WHAT WORRIES YOU? PAIN during intercourse HOW TO GET YOUR VIRGINITY BACK YOU DO NOT like the labia CYSTITIS after sex DARK perineum SIZE of the vagina INTIMATE life after childbirth LACK OF ORGASM WHAT IS YOUR INTEREST? Plastic surgery of the labia Restoration of virginity Surgical defloration Vaginal reduction Clitoral plastic surgery Intimate muscle training How to achieve orgasm HOW TO DO IT? Get intimate plastic surgery... Get contour plastic surgery... Intimate cosmetology... Take tests for a fee... See a gynecologist
Furuncles of the labia, or as they are popularly called “chiria,” are inflammation of the hair follicle, close to the sebaceous glands and surrounding tissues. A common disease of the intimate area that can have serious consequences if left untreated. It’s a pity that not everyone immediately goes to the doctor with this problem. Treatment must be carried out to avoid complications and side effects. Especially when a boil appears inside the skin of the labia. This can occur anywhere on the vulva (labia majora and minora), pubis, perineum, or closer to the anus. A boil in the intimate area may have the term “boil”.
If the process is characterized not by a single formation, but by multiple rashes on the external genitalia (from three units), then this is called “furunculosis.” This disease should not be confused with carbuncle - a purulent inflammation that affects the inner layers of the dermis and subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Pustules on the labia with syphilis
Pustules on the labia appear as a result of infection by the pathogen Treponema pallidum.
Upon examination, they look like acne.
Diagnosis is difficult with syphilis, without a laboratory base.
To confirm, a blood test is most often taken.
When pustules appear, be sure to check when the last time you had sexual intercourse.
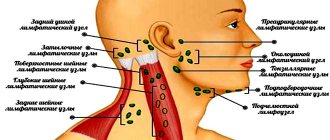
Syphilis is accompanied by enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Syphilis rashes are not accompanied by itching and pain.
Characteristic will be the absence of clearly manifested inflammation at the site of the abscess.
Diagnostics
Determining the nature of the pathology is the responsibility of the gynecologist. The primary diagnosis of STIs is made as part of a basic examination; if it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, the patient is referred to a venereologist. The diagnostic plan for pain in the labia area may include the following procedures:
- Survey.
The specialist determines the nature and duration of the pain, the circumstances of its occurrence, and other symptoms. To determine the possible causes of pain, a detailed medical history is collected: features of the menstrual cycle, the number of pregnancies and births, the presence of gynecological, allergic and somatic pathologies. - Gynecological examination.
The doctor assesses the condition of the labia minora and majora, perineum, and anus. Performs speculum examination and vaginal examination. The technique allows you to detect swelling, redness, atrophic changes, ulcers, erosions and other signs indicating the etiology of the pain syndrome. - Bacterioscopy.
When examining a smear in patients with inflammatory diseases, a large number of leukocytes are revealed. The nature of the microflora depends on the type of infection. In bacterial vaginitis and vulvovaginitis, cocci often predominate. In patients with candidiasis, fungal cells and mycelial threads are detected. - Microbiological research.
Based on the culture results, the characteristics of the microflora and the sensitivity of pathogenic microbes to antibiotics are determined. The persistent recurrent course of candidiasis is considered as an indication for determining the subspecies of fungi and their sensitivity to antimycotic agents. - PCR analysis.
It is an accurate, highly informative way to identify STI pathogens. The advantage of the technique is the ability to identify any microorganisms: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, viruses. - Vulvar biopsy.
Recommended for ulcers, erosions, and atrophy areas on the labia. Carried out to exclude malignant neoplasms. The obtained material is examined during histological or cytological analysis. - Colposcopy.
Indicated for nonspecific vulvovaginitis, ascending spread of specific infections. Allows you to visualize erosions and inflammatory changes. - Gynecological ultrasound.
It makes it possible to assess the condition of the internal genital organs, diagnose concomitant pathological processes or establish the cause of the development of inflammation of the labia (for example, when irritated by secretions against the background of salpingoophoritis). - Other tests.
If there are signs of intoxication, a general blood test is prescribed to assess the severity of inflammatory changes. All patients undergo a general urinalysis. If irritation of the vulva due to parasitosis is suspected, a scraping is performed for enterobiasis, and stool is examined for worm eggs. In case of provoking endocrine and metabolic disorders, the indicators of a biochemical blood test are studied.
Gynecological examination
Pustules on the labia with molluscum contagiosum
A small nodule is formed, dense to the touch.
The formation has a depression in the middle.
Infection with molluscum contagiosum occurs through the use of other people's personal hygiene items, close contact, and sex.
Molluscum contagiosum can cause formations that look like pustules.
When squeezed out, the contents are whitish in color.
HPV provokes spontaneous cell division at the site of infection by the virus.
Characteristic formations begin to appear in this area, but no pain occurs.
Over time, the formations grow and resemble cauliflower in appearance.
At first they can be confused with pustular elements.
Remember! If pustular rashes appear, you should visit a doctor.
Causes and mechanisms of the disease
Pathogenic bacteria begin to spread through microscopic breaks in the integrity of the skin, and also through the blood and lymphatic vessels. Direct penetration of pathogenic flora into the mouth of the sweat gland is possible. Subsequently, the process involves the sebaceous glands, hair follicles and subcutaneous tissue.
Provoking factors are non-compliance with personal hygiene rules and careless hair removal during depilation. Wearing uncomfortable synthetic underwear can contribute to the development of skin irritation or diaper rash. Excessive sweating promotes the proliferation of microflora and the development of the pathological process. Metabolic disorders - obesity. Diabetes mellitus and endocrinopathies also create a favorable environment for the development of inflammation. A decrease in immunity after a serious illness or during pregnancy can help reduce the barrier functions of the skin and facilitate the entry of pathogens into tissues.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
Pustules on the labia: tests
When rashes appear, many women are interested in the question, “which doctor and where should I go?”
If a pustular rash forms, you should see a gynecologist.
You can consult the following doctors:
- Dermatologist
- Venereologist
- Urologist
- Virologist
During the consultation, the specialist conducts a full examination of the genital organ and studies the nature of the rash.
Laboratory tests will be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
They help differentiate the diseases that caused the rash.
For research, a smear and blood are taken.
will help make a diagnosis .
This method allows you to detect the DNA of the causative agent of a particular disease.
The doctor takes the material for the study during the examination.
The manipulation is carried out using a special spatula.
The material is collected from the genital organ.
The contents of the abscess can also be taken for research.
A sample of the material is placed in a sterile tube and sent to the laboratory for further study.
blood tests on an empty stomach, from a vein.
Research can be carried out using several methods:
- 1.ELISA
- 2.RPGA
- 3.RIF
With the help of serological reactions, not only the presence of the disease is established, but also the stage of development of the pathological process.
If syphilis is suspected, the Wasserman reaction or rpr test is performed.
This diagnostic method allows you to diagnose the disease at the initial stages.
The result form will contain a mark indicating a positive or negative result.
Taking out! If a positive result is obtained, the study should be repeated.
Violation of the rules for preparing for analysis may cause an unreliable analysis result.
After the diagnosis has been completed, based on the result, the doctor will prescribe an effective course of treatment.
Clinical manifestations
A boil in intimate places in women has the following symptoms. Firstly, the development of a boil on the labia, chiria, occurs in several successive stages.
1. At the initial stage, there is slight swelling and slight itching in the labia area. The area of skin where the inflammation has formed becomes red and swollen. This phase usually lasts 3-5 days.
2. The next stage, suppuration, is the most worrying. Focal inflammation intensifies and a necrotic core consisting of pus (dead cells) is formed. In an intimate place, the forming boil becomes purple-reddish in color, and a white dot appears in the center of the boil. This period is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain at the site of inflammation, which sharply intensifies with pressure.
- Feeling of fullness in the vagina.
- Swelling of the labia minora or majora.
- Difficulty performing normal movements.
- Increased body temperature (sometimes above 38°C).
- Weakness and deterioration in general health.
3. At the third stage, the boil inside the labia (minor or major) opens on its own and its contents come out. After this, pain and swelling in the intimate area decrease. The recovery stage begins, which lasts 8-12 days. During this period, healing of the wound surface occurs.
Causes of a boil on the labia minora
On the external genitalia (outer and inner labia), a boil arises due to infection with a bacterial infection, most often Staphylococcus aureus. A number of factors contribute to the development of the disease. All these factors, individually or together, can lead to infection and the appearance of chiria. These gynecologists include:
- Decreased immune defense;
- Hypovitaminosis;
- Lack of adequate intimate hygiene;
- Violation of metabolic processes;
- Hypothermia, and in more rare cases, overheating of the body;
- Increased sweating;
- Microtraumas that occur during shaving or epilation of a deep bikini;
- Significant mechanical loads on the perineum, especially in the presence of hypertrophy of the labia minora;
- Any injuries in the groin area;
- Diabetes mellitus, hyperandrogenism;
- Chronic infectious disease;
- Synthetic underwear;
- Pregnancy (hormonal changes and decreased immunity).
Possible complications
You should not try to press or puncture the lesion even with a needle treated with alcohol - this can lead to the penetration of infectious agents into the blood vessels and the development of complications, including an abscess or blood poisoning. If the boil is squeezed out, not kept clean, or treated incorrectly, other serious complications can develop. There are a huge number of blood vessels in the groin area, which contributes to the rapid spread of infection.
The most typical complications of private boils:
♦ Furunculosis. In this condition there are many forms of boils, which are in different stages of development; ♦ Phlegmon (purulent process in the subcutaneous tissue, which is not a restrictive capsule); ♦ Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes, often inguinal); ♦ Phlebitis (inflammation of the walls of the veins); ♦ Peritonitis is an inflammatory process involving the peritoneum. ♦ Sepsis - the penetration of infectious agents into the general bloodstream with the development of inflammatory reactions throughout the body.
Ulcers on the labia: treatment
Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
Remember! Self-medication leads to the development of complications of the disease.
The treatment regimen depends on which flora contributed to the appearance of pustules.
Conservative therapy is used as treatment.
If necessary, surgical removal is prescribed.
Pustules on the labia, what to apply?
There are a wide variety of creams and gels available to remove skin rashes.
They can be easily used at home.
It should be noted! The dosage and frequency of application should be prescribed by a specialist.
Ointments may have antiviral or antimicrobial effects.
To eliminate a viral infection, Viferon, Acyclovir or Panavirin are prescribed.
It is recommended to lubricate the rash for two weeks.
The frequency of application is up to 5 times a day.
For a bacterial infection, antibiotic ointment is prescribed.
Sometimes a complex drug is recommended, for example Triderm.
Pustules on the labia, what pills to take?
If there is an infection, antimicrobial drugs should be taken.
As a rule, antibiotics with a broad spectrum of action are prescribed.
They are a universal remedy against sexually transmitted infections.
The following groups of antibacterial drugs can be prescribed for treatment:
- Penicillins
- Tetracyclines
- Fluoroquinolones
- Macrolides
Tetracyclines are prescribed in an amount of 250 milligrams per day.
The duration of treatment will depend on the degree of damage to the body.
Penicillins are drugs that are used in the fight against the causative agent of syphilis.
The drug can be used in the form of tablets or intramuscular injection.
Macrolides are prescribed in an amount of 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-10 days.
This group of drugs is used in cases where there are allergies to other antibiotics.
If the pustules are caused by fungal flora, antifungal agents are prescribed.
For the treatment of candidal diseases, local drugs are prescribed.
Vaginal suppositories can be used as therapy.
In case of severe damage to the body by the fungus, general medications are prescribed in the form of tablets.
The type of medication is selected by the attending physician.
To combat the fungus, Diflucan, Polygynax, and Pimafucin can be used.
Important! Self-treatment can lead to a deterioration in well-being, so you should entrust the appointment of therapy to a specialist.
At the end of the course, it is necessary to pass control tests.
This will allow us to determine the effectiveness of drug treatment.