The dental disease pericoronitis (pericoronitis) is a specific inflammation of the gum mucosa, most often caused by the appearance of the third molars of the lower jaw (wisdom teeth). People aged 18-25 years and older are at risk.
The symptoms of acute pericoronitis are similar to those of periodontitis and pulpitis. The disease begins with damage to the gums in the area of a partially erupted wisdom tooth. Then the inflammatory process covers the periodontium and spreads further. It can affect the area of the pterygomaxillary fold, the lower arch of the vestibule of the mouth, and the palatine arch.
The situation is corrected with surgical and therapeutic methods. To determine the position of erupting molars and select an effective technology for medical care, a computed tomography scan is performed.
Reasons for the development of wisdom tooth pericoronitis
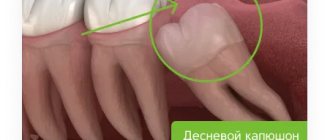
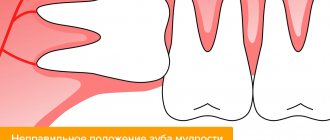
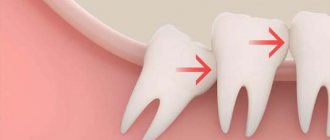
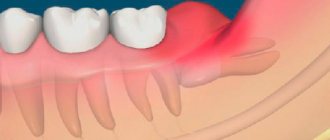
In 90% of cases, pericoronitis is associated with wisdom teeth, since there is a bulky area of gum behind the third molars. If teething occurs incorrectly, the soft tissues become inflamed and accumulate pathogenic bacteria around them. The most common visual manifestation of pericoronaritis is the so-called gingival hood, when part of the inflamed mucosa hangs over the coronal part of the wisdom tooth. Most often this occurs with the lower eight - approximately 70 - 80% of the total number of cases of pericoronitis. The main reason for pericoronaritis of wisdom teeth lies in the fact that during the process of evolution, the human jaw arch has decreased, so now wisdom teeth often simply do not have enough space and they erupt at the wrong angle in conditions of limited space. The development of pericoronitis is also influenced by other factors, which largely determine how to treat pericoronitis.
What it is
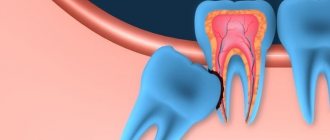
Pericoronitis, or, as it is also called, pericoronitis, is an inflammation of the gum tissue that occurs during prolonged and difficult tooth eruption. Most often, acute pericoronitis of the third lower molars, or, as they are popularly called, lower wisdom teeth, occurs. If timely treatment is not started, the disease can develop into acute purulent periostitis.
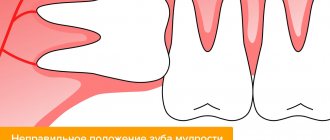
In the process of evolution, the urgent need for wisdom teeth disappeared, as humanity began to consume softer, thermally processed foods. And over time, the lower jaw shrank and became shorter. As a result of these processes, the distal part of the alveolar part of the jaw has decreased, and there is almost no space left for wisdom teeth. This is why the eruption of lower wisdom teeth is so often accompanied by pericoronitis.
Due to lack of space, wisdom teeth are positioned incorrectly in the jaw, which complicates their already difficult eruption. As a result of prolonged trauma, the gums that cover the unerupted tooth on top become inflamed. Sometimes the wisdom tooth does not fully erupt; only 1-2 medial cusps are visible above the gum. In this case, pericoronitis of the tooth also very often occurs.
Symptoms of pericoronitis
All of the above factors negatively affect the development and eruption of wisdom teeth, but at the same time, pericoronitis itself is caused by the activity of bacteria that accumulate in the resulting gingival fold. As for the symptoms of the disease, until the wisdom tooth begins to actively erupt, the patient does not feel any concern, however, when performing an orthopantonogram, the risk of pathology can often be predicted. At more advanced stages, wisdom tooth pericoronitis has quite obvious symptoms:
- itching in the area of the wisdom tooth (in the early stages);
- swelling, redness, pain;
- formation of a gingival hood;
- elevated temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- abscesses, purulent discharge, unpleasant odor.
Diagnostics
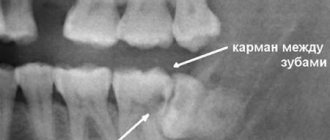
Diagnosis of pericoronitis is not difficult for a dentist. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to take an x-ray and carefully ask the patient about the main symptoms of the disease. In the image, the doctor will be able to see the position of the wisdom tooth, the condition of the surrounding bone tissue and the periodontium of the tooth itself, and in the chronic course of the disease - bone resorption.
When diagnosing chronic pericoronitis, it should be differentiated from periodontitis and pulpitis.
Types of pericoronitis
| Type of pericoronitis | Description |
| Catarrhal | The initial form of the disease, in which the inflammatory process has just begun, and the gingival hood has not yet formed. |
| Ulcerative | Noticeable swelling, formation of ulcerative rims, bleeding of the gums in the affected area. |
| Acute pericoronitis | An acute form of the disease, rapidly developing and progressing to more severe stages. |
| Retromolar | Deep inflammation affecting the periosteum and going deep. Visually expressed by severe swelling. |
| Chronic purulent | It affects soft and hard tissues in the area of the wisdom tooth, as well as neighboring parts of the jaw. At this stage, the risk of developing phlegmon and osteomelitis is highest. |
Classification
Pericoronitis is divided into acute, which occurs most often, and a rarer form - chronic pericoronitis. According to the flow, the following types of pericoronitis are distinguished:
Catarrhal – characterized by slight swelling and pain when touched; Purulent - constant pain and the presence of purulent discharge; Ulcerative – leads to the formation of ulcerative defects on the gums;
Retromolar is distinguished as a separate form - it is distinguished by its location, which does not allow it to be easily seen and treated, which makes it difficult to combat this disease and increases the likelihood of complications.
Treatment of pericoronitis
You need to understand that treatment of wisdom tooth pericoronitis with conservative methods is possible only in the early stages and in cases where there are good prospects for preserving the wisdom tooth. Conservative treatment involves the use of anti-inflammatory ointments and gels (Cholisal, Metrogyl Denta, etc.), as well as rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin). However, in more than 90% of cases, exclusively surgical treatment methods are used - wisdom tooth removal.
How is pericoronitis treated?
- The gingival hood is dissected and the affected area is treated with antiseptic and antibacterial drugs.
- The gingival hood is removed. Excision of the hood for pericoronitis (removal of excess soft tissue) allows you to get rid of the source of infection and facilitate tooth eruption.
- Wisdom teeth are removed. The most common measure used for developmental disorders (retention, dystopia). Tooth extraction is also carried out in case of relapse of the disease and the appearance of a new hood.
How to treat pericoronitis?
Treatment tactics for pericoronitis are selected by CELT dentists on an individual basis, depending on the diagnostic results and the patient’s indications. It is aimed at:
- pain relief;
- relief of inflammatory processes;
- restoration of the functionality of the dental system;
- excluding the development of complications.
Therapeutic manipulations are carried out on an outpatient basis, taking into account the severity of inflammatory processes, the local and general picture of the pathology and radiographic data. Treatment of the catarrhal form of acute periocoronaritis involves:
- antiseptic treatment of the area under the hood;
- application of antiseptic and anesthetic dressings;
- lifting the hood using a gauze strip soaked in iodine solution.
Prevention and prognosis
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent the development of pericoronitis. The only preventive measure is regular visits to the dentist - which will make it possible to diagnose the disease at the initial stage of development, as well as cure dental diseases that provoke the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the gum tissue.
The prognosis of pericoronitis in the vast majority of situations is favorable - timely therapy begins to achieve complete recovery, and complications develop quite rarely. However, patients should not forget about the tendency of the disease to relapse and become chronic.
Clinic doctors
How do you know if you have the flu or pericoronitis?
The onset of pericoronitis is easy to miss. Many patients are surprised by this diagnosis, thinking that their pain when swallowing is caused by a common cold or flu!
However, the advanced stage of the disease often causes complications. We recommend reading right now about the causes and signs of pericoronitis so that you can contact your dentist at the first symptoms!
Pericoronitis is a fairly serious disease that requires mandatory treatment. Most often it bothers children and adolescents, but many older patients are also familiar with this problem.
What is pericoronitis?
This is an inflammation of tissue associated with tooth eruption (in particular, the third molar). The process of eruption of a wisdom tooth can last several months, and most of this time the tooth is covered with a gingival hood, in which food debris accumulates. They serve as an excellent breeding ground for microbes that provoke the development of pericoronitis.
What are the causes of pericoronitis?
Inflammation is caused by normal oral microflora. Since the gingival hood is very difficult to clean from food debris, favorable conditions are created for the increased proliferation of bacteria, which normally do not cause inflammation. Pericoronitis can also result from injury to the gums when chewing hard food or incorrect position of an erupting tooth.
What are the symptoms of pericoronitis?
Acute pericoronitis is manifested by gradually increasing pain in the area of the wisdom tooth. The gums turn red, and pus comes out from under the hood. As inflammation progresses, painful sensations appear when swallowing and opening the mouth; pain can radiate to the temporal region or ear. Sometimes the body temperature rises to 37.2 - 37.5 ° C, and the submandibular lymph nodes may enlarge.
What is the danger of pericoronitis?
If the disease is advanced, complications may develop in the form of retromolar periostitis, ostemyelitis, phlegmon or subperiosteal abscess. Therefore, when the first symptoms of inflammation occur, you should immediately contact your dentist to begin treatment for pericoronitis.
What are the indications for excision of the hood for pericoronitis?
The indication for the operation is difficulty in the eruption of a WISDOM TOOTH when it is possible to preserve it. Excision of the hood is performed when there is enough space in the dentition for an erupting tooth, and its crown is not damaged.
What is the technique for excision of the hood for pericoronitis?
Excision of the hood over a wisdom tooth takes only a few minutes and is performed under local ANESTHESIA. Using a scalpel or surgical scissors, the dentist removes part of the gum, freeing the surface of the emerging tooth. Then the crown part of the tooth is cleaned of pus and disinfected. After the operation, the doctor prescribes restorative and anti-inflammatory therapy.
What are the indications for wisdom tooth removal for pericoronitis?
The tooth must be removed if, after excision of the hood, the disease remains and even progresses. The third molars are not involved in chewing and do not have much functional significance for humans. In addition, due to their remote location, their hygiene is difficult. Therefore, extraction of “eights” will not cause any inconvenience in the future.
What is the technique for removing wisdom teeth for pericoronitis?
In the presence of this disease, the wisdom tooth is removed only after the acute inflammatory process has subsided. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor cuts the gum, providing access to the problem tooth. Then the tooth is removed, the hole is treated with an antiseptic solution, and sutures are placed on the gum.
What are the recommendations in the postoperative period?
For several days after excision of the wisdom tooth hood, the patient is advised to abstain from alcoholic beverages and spicy foods. It is also necessary to use antiseptic drugs to neutralize the inflammatory process.
What are the possible complications?
After the operation, the patient may experience pain in the area where the hood or wisdom tooth was removed, pain when opening the mouth and swallowing, fever, swelling of the gums and cheeks. Depending on the individual characteristics of a person, the presence of these symptoms may be natural, but may also indicate the development of complications. Therefore, if such discomfort occurs, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
What are the quality criteria for the treatment of pericoronitis?
The main criterion for the cure of pericoronitis is the absence of clinical symptoms of the disease. A satisfactory treatment result must be confirmed by instrumental examination and x-ray examination.
How much does it cost to treat dental pericoronitis?
Treatment of wisdom tooth inflammation can be carried out using different methods, which is reflected in its cost. The prices of our clinic can be found in the price list, and if you need specialist advice, click on the “Make an appointment” button.
How is dental treatment carried out?
If you do not receive professional help in time, the disease will develop into a chronic form. Due to structural changes in the gum tissue, pain is dulled. But the inflammatory process itself only intensifies, the lesion increases in size. With chronic pericoronaritis, purulent exudate and inflammation of regional lymph nodes can form.
Pericoronitis is treated in various ways. It all depends on the stage of the disease and its characteristics. The most popular surgical method. The dentist-surgeon will remove the gum fold and provide access to the tooth for normal eruption. The procedure is carried out using modern painkillers. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the problematic tooth.
The NAVA dental clinic has the necessary equipment and a staff of real professionals; here you can treat any diseases of the oral cavity. You can make an appointment by phone: 8 (495) 256-01-03.
This article was checked and approved by the doctor Natalya Mikhailovna Vasilevskaya.
Pericoronitis: symptoms of the disease and photos
How to recognize pericoronitis in time? Symptoms become acute and become noticeable approximately 2-3 days after the onset of the disease (symptoms of pericoronitis are visible in the photo on the right).
The first symptom will be pain, which with the progression of pericoronaritis becomes unbearable and can be localized not only in the area of the erupting tooth, but also radiate to the upper jaw, ear, temple, and periorbital region. Painful sensations when opening the mouth, swallowing, difficulty chewing - these symptoms also almost always accompany pericoronitis.
General symptoms may include weakness, malaise, increased body temperature (to 37.5-38°C), headache, and enlarged regional lymph nodes.
Pericoronitis (photo above) can also be recognized upon examination. Attention is drawn to the inflamed, hyperemic, enlarged, swollen gingival hood. When you try to move the hood, pus comes out from under it. It is pus that causes such a symptom as an unpleasant, foul odor from the oral cavity.
If this is advanced pericoronitis, a photo of which can be seen on the left, the inflammation spreads to adjacent areas (gums, cheeks, palatoglossus). Often there may be pathological mobility of the tooth, its displacement, or tilting forward.