Inflammatory gum disease in adults and children is called gingivitis. It is most often observed in children a few months from birth to 13 years of age, which is explained by the characteristics of the child’s body and poor oral hygiene.
According to statistics, in a child from 2 to 4 years old, gum inflammation occurs in 2% of cases, and by the age of 13, the proportion of this disease in children reaches 80%. Gingivitis cured in time does not become chronic, but if left untreated it can cause the development of periodontitis.
Causes of gingivitis in children
There are many causes for childhood gingivitis. The gums become inflamed due to the functional immaturity of their tissues. In babies under one year of age, the cause of the disease is often teething, when the gums become red and sore. Sometimes inflammation is caused by an allergic reaction to food.
In adolescents, the disease may manifest itself due to the eruption of a permanent tooth. When soreness during brushing does not allow this procedure to be performed efficiently, microbes multiply and gum inflammation develops.
The most common factors that provoke the development of gingivitis in older children are:
Action of microbes
In 90% of cases, the disease appears in a child due to insufficient oral hygiene, as a result of which microorganisms multiply intensively, plaque and tartar form, and stomatitis develops.
Mechanical injury
The integrity of the mucous cavity can be compromised by teething, cuts, scratches, burns, biting, improper brushing of teeth, and eating solid foods.
Foci of infection in the oral cavity
If children have carious teeth, there is a chance that they will develop infectious gingivitis, which affects the gums. Therefore, teeth that require treatment must be treated as soon as possible.
Excessive loads on the dental system
Other causes of gum damage in children may include:
- presence of malocclusion;
- poor nutrition with a lack of vegetables and fruits;
- uneven load on the dental system due to bad habits;
- defects of the oral cavity (short frenulum of the tongue, lips);
- the presence of caries, various infections;
- thermal burn from hot food;
- wearing braces.
What does thrush look like in a child?
Any part of the oropharynx can be affected: tongue, lips, corners of the mouth, gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate, pharynx, tonsils. White grains (spot coating) appear, reminiscent of curdled milk, or a film (solid coating) of a cheesy appearance. These elements are easily removed by scraping with a spatula, revealing a bright red base, sometimes with a bleeding surface. As a rule, the course of the infection is painless and has only local manifestations. General health is not affected.
Symptoms
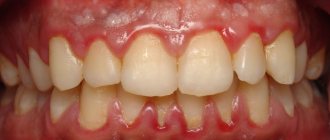
Gingivitis has a main symptom by which it is easily identified - inflammation affecting the child’s gums. The process begins with a slight redness that quickly gains strength. This signal often goes unnoticed by parents, and children go to the dentist with an active inflammatory process, bright red swollen gums, burning, and pain. These signs indicate that the disease has entered an acute phase.
Children suffer most from the catarrhal form of this disease, which can be chronic or acute. In the first case, the symptoms are not pronounced, pain occurs only when brushing, there is slight swelling, redness, and cyanosis of the gums.
A sign of an acute form of the disease is intoxication of the child’s body. It manifests itself as headache, nausea, lethargy, and fever.
The most complex type of disease, ulcerative gingivitis, manifests itself as follows:
- the inflammatory process progresses;
- their structure changes;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- lymph nodes in the neck enlarge;
- saliva is produced profusely;
- the skin turns pale.
If these signs are left unattended, an ulcerative-necrotic form of the disease may occur, when necrotic areas with a gray-green coating and a putrid odor appear on the gums, saliva becomes viscous, body temperature rises and the general condition significantly worsens.. All this indicates severe intoxication in organism.
During puberty in a teenager or if he has problems with hormones, hypertrophic gingivitis occurs. It occurs due to improper orthodontic treatment of dental anomalies. The inflammatory process is accompanied by increased growth of gingival tissue, which leads to partial closure of dental crowns. This form of the disease is usually localized. One or two gums are affected, sometimes the affected area expands. The most common location is the lower anterior incisors and canines.
Atrophic gingivitis does not have a pronounced inflammatory process and occurs without pain, although over time it can be complicated by periodontal disease.
Baby dental care
The appearance of your baby's first teeth means it's time to use a toothbrush and toothpaste. Brush your baby's teeth twice a day using a soft-bristled baby toothbrush and a small amount of baby toothpaste. You will need a special brush with a small cleaning head designed for teething babies.
When you see that two or three teeth are already located next to each other, start using dental floss regularly: it helps remove plaque and food debris from between the teeth and from under the gums.
Early childhood caries
An infant's oral hygiene is extremely important because, just like adults, they can develop tooth decay. In the early stages, carious lesions appear as chalky stains on the teeth. As they increase in size, they become black or brown. An unpleasant odor from the baby’s mouth may also be a sign of the formation of a carious cavity.
Although baby teeth will eventually be replaced by permanent teeth, baby tooth decay still needs to be treated. As experts explain, baby teeth contribute to the development of chewing and speech skills. They also create space for future permanent teeth, so if a child loses baby teeth too early due to tooth decay, the permanent teeth may begin to grow slanted or crowded.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on the results of studying the medical history and life of the child in combination with a dental examination. The patient’s complaints, the presence of somatic diseases, and whether he is taking medications that may cause the development of gingivitis are clarified.
Then the doctor conducts an external examination, paying attention to maxillofacial anomalies, the condition of the teeth and gums, and makes a diagnosis. The dentist does not require the help of other specialists, since the disease clearly manifests itself externally and does not require instrumental examination.
Types of plaque
- White.
By the end of the day, all children have a small amount of harmless white residue. Abundant formation indicates vitamin deficiency, reduced immunity or insufficient hygiene. This type of plaque can be removed from a child’s teeth if you brush your teeth thoroughly every day. The presence of hard fruits and vegetables in the diet, such as apples and carrots, promotes mechanical cleaning. If no action is taken, the layer will harden, mineralize and turn into tartar.
- Yellow.
Indicates insufficient hygiene and poor nutrition. In children under two years of age, it can occur, for example, due to the consumption of sweet liquids from a bottle. It may also indicate the initial stage of caries. By choosing the right toothpaste and brush, as well as brushing your teeth more thoroughly, this problem can be solved.
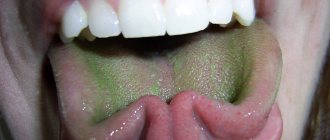
- From light gray to green.
Gray - possible with abundant release of chlorophyll, sometimes acquires a greenish tint. Green - provoked by a fungus - chromogenic bacteria. Damages the pellicle, the natural protective film on the teeth. Only a dentist can help remove such plaque.
- Brown.
Indicates a fungal infection of the oral cavity and a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract. The result is darkening of the enamel. Iron supplements can also stain teeth brown. How to remove such plaque from a child’s teeth? Sometimes it goes away on its own after you stop taking iron-containing foods or medications. If the deposits have hardened, you will need professional teeth cleaning - ultrasound or chemical whitening. It is also necessary to adjust the child’s nutrition.
- Black.
Black plaque is the first harbinger of caries. Especially if it has a point character. In such cases, it is better not to postpone a visit to the dentist.
Treatment
Treatment for childhood gingivitis is practically no different from how adults are treated. Only medications used for them are softer and more gentle. Treatment begins with professional cleaning of hard deposits and plaque of tooth enamel - mechanical or ultrasonic.
If caries is detected during the examination, then therapeutic treatment is carried out. Gingivitis is then treated with medications with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. Measures are taken to eliminate detected pathologies (bite, frenulum, etc. are corrected).
Ointments and gels are considered effective for children under 4 years of age. For example, Cholisal ointment has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, which makes it possible to prescribe it to alleviate the patient’s condition, especially when baby or permanent teeth are cutting. Ointments and gels are applied directly to the inflamed area.
Antibiotics in tablets or in the form of injections are prescribed to children in difficult cases (the presence of infections of bacterial origin in the body). At elevated temperatures, rinses, drinking plenty of fluids, antioxidants, antipyretic drugs for children, and taking vitamins are prescribed.
Prevention measures should include regular visits to the pediatric dentist, training in oral care rules, and parental monitoring of the development of hygiene skills.
Prevention
To prevent oral diseases, regular examinations by a doctor are necessary.
It is important to understand that the fragile body of a newborn child is especially vulnerable. Therefore, you need to make enough efforts to prevent the occurrence of diseases, because then you will not have to deal with their treatment.
Oral health care includes, first of all, regular examinations of the baby's mouth for the presence of any formations, be it stains or plaque. If after eating a white coating appears on the child’s gums, then you need to try to gently clean it off with special means.
If you suspect the development of any disease, you should show the child to a doctor who will conduct an examination and establish an accurate diagnosis. After which he will be able to select the appropriate and most effective treatment.
Prevention of white gums in a newborn
To prevent the occurrence of pathological white spots on a child’s gums, it is necessary to carefully monitor the hygienic condition of the oral cavity, as well as maintain immunity and health at a high level.
To do this you should:
- organize a balanced and rational diet that will saturate the baby’s body with minerals and vitamins;
- Regularly wash the mother’s hands when preparing food and feeding the baby;
- avoid contact with carriers of infectious diseases;
- do not allow the baby to put into his mouth and chew contaminated and sharp objects that can damage the mucous membrane of the gums;
- keep toys and personal belongings clean;
- The baby should have an individual spoon, cup and plate.
If you find white areas on the gums of a small child, there is no need to panic and ask friends or relatives for advice. Most likely, your baby has nothing terrible or serious, but it is still better to seek advice from a pediatrician or dentist. If an illness is detected, the baby will be promptly prescribed treatment.
Author: Violeta Kudryavtseva, dentist, especially for Karies.pro
What to do for preventive purposes
- The diet should be balanced with sufficient amounts of calcium, fluorine, and phosphorus.
- It is necessary to include raw hard fruits and vegetables in the diet, and reduce the amount of sugar-containing foods.
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with plain water, and in the morning and evening, thoroughly brush your teeth.
- Reduce the number of daytime snacks and, if possible, eliminate night meals.
- Visiting your dentist at least twice a year will help you identify causes that contribute to plaque formation, such as a bad bite, chewing on one side, or damage to your gums or enamel.
- It is important to choose the right toothbrush and change it every three months. Choosing age-appropriate toothpaste is also important.
- It is recommended to eliminate such bad parental habits as tasting the child’s food with his own spoon or licking the baby’s pacifier. If an adult's saliva gets into a child's mouth, it can worsen the condition of his teeth, since the composition of saliva in children and adults is different.
Examine your child's mouth frequently to spot problems early. Do not try to remove plaque yourself, as you can cause even more harm, because the child’s teeth are sensitive and the enamel is very thin. Only a doctor can answer the question of how to remove plaque from a child’s teeth. Having correctly diagnosed, he will prescribe adequate treatment.
Vulnerability zone
Let's look at gum disease in children. Your child's healthy gums are delicate and very vulnerable tissue of a pale pink color. Unlike adult gums, they can be easily injured, but they are capable of rapid regeneration. Another peculiarity of children's gums is that they often reflect the general condition of the body, being a litmus test for systemic diseases.
The most common diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues: gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs as a result of the adverse effects of local and general factors, occurring in 80% of children; gum atrophy, which develops in more than half of the child population; various types of childhood stomatitis, which most often occurs in infants and preschoolers; Periodontitis is a disease in which all periodontal tissues become inflamed and affects up to 5% of young patients. Periodontal disease (dystrophic changes in periodontal tissue) and other pathologies practically do not occur in childhood.
Diarrhea in a baby - parental behavior tactics
12.04.2021
Diarrhea in a baby can drive parents crazy - bowel movements are disrupted, the child is worried, sleeps poorly or a lot, does not eat, cries. This may increase the temperature. When the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to understand the cause, take the first measures and follow the basic recommendations.
Causes of diarrhea
Diarrhea in infants refers to a change in stool consistency. It becomes watery, with mucus and undigested food particles, the number of bowel .
Causes of this condition:
- viral or bacterial intestinal infections;
- improper nutrition of the baby or mother if she is breastfeeding ;
- food intolerance to lactose, gluten and other elements;
- surgical pathologies;
- changing the formula or abrupt transition to artificial feeding with breastfeeding;
- taking certain medications, such as antibiotics.
Normally, diarrhea is not observed teething . If the condition occurs, most likely due to a weakened immune system , a bacterial or viral intestinal infection has occurred. The reason for this is that to facilitate teething , babies often put toys and objects in their mouths that may not be processed or washed.
Doctors call dysbacteriosis a common cause of diarrhea . Many experts refute this diagnosis.
What should mom do?
diarrhea occurs in a child of the first year of life, you should consult a doctor . Assigned groups for this symptom:
- sorbents;
- antibacterial drugs;
- medications to normalize intestinal ;
- antipyretics for high temperatures;
- antiviral agents.
Sorbents bind allergens , toxins, bacteria and their waste products, and other factors that provoke diarrhea and remove them from the child’s body. As a result, nausea , vomiting, and diarrhea .
If the cause is determined to be a bacterial intestinal infection and the causative agent is identified, antibacterial drugs may be recommended by the pediatrician . It is unacceptable to take them on your own.
For a quick recovery and elimination of imbalances in the intestinal , probiotics and prebiotics are indicated. These drugs are taken in a course and after the symptoms disappear for 10 days. When purchasing medications, you must pay attention to the storage conditions.
If diarrhea , antiviral drugs in the form of suppositories can be used.
Recommendations
A dangerous consequence of diarrhea in infants is dehydration. To prevent it, you need to give your baby water more often. If this is not possible with a cup or bottle, you can use a teaspoon or a syringe without a needle. If you have severe symptoms of dehydration, call an ambulance.
If your baby is breastfed, put him to your breast . This helps satiate the baby, replenish lost fluids and calm the baby. This is especially important in cases where it is not possible to drink with clean water.
Another recommendation concerns the child's nutrition. vegetables, dairy products, fruits and juices should be removed during diarrhea
For several days, you need to observe the baby's skin - dryness, the appearance of a rash, pallor and feces - the presence of streaks of blood , foam, mucus, color changes.
When do you need to see a doctor?
a doctor diarrhea occurs in a child under one year of age . Immediate attention is required in cases where there are streaks of blood and mucus in the stool, the baby has a high fever and is vomiting.
Self-medication of such a symptom in children of the first life is contraindicated. There is a high risk of dehydration and complications.
Signs of dehydration:
- dry skin, mucous membranes, tongue;
- retraction of the fontanel;
- dry mouth , crying without tears;
- weight loss due to decreased fluid in stool and vomit;
- decreased urination , urine becomes darker;
- capriciousness, lethargy of the child.
diarrhea in an infant requires qualified medical care - the pediatrician, together with the mother, will determine the possible cause, prescribe treatment and select the dosage of medications. During therapy, it is extremely important to give more liquid or put the baby to the breast , monitor the amount of urine , feces, and skin excreted.
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic
How to prevent gum disease
For the reasons listed above, we recommend that you:
- Closely monitor how thoroughly and correctly your child brushes his teeth;
- Use a special fingertip to massage the baby’s gums during teething;
- Explain to your child how important it is to actively chew food on both sides;
- Contribute to timely correction of bite and solution of other problems;
- Monitor the temperature of your baby's food and drink and ensure that he does not have the opportunity to injure the delicate gum tissue.
Modern pediatric dentistry believes that minimizing the unpleasant consequences of developing a serious disease by strengthening preventive measures is the easiest way to protect your child from diseases of the gums and other periodontal tissues.