Home|Facial malformations (cleft lip and palate)|Cleft palate (cleft palate)
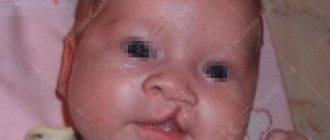
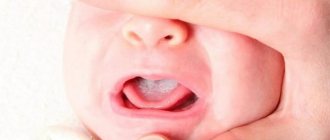
Congenital defect of the hard and soft palate (cleft palate pathology) is a common facial malformation in infants. About a hundred babies are born every day in the world with this anomaly, most of whom are boys. It manifests itself as a rupture in the middle part connecting the oral cavity with the nasal cavity. Half of the children with this defect have a cleft lip defect. With timely treatment, cracks in the palate of a child are not dangerous to the life and health of the baby. The Towards Life project allows you to receive qualified medical assistance in correcting such defects free of charge.
Causes of cleft palate formation in humans
Experts do not have a consensus on the question of why children are born with a cleft palate. The appearance of the defect is associated with the presence of one or more provoking factors:
- inferiority of the germ cells of the parents: age over 40 years, hereditary gene mutations;
- infections and chronic diseases of the mother: rubella, chicken pox, herpes, syphilis, chlamydia, etc.;
- chemical intoxication: alcohol, drugs, smoking, chemicals, etc.;
- physical impact: amniotic fluid pressure, body overheating, radiation, falls, blows to the stomach, etc.
Often the cause of cleft palate is a metabolic disorder in the early stages of pregnancy, when it is accompanied by a lack of vitamins and minerals, toxicosis, lack of oxygen, and the threat of miscarriage. Taking antibiotics, sleeping pills and sedatives, medications for thyroid diseases, tumors, and arthritis can provoke a cleft palate in newborns. Psychological factors increase the risk of developing a defect: stress, prolonged experiences, lack of rest.
Types and manifestations of anomalies
The defect in newborns is manifested by a complete cleft of the soft and hard palate, passing through, or a small crack only in the soft tissues. According to the degree of bifurcation, the defect is classified into:
- complete – with splitting of soft and hard tissues up to the incisive foramen;
- incomplete - with a cleft only in the soft palate or with partial cleft of the hard palate;
- through – one- or two-sided clefts of the hard and soft palate with the inclusion of the alveolar process;
- hidden - the gap cuts only the muscles while preserving the oral mucosa.
“Cleft palate” in newborns, in addition to a cosmetic defect, is accompanied by a number of symptoms indicating disorders of the vital functions of the body. From the moment the baby is born, disturbances in sucking and swallowing of food appear. Shallow breathing develops, leading to oxygen deficiency and a tendency to inflammation of the middle ear, which negatively affects hearing. With the active growth of the baby, disorders of the speech apparatus (pronunciation of sounds through the nose) and delayed development of all body structures are detected.
Causes and consequences of the Gothic sky in a child
According to most experts, the cause of this anomaly is a violation of the formation of the palate rudiments at the embryonic stage (including underdevelopment of the palatine plates).
Among the main reasons are:
genetic mutations;- exposure to unfavorable exogenous factors on the body of a pregnant woman;
- traumatic injuries;
- intoxication;
- Rh conflict between mother and fetus;
- endocrinopathies in a pregnant woman;
- various diseases of viral origin.
Important
One of the predisposing factors in the development of the anomaly is the child’s mouth breathing.
The arched shape of the palate causes the formation of malocclusions, which leads to incorrect pronunciation of sounds.
Symptoms include difficulty pronouncing sibilant sounds and rhoticism (trouble pronouncing the “r” sound). Speech may be burry, and the pronunciation of “r” may be guttural. Problems with sigmatism and paparasigmatism (impaired pronunciation of hissing sounds) are caused by the fact that the tongue bends, going beyond the tubercles.
Diagnosis of the defect
The intrauterine development of the fetal facial bones suggests their fusion at the 7-8th week of pregnancy. The formation of the oral and nasal cavities occurs in parallel. Disruption of these processes can become a turning point in normal development, causing abnormalities, and the cause of cleft palate in children. By 2 months, the embryo’s upper jaw is finally formed from halves growing towards each other. A delay in their fusion leads to a defect that is diagnosed in the womb.
A routine ultrasound examination reveals the defect at 14-16 weeks of pregnancy. The volume, shape of the lesion and the complexity of the disease can only be assessed after the baby is born. The diagnosis of “cleft palate” in a newborn child is clarified by examination of the pharynx and a number of additional studies. Their goal is to determine possible pathologies of skull development, breathing disorders, smell, hearing and sound production.
Gothic taste - effects
The effect of the Gothic palate on the patient is described in the previous paragraphs. In some people, the defect is diagnosed immediately after exposure because it does not cause any symptoms visible to the naked eye and the patient does not experience pain.
If left untreated, the disease causes: difficulties in eating and breastfeeding, malocclusion, articulation disorders and many others.
Vorobyova Marina
Neurologist of the highest qualification category (work experience 14 years), doctor of neurofunctional diagnostics (work experience 12 years); author of scientific publications on vertebroneurology; participant of scientific conferences on neurology and functional diagnostics of all-Russian and international significance.
About
What should parents of a child with such an anomaly do?
The main thing is not to panic at the thought, my child has a cleft palate, and not to try to terminate the pregnancy. You shouldn’t risk the mother’s health by postponing the birth of a baby because of a defect that can be successfully treated with modern surgery. Abortion is too high a price, especially if the cause of the defect is hereditary, and it may appear during the next pregnancy. Timely surgical treatment of congenital cleft palate makes this anomaly safe for the life and health of children.
It is important to seek qualified medical help from specialists in time to correct the defect and prevent the development of numerous complications, including:
- respiratory failure leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen);
- frequent infectious and colds that weaken the immune system;
- speech and hearing disorders;
- delayed growth and development of the jaw.
How and where to treat a cleft palate?
Cleft palate surgery and cosmetic facial plastic surgery can eliminate external defects and restore the functionality of the oral and nasal cavities in a newborn (questionable, the operation is performed at the age of two years).
During the surgical operation, the palatine and pharyngeal muscles are connected in the correct position, the integrity, normal shape and functioning of all structures are restored. The extent of surgical interventions and the appropriate age for this are determined by the type of anomaly and the complexity of the case. After a thorough examination of the baby by the surgeon, one of the treatment tactics for children with cleft palate is selected:
- Uranoplasty (corrective surgery) from the age of 2 years – for incomplete clefts in children with regular upper jaw dentition.
- Uranoplasty at 4-6 years of age with preoperative orthodontic therapy - with a narrowed upper jaw and clefting, including the alveolar process.
- Two-stage correction (soft tissue plastic surgery with narrowing of the pharynx and, 6-8 months later, surgery on the hard palate with the alveolar process with simultaneous bone grafting).
Underdevelopment of the soft palate. Causes. Symptoms Diagnostics. Treatment
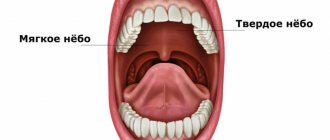
Underdevelopment of the soft palate owes its origin to a disruption in the development of the embryonic rudiments of the palatine plates, which can also lead to an anomaly in the development of the hard palate (Gothic vault of the oral cavity, underdevelopment of the posterior parts of the palatine plates).
In this case, the posterior edge of the hard palate, to which the soft palate is attached, appears reduced in the form of an angle open posteriorly.
This defect is masked by the soft palate, however, as a result of its underdevelopment, the nasopharynx remains open both during the phonation of nasal consonants and during the act of swallowing, which causes open nasal sound and the entry of liquid food into the nasopharynx. This defect also facilitates the penetration of foreign bodies from the oral cavity into the nasal part of the pharynx.
The presence of an uncompensated defect of the soft palate requires a significantly higher consumption of pulmonary air necessary for phonation, therefore such patients take frequent pauses to inhale during a conversation.
With such defects, removal of adenoids is contraindicated, since it leads to an increase in tubo-otitis and acute purulent otitis due to the more accessible entry of liquid food into the auditory tube.
Treatment of underdevelopment of the soft palate is difficult. The principle of treatment is to narrow the nasopharyngeal cavity, which in the past was achieved by injecting paraffin (vaseline) oil into the back of the pharynx.
Later, various surgical methods to narrow this space, one of which is to mobilize the medial plate of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone with a pterygoid hook located at its end and bring it down. This process is identified by palpation directly behind and medially from the last upper molar, then a straight chisel is struck at its base.
This manipulation achieves the mobilization of the muscles attached to this process, which by their own traction descend downwards and are located on the lower surface of the palatine aponeurosis, which leads to a certain narrowing of the nasopharynx. The operation is performed on both sides.
Stages of uranoplasty
Before surgery, your baby needs to learn how to feed from a spoon. Sucking after surgery for a cleft soft and hard palate in a child causes pain, impairs wound healing and scar formation. The correction is performed under general anesthesia due to the proximity of the airways and the need for complete immobility of the patient. If it is impossible to close the gap with local tissues, plastic surgery is performed with flaps taken from the cheeks or tongue. Repeated surgical interventions are possible no earlier than six months later, necessary to restore tissue and blood supply.
The operation for cleft of the hard and soft palate is carried out in several stages:
- The peeling away of plastic material on both sides of a gap to close the hole.
- Lengthening of soft tissues by cutting off the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
- Stitching the gap at the midline.
- Reducing the pharynx in the middle section by moving its lateral tissues to the middle.
- Step-by-step suturing (first on the nasal mucosa, then on the muscle tissue and oral mucosa) with treatment with an antiseptic solution.
- Attaching a plate that protects against infection.
Rehabilitation period
The duration of postoperative rehabilitation is determined by the complexity of the case and the age of the patient.
If your child was born with a cleft palate, be prepared for the fact that his treatment will not be limited to surgery. The restoration of many functions depends on the quality of rehabilitation measures. In a hospital setting, they are aimed at improving the patient’s well-being, organizing proper nutrition, preventing disorders of the upper respiratory tract, and preventing infectious diseases and complications. In the future, the baby needs:
- additional treatment by an orthodontist for the correct relationship between the sizes of the dental arches and the development of the upper jaw;
- systematic observation by an otolaryngologist to monitor communication of the oral and nasal cavities, the functioning of the respiratory and hearing organs, and the prevention of ENT diseases;
- classes with a speech therapist to establish proper breathing, sound production, articulation, and correction of speech defects;
- consultation with a defectologist to identify possible developmental delays.
Gothic palate – chamber
When the defect is more severe, a palate expansion device designed to widen the jaw must be used. Palatal suture expansion devices such as the Hass device are best suited for this purpose.
Jaw enlargement in adults requires a lot of effort, and the orthodontic appliance is sometimes insufficient for this purpose as the only treatment for a gothic palate. The orthodontist must collaborate with the surgeon because in such situations an operation is sometimes necessary - the so-called jaw distraction, which will allow the palatal bones to be properly expanded and the correct occlusal conditions between the dental arches to be obtained.
Help from the project “Towards Life”
The scope of rehabilitation activities, the number of doctors involved in the treatment, and the cost of cleft palate surgery in well-known medical centers should not diminish your determination to improve your child’s health. After consultation with specialists, you can do a significant part of the work to restore functions (breathing exercises, exercises to develop the speech apparatus, preventive measures, etc.) with your baby yourself at home. Your persistence and patience are an important component of success in treatment.
There is also an answer to the question of where surgery for congenital cleft palate is performed free of charge - in Yaroslavl. With the support of charitable organizations (Rusfond, “Beautiful Children in a Beautiful World”), we offer medical care from the best specialists without payment. To receive free surgical treatment from our maxillofacial surgeons: Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.N. Bessonova and L.A. Eremeyshvili, you need to collect the necessary documents according to the list, send them for consideration and wait for the call for treatment.
You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone: 8 on weekdays from 9.00 to 19.00 Moscow time Or through the form on the website Sign up for a free consultation