in its pure form for making crowns and only for the front teeth; Dental materials made from glass ceramics are in great demand; famous world brands: Empress Esthetic (Ivoclar Vivadent, Liechtenstein) - glass ceramics based on lithium disilicate - a hard but quite elastic material, dental prostheses made from which can last a lifetime;
- E-max (Ivoclar Vivadent, Liechtenstein) - glass ceramics based on lithium disilicate; used for the production of crowns, inlays, veneers, bridges of the highest quality - hard, durable and very aesthetic, completely consistent with natural teeth; the crowns are very thin, so the teeth underneath do not require significant grinding;
- Ceramage (SHOFU Dental, Germany) - microceramics based on zirconium silicate;
- acrylic - the advantages of this material include lightness, plasticity, and affordable price; cons – removable acrylic dentures can cause allergies and often break;
You should trust your dentist in choosing the material. He will select the material that is most suitable in terms of properties, quality and price for a particular patient.
Advantages and disadvantages of metal ceramics
Compliance with manufacturing standards and installation technology almost completely eliminates possible harm from installing the structure. The use of modern materials eliminates the release of toxic substances, but it is important to remember that an individual reaction may occur.
The ceramics itself, used in the manufacture of artificial teeth, does not cause allergies - a possible reaction is provoked by the metals in the frame of the structure. For example, chromium-nickel alloys can provoke an allergic reaction to nickel, and the use of base metals under the influence of saliva can be susceptible to oxidation reactions. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- burning in the mouth;
- metallic taste;
- swelling of the gums in the area of contact of soft tissues with the crown.
If such symptoms occur, it is important to consult a dentist - you will probably need to replace the structure with an all-ceramic crown or use another prosthetic method.
Other disadvantages include the possibility of exposing the metal frame in the event of receding gums. It is worth noting that structures made of zirconium dioxide are not subject to this phenomenon. In addition, the technology of metal-ceramic dental prosthetics involves grinding the tooth under a crown and removing the pulp in many cases, which is also a disadvantage.
The advantages of metal ceramics include high strength and long service life. Today, metal-ceramics are used for both single crowns and bridges - it is in demand when it is necessary to replace teeth with a significant chewing load. The frame made of aluminum dioxide or zirconium is strong enough, so the dentures can withstand heavy loads.
A long service life - 10-12 years for alloys of base metals and about 15 in the case of using a gold-platinum alloy - is a key advantage of the designs. This is only relevant for those prostheses that are made using individual casts. It is also important to follow the doctor’s recommendations for care - in this case, the prosthesis will last as long as it should. This is necessary because one of the common reasons for premature crown removal is the development of secondary caries at the junction of natural and artificial tissues, so it is very important to visit a doctor in a timely manner.
To summarize, we can say that the advantages of metal ceramics are as follows:
- comfort of wearing structures;
- functionality - function is restored due to the flawless modeling of masticatory hillocks;
- strength;
- long service life;
- acceptable aesthetics;
- biological compatibility - in the absence of allergic reactions to metals;
- the possibility of prosthetics for both anterior and chewing teeth;
- shade fastness - ceramics are not susceptible to the action of dyes;
- comparative cheapness;
- the possibility of restoring the structure without removing it in the event of minor chips.
How are dentures made?
The process requires highly qualified orthopedists and dental technicians, an individual approach and precision of execution. All work consists of several stages.
Stage one - taking impressions
An impression is an impression of the oral cavity using dental elastic material that can retain its shape. For prosthetic restoration of 1 – 2 crowns or a bridge, anatomical casts are used, reflecting the condition of only part of the dentition. If prosthetics is necessary with complete edentia, a functional cast is required that reflects the relief of not only the dentition, but also the adjacent tissues (gums, palate).
Taking an impression of the jaw
Depending on the type of structure and the characteristics of the patient’s tissues, different materials are used to obtain impressions: gypsum (almost not used today due to uneven hardening and fragility), silicone masses (the most popular type), dental wax masses (give clear imprints, but do not keep their shape for a long time), etc.
The impression taking procedure takes about half an hour and includes:
- drying the oral cavity - some types of impression materials lose their properties from moisture; it is removed with napkins or an air stream;
- selecting the material for the impression and placing it in a special standard tray for impressions; if there are significant defects in the dental system, individual spoons are made;
- the spoon is applied to the dentition, the patient clenches his jaws and waits 2 - 3 minutes until the impression mass hardens;
- The impression is washed under running water, placed in a special solution and sent to a dental laboratory.
An impression can also be taken using a more modern method using a 3D scanner. It can be immediately transmitted via the Internet to the dental laboratory.
Stage two - creating a plaster or computer 3D working model
Based on the impression obtained, a working model is made in a dental laboratory - an exact copy of the prosthetic area. A working model is necessary for maximum fit of the future prosthesis. It can be made in a traditional way - the model is cast from a cast from various materials (gypsum, epoxy resin, etc.) or digitally, based on a 3D image. The digital method is more accurate, therefore it saves the orthopedist’s time and reduces the frequency of patient visits.
Stage three - making a prosthesis
Based on the working model, the final version of the denture is manufactured in a dental laboratory at a dental clinic or in independent production. It can be made in the traditional way by hand or using modern CAD/CAM technologies. These technologies make it possible to create individual parts of a structure from different materials on robotic machines. If necessary, the laboratory repairs the product.
Dental prosthetics technologies
Modern technological processes associated with dental prosthetics are constantly being improved. Dental laboratories are developing new, more effective methods, replacing outdated, ineffective ones. They are also developing new methods for carrying out the procedure and identifying new materials for the manufacture of prostheses.
Modern prosthetics and developed procedures for carrying out the procedure imply the use of high-tech computer equipment at each stage of diagnosis (using X-rays in 3D mode), as well as in the production of prostheses and during their installation. The latest technologies in the field of dentures are CAD/CAM systems, which make it possible to produce the most accurate dentures using computer models in 3D mode. Using this equipment, dentures are cut out on a milling machine from high-strength ceramics. Previously, the process of manufacturing dental elements involved casting ceramics onto metal frames.
Due to the latest technologies and developed methods for carrying out the procedure, it can be carried out in one trip to the dentist, since the prosthesis can be made on a modern special machine in a short period of time.
Installation of dentures
Installation of the finished model is carried out according to certain rules (protocols). In this case, at the first consultation, the orthopedist develops an examination and preliminary treatment plan, and then works closely with the dental technician, adjusting the working or finished model to the required parameters and eliminating discomfort in the patient’s oral cavity.
Installation of prostheses is carried out according to a specific protocol
Oral preparation
This stage includes a thorough examination of the patient and treatment of all identified pathologies. Professional teeth cleaning and treatment of caries of teeth that serve as a support for the prosthesis are also carried out. Sometimes, in the process of preparation, the patient receives surgical assistance: removal of a tooth, a cyst at the root apex, hypertrophied (excessively overgrown) soft tissue, etc.
If the patient requires orthodontic care before prosthetics, the teeth are straightened and braces are installed for this purpose. Orthopedic preparation is necessary if, after a long absence of one or more teeth, the interdental spaces are reduced. Depending on the existing problems, this stage can take from one day to several weeks and even months.
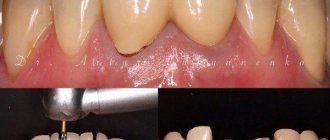
Preparing the support for the prosthesis
To install dentures (except for plate products with complete edentia), it is necessary to prepare a support. It can be of two types:
- the patient’s own teeth – they are ground down so that they can be fitted with a crown or a retaining lock; will take no more than 30 minutes, no anesthesia is required;
- implants (titanium roots) – implantation can be carried out simultaneously (immediately after tooth extraction) or delayed, after some time; performed under local or general anesthesia and will take about an hour; The doctor decides after what time to perform prosthetics.
How are dentures attached?
After taking an impression, a working model is made in the dental laboratory. It is tried on in the orthopedist's office. If there are any discrepancies or the patient feels discomfort, the orthopedist notes this and sends the model to the dental laboratory for revision. He can also correct something in the model himself. Fittings are carried out until the working model fully matches the area of the dentition to be replaced. Usually two fittings are enough at intervals of 2 - 3 days. Each fitting will take about half an hour.
A week later, the finished model is installed in the orthopedist’s office. If necessary, the doctor slightly adjusts the finished product. The total manufacturing time of the structure depends on what type of dental prosthetics was performed. So, it will take about three weeks to make a removable clasp denture.
Color of metal-ceramic structures
Separately, I would like to note the advantage of metal-ceramics, due to which many patients prefer it - ceramics, which is used for the manufacture of structures, allows you to imitate the shade and structure of your own tooth enamel. Therefore, the prosthetic tooth is similar to the patient’s natural teeth. The shade is selected according to the Vita scale - the selected color will remain that way throughout its entire service life, since ceramics are not subject to darkening and do not tend to absorb dyes from drinks and food.
The only thing that can change the shade of an artificial tooth is pigmented plaque, which is easily removed with professional oral cleaning.
Possible complications after dental prosthetics
If you choose the right clinic with qualified specialists, the risk of complications is minimal. But complications are sometimes associated not with medical errors, but with the characteristics of the dental tissues and the general health of the patient. Therefore, it is impossible to completely exclude them. Main causes of complications:
- incorrect choice of prosthesis design and material for its manufacture;
- untreated infectious and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- violation of the technology of individual stages of prosthetics;
- patient's failure to comply with oral hygiene;
- the patient has common diseases that reduce immunity - diabetes, etc.
Types of complications:
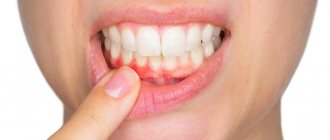
- Infectious and inflammatory processes of the gums and oral mucosa (gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis) due to rubbing of soft tissues by the prosthesis or compression of blood vessels and nerves; if the problem cannot be resolved with antibacterial therapy, the prosthesis is removed, the pathology is treated and prosthetics are re-placed.
- Secondary caries – develops in supporting teeth under crowns; Thorough daily oral hygiene and professional teeth cleaning twice a year will help.
- Allergy to dental material – severe swelling of the mucous membrane, headache; requires immediate removal of the prosthesis, treatment and subsequent re-prosthetics using a product made of a different material.
- Destruction of the prosthesis - chips, cracks, etc. - can occur when eating hard food, hitting the jaw area, etc.; a small chip can be eliminated using modern filling materials; but if the product is completely destroyed, it must be replaced.
- Crowns that are too high or low - the chewing process and the load on the jaw tissue are disrupted; replacement of the prosthesis is necessary.
- A denture has fallen out - you need to save the fallen product and urgently contact a dentist.
Moderate pain after prosthetics is normal. They are associated with the adaptation of tissues to new designs and pass over time. But if the pain increases and is accompanied by swelling and redness of the tissues, you need to consult a doctor.
Signs of denture rejection
Sometimes (very rarely) rejection of the implant root occurs - the titanium root (the basis of the prosthesis) for some reason does not take root in the patient’s tissues. This can happen either one or two days after implantation, or much later. More often, implants do not take root in smokers and in patients who do not maintain oral hygiene. Signs:
- the gums bleed for a long time (more than three days);
- body temperature rises, it may not be high, but it can rise to significant numbers;
- moderate pain, which normally appears after implantation, sharply intensifies and becomes acute;
- the gum and adjacent cheek swell;
- after some time, pus appears from the gums;
- there will be a feeling of weakness, weakness, headache;
- the titanium root and the prosthesis installed on it can become mobile and even fall out of the gums.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Reviews from our patients
I would like to express my deep gratitude to the doctors of the clinic Alexey Redovich Grivtsev and Alexey Vyacheslavovich Sychugov, as well as their assistants Olga and Alexey!!!
A huge thank you to you all for your professionalism, experience, philanthropy, and compassion. I wish you health, good luck and success in your difficult but important work. Special thanks to the girls administrators! Pro! Prosperity for your entire clinic! Well done!!!! Sincerely, Marina Vladimirovna
I went to the clinic for help. I would like to express my deep gratitude to the clinic staff. The attitude towards the patient is always warm and friendly. I went to have my teeth treated as if it were a holiday. I wish there were more doctors like this! Thank you very much.
Sincerely, Korshun I. Yu.
Rules for caring for dentures
When installing any type of dentures, you must follow the oral care rules recommended by your dentist. They depend on what kind of dental prosthetics was performed. If removable dentures are installed:
- immediately after installing the structure, do not remove it for several days in a row at night, while eating, talking (even if it interferes), until the tissues get used to the pressure exerted on them;
- when the pain and discomfort from wearing the prosthesis go away, it can be removed at night; but modern construction materials make it possible to wear them constantly;
- Every morning and evening after removing the denture, it is washed with cold running water and cleaned with a soft toothbrush and toothpaste without abrasive;
- at night, the prosthesis can be placed in a special protective container or in a container with a disinfectant solution intended for long-term storage; it can be bought at the pharmacy in finished form or in the form of tablets that dissolve in water; clasp dentures with metal parts must be stored in a solution with anti-corrosion properties;
- after each meal, it is advisable to remove the denture and rinse it with water, as well as rinse your mouth;
- Once every six months, the denture can be taken to the dentist for professional cleaning;
- if severe pain, erosion, or inflammatory processes appear in the oral cavity, you should contact a dentist; In this case, it is necessary to install a removable dental prosthesis three hours before the appointment so that the doctor can see exactly what is happening.
Maintenance of the fixed structure:
- In the morning and evening, you need to brush your teeth with toothpaste without abrasive;
- after eating, rinse your mouth with boiled water or mouthwash, and also rinse the interdental spaces with an irrigator;
- It is better not to use dental floss - as a result of their use, the product may be damaged;
- Carry out professional cleaning every six months.
How long does it take to make a prosthesis?
The timing of dental prosthetics with permanent structures varies. The process can take 5–7 days to 3–4 weeks. How long it takes to make dentures depends on the size, shape, material used, and the presence or absence of metal fasteners. Production times are strictly individual. The patient should not be upset if he has to wait longer than he planned for new teeth - while the permanent structures are being manufactured, he will be offered temporary templates, the installation of which will take only a few hours.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Fixation of dentures
Fixing agents are used only if removable dentures are installed, since they allow the structure to stay more firmly in the oral cavity and also have a shock-absorbing effect, reducing irritation of soft tissues. Most of these products also have antibacterial properties.
Cream for fixing dentures
These include:
- fixing creams, gels, adhesives - they are applied to the surface of the prosthesis adjacent to the patient’s tissues, strictly according to the instructions (some are applied only to dried mucosa); Please note that creams and gels have different durations of action: the widely advertised Corega cream lasts 3–4 hours, Rocs cream lasts up to 12 hours (optimal duration), and Lacalut - 24 hours; You should also keep in mind that some fixatives contain zinc, which has a good anti-inflammatory effect; but with prolonged use of such drugs, an overdose of zinc occurs, which is harmful to the body, therefore zinc-containing fixatives can only be used in courses of 3 to 4 weeks with long breaks;
- powdered products - sprayed onto the surface of the removable dental prosthesis, then the product is put on in the usual way and lightly pressed against the gums and palate;
- strips of fabric - designed to tightly fix a removable denture in the absence of teeth and make it more comfortable to wear.
An orthopedic dentist will help you choose the right fixation agent.
Production time for removable devices
| View | Production time, in days |
| Clasp with hooks | 10–12 |
| Clasp on attachments | from 20 |
| Clasp dental crowns on telescopic crowns | from 20 |
| Nylon | 7–10 |
| Soft plastic | 5–10 |
| Plate and acrylic | 5–7 |
The table shows only the average time for dental technicians to complete work. Depending on the workload, the patient may be asked to complete the work much faster than the stated deadline. However, many dental laboratories operate using the “urgent order” system. Production time can be halved, but at the same time you will pay for urgency.
Contraindications for prosthetics
Currently, there are many methods of prosthetics and the dental materials used, so in most cases the patient can choose the type of dental prosthetics that is most suitable for him. The dentist decides which dental prosthetics is suitable for the patient. There are a minimum of contraindications for the installation of fixed and removable dentures; all of them are divided into absolute and relative.
Absolute
Contraindications to any type of prosthetics are severe mental illness with social adaptation disorder. The rest relate mainly to prosthetics on implants. These are diabetes mellitus, cancer, systemic connective tissue diseases, and significantly reduced blood clotting.
Relative
These are currently existing contraindications. They can be general and local. Common ones include acute infectious and inflammatory processes and exacerbation of any chronic diseases, pregnancy.
Local - gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucosa), periodontitis and periodontal disease (inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the periodontal tissues) in the acute stage, bruxism (involuntary grinding of teeth), increased tone of the masticatory muscles. After eliminating these contraindications, prosthetics can be performed.
Approximate production times for fixed dentures
How long it takes to make a dental crown depends on the method of its fixation. Will it be on a natural tooth, a post and an implant?
| Crown material | Production time, in days |
| Metal-ceramic dental crowns | 5–10 |
| Metal dental crowns | 4–7 |
| Ceramic dental crowns | 4–7 |
| Metal-plastic dental crowns | 5–10 |
| Crowns based on zirconium dioxide | 4–5 |
How long work on dental bridges takes depends on the number and type of crowns that are used as part of the bridge. In general, the technician’s work takes 10 days or more.
Installation of crowns on implants within the framework of one-stage implantation protocols (All-on-4, All-on-6 and others) is possible already on the 3rd day after implantation, since the creation of prostheses begins already at the time of planning the operation itself.