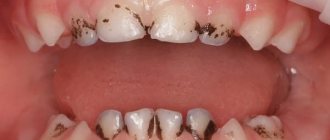
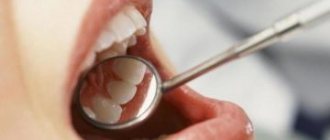
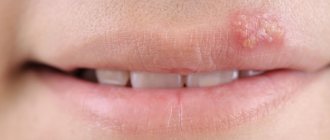
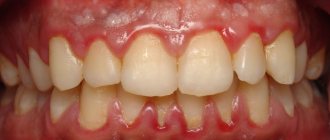
When thrush appears in the mouth, the tongue becomes covered with a mucous membrane, where bacteria accumulate. This will become a provoking factor for the appearance of white plaque in the oral cavity. Candidiasis involves the covering of the upper layer of the oral mucosa by a fungus. It is necessary to differentiate pathological plaque from normal plaque. If unpleasant symptoms occur, you should consult your doctor.
Development mechanism
If there are no pathological processes and the internal organs function properly, then white plaque in the oral cavity will appear as a thin film, which can easily be removed after brushing the teeth.
The color of the tongue also changes after consuming various food products that contain a coloring enzyme. However, there are situations when white plaque can cover the oral cavity in a thick layer. Eliminating it is quite difficult, which can be a consequence of improper care, the use of certain medications, or viral diseases.
Doctor about oral candidiasis:
Causes
Often the appearance of white plaque in the mouth and the appearance of a persistent unpleasant odor indicate the formation of a fungal infection or diseases of the digestive tract.
Often the following diseases are the triggering factors:
- Acute and chronic gastritis.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Gallbladder diseases, hepatitis.
- Acute and chronic pancreatitis.
- Stomach cancer.
Important! In addition, the appearance of white plaque in the oral cavity indicates a deterioration in the immune system, metabolic failure, and fungus. Therefore, if there are initial symptoms of pathology, it is necessary to consult a specialist for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Identifying thrush begins with taking an oral history of the patient.
He must tell the dentist in detail when the first signs appeared, what worries him, and whether there are concomitant diseases. After examining the oral cavity, the patient is sent for a general blood test to determine glucose levels. Microscopic examination of the oral mucosa and biochemistry are carried out to confirm the causative agent of the disease. To do this, a scraping is taken from the surface of the tongue. It is not recommended to eat or brush your teeth for about three hours before the procedure.
Diagnosis should be aimed at identifying the cause that provoked the disease. Only in this case can you correctly draw up a treatment plan. In this case, if necessary, the patient may be referred for consultation to an endocrinologist or dermatologist.
Which doctor treats candidiasis:
Kinds
Infection with oral fungus is accompanied by the creation of favorable conditions. Based on general health, oral candidiasis has a different course and location.
Often the pathology develops in infants and older people. If the body is weakened by constant ARVI or chronic diseases, then the immune system will not be able to counteract the pathogenic microflora and the disease will manifest itself.
By localization
The following types of diseases are distinguished by location:
- Oropharyngeal thrush . The cause is long-term use of antibiotics.
- Mycosis of the gums . A common occurrence associated with fungal infection. It also appears due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, smoking or the use of oral contraceptives.
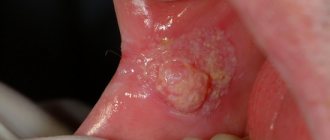
- Damage to the corners of the mouth . During the development of pathology, cracks may bleed when opening the mouth. Mostly the disease is treated with ointments and creams.
Oropharyngeal thrush
Mycosis of the gums
Damage to the corners of the mouth
By shape
The disease can occur in various forms.
There is the following classification:
- Pseudomembranous acute candidiasis . Almost everyone is susceptible to the disease, but infants often suffer. Pathology can affect various parts of the oropharynx.
- Acute atrophic candidiasis . Formed due to inappropriate therapy. The tongue and corners of the lips become bright red. Plaque at this time is absent or appears only in hard-to-reach places.
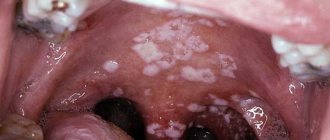
- Chronic hyperplastic type . The disease affects the cheeks and tongue. The patient has white spots that differ in shape. The damaged areas become inflamed and redness forms near the white spots. If not treated promptly, the fungus leads to malignancy.
Pseudomembranous acute candidiasis
Acute atrophic candidiasis
Chronic hyperplastic type
Diagnostics of the oral cavity:
Causes of thrush in the mouth
Oral candidiasis is a common disease.
Very often a person does not even suspect that he is a carrier of Candida fungus. Its rapid reproduction occurs under the influence of several factors:
- long-term use of antibiotics, cytostatics or glucocorticosteroids;
- vitamin deficiency or hypovitaminosis, lack of iron in the body;
- impaired carbohydrate or fat metabolism;
- diabetes mellitus, problems with the thyroid gland, ovarian function;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary or reproductive systems in a chronic form;
- malignant neoplasms, AIDS;
- mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the gums;
- caries, impaired salivation, cyst, periodontitis;
- lack of regular cleaning of acrylic dentures;
- alcoholic beverages, tobacco products; bad ecology;
- frequent stress, overwork.
Reference! Oral thrush cannot appear on its own. It is a consequence of a violation or weakening of the body’s protective properties.
More information about the disease:
Treatment
To get rid of fungus in the mouth, you need to seek help from a doctor. Therapy for candidiasis is also carried out by influencing damaged mucous membranes with Decamine, Fluconazole and other antibacterial agents.
Ointments/gels for topical treatment
White plaque in the mouth can be effectively treated with the use of topical antibacterial ointments.
The following ointments are effective:
Nystatin
Levorinova
Advice! If you eliminate the disease by alternating these medications or combining them, then the unfavorable symptoms will disappear more quickly.
Pills
During the treatment of pathology, it is possible to use medications in tablet form. Levorin and Nystatin stand out. The tablets must be kept under the tongue until completely dissolved.
Levorin
Nystatin
Decamine will also be effective. It helps to quickly eliminate the lesion caused by oral candidiasis.
Caramel with Dekamin
Diflucan, Fluconazole and Nizoral are produced in capsules. They are used after consultation with a doctor.
Diflucan
Fluconazole
Nizoral
Rinse solutions
If the mouth is covered with a white coating, rinsing with disinfectant and alkaline solutions, which reduce the inflammatory process, helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
They are:
Boric acid
Sodium tetraborate
Baking soda
Iodinol
Rinsing should be regular after meals.
Traditional methods
Many patients prefer to eliminate white plaque in the mouth through traditional therapy.
The most common means:
- Calendula infusion.
- Juniper tincture.
- Infusion of oak bark.
- Rinse your mouth daily with viburnum, carrot or cranberry juice.
Treatment must be agreed with a doctor.
Features of treatment in children
In childhood, the disease can occur in an acute form and be accompanied by redness and swelling of the oral mucosa.
Pathology in a child occurs due to the following factors:
- Deterioration of the immune system.
- Infection during lactation.
- Transmission of bacteria during childbirth.
- Infection through household items.
Important! When the disease is not detected in a timely manner, a white coating forms in the child’s mouth, and in severe situations, ulcers appear.
Komarovsky on the treatment of oral thrush:
In adults
In adulthood, such a disease appears due to excessive consumption of foods that contain many carbohydrates.
White plaque can also appear due to various diets and poor drinking regimen. This can be affected by poor oral hygiene, smoking, and drinking alcohol. A balanced diet and plenty of drinking water, compliance with hygiene rules, and giving up bad habits prevent the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms.
Candidiasis can occur due to deterioration of the immune system, hormonal imbalance and due to complications after various diseases.
Oral candidiasis: causes
There are many subspecies of fungi of the genus Candida. Previously, candidiasis in the mouth in approximately 80% of cases was caused by the species Candida albicans (C.albicans), and only in other cases by the more pathogenic species C.glabrata, C.krusei, C.tropicalis. Currently, C. albicans is the cause of candidiasis in only 50% of patients, i.e. The causes of candidiasis are increasingly becoming the most aggressive species of Candida fungi, which are resistant to many antifungal drugs.
Fungi of the genus Candida under a microscope –
We have already said that the main reason for the appearance of thrush in the mouth is a weakened immune system. For example, this is typical for very young or, on the contrary, very old age. This is typical for patients who take systemic antibiotics and corticosteroid drugs. This is also typical for patients with immunodeficiency conditions - patients with diabetes mellitus, blood diseases (neutropenia, anemia), intestinal dysbiosis, as well as for patients with HIV/AIDS (in the latter, oral candidiasis is diagnosed in 90% of cases). At risk are patients with oncology, including those who have undergone chemotherapy and radiation therapy), as well as women taking oral contraceptives.
Thrush in the mouth of a baby (newborn) is most often associated with the presence of undiagnosed vaginal candidiasis in a woman, which, according to statistics, is present in at least 25-30% of pregnant women. And most often, infection of a newborn occurs precisely during its passage through the birth canal. Thrush in the mouth of children can also be associated with breastfeeding if the woman’s nipples are colonized by fungi of the genus Candida. Infection can occur even simply because you tasted your child's food with his spoon or kissed your child on the lips.
Learn more about some of the causes of thrush –
- After taking antibiotics, the oral cavity normally contains many types of microorganisms that not only coexist, but also inhibit each other’s growth. Taking broad-spectrum antibiotics eliminates some types of bacteria in the oral cavity, which disrupts the balanced composition of the microflora. The disappearance or reduction of certain types of bacteria can lead to the growth of Candida fungi.
- While taking corticosteroids - in patients with diabetes, the use of inhaled corticosteroids can cause oral thrush.
According to statistics, thrush occurs in approximately 5-10% of adults and 1% of children using inhaled corticosteroids. In cases where the cause of thrush is inhaled steroids, candidal lesions usually have the appearance of erythema (redness) rather than snow flakes. Candidiasis lesions appear precisely in those areas of the mucous membrane with which the steroid came into contact (as a rule, this is the back of the tongue, the palate). For this reason, patients taking such medications are advised to rinse their mouth with water after each use of corticosteroids.
- Diet – Research shows that a diet high in carbohydrates also predisposes to oral candidiasis, and therefore it is very important to avoid sweets, including sugar-sweetened drinks, in these patients.
Research shows that the growth of Candida and its adhesion to the mucosa are significantly enhanced in the presence of sugars (glucose, galactose, sucrose). It should also be taken into account that malnutrition can lead to a lack of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid in the body, which is also a predisposing factor to oral candidiasis.
- Taking oral contraceptives - systematic use of contraceptives (containing estrogens, progestin) leads to an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, saliva, and vaginal secretions. The consequence of this is an increase in both the frequency of Candida carriage and the incidence of candidiasis of the oral mucosa, vagina, etc.
- Smoking and other factors – Other factors may include smoking, endocrine disorders (such as diabetes), and the presence of certain diseases of the oral mucosa such as lichen planus and leukoplakia. Often oral candidiasis occurs in patients with a folded tongue or after tongue piercing.
- In patients with removable dentures – most often in patients with removable dentures, candidiasis occurs due to insufficient hygiene of the denture.
In this case, the prosthesis is covered with a biofilm containing a large number of fungi of the genus Candida. At the same time, when chewing, a removable denture always rubs against the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed, reducing its barrier properties (this facilitates the penetration of fungal microflora deep into the mucous membrane). For this reason, denture disinfection is a very important part of the prevention and treatment of oral candidiasis in people with removable dentures. A predisposing factor may be if the patient does not remove his prosthesis while sleeping. In this case, the mucous membrane is constantly deprived of oxygen and washed with saliva, which creates the preconditions for the proliferation of bacteria and fungi. Another reason may be that the prosthesis does not fit well with the tissues of the prosthetic bed (for example, because its service life has expired), and therefore it injures the mucous membrane. Such microtraumas to the mucosa also contribute to the onset of the development of oral candidiasis.
- Chronic dry mouth - a decrease in the amount of saliva and the content of various enzymes and antibodies in it is an important predisposing factor in the development of oral candidiasis. Dentists call constant dryness in the mouth the term “xerostomia.” Its treatment is a big problem in dentistry.
- Poor oral hygiene – untreated carious teeth and irregular tooth brushing increase the risk of developing candidiasis. Infection in carious defects, soft microbial plaque, hard dental deposits worsen the local immunity of the oral mucosa. Because of this, Candida fungi begin to actively multiply and can penetrate deep into the oral mucosa.
- Oral candidiasis in an infant - at a very young age, the immune system has not yet fully developed. Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis occurs in approximately 5% of newborns. Candida species are acquired from the mother's vaginal canal during childbirth. At an early age, the immune system has not yet fully developed and therefore infants do not have an individual immune response to Candida fungi (infant antibodies to fungi are usually supplied in the mother's breast milk).
Why candidiasis does not develop in people with good immunity:
Patients with a well or satisfactorily functioning immune system almost never get oral thrush (even if Candida fungi are present on the oral mucosa). Prevention of candidiasis is normally ensured by the functions of the innate immune response, and above all, by the effectiveness of the phagocytosis process (24stoma.ru). Let us recall that phagocytosis is the process of absorption and digestion of infectious agents by cells of the immune system - primarily professional phagocytes (macrophages, neutrophils).
The development of candidiasis will also be facilitated by low opsonizing activity of blood cells (opsonization is the process of adsorption of antibodies and complement factors on the surface of infectious agents, which allows for increased phagocytosis). The threat of developing a fungal infection is increased by the functional insufficiency of the T- and B-cell immunity, low levels of immune response mediators (γ-interferon, interleukin-1α, tumor necrosis factor α). A consultation with an immunologist + a general blood test with an extended leukocyte formula and an immunogram will help identify defects in the immune system.
Diet during treatment
When a patient is diagnosed with white plaque in the oral cavity, he is required to follow a dietary diet throughout the treatment.
It is advisable to exclude sweet, fatty, sour, smoked and spicy foods. The diet, in the presence of a disease, involves a ban:
- chocolate products and other products with high sugar content;
- food containing yeast;
- seasonings;
- smoked meats;
- fatty fish and meat;
- alcoholic drinks;
- highly carbonated water.
Following a healthy diet helps reduce unpleasant symptoms.
How does the disease manifest itself?
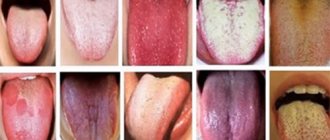
Candidiasis has several varieties, which differ from each other in course and etiology. But they have one common feature - a creamy-white plaque in the mouth.
Loose and dense spots are localized on the tonsils, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks.
An easy way to identify candida at home:
Types of candidiasis and their symptoms
| Form of the disease | Symptoms |
| Acute pseudomembranous |
|
| Acute atrophic |
|
| Chronic hyperplastic |
|
| Chronic atrophic |
|
All types of candidal thrush in adults are accompanied by the appearance of a metallic taste, sometimes the temperature may rise or intoxication of the body may begin. The patient complains of poor health and fatigue.
Attention! Chronic candidiasis worsens with any infectious diseases or decreased immunity. It can affect not only the oral cavity, but also the esophagus.
Possible complications
The disease can become chronic, go inside the body and provoke unpleasant consequences:
- respiratory diseases;
- dehydration;
- disorder in the functioning of the digestive tract, dysbacteriosis;
- the formation of sepsis due to infection in cracks and erosion.
To prevent the occurrence of adverse consequences, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis in a timely manner and implement appropriate treatment.
Quick treatment for oral thrush in children and adults:
Preventive measures
Prevention is aimed at improving the condition of the oral microflora.
It assumes:
- Compliance with oral hygiene rules.
- A balanced diet high in protein and low in foods containing glucose.
- Getting rid of bad habits (smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages).
- Timely diagnosis by the attending physician for preventive purposes.
- Avoid the use of various medications without prior consultation with a specialist.
- If the patient has dentures, regular treatment in a special solution will be a preventive measure.
Compliance with these instructions helps prevent the occurrence of unfavorable symptoms.
If white plaque appears in the mouth, you should seek help from a doctor. This will allow you to eliminate the disease as soon as possible and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Diet for oral thrush
For a speedy recovery, it is very important to eat right. The patient should avoid foods that contain yeast, spices and spicy foods .
It is not recommended to drink carbonated and alcoholic drinks. Until the white coating on the oral mucosa completely disappears, it is better to give preference to juices, herbal tea, cereals, nuts, weak meat broths and dairy products.
Following a strict diet as such is not a treatment. With the right therapy, it will help you recover quickly.
Vitamins and minerals
Drugs in this group help maintain immunity and improve the patient’s condition. For this purpose, Ascorbic acid is prescribed. Pyridoxine and Thiamine. When taking antibiotics, they restore the intestinal microflora.
Ascorbic acid
Pyridoxine
Thiamine