Ointments for bruises and other injuries not only eliminate pain, but also counteract inflammatory processes. They also dilate blood vessels, warm the tissue and promote its nutrition. Therefore, the therapeutic effect occurs within the first 30-40 minutes after application. The most popular drugs for adults and children are discussed below
Causes of pain
There is a division of causes that cause pain - they are natural and pathological.
Natural causes include muscle fatigue resulting from physical activity.
The list of pathological causes is much wider:
- osteochondrosis - can be lumbar, cervical, thoracic;
- presence of intervertebral hernia;
- damage to the joints of the spine;
- radiculitis;
- rheumatism;
- osteoarthritis.
The most common cause of back pain is damage to the skeletal muscles in acute and chronic forms. The development of the disease occurs due to pinching, squeezing and hypothermia in the cold season.
Medicines for prevention
Prevention with antibacterial agents is a common technique in oral surgery and dentistry. Antibiotic therapy before and after surgery reduces complications.
It is advisable to use products with high bioavailability and minimal side effects. Requirements for medications used for preventive purposes:
- increased activity against pathogenic bacteria, more often found in ondontogenic inflammatory lesions;
- correspondence of the spectrum of action to representatives of the microflora located in the oral cavity;
- good penetration into tissue, especially during operations to open phlegmon and abscess.
An antibiotic when implanted in dentistry minimizes the risk of side effects. Actively fight against foci of infections and bacteria. Selected based on weight and age. Common drugs are penicillins and cephalosporins.
The prescription of drugs depends on the complexity of the surgical intervention and possible complications. Prevention is mandatory in case of prolonged surgery or unfavorable treatment.
Indications for use of ointments
Ointments for back and lower back pain are used as individual therapy when feeling discomfort, expressed in varying degrees of pain.
Problems appear during the period of exacerbation of chronic pathological disorders when weather conditions change and the body becomes hypothermic. Moderate pain is characterized by minor muscle inflammation and pinched nerve endings.
When choosing an ointment for an individual prescription to a patient, the doctor must take into account the circumstances that caused the discomfort:
- homeopathic medicines with anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed to treat the inflammatory process;
- drugs that have a warming effect are prescribed for the treatment of osteochondrosis and spondyloarthrosis;
- ointments with the effect of local irritation - used to treat pathological changes with moderate pain.
To prescribe a specific drug, it is important to make the correct diagnosis.
Mode of application
Methods of using antibacterial liniments depend on the specific drug and the inflammatory process. The process is described in the instructions.
Basically, ointments are applied as follows:
- For burn and wound injuries, ointments are applied in a layer 1-2 mm thick. The procedure is repeated 1-3 times during the day. The course of treatment is 7 days;
- for inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eye, liniment is placed under both eyelids no more than 3 times a day. The course ranges from 3 days to a week. In case of complications, it can be extended to 2 weeks;
- for skin inflammations, liniments are used up to three times a day for no longer than one week;
- for dermatological diseases, the drugs are used 2 times a day, for up to 7 days. Ointments are applied in a thin layer or pointwise.
Contraindications for use
Absolute contraindications for the use of anesthetic ointments include sensitivity to the constituent components of the drug.
A large proportion of anesthetic ointments for back pain are contraindicated for children and adolescents, pregnant and lactating women.
The presence of injuries, damage or violations of the integrity of the skin (burns, scratches, cuts, dermatitis) on the skin is a contraindication for applying an external product.
Local irritation preparations with a warming effect are approved for use during the period of reducing the exacerbation of the inflammatory process in order to avoid increased pain with further spread to healthy tissues.
Warming ointments contain red pepper extract, as well as bee and snake venoms. Therefore, the use of such an ointment for dry, thin and sensitive skin is contraindicated, as a chemical burn may occur. A replacement for such drugs are drugs with an analgesic or cooling effect.
To relieve discomfort in the back or lower back, pregnant women are prescribed painkillers only after examination by a doctor. The safety of drugs for expectant mothers is determined taking into account the threshold of susceptibility to the individual components included in the ointments or gels.
What to apply to a severe bruise: “Viprosal”
This medicine contains the venom of a common viper and auxiliary components - turpentine, camphor and silicylic acid, which provide additional heating of the affected area.
The product serves as an analgesic, inhibits inflammatory processes, and also improves tissue nutrition by dilating blood vessels. You can buy the product without a prescription and can be taken by adults and children over 12 years old.
Side effects include allergic reactions, including itching and swelling. It is worth remembering that Viprosal cannot be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is important to avoid contact of poison with mucous membranes, including eyes, and damaged areas of skin (wounds, abrasions, ulcers).
Carrying out treatment
The algorithm is as follows:
- before applying ointments, the skin should be washed and dried;
- ointments are applied in an even layer to the painful area;
- rub in with light pressure, using massaging movements, excess is removed with a napkin.
It is recommended to apply ointments at night; in the evening, the effect of medicinal components is more active. The use of therapy at night promotes restful sleep without pain.
Vulvovaginitis: drugs
Local and oral agents are used for treatment.
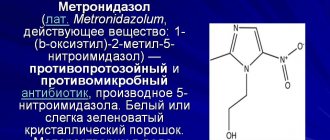
Vaginal suppositories and creams (Gynex, Clotrimazole, Lomixin) are indicated as local ones. Doctors also prescribe a course of tablet antibiotics (Pancef, etc.). For candidal etiology, antifungal agents are prescribed: Nystatin, Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Metronidazole.
Upon completion of treatment, doctors recommend taking probiotics (Lactozhinal, etc.) to restore the microflora.
If the cause of the disease is worms, anthelmintic drugs are needed: Aldazole, Pirantel.
Options for quick pain relief
The onset of the disease is accompanied by acute, piercing pain in the spine or lower back. Painful sensations often deprive a person of the ability to move; the slightest movement provokes the appearance of sharp pain. In this situation, it is important to choose a position in which pain symptoms will decrease:
- Lower back pain – lie on your back with your legs on a pillow.
- Pain in the thoracic region - lie down on your side. It is recommended to use a pillow or cushion under the lower back or between the legs, bent at the knees.
- Pain in the cervicothoracic region - sit in a semi-sitting position, place a pillow between the shoulder blades.
The best ointments for lower back pain
Vulvovaginitis
Vulvovaginitis is a disease of the female genital organs.
Inflammation may be of bacterial origin or be the result of mechanical irritation of the vulvar and vaginal mucosa. The natural structure of the female body allows us to protect the genitals from microorganisms from the external environment. The vaginal microflora of a healthy woman easily inhibits the growth of opportunistic bacteria that live on the mucous membranes. A decrease in immunity due to stress, intoxication or a viral disease can provoke a surge in the activity of pathogens, resulting in the development of acute vulvovaginitis.
List of the best ointments for back pain
The versatility of an effective ointment for back pain helps to provide an analgesic effect, as well as prevent relapse of the disease.
These drugs help reduce inflammation and stimulate the resorption of edema.
The selection of good ointments should be focused on treatment, and not provoke local adverse reactions.
Painkillers are divided into groups according to their effect.
Ointments with a warming effect
The use of these ointments is effective and safe for the treatment of back pain. When applied, a feeling of warmth appears and pain decreases. There is a rush of saturated blood, which helps reduce the inflammatory process.
A number of external effective and fast-acting remedies:
- "Capsicam" - composition: natural and synthetic ingredients. Used for pain in joints and muscles.
- “Finalgon” – pain is eliminated 5 minutes after use. Used for osteochondrosis.
Ointments for external use have a warming effect and help relieve muscle spasms. It is not recommended to use for diseases in the neck area, since the skin on the neck is thin and there is a possibility of burns.
Reddened skin is a characteristic sign when rubbed with warming ointments, but it is better to discontinue or replace the drug.
Ointments with analgesic effect
Used to reduce severe discomfort. The feeling of pain is eliminated within a few minutes after rubbing with the ointment.
The analgesic effect is characteristic of the following drugs:
- “Voltaren” – helps relieve pain, eliminates inflammation, and is completely absorbed into the skin.
- “Ibuprofen” is used even for children due to the fact that it is not absorbed into the blood.
Anesthetic ointments for back pain are suitable for quickly eliminating pain.
Ointments with anti-inflammatory effect
They influence the long-term improvement of a person’s well-being. Frequently used drugs in medical practice:
- "Fastum Gel" - has an analgesic effect and a cooling effect.
- "Diclofenac" - eliminates inflammation, swelling, pain. Due to its safe properties, it is approved for use by children and adolescents. Used for rubbing the back in the treatment of pathological disorders in the musculoskeletal system.
Ointments with local irritation effect
Famous for their strong analgesic and restorative properties. When rubbed with the ointment, a feeling of warmth and slight tingling appears.
Drugs with the greatest effect:
- “Nayatox” - the ointment contains cobra venom, which helps stimulate vasodilation. It is used for diseases such as lumbago, sciatica, rheumatism.
- “Apizartron” is an ointment based on bee venom that helps stimulate blood flow to damaged areas. Due to its anti-inflammatory effectiveness, it reduces the activity of pathogenic bacteria. Actively affects pain reduction and causes a feeling of coolness.
Chondroprotectors
Helps restore intervertebral discs and articular cartilage. Used for hernia and osteochondrosis.
These means include:
- "Chondroitin-Acos" - renews cartilage tissue.
- Teraflex – preserves bone mass, improves mobility of the spinal column.
The use of chondroprotectors is intended for a long period of treatment therapy (from a month to a year or more); they are characterized by accumulative properties.
Ointments with a combined effect
The different components complement each other, enhancing the therapeutic effect. The best products for frequent use:
- “Dolobene” – main actions: anti-inflammatory, decongestant, analgesic.
- “Indovazin” - its use will eliminate pain, reduce swelling, and restore damaged tissue.
The use of these ointments is recommended for use in men and women to strengthen blood vessels and improve their penetrating properties.
Homeopathic ointments
Homeopathic medicines - due to the low concentration of ingredients, are prescribed for mild discomfort:
- “Target T” – helps restore damaged tissues, has a weak analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- "Traumeel S" - affects the localization of the source of pain. It is used for the inflammatory process in the musculoskeletal system.
These drugs have a cumulative effect.
Share in the comments which of these ointments you used, what the effect was, were you satisfied with the result?
Ointment for bruises and injuries: “Apizartron”
"Apizartron" contains bee venom and auxiliary components. It has a pronounced analgesic effect, helps with sprains and bruises. Used to warm up muscles, including during sports activities. Stimulates blood circulation, eliminates symptoms of neuritis and sciatica, as well as rheumatic joint pathologies.
You can buy the ointment at the pharmacy without presenting a prescription. It can be used by both adults and children over 12 years of age (over 6 - with caution). It is not allowed to use during any trimester of pregnancy and during breastfeeding.
If you have an individual intolerance to bee venom, a number of allergic reactions may occur, including redness, swelling, itching and rash. In these cases, it is necessary to replace the drug.
Do excipients in the local form of NSAIDs matter?
Yes, they improve skin permeability and perhaps enhance the therapeutic effect in a certain way. In separate studies, for example, topical formulations of diclofenac with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diclofenac diethylamine 1.16% have been shown to penetrate the skin faster than “regular” diclofenac sodium gels. In addition, DMSO itself may have a slight anti-inflammatory effect. There is no solid evidence of an increase in the analgesic effect due to the listed supplements, but their use at least helps to overcome the individual characteristics of the skin [7, 9–11].
Which topical NSAID is best?
Everything is individual. If the analgesic effect of oral and injectable forms of NSAIDs can be more or less ranked, then an objective comparative assessment of topical drugs is very difficult. The reason for this is that, along with the actual active substance, the intensity of rubbing, excipients (for example, dimethyl sulfoxide) and the placebo effect play a significant role. Most studies on the effectiveness of topical NSAIDs have focused on diclofenac and ketoprofen. The increased attention to them is due to the fact that diclofenac is the only NSAID whose topical forms are approved by the American Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and ketoprofen, accordingly, is approved in most other countries of the world. Reliable data comparing these two drugs with each other have not yet been published. No one questions the effectiveness of other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for external use (ibuprofen, phenylbutazone, piroxicam, nimesulide, etc.); each of them was the subject of several clinical trials at one time, but the geography of their use is much more modest and is often limited to a few developing countries [2, 8].
Is it possible to use topical NSAIDs for stomach erosions or ulcers?
According to the instructions, it can be done “with caution.” The concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma after the use of topical NSAIDs is less than 10% of that achieved by oral administration. The incidence of adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract when using local forms of NSAIDs does not differ from that when rubbing placebo and is significantly lower than when using systemic agents. However, just in case, these drugs are not recommended to be applied to the skin during gastrointestinal bleeding and exacerbation of gastric or duodenal ulcers [5, 14].
How many times a day and for how long can you apply such drugs?
Typically three to four times a day for two weeks. Topical NSAIDs act quite quickly - the effect occurs within an hour - and help control acute somatic pain of moderate intensity. They cope worse with chronic pain. If there is no effect within two weeks of proper use, you should consult a doctor. There is a chance that he will recommend switching to oral forms or another group of drugs.
Sources
- Derry S, Conaghan P, Da Silva JA, et al. Topical NSAIDs for chronic musculoskeletal pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 4: CD007400. https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD007400.pub3/full
- Derry S, Wiffen PJ, Kalso EA, et al. Topical analgesics for acute and chronic pain in adults – an overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 5: CD008609. https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD008609.pub2/full
- Klinge SA, Sawyer GA. Effectiveness and safety of topical versus oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a comprehensive review. Phys Sportsmed. May 2013; 41(2): 64–74. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23703519
- Kloppenburg M, Kroon FP, Blanco FJ, et al. 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of hand osteoarthritis Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019; 78: 16–24. https://ard.bmj.com/content/78/1/16
- Honvo G, Leclercq V, Geerinck A, et al. Safety of Topical Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Osteoarthritis: Outcomes of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Drugs Aging. 2019; 36(Suppl 1): 45–64. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6509095/
- Hasler-Nguyen N, Fotopoulos G. Effect of rubbing on the in vitro skin permeation of diclofenac-diethylamine 1.16% gel. BMC Res Notes. 2012 Jun 21; 5: 321. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3424122/
- Hagen M, Baker M. Skin penetration and tissue permeation after topical administration of diclofenac. Curr Med Res Opin. 2022 Sep; 33(9):1623–1634. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/03007995.2017.1352497
- Rafanan BS Jr, Valdecañas BF, Lim BP, et al. Consensus recommendations for managing osteoarthritic pain with topical NSAIDs in Asia-Pacific. Pain Manag. 2018; 8 (2): 115–128. https://www.futuremedicine.com/doi/10.2217/pmt-2017-0047?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:…
- Pradal J, Vallet CM, Frappin G, Bariguian F, Lombardi MS. Importance of the formulation in the skin delivery of topical diclofenac: not all topical diclofenac formulations are the same. J Pain Res. 2019; 12: 1149–1154. https://www.dovepress.com/importance-of-the-formulation-in-the-skin-delivery-of-topical-diclofen-pee…
- Galer BS. A comparative subjective assessment study of PENNSAID® and Voltaren Gel®, two topical formulations of diclofenac sodium. Pain Pract. 2011; 11 (3): 252–60. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1533-2500.2010.00420.x
- Tieppo Francio V, Davani S, Towery C, Brown TL. Oral Versus Topical Diclofenac Sodium in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2022 Jun; 31 (2): 113–120. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15360288.2017.1301616?journalCode=ippc20
- Simon LS, Grierson LM, Naseer Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical diclofenac containing dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) compared with those of topical placebo, DMSO vehicle and oral diclofenac for knee osteoarthritis. Pain. 2009; 143(3):238–45. https://insights.ovid.com/article/00006396-200906000-00016
- Van Amburgh J. Can Topical and Oral NSAIDs Be Combined for Pain Relief? Medscape. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/861740
- Roth SH. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy: new avenues for safety. Clin Interv Aging. 2011; 6: 125–31. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3131982/
- Kowalski ML, Makowska JS, Blanca M, et al. Hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – classification, diagnosis and management: review of the EAACI/ENDA and GA2LEN/HANNA. Allergy 2011; 66:818–829. https://www.eaaci.org/attachments/668_Kowalski%20Hypersensitivity%20to%20nonsteroidal%20anti-inflamm…
- Rogers NV, Rowland K. An alternative to oral NSAIDs for acute musculoskeletal injuries. J Fam Pract. Mar 2011; 60 (3): 147–8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3183960/
What complications can there be?
Untreated vulvovaginitis can lead to serious consequences. In girls, the formation of dense adhesions of the labia minora is possible. Such a deformation will make sexual life difficult. In addition, this pathology is one of the factors that provoke cystitis.
The disease is especially dangerous during pregnancy. The expectant mother is at risk of spontaneous abortion, endometritis, or the birth of an infected baby.
Chronic vulvovaginitis leads to hardening of the mucous membranes. With this course, cracks and erosions occur more often, and prerequisites for the appearance of oncology appear.