How does dental caries develop?
A tooth consists of several layers of tissue:
- enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body, up to 2 mm thick
- dentin - bone tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth and is located under the enamel
- cement is another type of bone tissue that covers the root of the tooth and helps secure it in the socket
- pulp is a soft tissue penetrated by blood vessels and nerve endings, popularly called the “nerve of the tooth.”
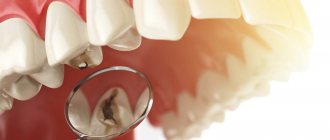
Caries is damage to hard tissues that results in the formation of cavities in the tooth.
Stages of caries
Carious spots (enamel caries or chalk spots)
Tooth enamel contains calcium, fluoride and other minerals. When these substances are not enough, demineralization of the enamel occurs, as a result of which it becomes loose, soft and thin. Where the enamel structure is damaged, carious spots form. At the stage of early caries, only a doctor can see the problem, because carious spots do not hurt, are not felt, and are not even always noticeable.
How to treat? To restore the enamel, the doctor treats the stain with a special product containing calcium and fluoride, for example, varnishes, which saturate the damaged area with the missing minerals and create a new protective layer.
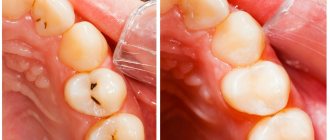
Superficial caries
At the second stage, the enamel at the site of the carious spot darkens and collapses, turning into a “gateway for infection.” The damaged surface may become rough, and sometimes patients feel it with their tongue.
Bacteria (most often streptococcus and staphylococcus) enter damaged enamel and further provoke the destruction of tooth tissue. The patient feels a sharp short-term pain in response to cold, sour and sweet foods.
How to treat? For superficial caries, the doctor removes the destroyed part of the enamel and places a small filling. At this stage, the dentin is not yet damaged, so the filling is small, and anesthesia is most often not required.
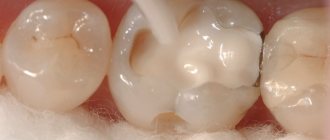
Average caries
Pathogenic microflora penetrates under the enamel and damages dentin - the softer tissue of the tooth, which is destroyed faster. The patient feels pain when cold or hot. A depression forms in the tooth, which can be easily felt with the tongue.
How to treat? In addition to the enamel, the doctor must drill out damaged dentin. It is important to remove all affected tissue so that caries does not develop again under the filling. When the cavity is ready, the dentist places a filling in it. Treatment usually takes 1-2 hours.
Deep caries
The carious process affects the deep layers of dentin adjacent to the pulp. The cavity increases, so food gets into it more often, causing additional trouble. The dentin softens, touching the tooth is painful.
How to treat To remove caries at this stage, anesthesia is used. The carious cavity is large, so a therapeutic pad can be installed in it under the filling. When determining treatment tactics, the doctor must understand whether the pulp is damaged and whether it needs to be removed and the canals treated. X-rays help to understand this.
Diagnostics
In some cases, using a mirror and analyzing one’s own feelings, the patient can make a diagnosis of “caries” himself. However, there are cases that only a specialist can correctly assess. We are talking about the initial stage, when there are practically no symptoms, but the doctor, using modern diagnostic tools, will detect the first signs of the disease. At later stages, it is important to distinguish caries from other dental diseases, which is also the responsibility of a certified physician. We will consider the symptoms that the patient himself should pay attention to.
The first symptom is a change in the color of tooth enamel. Spots of dark brown or, on the contrary, too white color appear on the surface of the tooth. Take a special look at the areas around the fillings. Also, do not ignore the fact that the tooth has begun to react to hot and cold. Another bad sign is damage to the dental floss when using it: caries may develop on the invisible side of the tooth. If you notice suspicious symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Unfortunately, statistics show that only ten out of a hundred patients can independently detect caries.
Complications
If deep caries is not cured in time, it turns into pulpitis - a disease in which the tooth pulp becomes inflamed. At this stage, patients complain of constant toothache. The inflamed pulp (nerve) must be removed.
Periodontitis is an even more advanced case when not only the pulp is affected, but also the bone around the tooth. The inflammatory process becomes dangerous: the patient’s temperature rises, chills appear, what’s left of the tooth festers and causes severe pain.
Complications of caries require removal of the pulp and thorough cleaning of the canals. It takes a doctor a lot of time to get to the most inaccessible branches and clean out all the infected tissue.
Some additional facts
Just like that, after some time, the fillings do not need to be changed. The filling may remain with you for the rest of your life. Reason for replacement: breakage of a filling or tooth, as well as caries arising from the filling.
Minor caries is asymptomatic. By waiting for pain to appear, you are dooming yourself to more expensive and complex treatment.
In the treated tooth, caries stops. It may return after a while if the filling comes off and bacteria begin to penetrate into the resulting space between the filling and the tooth.
Often, caries occurs in places that are difficult to reach with a brush, for example, in the interdental spaces. That's why we strongly advise you to use dental floss.
Any cracks in teeth or fragments of teeth are at risk.
Not all tooth sensitivity indicates tooth decay. It can be caused, for example, by gum disease, which exposes the root of the tooth. In any case, only a doctor can name the reason.
When caries is detected in primary teeth, it is recommended to treat them, if possible, rather than remove them. After all, baby teeth save space for molars. In the absence of primary teeth, molars may be positioned incorrectly.
Classification of caries by place of formation
Cervical - the most common type, occurs near the gums - where the enamel is thinnest. Plaque accumulates more actively near the gums. An infection settles in it, which provokes the destruction of enamel and dentin. In advanced cases, cervical caries leads to caries of the tooth roots.
Fissure - damage to the cavities on the chewing surface of the teeth. It is not always possible to remove plaque from the cavities with a brush, so microbes also actively multiply there.
Contact (interdental) - appears on the lateral surfaces of adjacent teeth, affecting two teeth at once. The root cause is still the same - the accumulation of plaque between the teeth. Diagnosis of such caries is difficult. Most often, the patient comes to the clinic only when pain occurs.
Root caries
Root caries
develops deep under the gum, violating the integrity of the tissues, while during visual inspection it may not be noticeable.
The basal species is localized on exposed roots and is characterized by a rapid course of the process. The enamel in the root zone has a minimum thickness, so it is quickly destroyed under the influence of external factors. How to treat root caries
is an important question that only a dentist can answer after an initial examination and a comprehensive diagnosis.
Causes of caries
Due to a lack of calcium and fluoride, the enamel softens. It is no longer able to protect the tooth from infection, and the infection lives in the oral cavity constantly. Within 2-3 hours after brushing your teeth, the number of bacteria can reach 1 million. Plaque and food debris serve as a beneficial environment for bacteria.
The development of caries is provoked by:
- Irregular or insufficiently thorough brushing of teeth
- lack of fluoride and calcium in drinking water
- poor diet, an abundance of foods high in carbohydrates, which are considered a favorable environment for bacteria
- anatomical features (in some patients the enamel is very thin and fragile)
- features of the composition of saliva (for example, due to a lack of enzymes that break down carbohydrates)
- genetic predisposition
- low immunity, due to which the body does not cope well with pathogenic bacteria.
Many people think that teeth are spoiled by sweets or that caries occurs when the patient does not have professional teeth cleaning. But it is difficult to say exactly what exactly caused tooth decay in each specific case.
It is impossible to protect yourself by eliminating all these reasons. Therefore, the best prevention of caries is a visit to the clinic once every six months, even if nothing bothers you.
Tooth hurts after caries treatment: what to do
Sometimes, after a filling is placed, patients complain of pain when biting or when touching something cold or hot. In this case, dentists advise waiting 1-2 weeks. If the pain does not go away, you need to contact the clinic again.
When pain is normal
1. It may not be the tooth or gums that hurt, but only the injection site if anesthesia was used. The wound will heal in a few days, there is nothing to worry about in this case.
2. If you feel a tingling sensation when you come into contact with cold or hot, it may be due to poor treatment of the cavity. In preparation for treatment, the cavity is treated with special agents and then dried. If it is over-dried or under-dried, the filling will not fit tightly to the dentin and may come into contact with it and cause discomfort. It usually goes away after 1-2 weeks, when the moisture inside the tooth is equalized by healthy tissue.
When to see a doctor again
If you're worried about pain and not just tingling, then don't wait two weeks. Perhaps pulpitis develops under the filling. The pain with pulpitis is strong, throbbing, especially annoying at night. In this case, you need to see a doctor again - and the sooner the better, because this problem “will not resolve on its own.”
How prices for caries treatment are determined
The sooner the dentist detects the problem and begins treatment, the cheaper it will cost. Deep caries is usually treated under anesthesia, which makes the procedure more expensive. The cost is also affected by the time a doctor needs to spend. If to eliminate early caries you need 1-1.5 hours and a small filling, then for deep caries the doctor must take a picture, drill a cavity of the required size, and thoroughly clean the canals, which can be very difficult to get into. And this is not the entire list of necessary actions.
To cure caries inexpensively, contact the clinic for a preventive examination - then you will be able to detect the problem at an early stage, and its treatment will be less expensive.
The cost may also be affected by:
- Localization location. Caries on the front teeth, incisors and canines is easier to treat than on chewing teeth and wisdom teeth. At least because access there is difficult.
- Cervical caries is more difficult to treat, even if it affects the front teeth.
- The level of the clinic and the experience of the doctor matter. If you choose between a prestigious clinic and an experienced dentist, the second, of course, is a priority.
Summary
To summarize what has been said, we repeat that the occurrence and development of caries is influenced by many factors, including lifestyle, eating habits, and personal hygiene. It is difficult to diagnose caries on your own, so it is better to visit a doctor regularly for a preventive examination. The only treatment for caries these days is surgical. You should not rely on traditional methods. The sooner you see a doctor, the fewer problems will arise during treatment.
The article material was approved by the doctor: Konishchev Vitaly Konstantinovich Oral and maxillofacial surgeon, dentist-implantologist
14 years