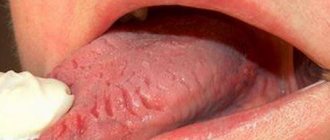
Glossitis: symptoms and treatment in adults
Contents:
What is glossitis
Symptoms of glossitis
Causes of glossitis in adults
Types of glossitis in adults
How and with what to treat glossitis in adults
Prevention of glossitis
Doctor's advice
Answers on questions
There are many factors that lead to pathologies in the oral cavity. Glossitis - what is it? This is a term that combines various diseases of the tongue.
How to treat
The treatment methods used will directly depend on the reasons that provoked the development of glossitis, so high-quality diagnosis comes to the fore.
It is impossible to say for sure which doctor treats glossitis, since it will depend, again, on the reasons that caused the disease: you should start by visiting a dentist, who, in turn, may need to consult a therapist and even a surgeon.
If glossitis is a consequence of diseases (syphilis, gastrointestinal problems, anemia), then it is necessary to eliminate these diseases.
To reduce pain, the doctor may recommend applying local lotions with Lidocaine, Pyromecaine and other anesthetics. This procedure can actually be carried out at home. In order to speed up recovery, the tongue is regularly cleaned of plaque with a cotton swab soaked in Chymotrypsin. If there are ulcers, lotions with Iruksol are prescribed. Traditional medicine methods are also allowed, for example, rinsing with a decoction of chamomile or soda, lubricating the affected areas with propolis and much more.
There are quite a few treatment options: the doctor will be able to choose the most effective one, so at the first signs of illness you should not delay visiting him.
Symptoms of glossitis:
- pain when eating and moving the tongue;
- difficulty moving;
- color change, plaque appearance;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- deformation;
- loss of taste sensitivity (partial or complete);
- sensation of a lump in the throat, a foreign object in the oral cavity;
- the appearance of solid formations and compactions.
If these symptoms are detected, you should immediately contact dentistry in Moscow to avoid complications or the disease developing into chronic glossitis.
Symptoms
Depending on the type of disease (and there are quite a few of them), typical signs will vary. Nevertheless, there are general symptoms that are similar for all forms.
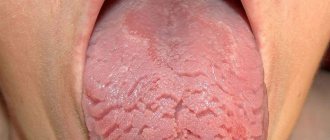
First of all, glossitis changes the appearance of the tongue: growths that are dense to the touch are formed on it or areas are formed whose color differs from the healthy mucous membrane (the shade can vary from red to burgundy). In addition to visual changes, there are other symptoms:
- burning of the tongue, often accompanied by swelling;
- increased salivation;
- feeling of a foreign body in the mouth;
- changes in taste sensations (foods may acquire an unusual taste, sometimes a person becomes completely unable to perceive the taste of food);
- difficulty swallowing;
- change in diction (speech becomes slurred; in order to express a simple thought, a person has to make serious efforts, because due to pain it is difficult for the patient to pronounce words clearly).
If treatment is neglected, there is a high probability that the disease will enter the chronic stage: its onset is indicated by a change in the structure of the tongue and a noticeable increase in its size.
Causes of glossitis in adults
There are many factors that lead to the occurrence of this pathology:
- infectious factor (viruses, bacteria, fungi);
- inflammatory gum diseases (periodontitis, gingivitis), carious teeth;
- poor oral hygiene;
- thermal, chemical burns;
- injury to the tongue with sharp objects, including sharp edges of fillings and dentures;
- smoking;
- reduced immunity.
Most often, patients have several factors that lead to
Glossitis
Folded glossitis
A folded tongue may be a normal variant or a manifestation of mutations in the genetic apparatus.
There is a high probability of this anomaly occurring in congenital pathologies of the central nervous system (Down's disease). A distinctive feature of the folded tongue are longitudinal and transverse folds. In this case, the longitudinal fold runs strictly along the midline of the tongue - from its tip to the root. Often a folded tongue is combined with macroglossitis (enlarged tongue) and areas of scaly peeling of the tongue.
Patients usually do not complain, but pay attention to the unusual appearance of the tongue. If atrophy of the tongue papillae is present, complaints of burning and loss of taste are possible. Bad breath often occurs due to food getting into the folds.
A folded tongue may be part of a set of symptoms when:
- acute gastritis;
- hypovitaminosis B;
- diabetes mellitus in combination with candidiasis;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Atrophic glossitis
An inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the tongue, which is accompanied by a decrease in the size of its papillae or their disappearance. As a result, the surface of the back of the tongue becomes red, smooth and shiny. Atrophic processes affect all tissues of the tongue, as a result of which its thickness decreases.
As the muscle volume of the tongue decreases, swelling and ulceration appear. The patient complains of a change in taste perception. soreness and bad breath.
Atrophic glossitis develops when:
- blood anemia (iron deficiency, B12 deficiency);
- hypovitaminosis (riboflavin - vitamin A, nicotinic acid - vitamin PP);
- streptococcal and fungal infections;
- HIV infections.
Hypoplastic glossitis
Damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, which develops due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and lack of vitamins B2 (riboflavin) and PP (nicotinic acid). It is characterized by a decrease or disappearance of the papillae of the tongue, so the tongue has a “varnished” appearance, with bright spots and stripes.
If the absorption of vitamins B2 and PP in the intestine is impaired, unpleasant sensations occur: burning, tingling and pain in the tongue when eating.
Exfoliative glossitis
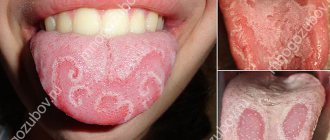
An inflammatory-dystrophic disease of the mucous membrane of the tongue, the etiology (cause) of which has not yet been definitively established. First described as "geographic tongue" and "benign migratory glossitis". Occurs in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, helminthic infestations, a tendency to allergies and menopause. It is believed that hereditary factors and infectious diseases play a role in the development of the disease.
Exfoliative glossitis is characterized by the periodic appearance and disappearance of round or irregularly shaped red areas of epithelial exfoliation on the back of the tongue and lateral surfaces, surrounded by a bright rim. The exposed areas quickly restore their structure and appear elsewhere on the tongue.
These peelings do not bother the patient, but if the desquamation intensifies, a burning, tingling, tingling sensation appears, especially while eating. The tongue reacts to spicy and spicy foods, hot foods, and is easily infected due to the large area of exposed mucous membrane, which is devoid of protective properties.
Ulcerative glossitis
This pathology of the tongue occurs with infectious lesions of the mucous membrane, as well as common severe somatic diseases. It is characterized by the formation of ulcerative and erosive-ulcerative elements on various surfaces of the tongue, which occur with a pronounced pain symptom, significant dysfunction of the tongue (swallowing, chewing, speech), regional enlargement of the lymph nodes and symptoms of general intoxication of the body (malaise, headache, fever ).
In clinical practice, ulcerative glossitis occurs in the following conditions.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Decompensated course of hypertension, decompensated heart valve defects, large-focal myocardial infarction. Ulcers appear on the bluish surface of the tip and the anterior third of the tongue, along the midline.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
In this case, against the background of an ash-gray coating, painful ulcers form on the root of the tongue.
- Blood diseases.
Acute leukemia, aplastic anemia. Ulcerative-necrotic formations are located over the entire surface of the tongue.
- Behçet's disease.
Systemic disease of the mucous membranes of the body of unknown etiology. Multiple, painful aphthae and ulcers appear on the tongue.
- Incorrect prosthetics.
Bright red erosions and ulcers are located on the lateral surfaces of the tongue.
Villous glossitis
A chronic disease of the mucous membrane of the tongue, which is characterized by the proliferation of filiform papillae with their subsequent keratinization. This is predisposed to:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis with increased and decreased acidity of gastric juice, diseases of the small and large intestines);
- infectious diseases (pulmonary tuberculosis);
- long-term antibacterial therapy;
- hereditary predisposition;
- Addison's disease;
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- hemolytic anemia.
In this case, on the tongue in the midline, a triangular or oval-shaped lesion is visible (longitudinal size - 2-3 cm), covered with thickened filiform papillae, dark gray, brown, sometimes green.
Villous glossitis is accompanied by a sensation of a foreign body in the mouth, a gag reflex (intensifies when talking), impaired taste sensitivity and dry mouth.
Catarrhal glossitis
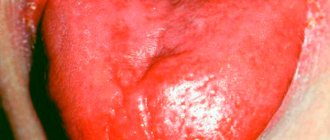
Acute damage to the superficial layers of the mucous membrane of the tongue. It is characterized by hyperemia (redness), swelling and pain (burning, discomfort when eating and talking).
Allergic glossitis
It is an inflammatory response of the tongue mucosa to the local action of allergens (often medicinal in nature). It develops acutely, with pronounced swelling of the tongue mucosa and severe pain. Hypersalivation (profuse salivation), fever, and enlarged regional lymph nodes are possible.
If there are dentures in the mouth, allergic glossitis occurs against the background of increased sensitivity to the materials from which the structure is made. On the lateral surfaces of the tongue that are in contact with the prosthesis, areas of redness of the mucous membrane appear.
Herpetic glossitis
Develops on the mucous membrane of the tongue when attacked by the herpes virus. It is accompanied by pronounced intoxication of the body (fever, malaise, muscle and headaches), regional enlargement of the lymph nodes (submandibular and parotid), severe soreness of the tongue, and disruption of its functions.
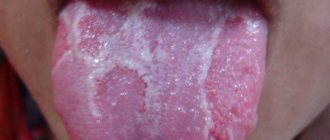
With herpetic glossitis, the tongue is covered with a dense coating that is difficult to remove; transparent, painful blisters filled with liquid are visible on the back of the tongue and its inner surface.
Interstitial glossitis
Sclerosing glossitis is one of the most severe forms of inflammation of the tongue, is a precancerous condition and requires immediate treatment. In this case, the pathological process occurs in two stages
At the initial stage, inflammation develops in all tissues of the tongue, as a result of which it increases in size.
Then, scar tissue forms at the site of inflammation, which leads to a decrease in the size of the tongue and its thickening. At the same time, the mucous membrane loses its papillae, becomes lumpy, and cracks and ulcers often form on it, which can become malignant.
Interstitial glossitis develops with syphilis and is chronic. In the absence of timely specific treatment, the muscle tissue of the tongue is completely replaced by connective tissue and a complete loss of tongue function develops.
Types of glossitis in adults
- Interstitial glossitis - occurs with syphilis, often leads to cancerous tumors of the tongue
- Gunterovsky - the initial symptom of pernicious anemia, manifests itself in the form of smoothing of the surface.
- Diamond-shaped tongue is a developmental anomaly.
- Folded is a congenital developmental anomaly.
- Hairy tongue - severe keratinization of filiform papillae, resulting in a black coating.
- Geographic (folded) - noticeable red spots, furrows.
- Ulcerative – bleeding ulcers and bad breath are observed.
- Catarrhal - a white dense coating covers the entire surface of the muscle.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Don't wait for your condition to worsen!
Sign up
Classification of glossitis and their characteristics
Based on external manifestations, there are 3 groups:
- Catarrhal
The inflammatory process affects only the superficial layers of the tongue. Characterized by redness, swelling and plaque formation. The main reason is a fungal disease of the oral cavity (candidiasis) or a burn of a muscle organ. In rare cases, catarrhal glossitis is a consequence of advanced stomatitis or vitamin deficiency.
- Purulent
The most severe form. The pathological process spreads deeper, causing pain and severe swelling. Sores with purulent contents form on the surface of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by high fever and intoxication. Treatment by a specialist is required.
- Ulcerative
With this type, multiple ulcers form on the surface of the tongue, which can bleed. The person experiences severe pain, which leads to a decrease in appetite. Speech disturbances are possible due to swelling and hypertrophy. Provoking factors are inflammatory diseases of the gums and oral cavity.
There is also a form of glossitis called folded. This is a congenital disease, the clinical manifestations of which are folds on the surface of the tongue. Treatment is not required, as this form does not cause pain or discomfort. In some cases, aesthetic correction is possible.
As a secondary disease, glossitis can be a sign of various diseases of the internal organs. In this regard, the following forms are distinguished:
- Desquamative or “geographic tongue” - the external surface of the tongue with this form is similar to a geographical map, that is, lines, grooves, and bright red spots are observed. It occurs in pregnant women due to changes in hormonal levels, as well as in people suffering from chronic gastrointestinal pathologies. A desquamated tongue is often a symptom of parasitic diseases or liver dysfunction.
- Villous - the main symptom is the proliferation of filiform papillae on the surface of the muscular organ. Subsequently, they become like villi. This form occurs with candidiasis or frequent injuries to the tongue. Taking certain medications and smoking can also cause villous glossitis.
- Gunterovskaya is a sign of B12 deficiency and folate deficiency anemia. The surface of the tongue is smoothed and appears shiny. The color is bright red, the papillae atrophy.
- Rhomboid (median) - characterized by thickening of the epithelium with the formation of diamond-shaped pathological areas. Has a chronic course. People with gastritis or low acidity in the stomach suffer from this form. There are flat, tubercular and warty glossitis.
The most dangerous form is considered interstitial, as it acts as a precancerous condition. Without treatment, the cells of the tongue affected by glossitis become malignant, which leads to cancer formation. Also, such glossitis is a characteristic sign of syphilis.
Answers on questions
What diagnostics are carried out before treatment?
The dentist examines the patient, collects medical history data: complaints, data on the patient’s general health (presence of chronic diseases). If necessary, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed: a smear (culture) from the oral cavity for microflora.
How to treat hairy tongue in adults?
The doctor prescribes complete sanitation of the oral cavity: removal of stone, plaque, and carious teeth. Selects individual home hygiene products. Prescribes a diet that includes plenty of fluids and solid vegetables. Smoking is prohibited. If necessary, the dentist prescribes rinsing solutions and antibacterial agents.
General symptoms of glossitis
The first signs of inflammation of the tongue are discomfort, burning and the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. Subsequently, the tongue noticeably swells and acquires a burgundy or scarlet hue. The symptomatic picture of the disease may include:
- increased salivation;
- dullness or complete loss of taste;
- perversion of taste;
- pain and difficulty eating;
- slurred speech;
- the patient's desire not to use the tongue when creating sounds.
Symptoms of chronic glossitis
Chronic glossitis is characterized by persistent swelling and changes in the structure of the tissues of the tongue. With bacterial inflammation, hyperemia, soreness, swelling of the affected area and a local increase in temperature can be observed. The development of glossitis, which is of viral origin, is accompanied by the appearance of small blisters on the surface of the tongue, which eventually open and form painful erosions. The disease, which is of a fungal nature, is manifested by the appearance of a dense or loose white coating on the affected surface, as well as hyperplastic changes in tissue.
Treatment of glossitis
The treatment of glossitis is based on the correction of underlying diseases and the elimination of factors that provoke the occurrence of the inflammatory process. In addition, the therapy program includes:
- adherence to a diet that includes the inclusion of various purees, slimy porridges and pureed soups in the patient’s diet;
- rinsing the mouth with solutions of furatsilin or chlorhexidine;
- applications with solutions of pyromecaine, trimecaine, lidocaine and other anesthetics;
- relieving signs of dry tongue using a mixture of glycerin and anesthesin;
- accelerating the process of regeneration of affected tissues using drugs made on the basis of solcoseryl and vitamin A;
- surgical intervention (in the presence of pronounced hyperkeratic changes).
It is important to know that with timely and competent treatment, inflammatory lesions of the tongue can be easily corrected. An unfavorable outcome of the disease, characterized by the development of abscesses, cellulitis and cancer, is observed only in the absence of adequate therapy.