How anesthesia and anesthesia work: myths, fears, side effects
An alternative to spinal anesthesia can be epidural, when a local anesthetic is injected into the epidural space located in the spine through a special catheter. Depending on the type of operation (chest, abdominal cavity), the anesthesiologist determines the place of its introduction. In this case, the doctor can inject not only a local anesthetic into the epidural space, but also opioid painkillers that enhance the effect. Sometimes the epidural catheter may be left in place temporarily to provide pain relief as required by the patient (called an extended epidural).
More complex and serious interventions are always associated with lengthy preparation on the part of the anesthesiologist - installation of a central venous catheter, administration of infusion therapy, correction of blood coagulation parameters and other important parameters. It is also important to consider whether the operation is an emergency or a planned one.
Can you tell me more about the difference between spinal and epidural pain relief?
During spinal anesthesia, the drug is injected at the lumbar level into the subarachnoid space (into the cavity between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater of the spinal cord, filled with cerebrospinal fluid). Usually everything is limited to a couple of injections. In this way, the soft tissues above the injection site are anesthetized and the drug is directly administered under the dura mater. This anesthesia lasts from two to six hours and is technically easier to administer.
During epidural anesthesia, the drug is injected into the space between the dura mater of the spinal cord and the periosteum of the vertebrae, which contains connective tissue and venous plexuses. It is located closer to the skin compared to the spinal one. Anesthesia is given at any level of the spinal column. It is considered a technically more complex manipulation.
I've read that epidurals can cause paralysis.
This is a common fear, but anesthesiologists say that today it is practically impossible. Such a complication could arise after surgery due to improper care of the catheter, as a result of which the patient developed purulent epiduritis, which caused neurological symptoms with loss of function of the lower extremities. Or due to incorrect actions of the anesthesiologist, when puncture of the epidural space occurs at high levels (there is a risk of unintentional damage to the spinal cord). But in most cases, epidural anesthesia does not threaten anything other than a headache for several days after surgery.
Can everyone have anesthesia?
In life-threatening situations when a person needs surgery, doctors almost always use anesthesia. For example, if there is a victim of an accident on the couch who urgently needs surgery, the risk of having it performed with anesthesia for any health condition will be less than the risk of refusing it.
If a patient comes for a planned operation, then the anesthesiologist is obliged, after collecting an anamnesis, to select the appropriate type of anesthesia taking into account the patient’s health. Doctors are guided by the rule: the volume and risk of anesthesia should not exceed the risks on the part of the surgeon. The patient's age cannot be a contraindication. Specialists take into account all severe chronic diseases that complicate the state of health, and allergic reactions to anesthesia components.
Is there a difference between old and new drugs?
Yes there is: in their consumption, efficiency and safety of use. However, it is invisible to patients; To appreciate the difference, you have to be an anesthesiologist.
How to prepare for anesthesia and how to survive recovery from it?
Preparation depends directly on the type of anesthesia and surgical intervention. The doctor will tell you what and how best to do before the operation. Just build a trusting relationship with your treating doctors, it will be much calmer.
Each patient experiences recovery from anesthesia individually; not everyone feels bad, but many feel nausea and drowsiness, and muscle tremors. It all depends on the characteristics of the body and the drugs that were administered during the operation. After waking up, it is important to listen to your body and report any deviations to your doctors.
How long should it take to freeze?
How long does anesthesia last after tooth extraction? The duration of the effect depends on several factors:
- The type and amount of pain medication administered;
- Type of anesthesia, injection depth, injection site;
- The presence of a vasoconstrictor in the drug (substances that constrict blood vessels and prolong pain relief);
- Human weight, individual parameters;
- Features of metabolism;
- The presence of chronic diseases of the urinary system.
Conduction anesthesia lasts 2-3 hours on the upper jaw and 3-5 hours on the lower jaw. Therefore, the pain relief effect may persist for several hours after visiting the doctor. Other types of local anesthesia have a shorter period of action - from 15 minutes to 2 hours.
Is there a risk of not waking up?
As for the real statistics of deaths from anesthesia, for every 200 thousand patients undergoing elective surgery, there is 1 death. Most complications are not related to anesthesia at all, but arise as a result of surgical problems. There is some dependence of survival within a year after surgery on the depth of anesthesia.
The risk of death is greater the greater the concentration of anesthetics used. This is due to the possible development of degenerative processes due to exposure to high doses of aggressive drugs, the manifestation of which is delayed in time. In addition, the risk of negative changes in organs and tissues increases if oxygen metabolism disturbances occur in the first hours after anesthesia.
It is advisable to have close people nearby after anesthesia.
What to do if the numbness does not go away?
There is no need to be afraid of prolonged tissue numbness; after a couple of hours, sensitivity will definitely return. If numbness in your teeth, tongue, jaw, or nose after anesthesia does not go away by the end of the day, you should call your doctor and report the situation. In rare cases, complications of anesthesia occur in the form of paresis and paresthesia - disruption of tissue innervation. They appear when a nerve is accidentally injured by a needle. In this case, you need to visit a doctor who will prescribe treatment for the pathology. When the anesthesia of the tooth wears off, discomfort and unpleasant sensations may appear.
In most cases, tissue anesthesia passes without a trace, so if there are indications for anesthesia, there is no need to be afraid to perform it. If you have had an unpleasant experience with pain relief or need emergency treatment under anesthesia, you should simply tell your dentist about it. The doctor will definitely take into account your wishes and will be able to control the amount of the drug and the duration of its action.
Other complications
You may also experience:
- nausea, indicating a negative effect of the anesthetic on liver function;
- temporary loss of coordination in space or disturbances in perception by the senses, which will return to normal after the drug is removed from the body;
- allergic itching.
Important! The patient cannot be prevented from sleeping after anesthesia. However, staying awake for the recommended period will help preserve your health and sometimes your life.
As soon as the doctor is convinced that the operation was well tolerated by the patient, and the anesthesia did not have a significant negative effect, it will be possible to sleep as much as the body requires. After a period of observation, pain medication may be administered to allow the person to rest.
Anesthesiology in dentistry
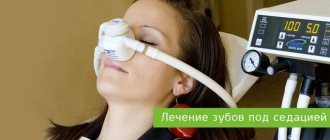
And a little more about outpatient anesthesiology and anesthesiology in dentistry, in particular. It is anesthesia (central anesthesia) that is used extremely rarely in modern outpatient dentistry and this is, as a rule, unjustified - like shooting sparrows from a cannon. The optimal option at the moment is to carry out sedation with simultaneous monitoring of the patient’s condition - monitoring. This enhances local anesthesia and reduces the amount of anesthetic required to achieve the effect. There are no contraindications to this method for people who have walked to the dentist’s office. According to his own feelings, the patient sleeps in the same way as during anesthesia, but wakes up quickly, is oriented and is able to move around on his own.
What is general anesthesia?
What is general anesthesia or, as Russian language “experts” say, “general anesthesia”? If you don’t go into details, but highlight the most important thing for the patient, then general anesthesia is anesthesia performed by an anesthesiologist. The patient does not necessarily have to sleep during general anesthesia. Sometimes a nap is enough—medically induced calm and indifference to the outside world. This condition is called sedation. Sometimes, due to such serious sedation (sedation), the patient falls asleep on his own, but at the right moment wakes up - at the doctor’s command he performs simple actions (open his mouth, turn his head, raise a limb, etc.).
Horror stories about anesthesia
No one will ask a traumatologist about gynecological diseases. However, questions about anesthesiology are asked to doctors of any specialty, who, as a rule, understand it no more than other ordinary people - anesthesiology is a very specific subject. Once I came across this: a patient came for tooth extraction under anesthesia, paid for the extraction and anesthesia, but refused the anesthesia, because a relative (therapist) said that EVERYONE dies from anesthesia.
Patients who undergo operations under general anesthesia write with pleasure in various forums how afraid they are of “general anesthesia,” and a chorus of well-wishers echoes them: “yes, yes, anesthesia is like dying a little,” “anesthesia has a lot of contraindications,” “maybe allergic shock!” It seems that you can do without anesthesia and there is no need to monitor the patient’s somatic condition during the most complex and traumatic interventions. At the same time, no one writes that pain has a very, very strong effect on health, that not everything can be tolerated, that a surgeon is a person who only performs an operation, and an anesthesiologist is precisely the specialist who cares for the patient.
How often can sedation be used?
During sedation, all the patient’s reflexes (cough, gag) are preserved, verbal contact is preserved: the doctor may ask you to follow simple commands like “open your mouth wider.” Sedation can be done as many times as you like. Every other day and every day. The drugs used to achieve sedation (no narcotic drugs are used) are eliminated from the body very quickly - within a few minutes. The anesthesiologist constantly adds them during the sedation process. A few minutes before the end of the operation, the administration of sedatives is stopped, and the patient wakes up on his own.
Anesthesia in the public consciousness
There is a saying: “Medicine has more fans than sports.”
If we expand on the topic, anesthesiology has the most “fans” in medicine. The saddest thing is that among such fans there are often doctors. I don’t want to offend anyone, but very often I hear amazingly illiterate and ignorant statements about anesthesia on this subject, not only from ordinary people, but also from surgeons, gynecologists, therapists and doctors of other specialties. Not a single anesthesiologist undertakes to judge surgery or ENT diseases, but almost any non-anesthesiologist will be happy to tell you thoughtfully something like “anesthesia is always anesthesia” or “anesthesia is not candy.” It’s good that at least the majority do not repeat the generally accepted nonsense that “anesthesia takes away five years of a person’s life” or “affects the heart.”