The long list of painful deviations from the normal state of the periodontium also includes those pathologies that are characterized by tumor-like formations.
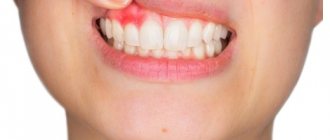
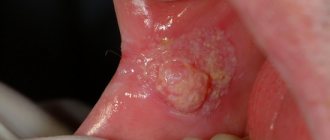
One of these diseases is epulis on the gums, which is often found in people of all age groups.
Epulis is a soft tissue tumor that appears near premolars (small molars). In color, the formation is identical to the shade of the gum tissue, but may differ in slight cyanosis.
Signs and features
Fungus epulis comes in different sizes. At advanced stages of development, the formation reaches up to 30 mm in diameter, and becomes visible when laughing or talking.
Epulis looks like gum tissue that is growing. The mushroom-shaped formation has a cap on the outside of the gum and a stalk for attachment to the tooth. Only a doctor can examine these features in detail.
When palpating the epulis, the dentist can observe both a hard structure of the formation and one that is too soft.
If the disease is formed as a result of trauma, ulcerative lesions appear on the surface of the formation.
Definition
Epulis refers to benign formations of gum tissue. The pathology is characterized by rapid growth of the granulation type, which, as the disease develops, can cover the entire length of the crowns.
Epulis is often confused with hypertrophied gingivitis and gum cancer. Unlike gingivitis, epulis is not accompanied by a change in the structure and color of the inflamed gum tissue.
In addition, gingivitis is characterized by bleeding and periodontal pain, which cannot be said about epulis. During differential diagnosis, symptoms are detected that distinguish this pathology from cancer.
In case of gum cancer, whitish inclusions in the form of precisely defined foci are located on the tumor. Cancer is also characterized by multiple accumulations of blood vessels on the surface and its ulceration.
Kinds
Depending on the clinical picture, the disease is divided into several types.
Fibrous
Fibrous epulis has a wide base and hard consistency. The color of the formation is almost identical to the shade of the gum tissue.
No bleeding is observed. The tumor grows in size slowly and has a round shape. The surface can be either rough and bumpy or even and smooth.
The formation forms on the vestibular surface of the gum near the premolars.
Methods for carrying out the procedure for cleaning tooth canals and a video with a detailed description of the stages. Click here if you are interested in reviews of the Amazing White teeth whitening technique.
At this address https://dr-zubov.ru/krasota-i-uxod/sredstva/opolaskivateli/glister-amvej-effektivnoe-sredstvo.html we invite you to learn about the action and composition of Glister Amway.
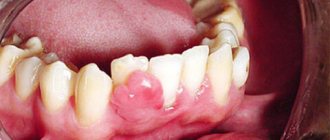
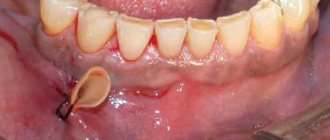
giant cell
The formation forms on the alveolar ridge. It usually affects older people, mostly women.
The tumor grows for a long time and reaches such volumes that the symmetry of the face loses its correct shape. On palpation, bleeding is observed, accompanied by pain.
Dental units near the affected area become wobbly. The color of the tumor is bluish with a brownish tint. The shape is oval or round with a bumpy surface. The formation has a dense and elastic consistency.
Angiomatous
This type of epulis contains many capillaries in its structure. The disease most often occurs in children and adolescents. The tumor grows on the neck of the bony organ of the oral cavity.
The tumor appears bright red with a rough surface and a wide base. When pressed, severe bleeding occurs. The tumor quickly increases in size and is dense and hard. After removal, relapse often occurs.
Acanthomatous
This type is quite rare in dental practice and is called a benign organ-specific tumor localized in the maxillofacial area of soft tissue.
The structure of the tumor tissue is practically no different from the enamel tissue of the isolated formation from which the tooth (tooth germ) is formed in embryogenesis. With progressive pathology, there is no pain. After removal, recurrent growth is possible.
Fibrous
Fibrous epulis is the safest of all existing ones. When it appears, the damaged gum is practically indistinguishable from the rest of the mucous membrane. The tumor itself is quite dense, most often localized externally, that is, vestibular, noticeable in the smile area. It looks like a small ball or bump. This neoplasm grows extremely slowly, and the capillaries on it do not bleed.
Fibrous epulis
Clinical forms
The disease has a malignant and benign clinical form. Depending on whether a particular case belongs to them, epulis will have characteristic symptoms characteristic of a neoplasm.
Benign
Signs of a benign form of the supragingival (epulis) include:
- slow growth;
- diameter up to 20 mm;
- proceeds painlessly.
Malignant
The malignant form of the disease is characterized by:
- swelling of the gums in the damaged area;
- intensive growth;
- painful sensations;
- destruction of the root canals of dental units located in the affected area;
- loosening of adjacent teeth with subsequent displacement;
- bleeding gums during hygiene procedures using a brush and when chewing food.
Composition and action of the Mexidol line of toothpastes, their advantages and disadvantages. Come here to see photos of the stages of dental implantation.
Follow the link https://dr-zubov.ru/lechenie/zuby/plomby/posle-bolit-kto-vinovat-i-chto-delat.html to find out what you can and cannot do if your tooth hurts badly after filling.
Causes
Epulis occurs due to hormonal imbalance in the body. However, more often the disease develops due to systematic trauma to the gums. .
They are provoked in the following cases:
- a dental filling protrudes and hangs over the gum;
- in the oral cavity there is a decayed tooth with sharp broken edges;
- mineralized deposits on the surface of the teeth have become neglected;
- teeth closure occurs in a deviation from the norm;
- the denture was made with a defect or was worn for a long time without correction;
- bruise of soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- tissue damage caused by thermal factors.
It is important to note that fibrous and angiomatous supragingival tissue is a consequence of the reaction of the gum tissue to regular irritation of the mucous membrane during a chronic inflammatory process.
Symptoms
You can distinguish epulis from other pathologies of periodontal tissue by certain symptoms:
- formation of a granulation tissue node from 1 cm, growing to 5 cm or more;
- the surface of the node has a red, brown or bluish tint ;
- the tumor is shaped like a mushroom : a wide platform of inflamed tissue is located on a narrow stalk;
- due to its mushroom-shaped shape, the node is mobile , as a result of which it is constantly injured by the teeth;
- tumor structure – soft, elastic, in some cases dense ;
- the teeth in the affected area are very mobile ;
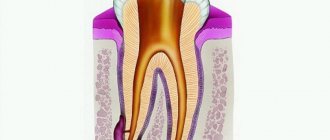
- X-ray examination reveals bone loss at the site of attachment of the node.
Diagnostics
To correctly diagnose the disease, the dentist examines the affected area visually and using instruments. To identify the cause of the disease, a histological method of studying biopsy material is used.
Also, a mandatory diagnostic method includes the study of the internal structure of a pathological object, which is projected using X-rays onto a special film. This method will allow you to determine the degree of damage to bone tissue by inflammation.
In addition, the patient is prescribed blood donation for the following tests:
- general;
- expanded;
- for polymerase chain reaction.
If, according to the general analysis, the level of leukocytes is too high, and hemoglobin levels have fallen, the doctor will order a repeat test to identify malignant cells.
Consequences
In the absence of the necessary treatment, the growth process will accelerate and involve surrounding healthy tissue . This can lead to inflammation of the entire periodontium, loosening of the crowns and their complete loss.
In addition, the pathology can spread to bone tissue, leading to disruption of its structure and inflammation. To prevent this from happening, you need to see a dentist as soon as possible.
Self-control of the disease at home is impossible.
Treatment
In modern medicine, epulis is treated using laser techniques, surgical removal, medication and folk remedies.
Surgical
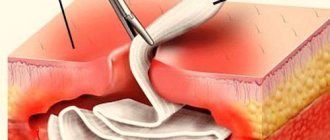
To remove epulis on the gum, the doctor makes a small incision and completely cuts out the formation along with the periosteum, after which the edges of the wound are closed. The wound area is treated with iodoform paste and covered with a sterile piece of gauze.
Adjacent teeth are removed in rare cases. Mainly with increased instability or significant exposure of the root. If the bone tissue is damaged or recurrent tumor growth occurs, the dentist performs partial circumcision of the affected area.
Such resection affects the bony organs and the part of the gum covering the alveolar process. This treatment gives a positive result. If the operation is performed incorrectly, the risk of relapse increases.
If the neoplasm is large, after removal I tighten the wound with sutures to speed up the restoration of tissue integrity.
Removal is performed using anesthesia. During the operation, it is very important to perform all actions efficiently and carefully, which guarantees rapid healing of the wound area and the absence of complications.
For information on excision of epulis, see the video.
Using laser
When removing epulis, doctors often resort to using a laser as a scalpel. During this operation, infiltration anesthesia is used, which blocks all nerve impulses in the place where the anesthetic was injected.
To put it another way, this method of pain relief is called “freezing” and is most often used in dental practice.
Removal of the pathological object is performed with a calibrated laser, followed by removal of the tumor using tweezers.
The use of a laser guarantees simultaneous disinfection and cauterization of the affected area. This allows you to significantly shorten the recovery period and reduce the risk of possible complications.
Medication
The drug treatment method for epulis is based on agents that can stop the growth of tumor cells and stimulate the properties of tissues for rapid recovery. This list may include the following drugs:
- Traumeel S is a multicomponent homeopathic medicine. Used for inflammatory diseases of organs and tissues. Promotes recovery from post-traumatic conditions. The drug prevents the formation of granulation tissues. The drug is taken 1 tablet 3 times a day before meals.
- Dimexide is a medicinal product for external use that has analgesic, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties.
The product can improve metabolic processes in the area of inflammation. Penetrating into the membrane of pathological cells, it increases biological membranes. Under the influence of the drug, the tumor stops growing. A sterile napkin is moistened in a solution of dimexide and applied to the affected area for 20 minutes. - Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic. Actively fights bacteria and viruses that can cause the formation of tumors. For epulis, the drug is prescribed in the form of a spray. To combat the disease, chlorhexidine is used to irrigate the mouth 3-5 times a day.
- Polycresulene is an antiseptic with bactericidal, fungicidal, antiprotozoal and hemostatic effects.
In dentistry it is used for all forms of inflammation of the oral cavity and in the presence of difficult-to-heal wounds. Using the drug, you can achieve the effect of tissue cauterization. For treatment, a sterile swab is moistened in the product and applied to the pathological area for 5 minutes. Manipulations are carried out no more than 3 times a week. - Resorcinol is an external antiseptic used in the treatment of soft tissues. For epulis on the gums, the drug is prescribed in the form of an ointment, which is used to treat the affected area. The components of resorcinol cauterize pathogenic tissue and have an enhanced effect, promoting its decay.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes in the treatment of epulis are used as an auxiliary therapy that promotes the rapid restoration of damaged tissues of the oral cavity. It is impossible to completely cope with the disease with herbal decoctions and infusions.
The recovery period will be shortened several times if you perform therapeutic rinses. Dentists recommend using several recipes.
Calendula decoction
Ingredients:
- 15 gr. dried calendula flowers;
- 250 ml boiling water.
Preparation: Grind dry marigolds in your palms and pour boiling water in a glass container. Cover with a lid, wrap with a thick cloth and let sit for 1 hour.
Application: rinse the mouth with a concentrated cooled infusion 4-5 times a day.
Efficacy: antiseptic, healing, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect.
Decoction of sage, eucalyptus and chamomile
Required:
- 10 gr. chamomile;
- 10 gr. dry sage;
- 10 gr. eucalyptus;
- 250 ml boiling water.
Preparation: combine dry herbs and pour boiling water over them. The decoction is infused for a day.
Application: the oral cavity is rinsed with a decoction in the morning and evening, after hygiene procedures.
Efficacy: bactericidal, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, healing effect.
Baking soda solution
Ingredients:
- 1 tbsp. spoon of baking soda;
- 0.5 liters of warm boiled water.
Preparation: Stir baking soda in warm water until completely dissolved.
Application: perform intensive rinsing with the prepared solution up to 8 times a day.
Efficiency: inflammatory processes and formation of pus are prevented.
Iodized table salt solution
Required:
- 1 tbsp. spoon of iodized salt;
- 0.5 liters of warm water.
Preparation: the substance is dissolved in water until the salt crystals completely disappear.
Application: take a small amount of solution into the oral cavity and rinse vigorously, focusing on the affected area. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times a day.
Efficiency: relieves swelling, prevents the spread of bacteria.
Pathology during pregnancy
A woman's pregnancy is accompanied by a significant restructuring of the entire body. This period is characterized by hormonal imbalances, which is a natural process. This is why the expectant mother may develop a disease such as epulis on the gums.
The root cause of development is often gum trauma. However, in such a situation, the growth of the tumor and the development of its internal structure occurs rapidly.
For this reason, frequent relapses occur. Moreover, during gestation, neoplasms form intensively.
How to remove epulis from gums
The only option to completely get rid of an unpleasant tumor is to remove it surgically. In mild cases, this is performed by a dentist under local anesthesia. If bone is involved or there is a risk of malignant cells being detected, this major operation should be performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. In the case of the giant cell form, all tissues that came into contact with the neoplasm are additionally removed.
You should not start epulis, the treatment of which at the very initial stage can be carried out quickly and easily for a person. The dentist will gently remove the small bump using a laser or liquid nitrogen. Such interventions are very gentle and practically do not damage the surrounding mucosa. After them, the gums quickly recover and heal. To speed up the process, apply compresses with Solcoseryl or Levomekol ointment to the wound. The latter contains a small amount of antibiotic, so it protects the sutures from infection.
During the entire rehabilitation period, the patient is recommended to treat the operated areas with hydrogen peroxide, and then rinse his mouth with antiseptics such as Chlorhexidine, Miramistin or Chlorophyllipt. In severe situations with suppuration, a course of antibiotics cannot be avoided:
- Biseptol;
- Amoxicillin;
- Azithromycin.
Unfortunately, epulis on the gums may appear again after some time. As a preventive measure, dentists recommend avoiding any injuries and protecting the mucous membrane from hypothermia and burns. It is imperative to visit a specialist every 6-8 months in order to notice the formation of a lump in time and remove it without consequences.
When a lump appears on the gum, most people mistake it for an abscess. However, such formations are not always infectious in nature. One of the types of gum tumors is the so-called epulis, which is usually painless and identical in color to the gum tissue.
Problem in children
Pediatric dentists note a pattern in the appearance of epulis in children during teething. In this situation, the appearance of a tumor can be associated with trauma to the gums and mucous membrane. The angiomatous type of the disease is more common, but other varieties are rarely diagnosed.
When the first signs appear, parents should immediately contact a qualified doctor. This will help prevent further growth of the tumor and the spread of pathogenic cells to healthy tissue. In females, the disease occurs more often.
The appearance of epulis during puberty is a common occurrence. Failures in girls occur due to improper use of hormonal drugs.
In children, a transition of the disease from one form to another is observed. Usually, in the first stages, the development of the disease is characterized by a granulomatous appearance, which, with rapid growth, acquires an angiomatous and subsequently fibrous form.
Relapse rates are about 15%.
Watch the video about using a dental laser to treat epulis.
Giant cell
The name is scary, isn't it? And rightly so, because giant cell granuloma is considered the most dangerous type of disease, which threatens to develop into a malignant tumor. Epulis of this type is most often found in middle-aged and elderly women. What worries patients: the rapid increase and growth of a hard and very dense neoplasm to the touch, its bluish or dark brown tint, pain when pressing and chewing, bleeding.
Giant cell form of epulis
Complications
As a rule, qualified specialists approach the treatment of the disease with special responsibility, which helps to avoid complications. In exceptional cases, a number of consequences appear:
- relapse;
- swelling of soft tissues after surgery;
- bleeding;
- empyema of soft tissue due to infection with pathogenic bacteria.
Patients are strongly advised to follow all specialist recommendations in the postoperative period.
Do not forget about careful oral hygiene, which will prevent the risk of infection at the wound site. If complications arise, it is not advisable to delay visiting the dentist.
Prevention
You need to regularly monitor the condition of your teeth and oral cavity. This will reduce the risk of epulis formation.
- visit a specialist in order to perform comprehensive health measures carried out to prevent various dental diseases.
- avoid injury to the gums and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- visit the dentist 2 times a year , which will allow you to recognize the tumor in the early stages of development and begin immediate treatment.
Reviews
Epulis in medicine is classified as a tumor neoplasm, but there is no need to be afraid of this disease. Unattractive appearance and aesthetic changes are perhaps the biggest problem during the course of the disease.
However, for many, the tumor causes a lot of inconvenience and is difficult to treat with medication. In addition to the information in this article, readers will be interested to know how the operation is performed and how long the recovery period lasts.
What medications helped reduce the tumor or get rid of it completely? Share your experience and impressions in the comments.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.